Method of regulating and controlling laser selective melting formed titanium alloy process based on flaw form
A laser selective melting and defect morphology technology, applied in the field of titanium alloy materials, can solve the problems of not establishing the relationship between defect types and forming processes, and lack of defect morphology evolution law.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
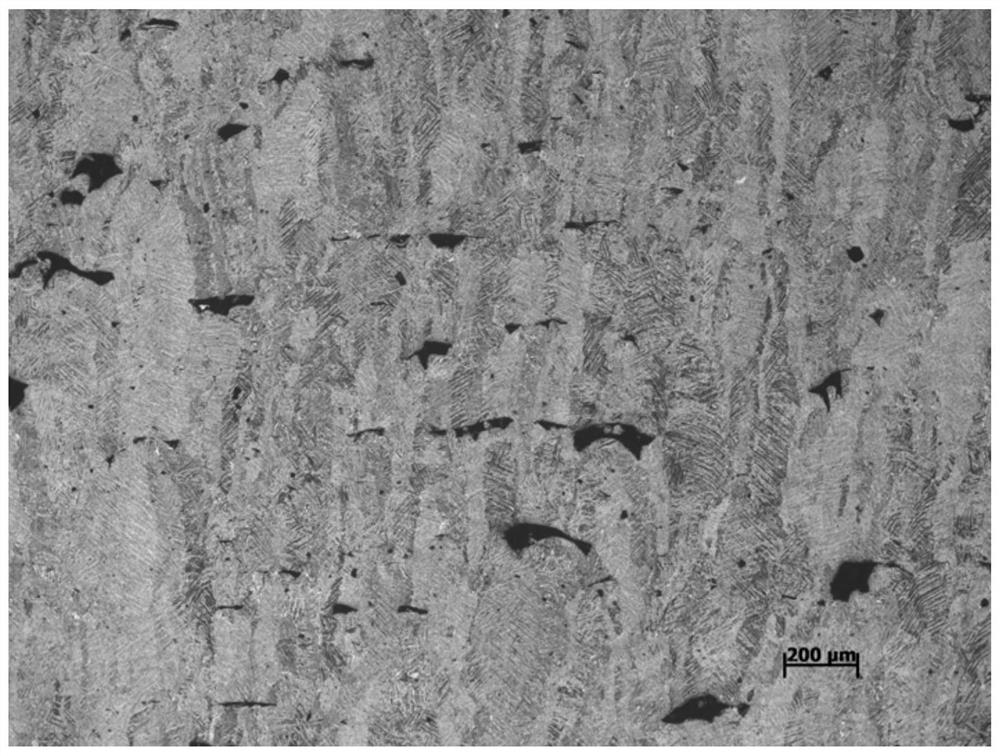
[0040] In this embodiment, the laser selective melting forming parameters: laser power 100W, laser scanning speed 900mm / s. Process parameter control process: such as figure 1 As shown, the microstructure analysis was carried out on the titanium alloy formed by the above process parameters, and the shape of internal defects. It can be seen from the figure that the defects inside the alloy under this process are irregular shape defects, indicating that the forming energy density is low. According to the present invention, parameters can be regulated by increasing the laser power or reducing the scanning speed.
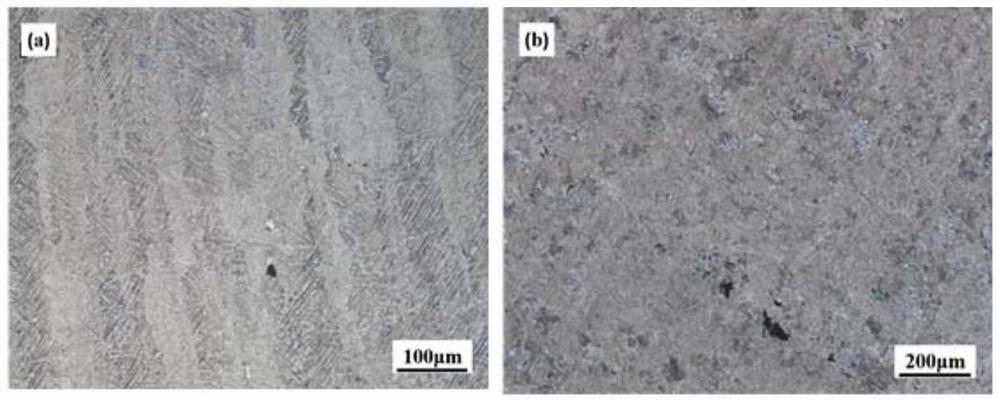
[0041] Regulation strategy 1: Increase the laser power to 160W, such as figure 2 As shown in (a), the internal microstructure of the titanium alloy after forming. It can be seen from the figure that the number and size of the internal defects of the alloy are significantly reduced.
[0042] Control strategy two: reduce the scanning speed to 300mm / s, such as figure 2...
Embodiment 2
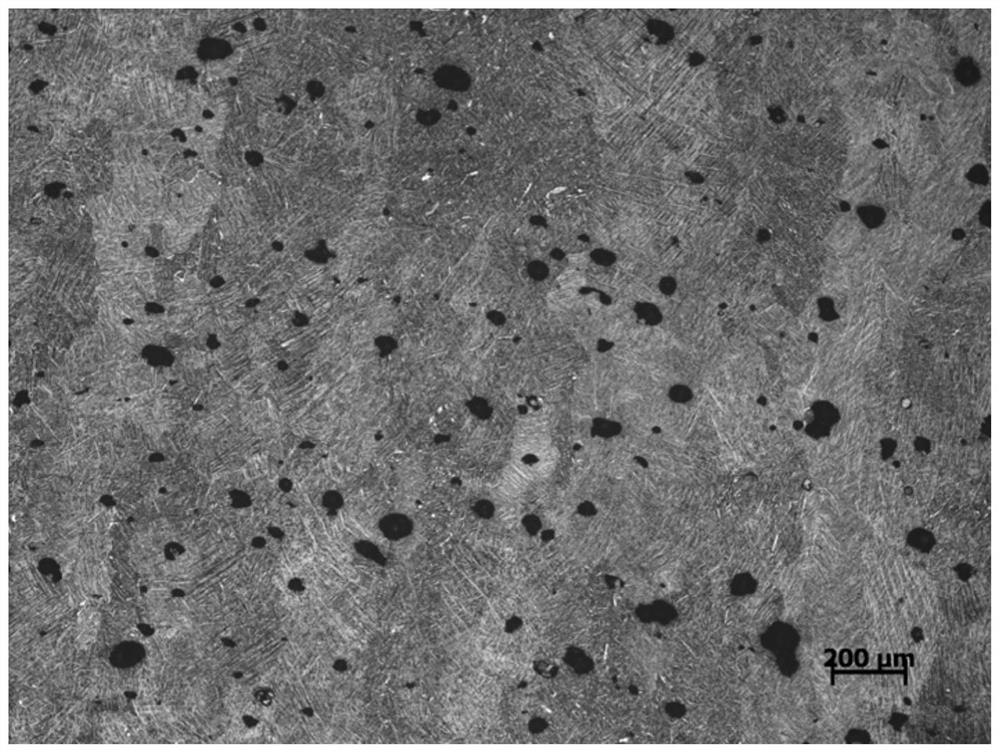
[0044] In this embodiment, the laser selective melting forming parameters: laser power 220W, laser scanning speed 600mm / s. Process parameter control process: such as image 3 As shown, the microstructure of the titanium alloy formed by the above process parameters was analyzed, and the shape of internal defects. It can be seen from the figure that the defects inside the alloy under this process are regular spherical defects, indicating that the forming energy density is too high. According to the present invention, parameters can be regulated by reducing the laser power or increasing the scanning speed.
[0045] Control strategy one: reduce the laser power, reduce the power to 160W, such as Figure 4 As shown in (a), the internal microstructure of the titanium alloy after forming, it can be seen from the figure that the number and size of the internal defects of the alloy are significantly reduced,
[0046] Control strategy two: increase the scanning speed and reduce the scann...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com