Molecular marker of rice brown planthopper-resistant gene BPH39 and application thereof
An anti-brown planthopper and molecular marker technology, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve problems such as differentiation, and achieve the effects of easy detection, high primer specificity, and production cost savings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: BPH39 Preliminary positioning and effect verification of
[0040] 1. ZS / PK BC 1 f 2 Population construction and phenotyping
[0041] (1) The Indian insect-resistant parent PAEDAI KALIBUNGGA (referred to as PK, IRGC number: 38545) is from the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI). The other parent Zhenshan 97B (ZS) used in this experiment showed high susceptibility to the brown planthopper population in my country. In order to locate the brown planthopper resistance gene in PK, the present invention crosses ZS with PK, and the obtained F 1 Selfing again, get F 2 Separate groups. then F 2 After the population was screened for resistance to brown planthopper, the resistant single plant was recrossed with ZS, and the obtained BC 1 f 1 Then self-bred to obtain BC containing 92 families 1 f 2 Separate groups; each BC 1 f 2 A single plant obtains the corresponding BC through selfing 1 f 2:3 family lineage.
[0042] (2) The improved group ident...
Embodiment 2
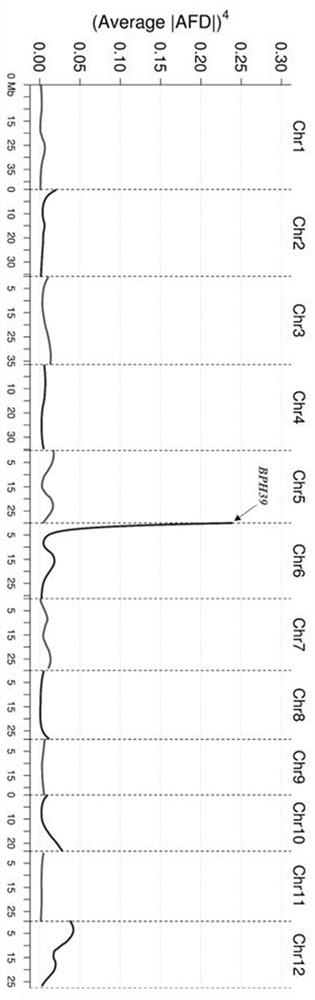
[0057] Example 2: BPH39 fine positioning of
[0058] 1 BPH39 Construction of near-isogenic lines and effect evaluation of
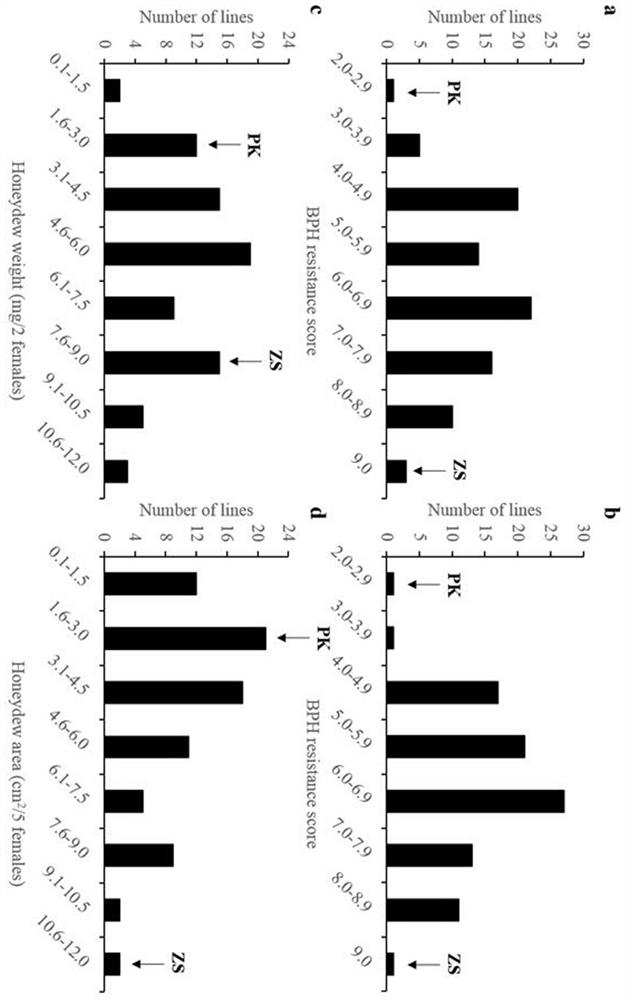
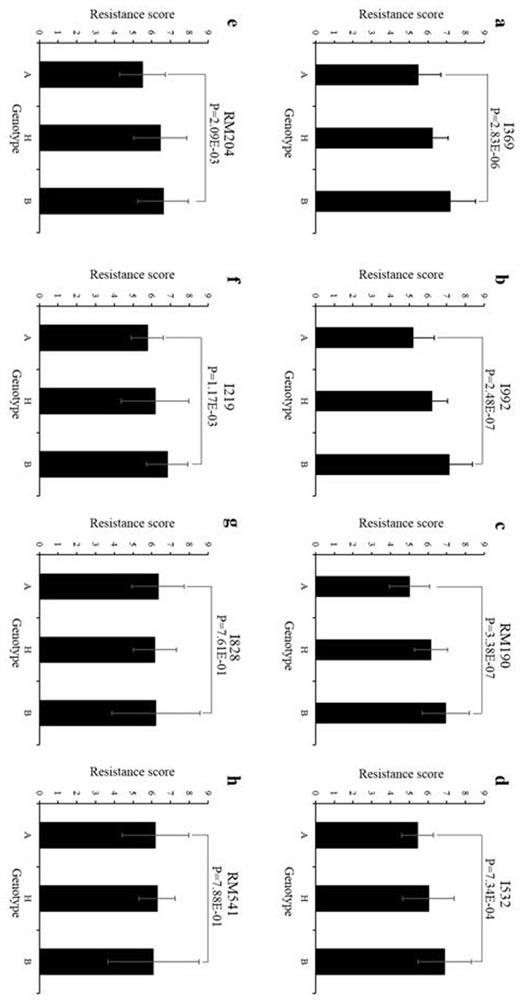
[0059] In order to fine-tune the gene and to construct a molecular marker-assisted selection system for the gene for insect resistance breeding, we constructed BPH39 A near-isogenic line against the Zhenshan 97 background. The specific steps are, first use the BPH39 flanked by molecular markers I369 and I992 (Table 3) in BC 1 f 3 family selection BPH39 The insect-resistant individual plant whose locus is the PK genotype of the homozygous insect-resistant parent, backcrossed with ZS to obtain BC 2 f 1 , then use ZS with BPH39 locus heterozygous BC 2 f 1 Further backcrossing to get BC 3 f 1 ,choose BPH39 BC 3 f 2 , and then select BPH39 The locus is a single plant of homozygous PK genotype, and then selfed to obtain BC 3 f 3 ,Right now BPH39 The near isogenic line (NIL-BPH39). We measured the seedling resistance and N. lugens honeydew a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com