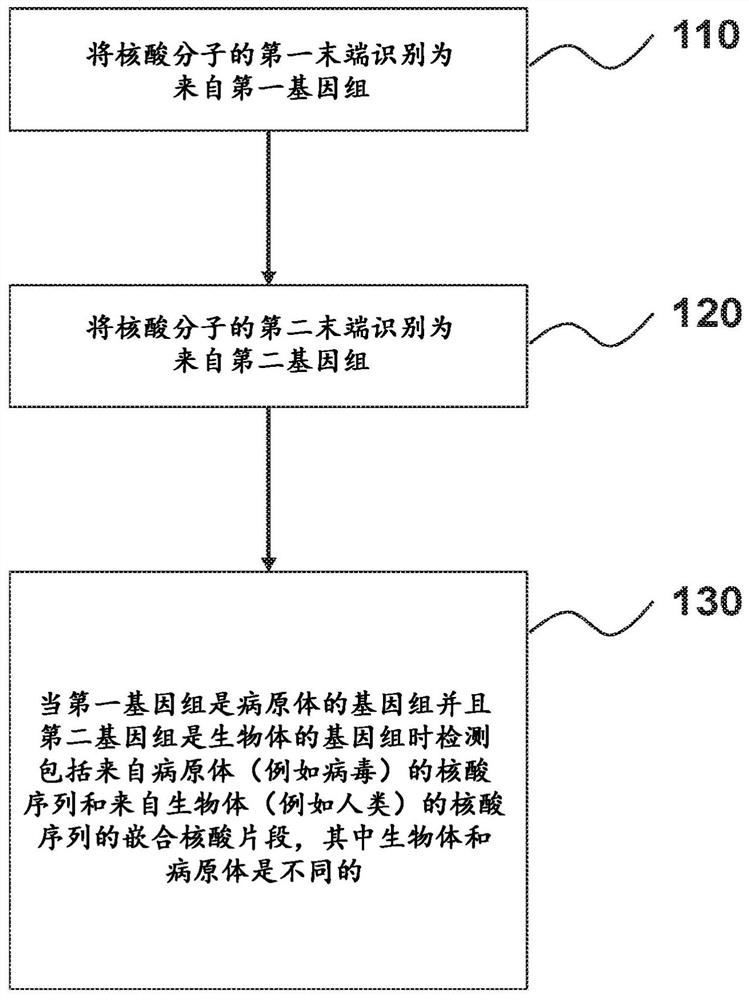
Nucleic acid rearrangement and integration analysis
A nucleotide and cell nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid rearrangement and integrated analysis, can solve risky, invasive, expensive and painful problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0195] Example 1. Analysis of HPV DNA Integration
[0196] This example tests an exemplary method for determining HPV integration breakpoints by analyzing sequence reads from cell-free DNA from plasma samples. This example also examines the different HPV integration profiles in samples from patients with cervical cancer and HPV-related head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and the EBV integration profile in samples from patients with EBV infection.
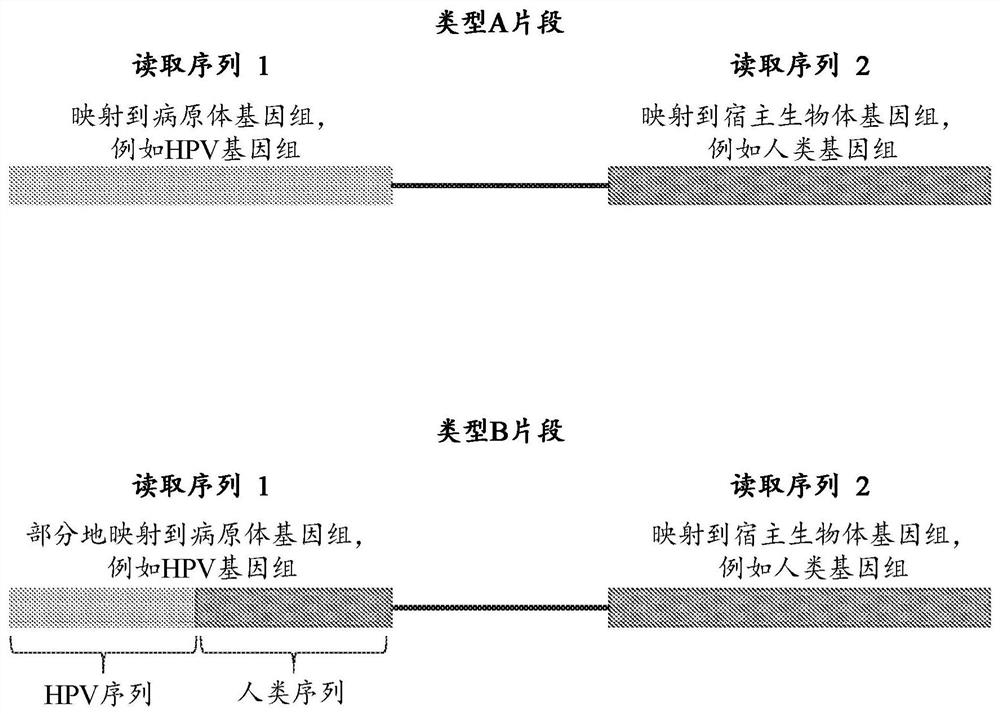
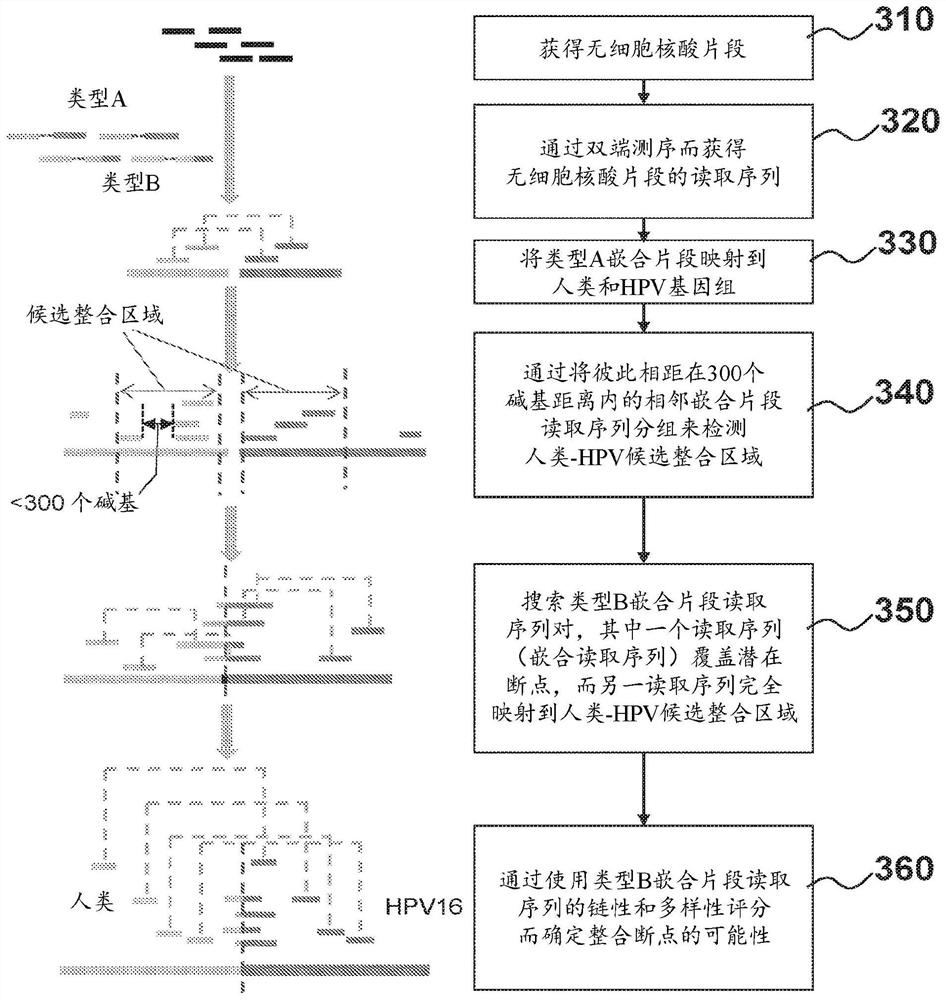
[0197] Plasma samples from patients with HPV infection were collected and processed. Cell-free DNA molecules from the plasma samples were then collected and paired-end sequenced. In paired-end sequencing data, such as figure 2 Reads from type A human-HPV chimeric fragments and type B human-HPV chimeric fragments were selected as shown in .
[0198] To identify human-HPV chimeric DNA in cell-free DNA samples, the obtained reads were aligned to a reference human genome and a reference HPV genome using the SOAP alignment tool. ...
Embodiment 2
[0207] Example 2. Analysis of HPV DNA Integration Index
[0208] This example examines the HPV DNA integration index in cell-free DNA from plasma samples of patients with cervical cancer and HNSCC.
[0209] Using these cell-free DNA fragments, paired-end sequencing was performed in order to analyze cell-free DNA fragments in plasma, thus showing integration of HPV into human chromosomes within the cancer genome. A protocol for paired-end sequencing was employed, which reads 75 nucleotides from each end of the cell-free DNA fragment. Cell-free DNA fragments with all 75 nucleotides in which one read mapped to the HPV genome and the other to the human genome were counted as human-HPV chimeric fragments. In paired-end sequencing, cell-free DNA fragments in which two reads mapped to the HPV genome were counted as plasma HPV reads. Samples from 11 patients with cervical cancer were analyzed.
[0210] Table 3. Plasma cell-free human-HPV fragment DNA in CC samples
[0211]
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0213] Embodiment 3. compare with public software ViFi
[0214] In this example, the performance of an exemplary algorithm according to the present disclosure in HPV integration detection was compared with that of ViFi (Nguyen et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 April 20; 46(7):3309-3325.doi: 10.1093 / nar / gky180), ViFi is a software that detects viral integration sites by a combination of phylogenetic methods and reference-based read alignment. A simulated data set was used to evaluate the detection performance of the exemplary algorithm and ViFi, the simulated data set has artificially constructed integration sites, and data from 26 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) patients, 26 cervical cancer (CaCx) patients and Biological data of tissue samples and paired plasma samples from seven patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Integration sites identified by exemplary algorithms were further confirmed by PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing.
[0215] m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com