PARMS marker based on rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14 and application
A technology of rice brown planthopper and resistance gene, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low degree of automation, low efficiency, cumbersome operation and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
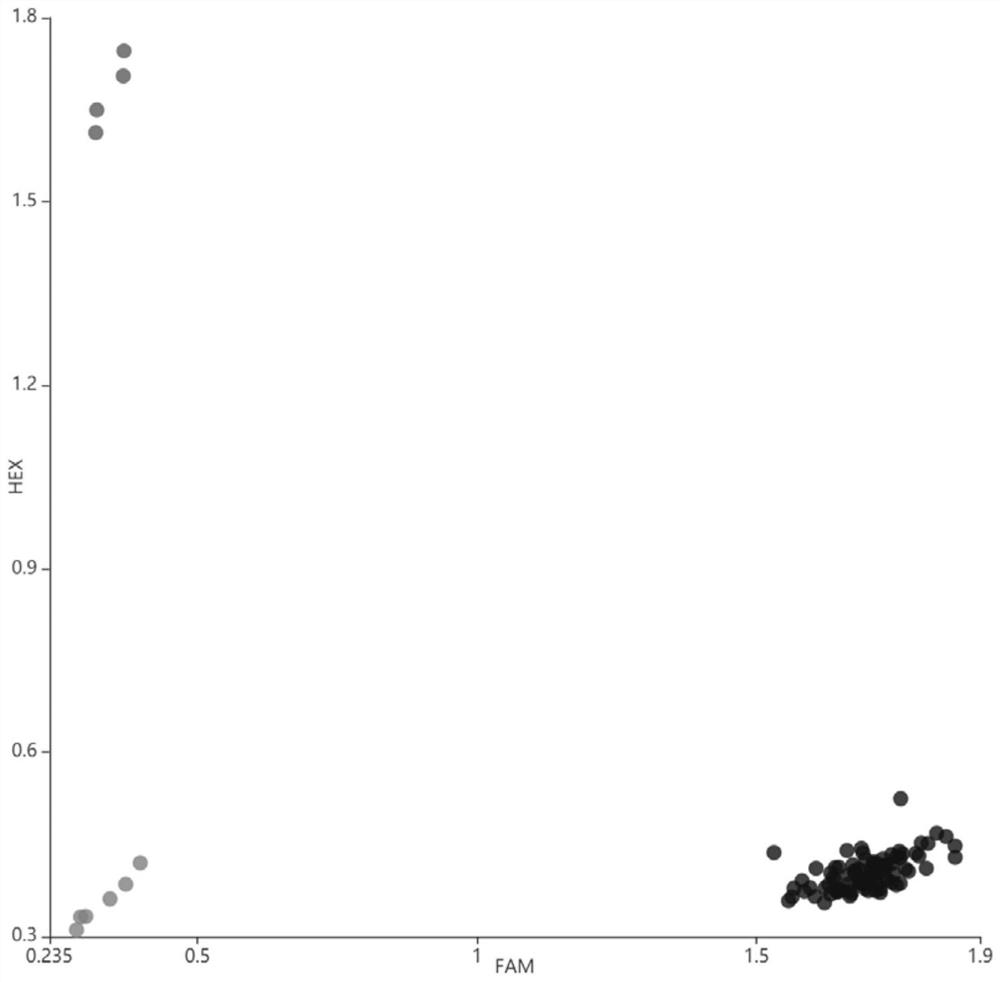
[0036] The PARMS marker and application based on the rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14 is based on the functional PARMS marker and application of the non-synonymous mutation of the first exon SNP of the rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14, including the following steps:
[0037] 1) Identification of rice material brown planthopper resistance: Taking Nipponbare as a control, 226 rice materials were artificially inoculated to identify brown planthopper resistance at the seedling stage, and the brown planthopper resistant material Y009 was screened out;
[0038] 2) Bph14 gene structure analysis: The DNA of fresh leaves of Y009 and Nipponbare was extracted by CTAB method, amplified in segments, purified and then sent to the biological company for sequencing. The software Vector NTI 11 was used to analyze the difference of Bph14 gene in the two rice materials, and found A T→C mutation occurs at the 448bp site of exon 1, resulting in a change from phenylalanine to...
Embodiment 2
[0060] The PARMS marker and application based on the rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14 is based on the functional PARMS marker and application of the non-synonymous mutation of the first exon SNP of the rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14, including the following steps:
[0061] 1) Identification of rice material brown planthopper resistance: Taking Nipponbare as a control, 200 rice materials were artificially inoculated to identify brown planthopper resistance at the seedling stage, and the brown planthopper resistant material Y009 was screened out;
[0062] 2) Bph14 gene structure analysis: The DNA of fresh leaves of Y009 and Nipponbare was extracted by CTAB method, amplified in segments, purified and then sent to the biological company for sequencing. The software Vector NTI 11 was used to analyze the difference of Bph14 gene in the two rice materials, and found A T→C mutation occurs at the 448bp site of exon 1, resulting in a change from phenylalanine to...
Embodiment 3
[0076] The PARMS marker and application based on the rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14 is based on the functional PARMS marker and application of the non-synonymous mutation of the first exon SNP of the rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14, including the following steps:
[0077] 1) Identification of rice material brown planthopper resistance: Taking Nipponbare as a control, 300 rice materials were artificially inoculated to identify brown planthopper resistance at the seedling stage, and the brown planthopper resistant material Y009 was screened out;
[0078] 2) Bph14 gene structure analysis: The DNA of fresh leaves of Y009 and Nipponbare was extracted by CTAB method, amplified in segments, purified and then sent to the biological company for sequencing. The software Vector NTI 11 was used to analyze the difference of Bph14 gene in the two rice materials, and found A T→C mutation occurs at the 448bp site of exon 1, resulting in a change from phenylalanine to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com