Application of MLN4924 in preparation of medicine for preventing or treating APAP-induced acute liver injury
A technology for acute liver injury and liver injury, applied in drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulations, organic active ingredients, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
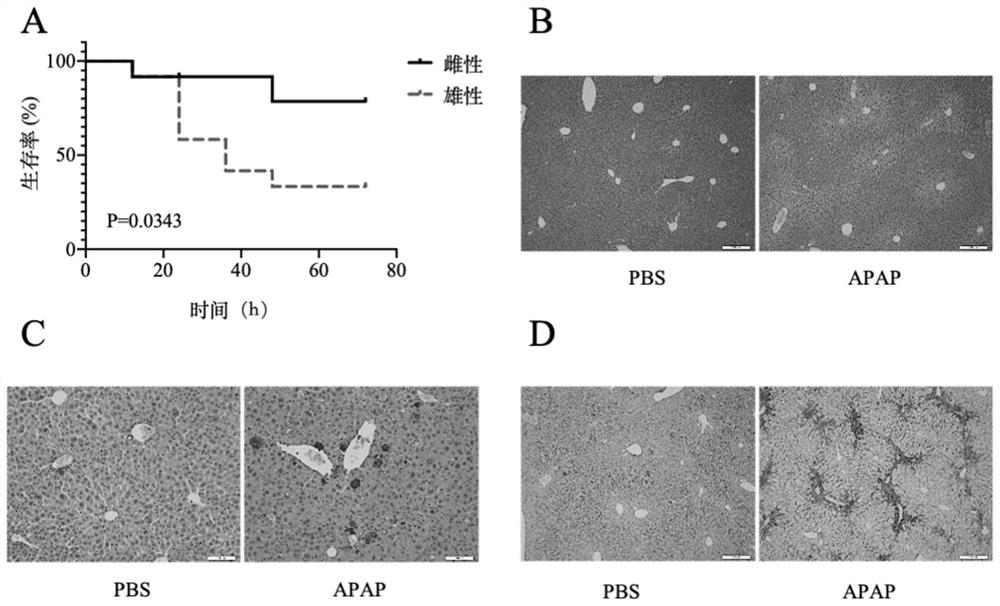
[0042] This example proposes the establishment of an APAP-induced acute liver injury model and related mechanisms.
[0043] 1. Experimental program design
[0044] The mouse model of acute liver injury induced by excessive APAP is a classic model of drug-induced liver injury. Previous studies have shown that the severity of APAP liver injury has a certain relationship with the gender of mice. In order to better establish the model, we purchased 6-8 week-old C57BL / 6 mice, 12 males and 12 females, and counted the survival rate of the mice within 72 hours. In order to further study the indicators of APAP-induced acute liver injury model in wild mice, after intraperitoneal injection of 350 mg / kg APAP in mice, APAP-induced acute liver injury was observed by HE staining, TUNEL staining, and F4 / 80 immunohistochemical staining. In the model, liver injury, apoptosis, immune cell recruitment and other conditions in mice.
[0045] 2. Results Analysis
[0046] The results showed that ...
Embodiment 2
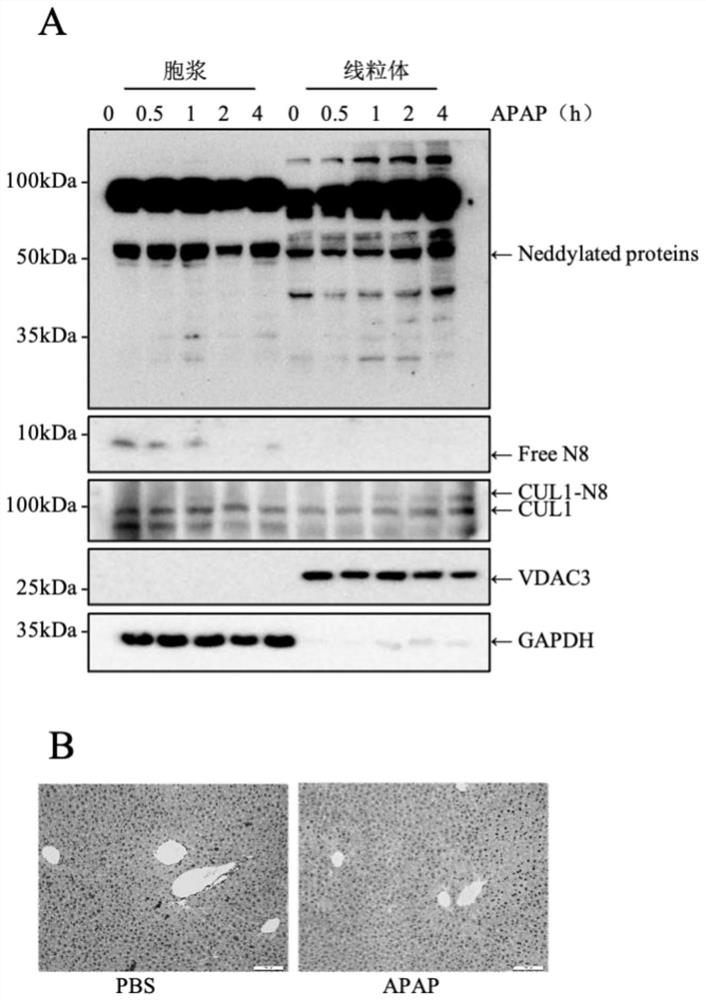
[0048] This example presents changes in Neddylation modification in an APAP-induced acute liver injury model.
[0049] 1. Experimental program design
[0050] Preliminary studies have confirmed that Neddylation modification can occur in mitochondria. Based on this, the design of this experiment is divided into in vivo experiment and in vitro experiment to study the changes of Neddylation modification in APAP-induced acute liver injury model. In animal experiments, mice were killed by cervical dislocation at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 hours after 350 mg / kg APAP injection, and about 100 mg of fresh liver tissue was taken and washed with pre-cooled PBS buffer Twice, and then ground with liquid nitrogen to separate the mitochondria and cytoplasmic proteins of the liver tissue. The mitochondria were fully lysed with RIPA protein lysate, and then samples were prepared together with the isolated cytoplasmic proteins, and western blot experiments were performed to detect changes in the lev...
Embodiment 3
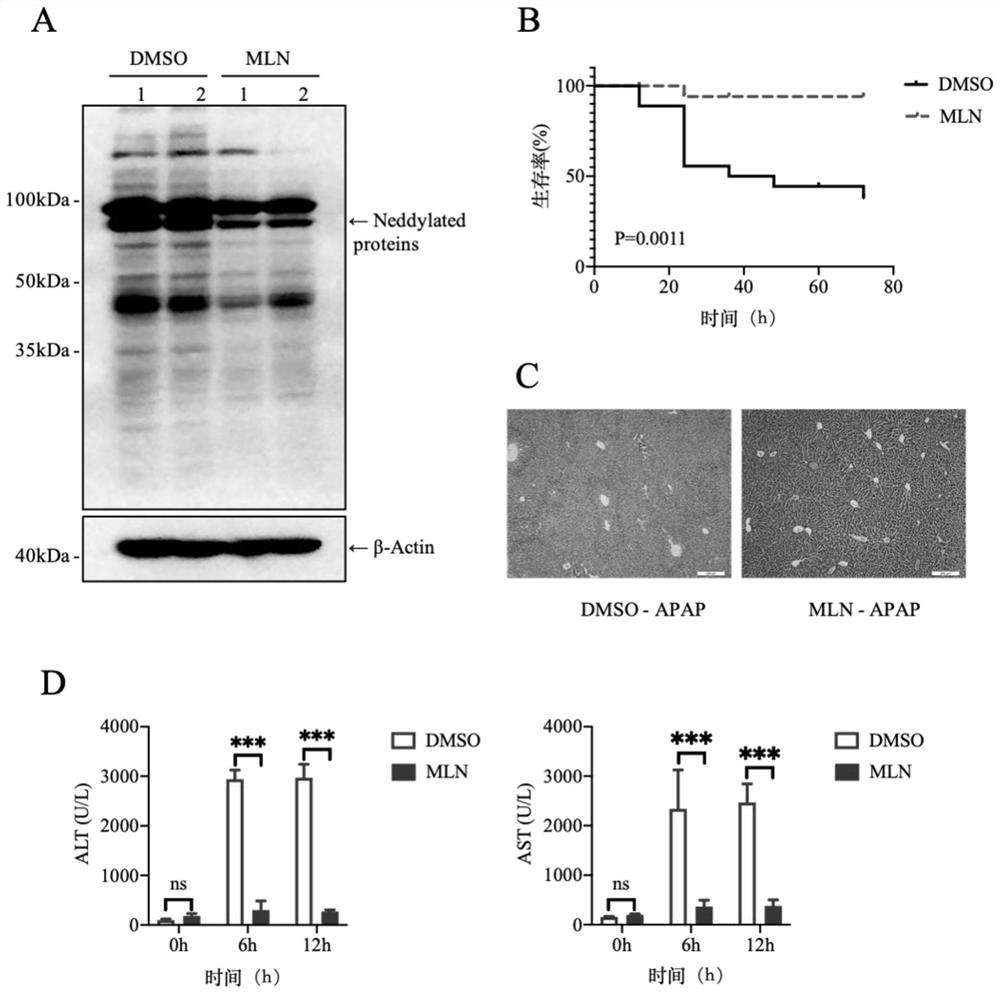
[0054] This example proposes to use MLN4924 to inhibit Neddylation modification and analyze the changes of acute liver injury in mice induced by APAP.
[0055] 1. Experimental program design
[0056] Mice were injected with MLN4924 to inhibit Neddylation modification, and the changes of APAP-induced acute liver injury in mice were analyzed. Initial experiments found that excessive injection of APAP in mice damaged liver cells accompanied by enhanced Neddylation modification. We further studied the role of APAP-induced acute liver injury and its related mechanism through the inhibition of Neddylation modification in vivo by MLN4924. MLN4924 was dissolved in DMSO, and the mice were injected intraperitoneally at a dose of 60 mg / kg. The control mice were injected with the same volume of DMSO, and the injection volume of each mouse did not exceed 70 μl. Mice were sacrificed 12 hours after administration, and liver tissue samples were collected for western blot experiments to detec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com