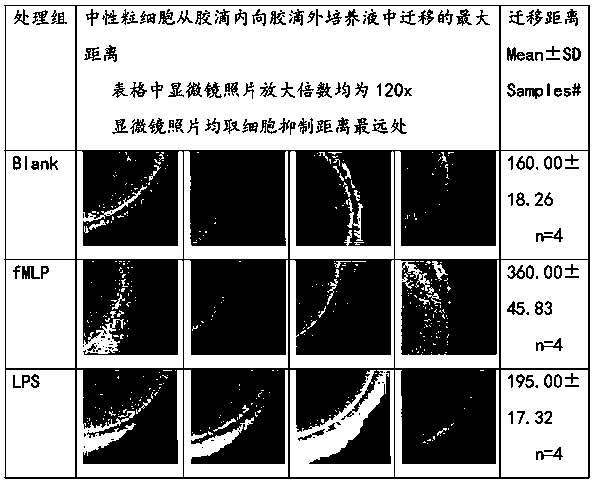
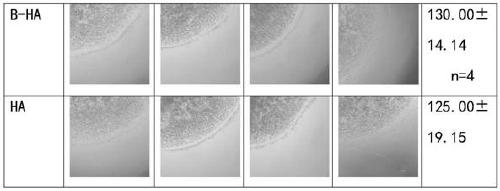
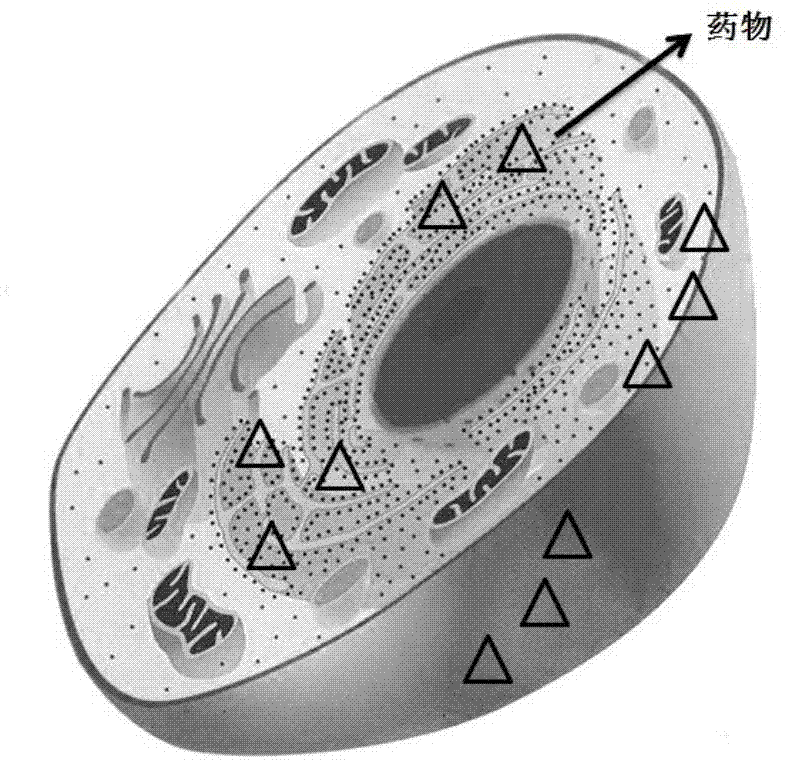
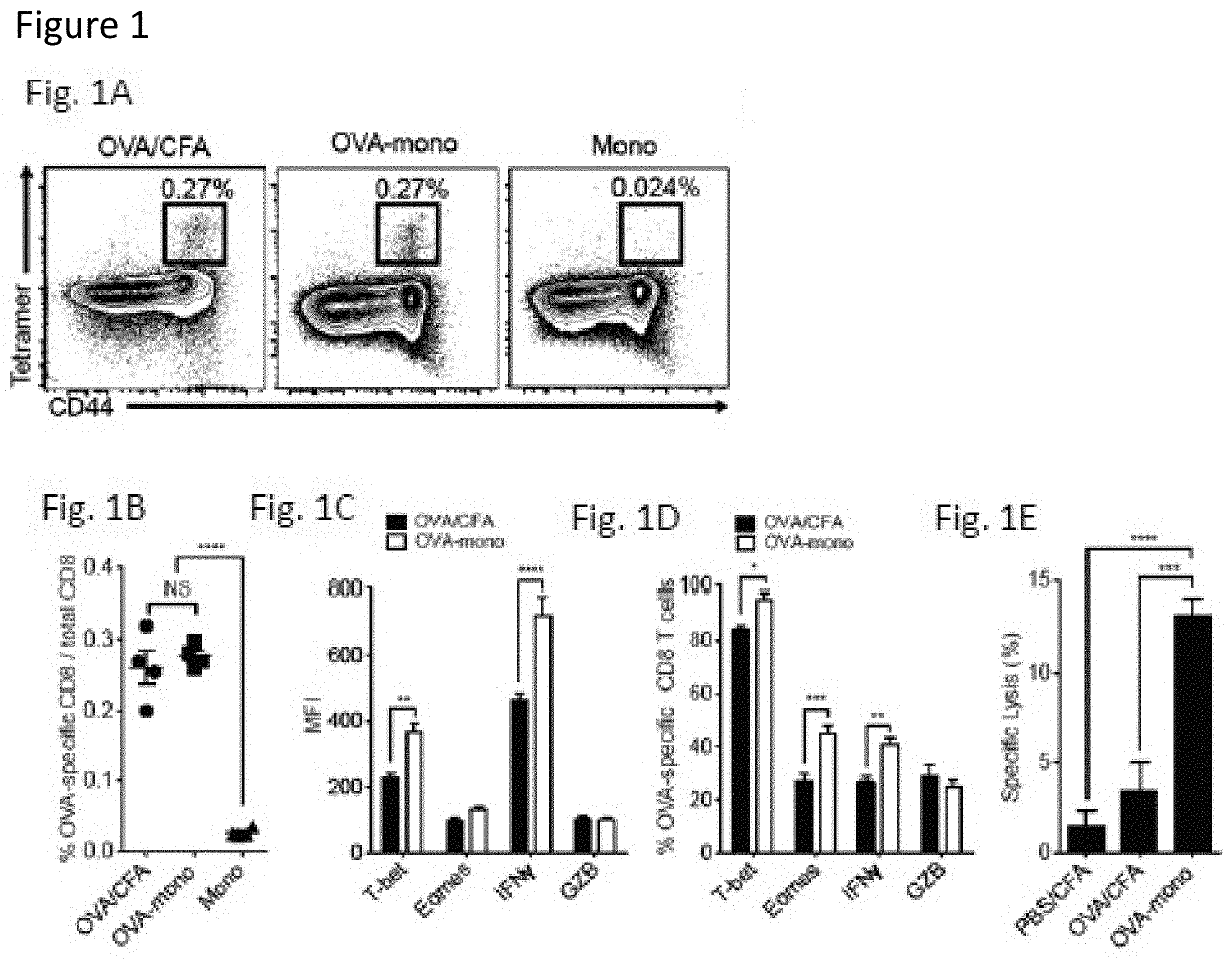
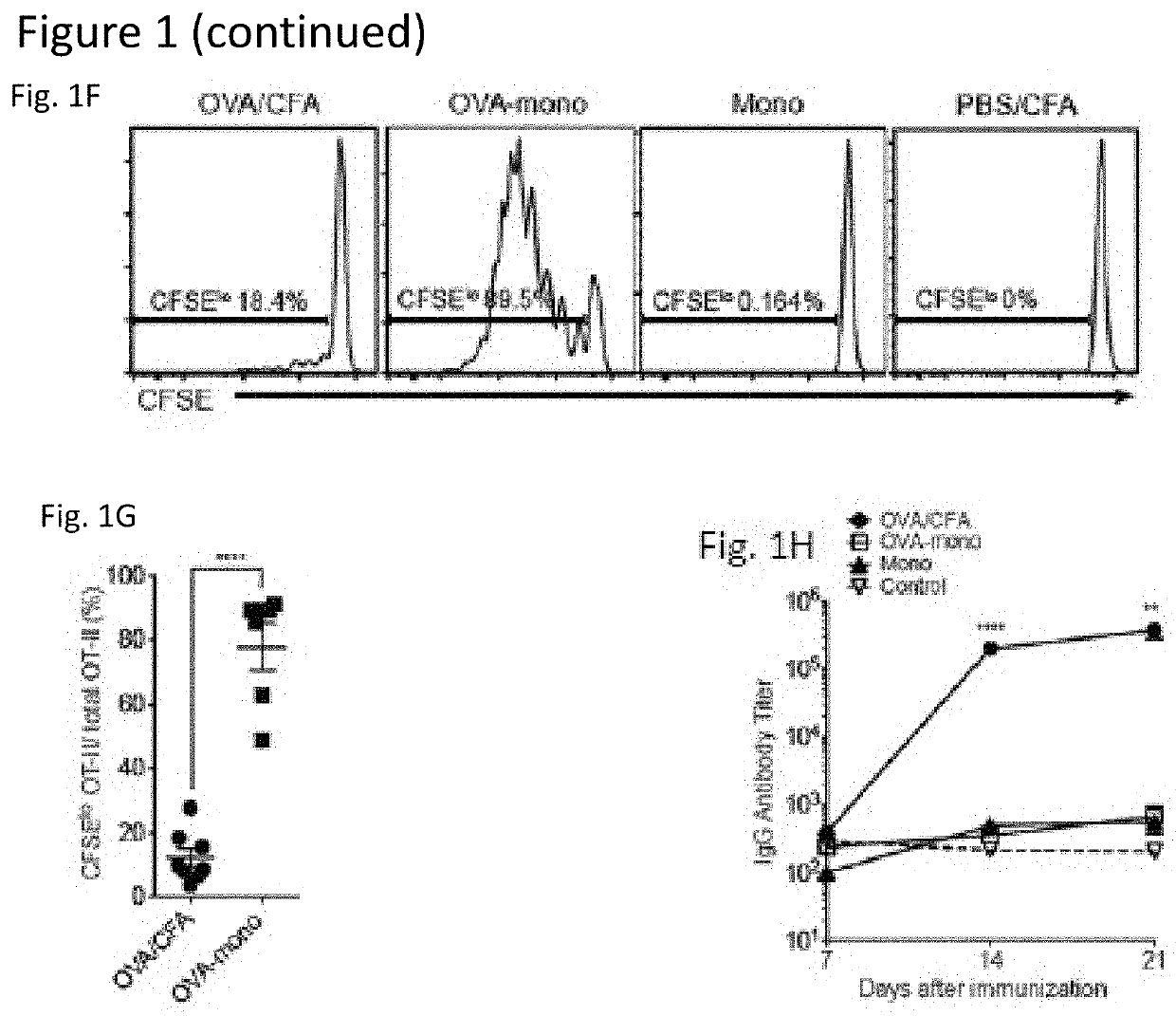
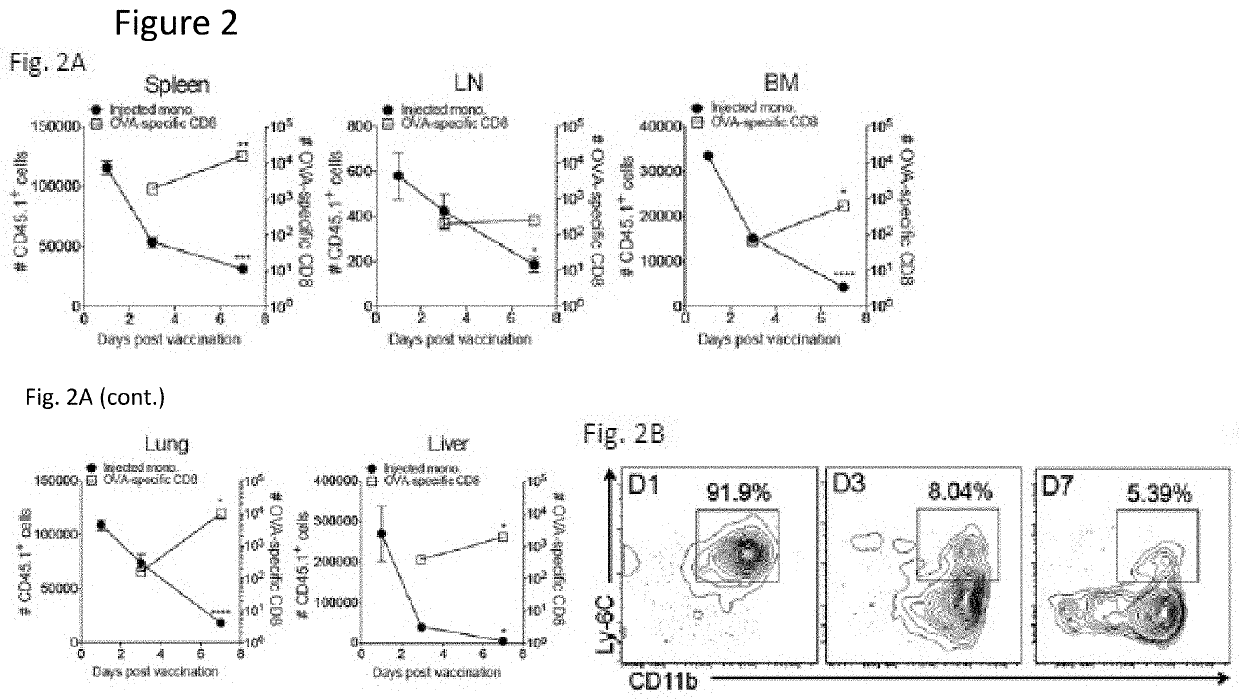
Patents
Literature
64 results about "Neutrophilic cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
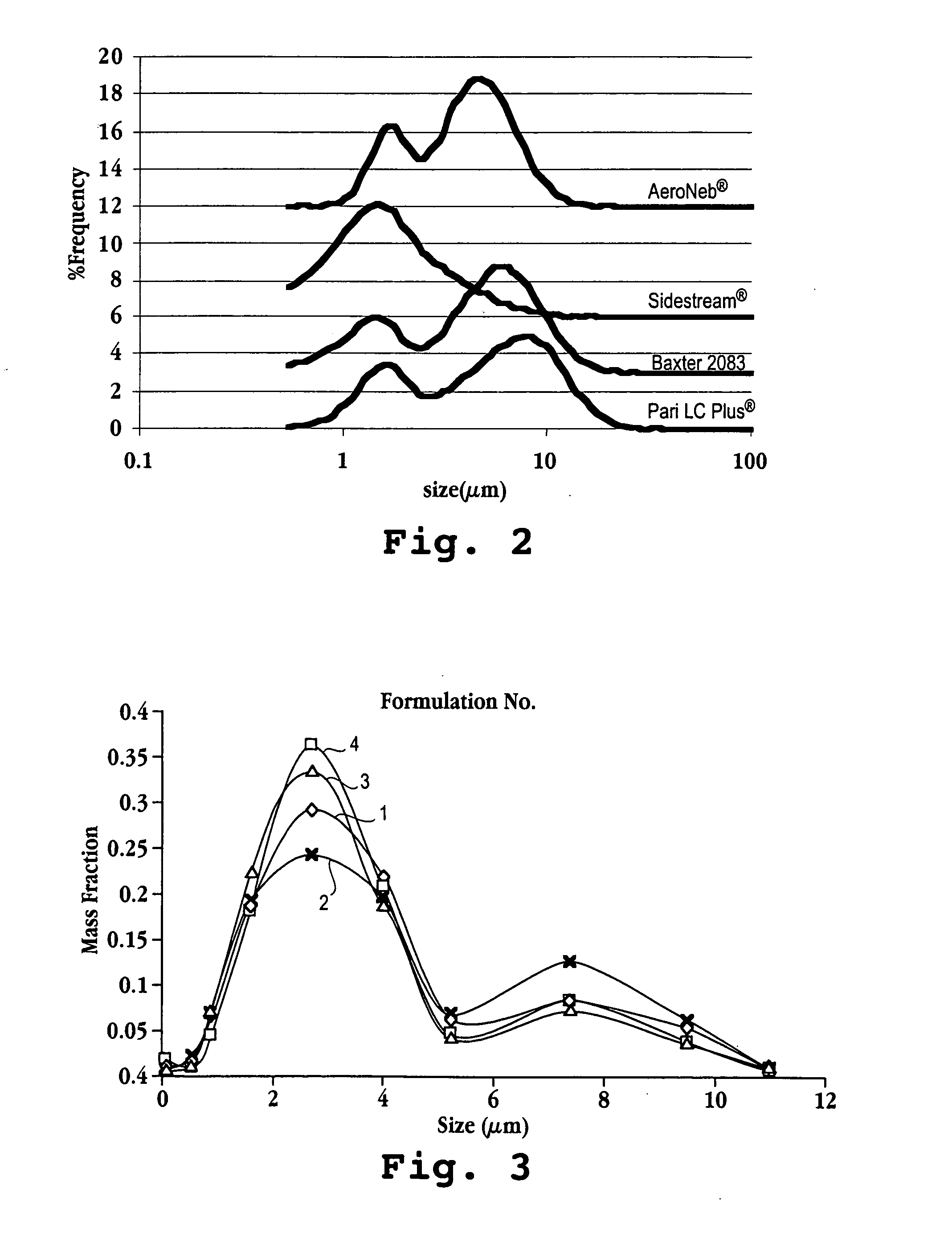
Method of pulmonary administration of an agent
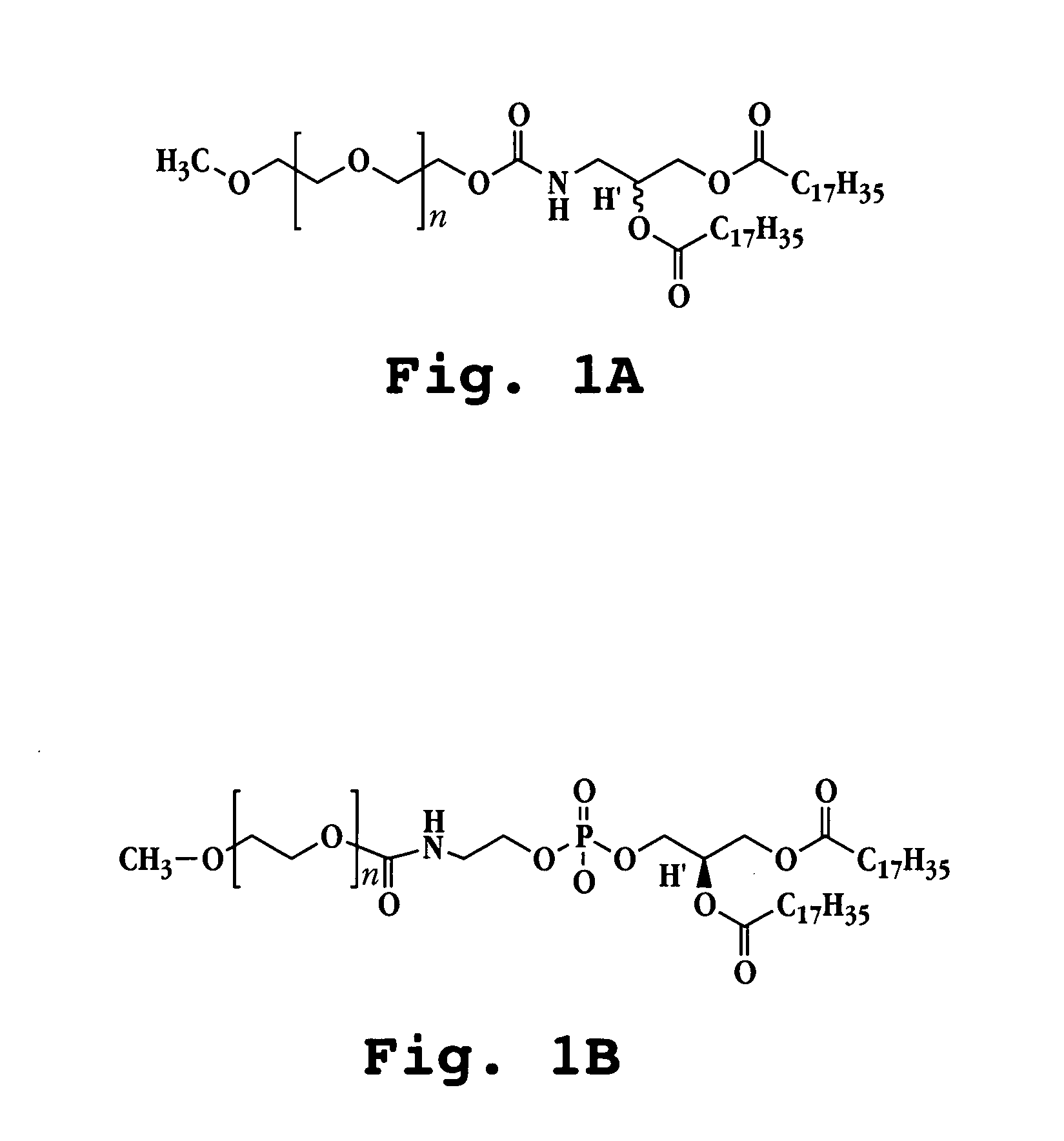
A method for administering a therapeutic or diagnostic agent to a subject is described. The method includes providing a suspension of liposomes comprised of one or more of vesicle-forming lipids selected from (i) a vesicle-forming lipid derivatized with a hydrophilic polymer and (ii) a neutral lipopolymer, said liposomes being associated with said therapeutic or diagnostic agent, forming an aerosol of said liposome suspension; and administering the aerosol to the subject by inhalation. The liposome formulation delivers intact liposomal particles to the respiratory tract of said subject to form a depot of therapeutic agent therein with no observable provocation of an immune response, as measured by neutrophil or macrophage cell count in the lung after administration.
Owner:ALZA CORP
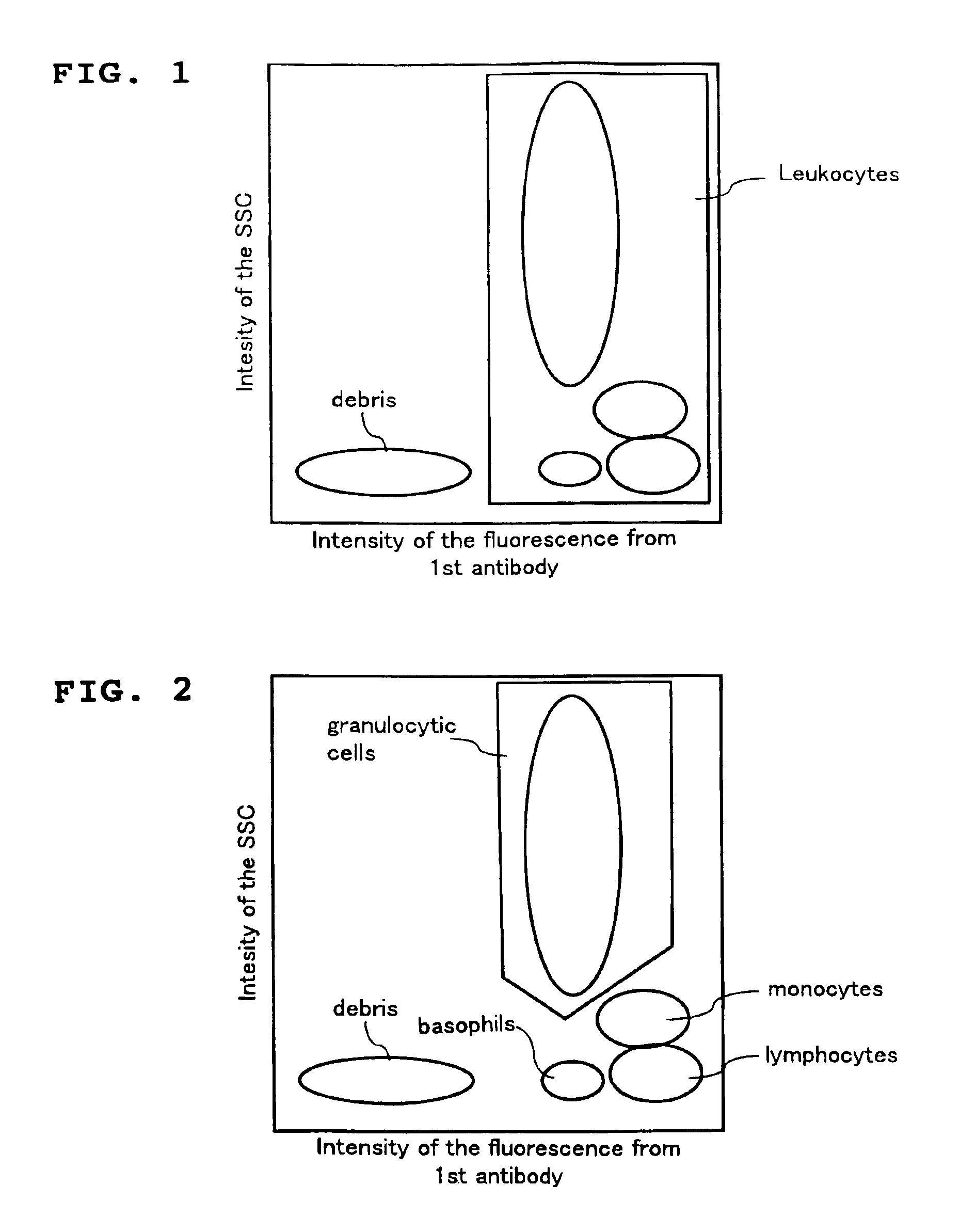
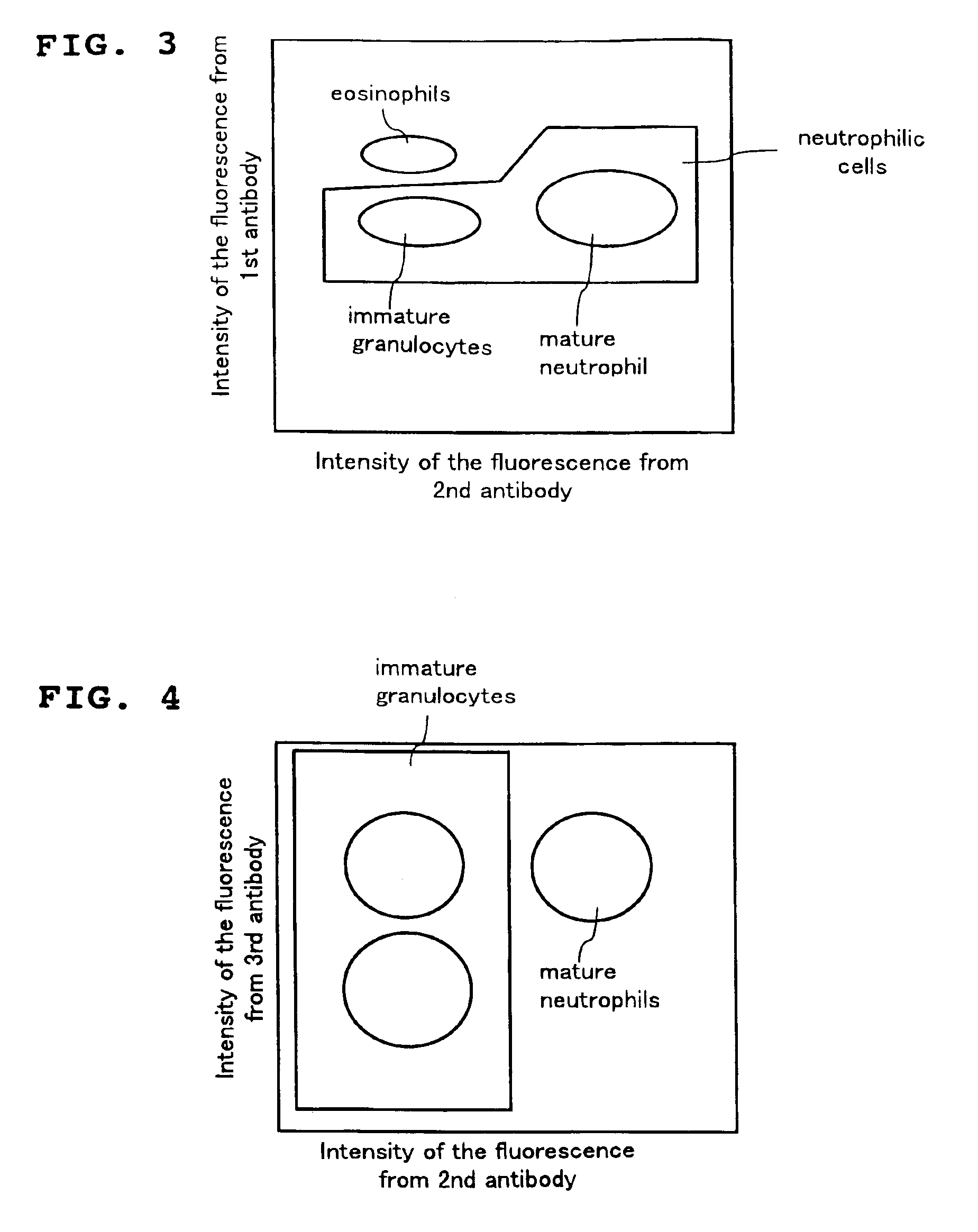
Method for classifying and counting leukocytes
InactiveUS6900023B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellRed Cell
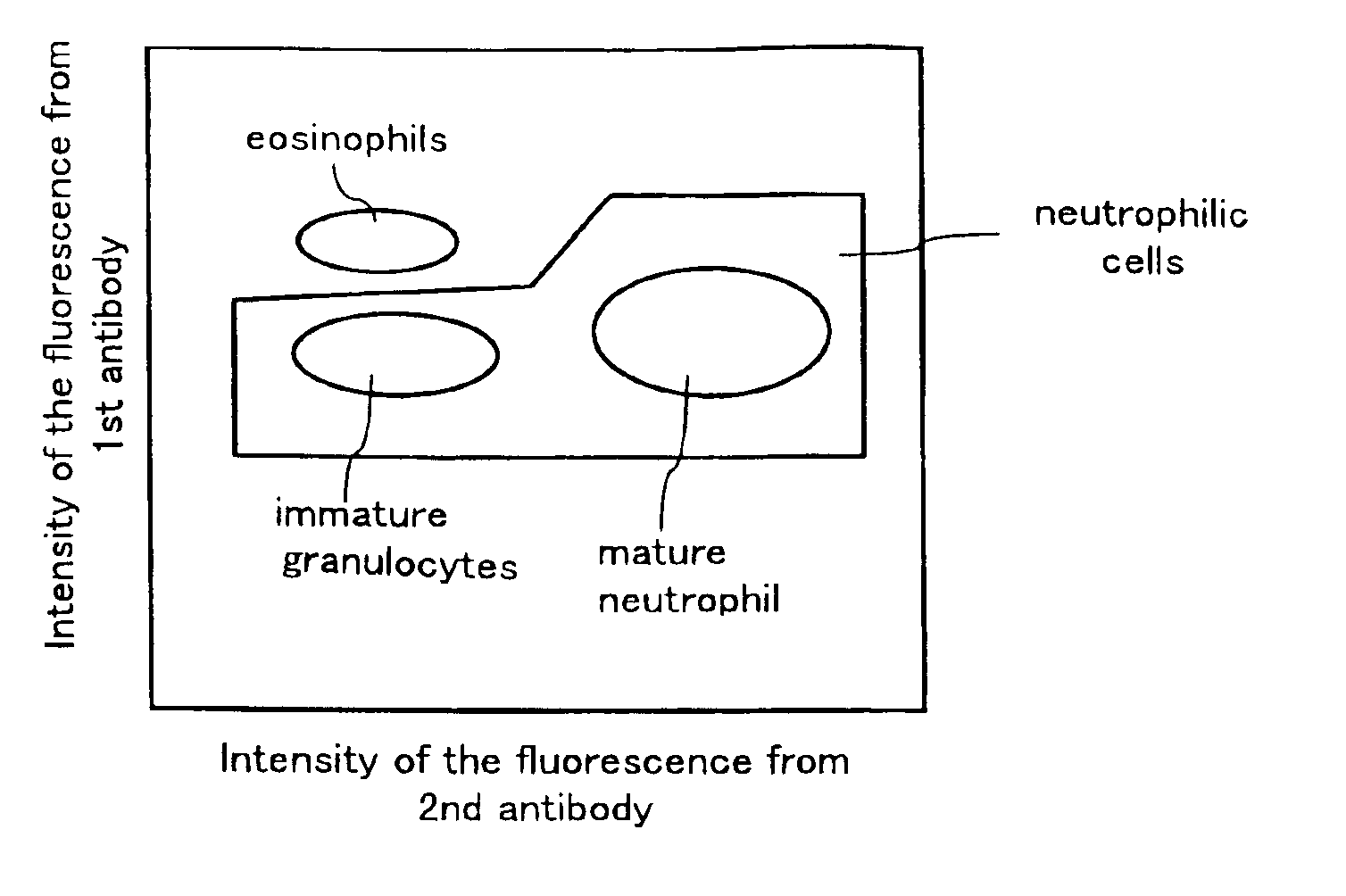
A method for classifying and counting leukocytes comprises the steps of: (1) adding to a hematological sample the following fluorescence-labeled antibodies labeled with fluorescent dyes which emit fluorescences distinguishable from each other; (a) a first fluorescence-labeled antibody (1st antibody) which bonds specifically to leukocytes, (b) a second fluorescence-labeled antibody (2nd antibody) which bonds to at least one kind of neutrophilic cells, and (c) a third fluorescence-labeled antibody (3rd antibody) which bonds to at least one kind of immature granulocytic cells, in order to stain leukocytic cells in the sample, and removing erythrocytes from the sample; (2) analyzing the resulting sample using a flow cytometer to measure at least one scattered light signal and three separate fluorescence signals; (3) defining a group of granulocytic cells on the basis of intensity of the scattered light and intensity of fluorescence from the 1st antibody; (4) defining neutrophilic cells in the defined group of granulocylic cells on the basis of the intensity of the fluorescence from the 1st antibody and intensity of fluorescence from the 2nd or 3rd antibody; (5) classifying the defined group of the neutrophilic cells into groups of neutrophilic cells different in degree of maturity on the basis of the intensity of the fluorescence from the 2nd antibody and the intensity of the fluorescence from the 3rd antibody, and counting the number of cells in each of the groups.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
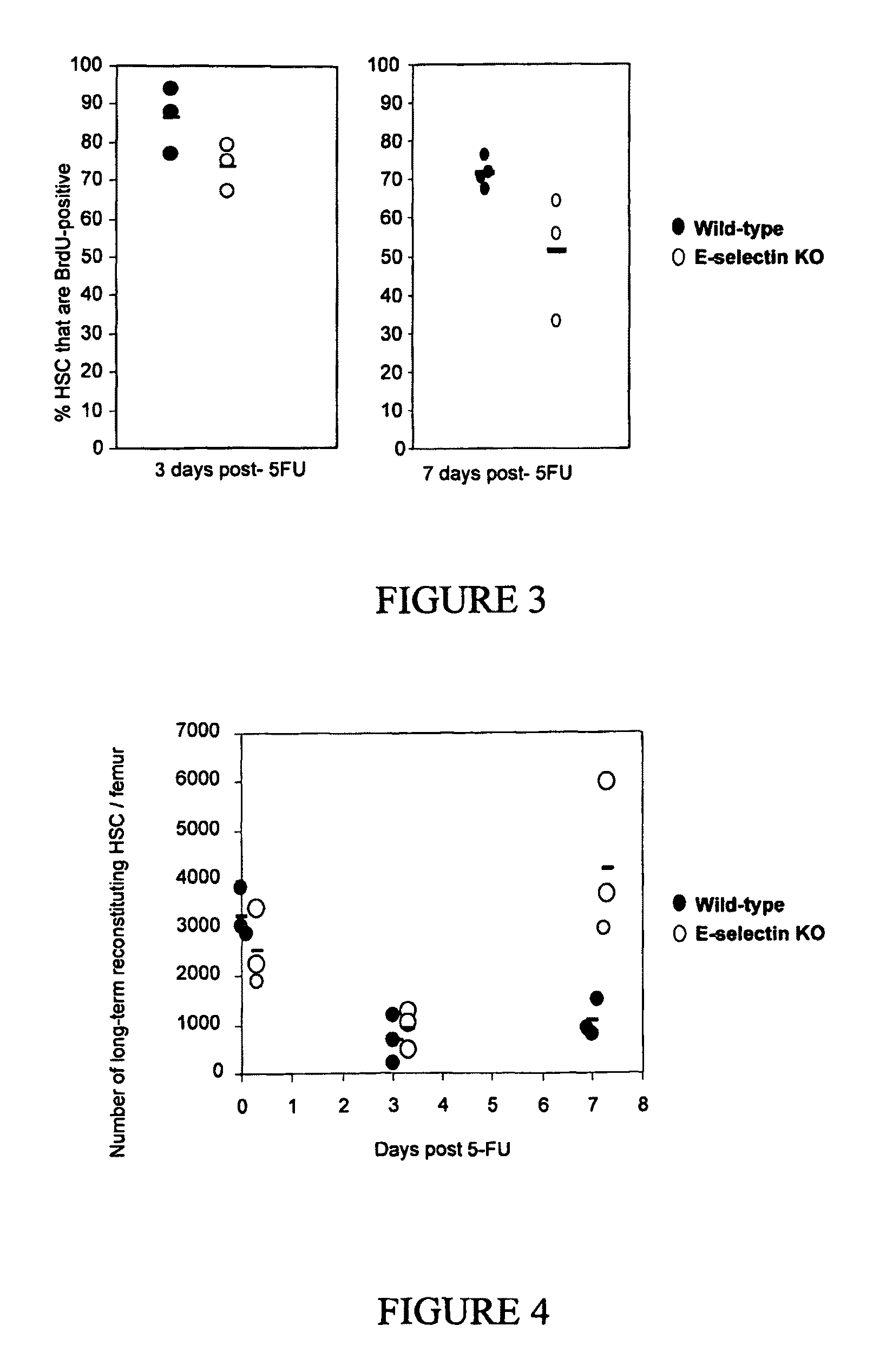
Compositions comprising E-selectin antagonists and uses therefor
ActiveUS9254322B2Stimulating and enhancing hematopoiesisAvoid adjustmentPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsProgenitorSurgery
This invention discloses the use of an E-selectin antagonist and a mobilizer of hematopoietic stem cells or progenitor cells in methods and compositions for treating or preventing immunocompromised conditions resulting from medical treatment. The present invention is particular relevant for prophylaxis and / or treatment of hematopoeitic disorders including neutropenia, agranulocytosis, anemia and thrombocytopenia in individuals receiving or proposed to receive treatments that target rapidly dividing cells or that disrupt the cell cycle or cell division.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
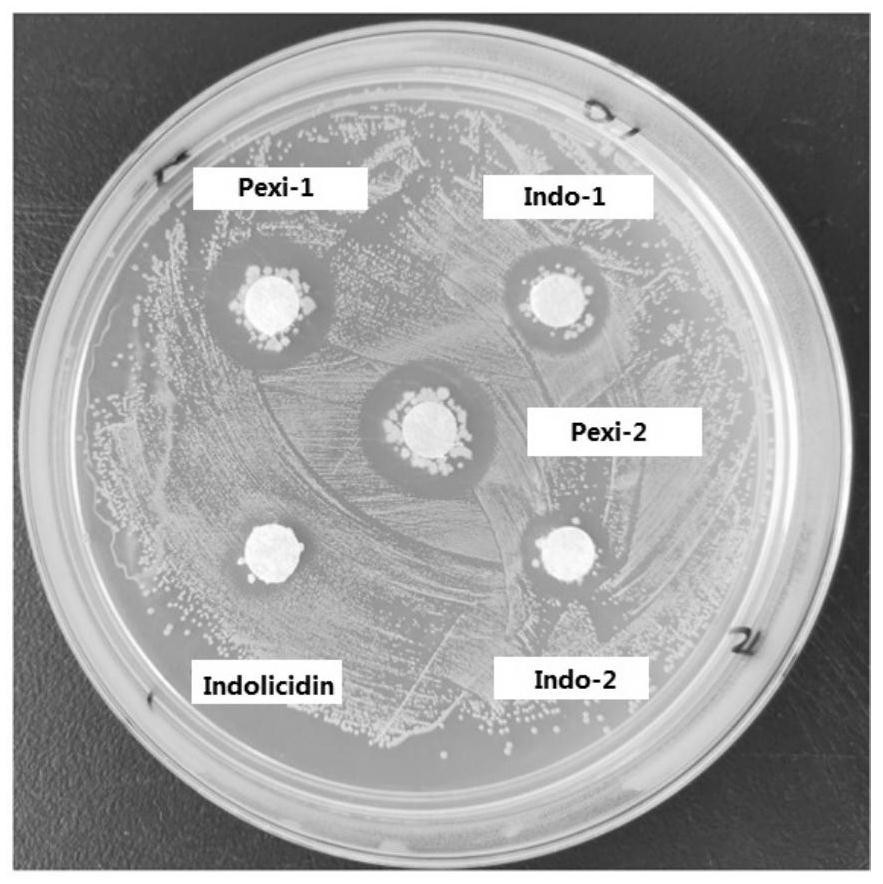
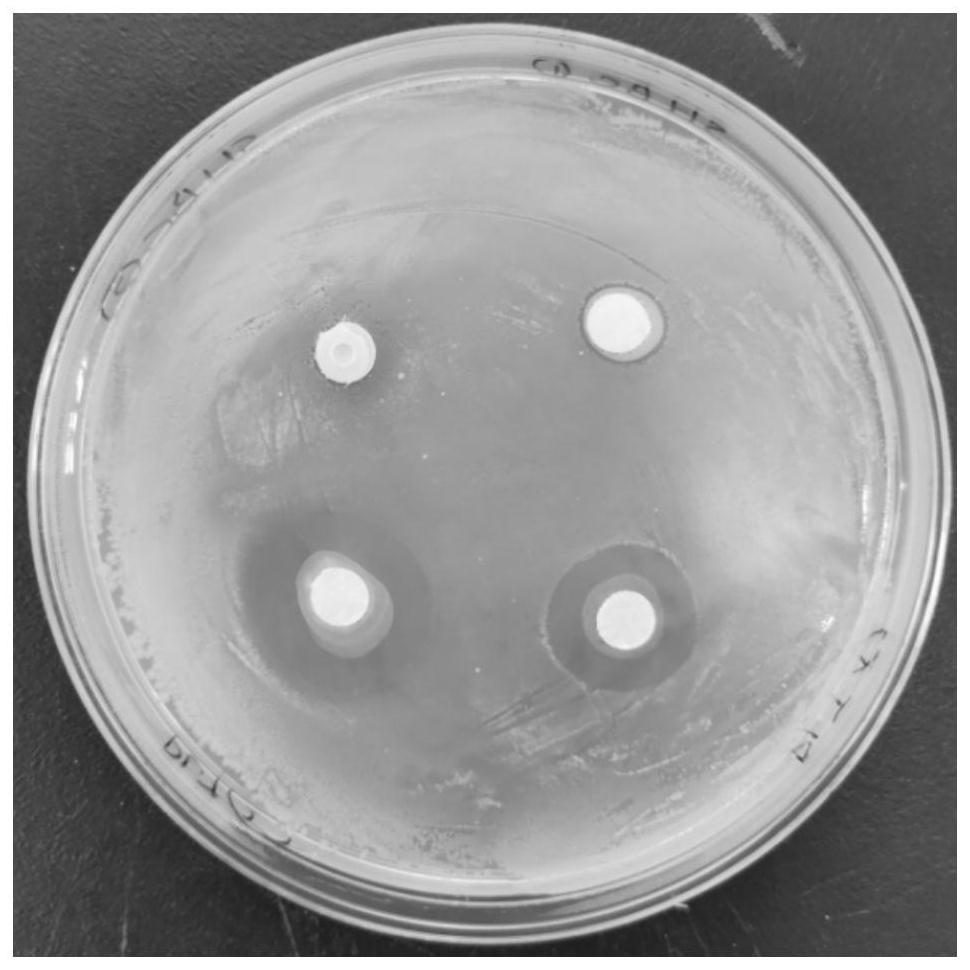
Antibacterial peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN111944020AImprove structural propertiesGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsHemolysisCytotoxicity
The invention provides an antibacterial peptide and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The antibacterial peptide is obtained through rational molecular design on the basis of antibacterial peptide Indolicidin separated from bovine neutrophils; and the antibacterial peptide is antibacterial peptide Indo-1 with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 or antibacterial peptide Indo-2 with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. The antibacterial peptide provided by the invention has good structural characteristics; the antibacterial effect on staphylococcus aureus, salmonella and aspergillus flavus can be obviously improved; and meanwhile, the hemolysis rate and the cytotoxicity of chicken red blood cells can be effectively reduced; the antibacterial peptide can be effectively used in animal-related production activities.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Cell therapy for limiting overzealous inflammatory reactions in tissue healing
ActiveUS20110178502A1Promote recoveryImprove cleanlinessBiocidePowder deliveryImmediate releaseNeutrophil granulocyte
Cells of the B cell lineage including pre-pro-B cells, pro-B cells, pre-B cells, immature B cells, and some mature B cells, and / or cells of the T cell lineage, especially those with helper or regulatory function, most preferably autologous to the recipient, can be transplanted into damaged tissue to enhance recovery following injury. In a preferred embodiment, the cells are selected based on those cells which appear at the site of injury a few days after injury, such as macrophages, lymphocytes, which accelerate clean up and repair of the injured site and to mitigate the overzealous inflammatory response, presumably by inhibiting the inflammatory cells such as neutrophils and signals released thereby immediately following injury.
Owner:HOLY CROSS HOSPITAL
Leukocyte regulatory factors 1 and 2
InactiveUS20060063924A1Enhancing and inhibiting biological activityImprove bindingSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseWhite blood cell
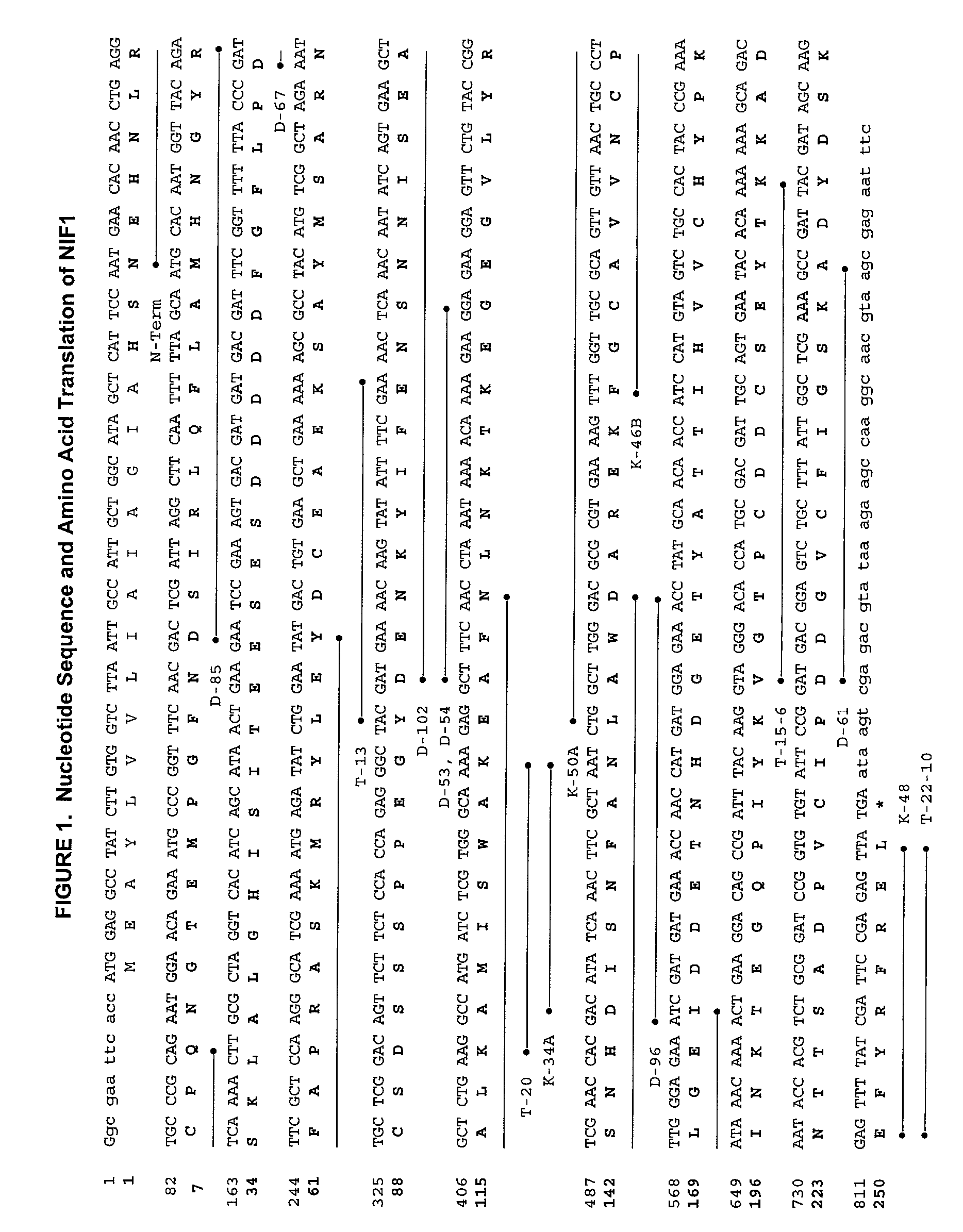
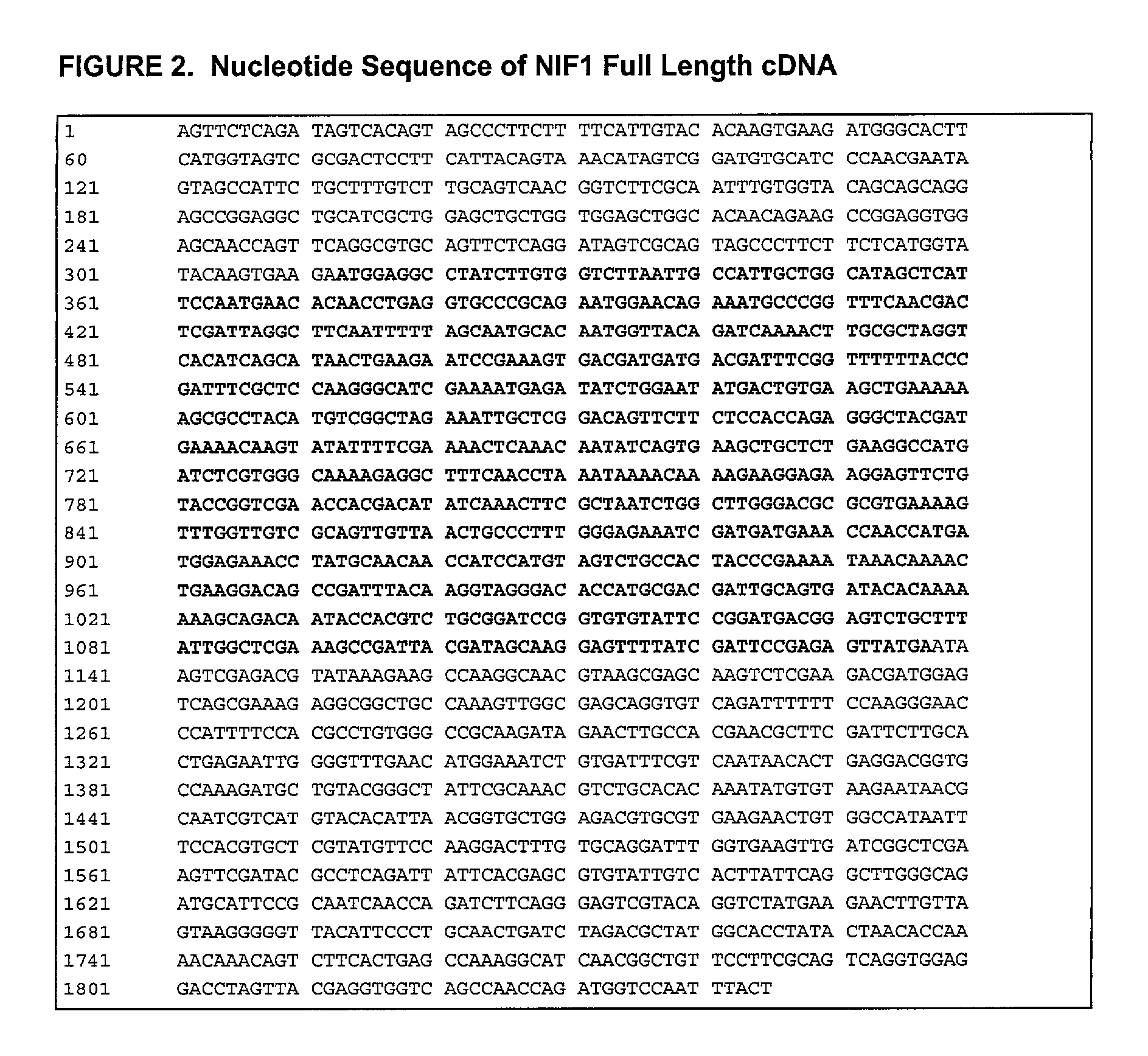
The present invention relates to novel LRF-1 and LRF-2 proteins which are related to the CRISP family and a protein called “Neutrophil Inhibitory Factor (NIF)” isolated from the canine hookworm (Ancylostoma caninum) that potently inhibits CD11 / CD18-dependent neutrophil function. In particular, isolated nucleic acid molecules are provided encoding the human LRF-1 and LRF-2 proteins. LRF-1 and LRF-2 polypeptides are also provided, as are vectors, host cells and recombinant methods for producing the same. The invention further relates to screening methods for identifying agonists and antagonists of LRF-1 or LRF-2 activity. Also provided are diagnostic methods for detecting immune system or other LRF-1- or LRF-2-related disorders and therapeutic methods for treating such disorders.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
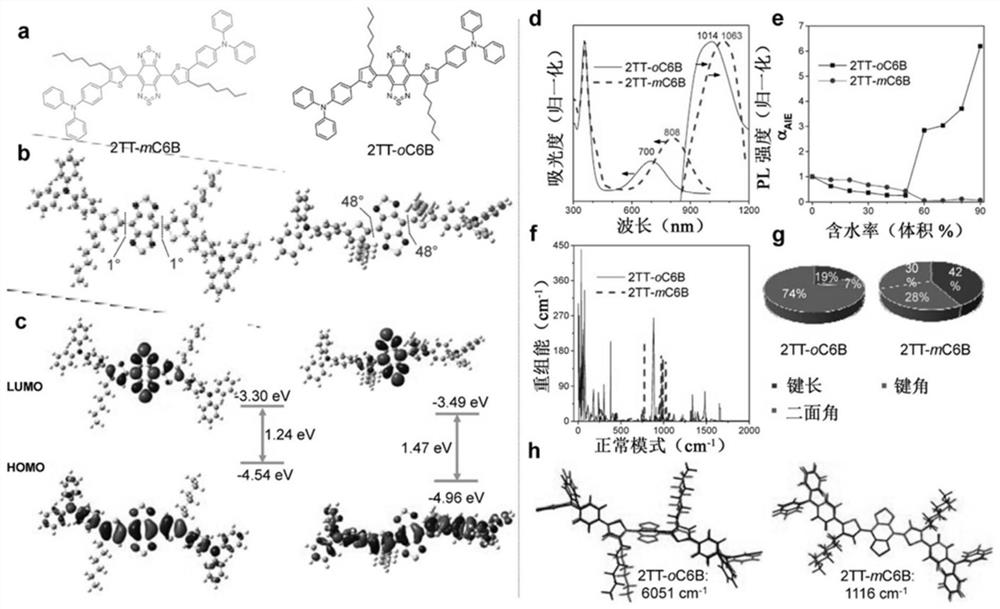
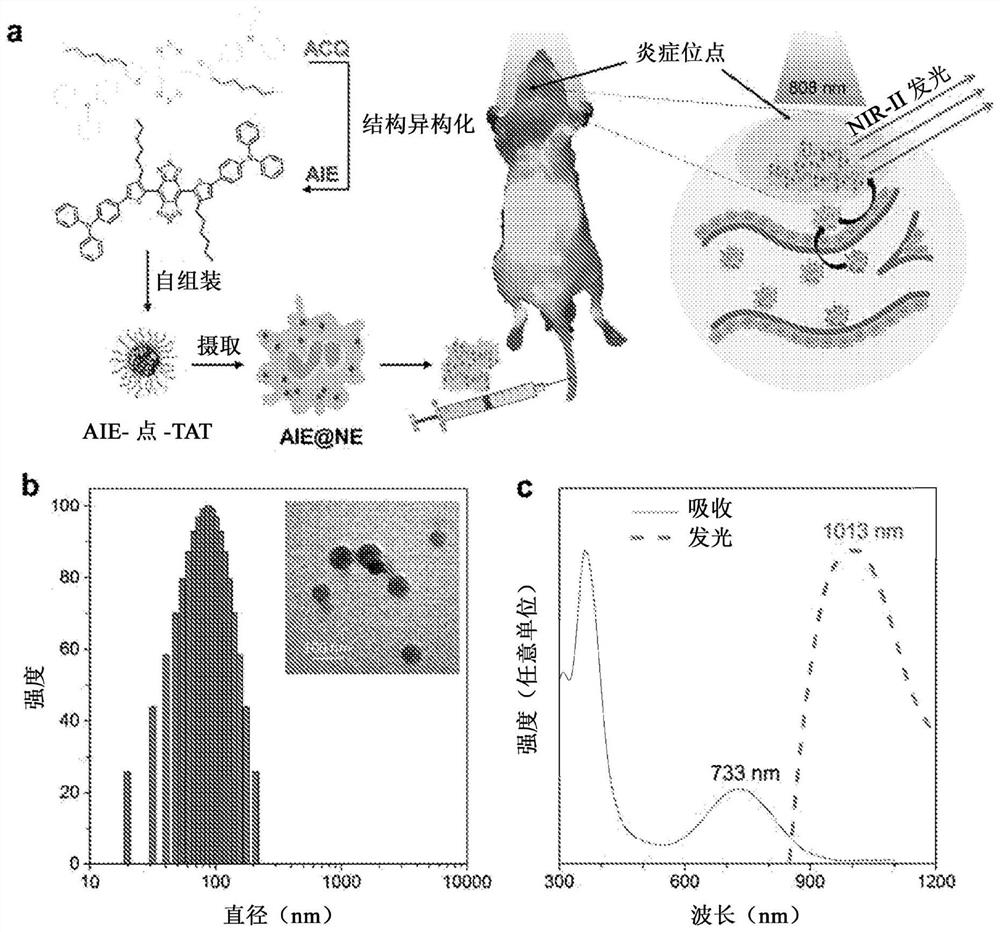
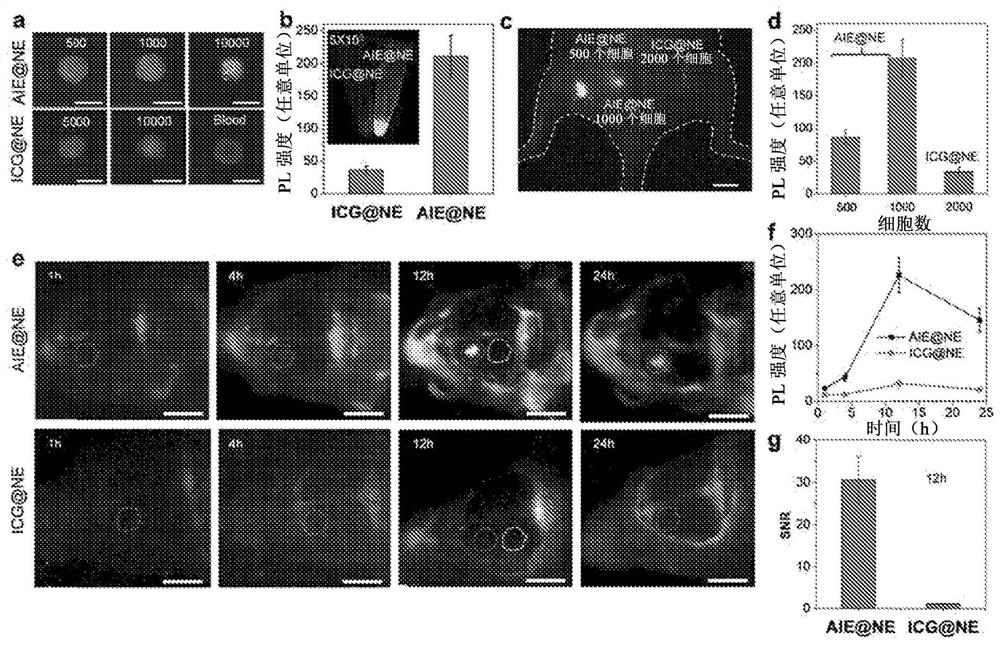
Ultrabright nir-ii aiegen for bioimaging
The present subject matter contemplates small molecule, fluorescent compounds having aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics. The compounds can exhibit emission in the second near-infrared window (NIR-II) (1000 nm-1700 nm). The compounds can provide imaging for deeply located diseases with ultrahigh signal background ratio. For example, neutrophils carrying the present compounds can penetrate the brain and visualize inflammation deeply located within the brain tissue through intact scalp and skull.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
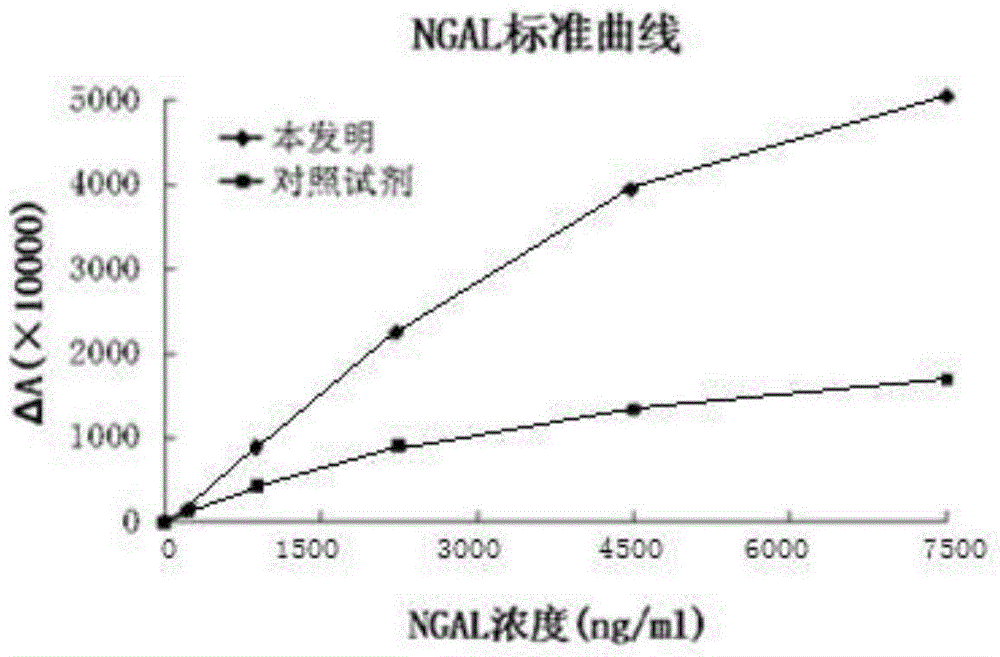
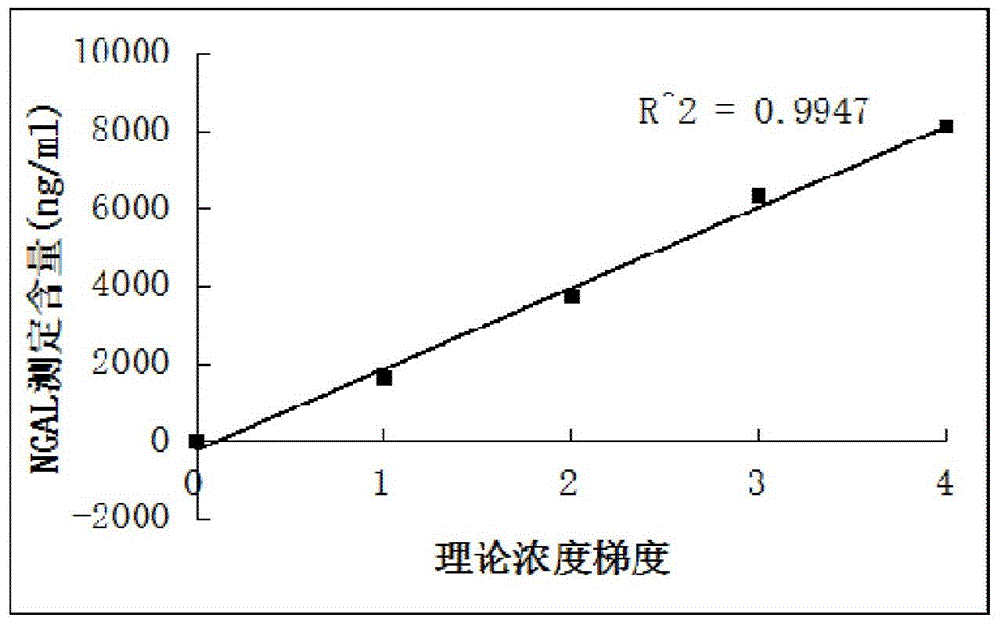
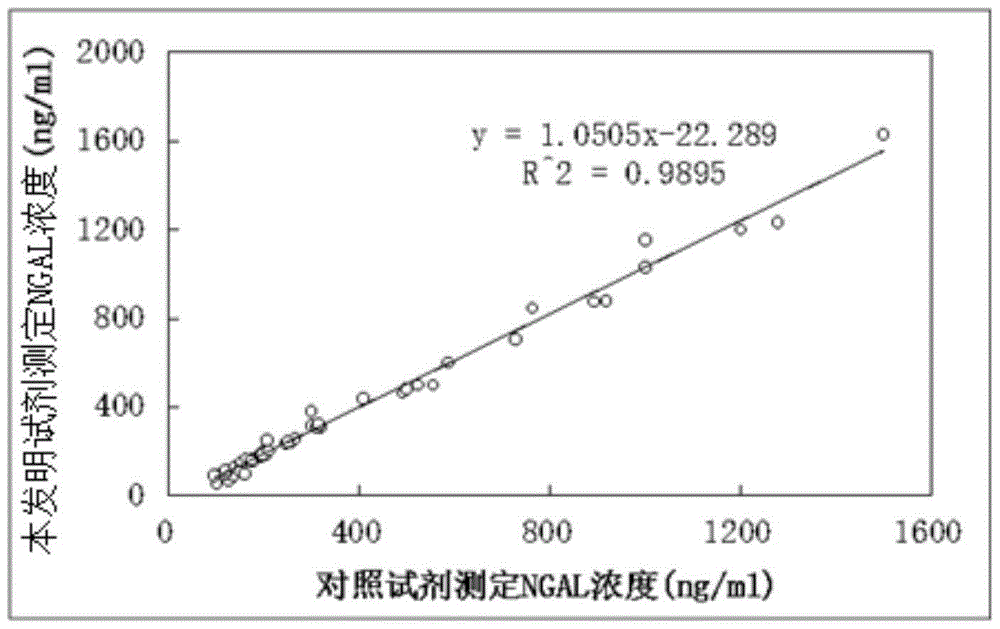
Kit for content detection of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
The invention discloses a kit for content detection of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, wherein a reagent R1 comprises Tris, NaCl, BSA, Tween-20, PEG and NaN3; a reagent R2 comprises Tris, NaCl, BSA, Tween-20, NaN3, sucrose and NGAL antibody sensitized latex particles; a NGAL reagent reference standard sample comprises Tris, NaCl, BSA, Tween-20, EDTA, NaN3 and NGAL of different contents; the NGAL antibody sensitized latex particles comprise PS nanometer latex particles and PVN nanometer latex particles, and the particle size of the PS nanometer latex particle is larger than the particle size of the PVN nanometer latex particle. The invention has the advantages of simple reagent composition, good test sensitivity, wide linearity range, good stability, low test cost and high precision, and the kit is convenient for popularization.
Owner:NINGBO RUI BIO TECH
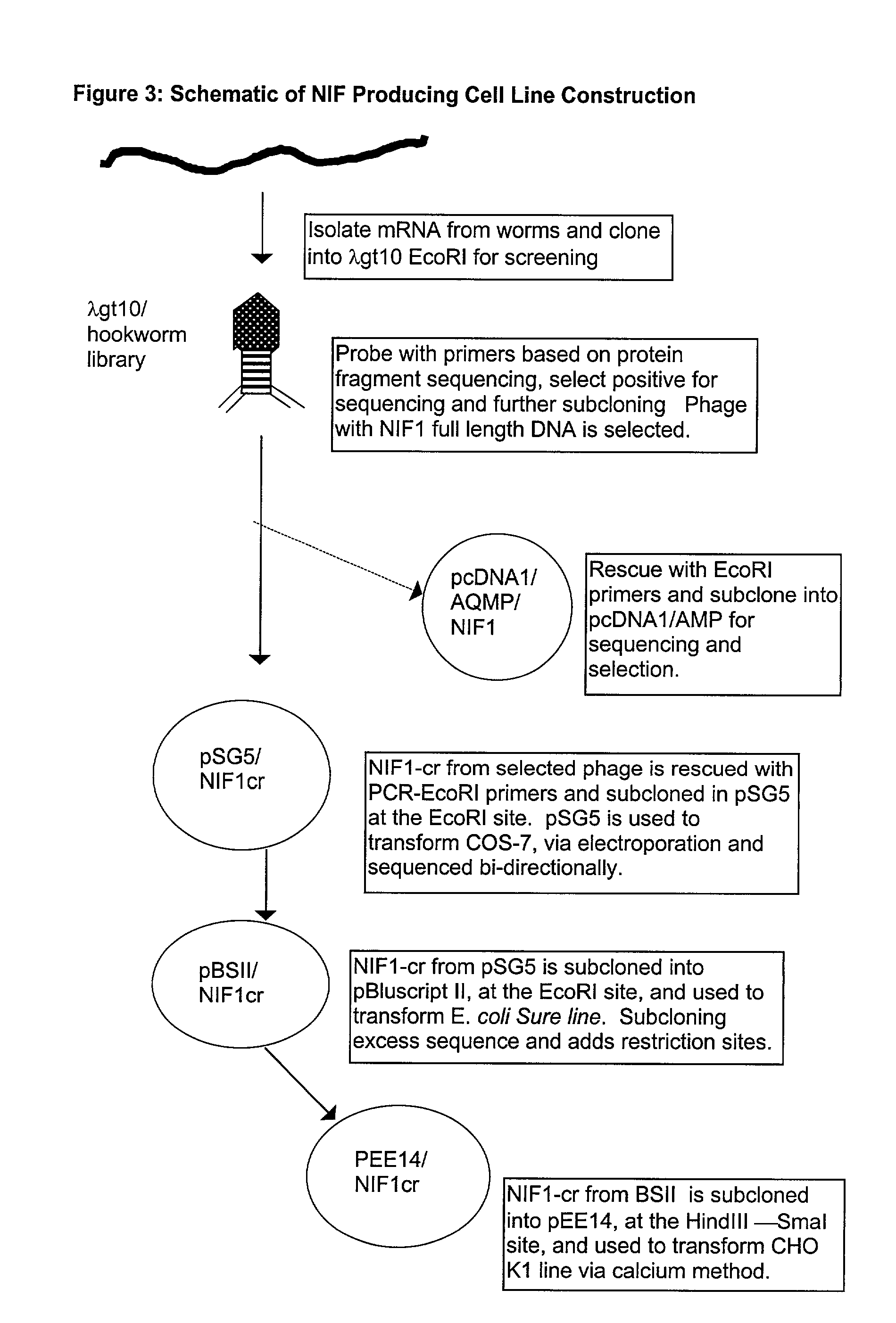
Process for the preparation of neutrophil inhibitory factor
InactiveUS20020099183A1High yieldShort maintenance periodPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsCell culture mediaNeutrophil granulocyte
The present invention relates to a method for the preparation of a Neutrophil Inhibitory Factor (NIF) comprising the cultivation of mammalian cells expressing NIF in an animal component-free growth medium. The present invention may be employed in large-scale preparation of NIF. The invention also relates to a method for the preparation of recombinant proteins comprising the cultivation of mammalian cells expressing an exogenous recombinant protein in an animal component-free growth medium.
Owner:WALDRON ROY F PH D
Novel application of hyaluronic acid fragment and stable making method
InactiveCN111249302AInhibition removedPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticApoptosis PromoterApoptosis
The invention discloses application of a hyaluronic acid fragment as a human neutrophil migration inhibitor, a human mononuclear cell migration inhibitor, a human mononuclear cell apoptosis promoter and / or a human neutrophil beta sozin secretion promoter. The hyaluronic acid fragment is hyaluronic acid fragment which is of a use structure made through sufficient or slightly excessive sufficient enzymolysis of a high or medium molecular weight hyaluronic acid raw material by using hyaluronidase PH20 with two binding zones, and the hyaluronic acid fragment has an average molecular weight of 35+ / -8KDa. The invention further discloses application of the hyaluronic acid fragment in preparing a medicine for treating neutrophil and mononuclear cell mediated inflammation diseases. The invention further discloses a stable making method of the hyaluronic acid fragment and a combined application method of a hyaluronidase injection and a hyaluronic acid injection made on the basis of the stable making method. Through research, the invention finds the stable making method, making principles and anti-inflammation mechanisms of the hyaluronic acid fragment, and bases are made for medicinal research on the hyaluronic acid fragment.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV +2
Inflammation targeted compound, preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to an inflammation targeted compound, a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of pharmacy. The compound comprises a part A and a part B, wherein the part A is inflammation related cells the number of which is 1*10<5>-1*10<8>; the part B is a treatment medicine, and the dosage is clinically acceptable effective treatment dosage. According to the preparation method, a cell-medicine compound is formed after the treatment medicines and a monocyte or neutrophil are incubated in vivo, is applied to the affected host, and is recruited to pathological part in the recruitment of inflammatory reactions of tumors, rheumatoid arthritis or atherosclerosis, so that targeted treatment to the diseases can be realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Free ngal as a biomarker for cancer
InactiveUS20110081650A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisGelatinaseNGAL Protein
Uncomplexed neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) is present at increased levels in individuals with atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH), a major risk factor for future breast cancer development; in individuals that have ovarian cancer; and in individuals that have breast cancer, both invasive and noninvasive. Accordingly, the present invention is directed to measuring uncomplexed NGAL levels in urine as a primary screen to determine if an individual is either at risk of developing, or has developed cancer, e.g., cancer of epithelial origin including breast and ovarian cancer.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Method to mitigate morbidity and mortality in virally induced forms of ACE2 receptor pathology progressing to SARS or ARDS.
InactiveUS20210315910A1Reduce infectionMaximize resultTetracycline active ingredientsMucoid impactionBronchial epithelium
ACE receptors are affected in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome related coronaviruses. ACE genes are directly related to the morbidity and mortality of those with cystic fibrosis. The thick, sticky mucus in the respiratory, and digestive systems, is seen in the inherited disease cystic fibrosis. Viral induced sticky mucus in the respiratory and digestive systems can also be appreciated as a response to viral pathogens where the cycle of mucus production in vivo induces the recruitment of more mucus production to the extent that cellular damage occurs within the lower respiratory track requiring intubation as a life saving measure. In the most severe cases mechanical intubation fails due to the fact that no control over the recruitment of mucus production was achieved at the onset. SARS pathology shows inflammatory exudation in the alveoli and interstitial tissue, with hyperplasia of fibrous tissue and fibrosis. Inherited cystic fibrosis pathology shows atelectasis, mucoid impaction, acute and chronic inflammation, bronchiectasis, cyst formation, and fibrosis widespread. A virally induced disorder in relations to ACE2 receptors can be treated successfully at the early onset with inherited cystic fibrosis disease mimicking techniques with the efforts of minimizing the activity and utilization of the ACE2 receptor. Cystic fibrosis lung infections, and opportunistic pathogens contribute to chronic airway inflammation that is characterized by neutrophil / macrophage infiltration, cytokine release and ceramide accumulation. In terms of virally induced forms off ACE2 receptor pathologies, as it related to coronavirus such as Covid 19, presumably ceramide precursors which aid in intracellular transport of the virus into the cell via inflammation and remodeling is present in alveolar tissues of the lung in patients with cystic fibrosis while the same pathology occurs in patients with virally induced forms of ACE2 pathology which to often progresses to SARS or ARDS.
Owner:STAFFORD VIVI ROBYN
Cell-based vaccine compositions and methods of use
Methods of generating an autologous cellular vaccine comprising monocytes or neutrophils and an antigenic polypeptide or nucleotide encoding the antigenic polypeptide are provided. The antigen-loaded cell-based vaccine compositions made using these methods are also provided. Methods of using the antigen-loaded cell-based vaccine compositions are also provided and these vaccines may be used to treat cancer. Kits for carrying out the methods described herein are also provided.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
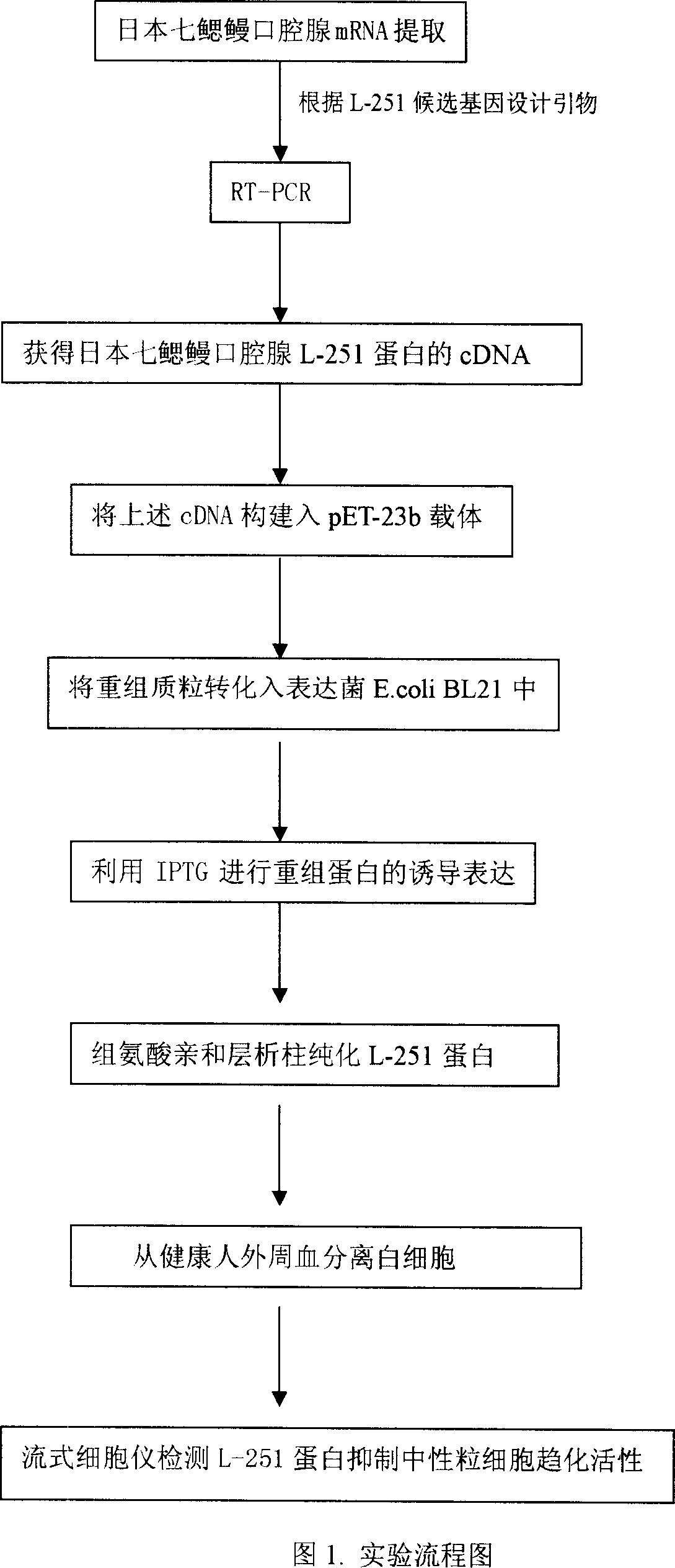
Recombinant L-251 protein with anti-inflammatory effect secreted by Japanese lamprey oral gland
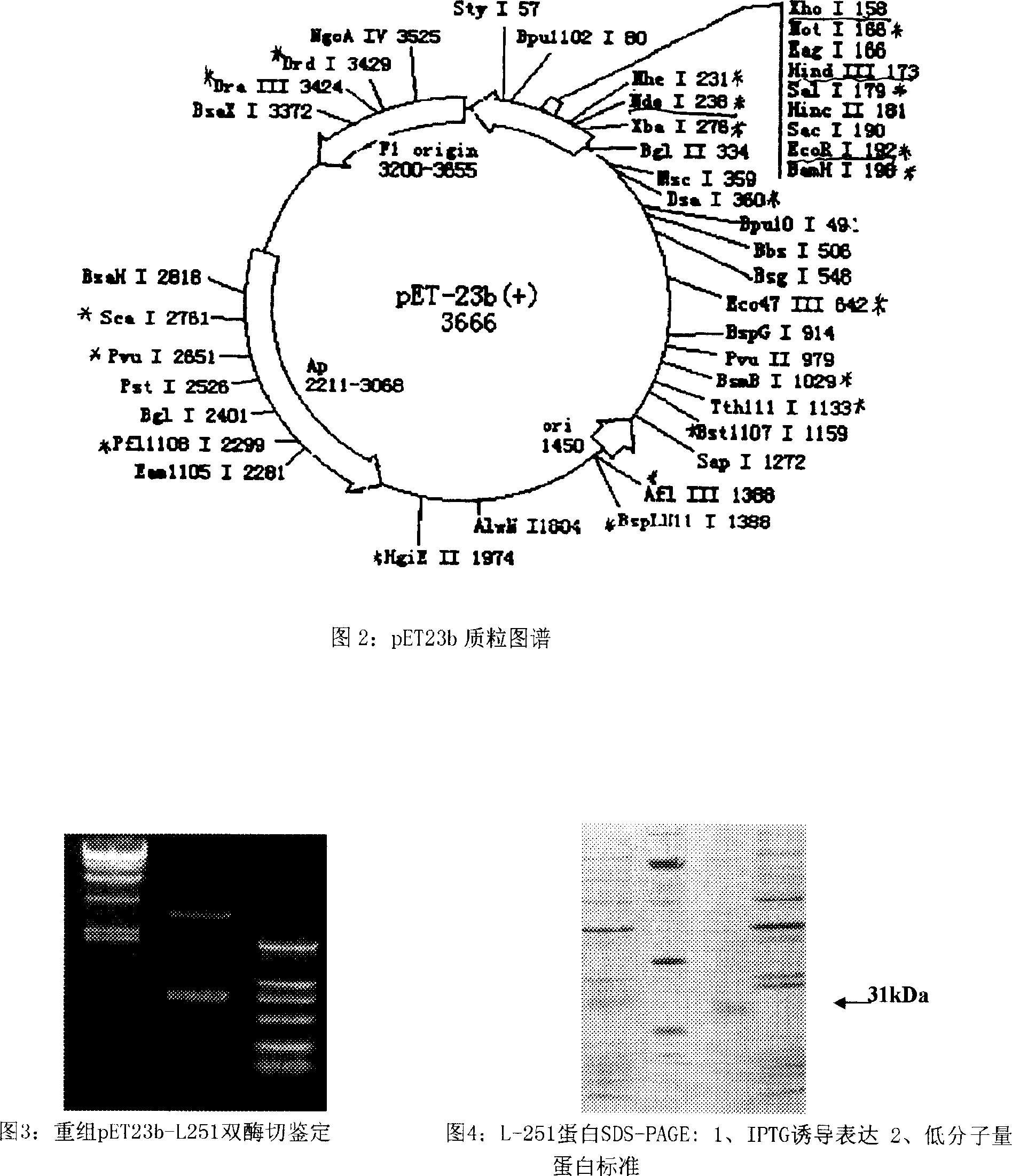
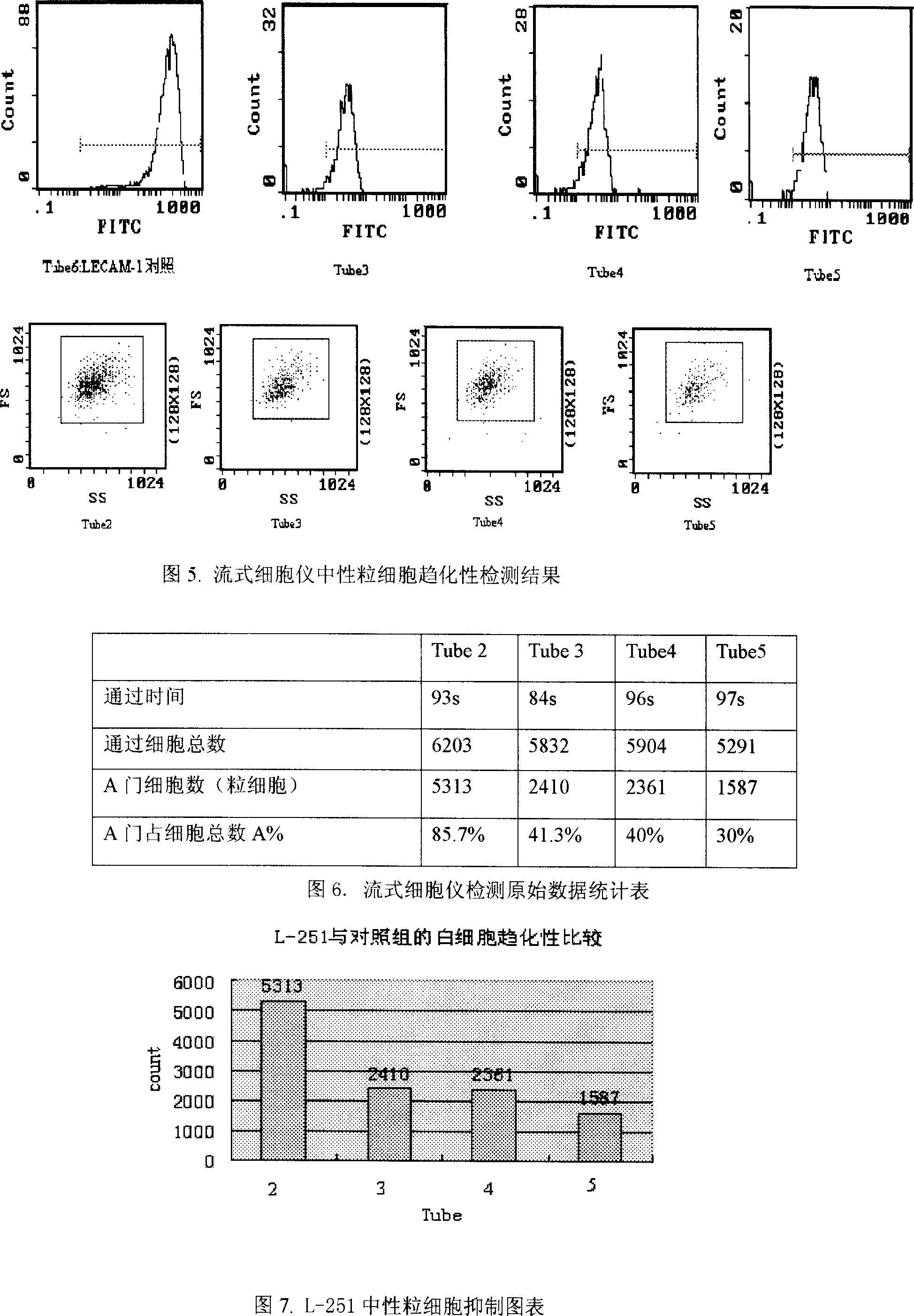
InactiveCN1995345AChemotaxis determinationInhibit migrationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsCD11aNeutrophil granulocyte
The invention discloses a cDNA sequence and cloning of L-251 protein excreted by Japanese lamprey oral gland and amino acid sequence corresponding to cDNA and expression in the engineering bacteria as well as connecting protein of CD11a and CD11b beta2 integrated agent (CR3 receptor), which inhibits neutrophil leucocyte from transmitting from endothelium cell to inflammation point.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Cerebrospinal fluid cell feature extraction method based on gray level co-occurrence matrix
PendingCN112634338ACalculation speedEasy extractionImage enhancementImage analysisPlasma cellBiochemistry
The invention relates to a cell feature extraction method, in particular to a cerebrospinal fluid cell feature extraction method based on a gray level co-occurrence matrix. The invention aims to segment and extract textural features of plasma cells, lymphocytes and neutrophils in autoimmune encephalitis cerebrospinal fluid. The method comprises the step of extracting textural features of plasma cells, lymphocytes and neutrophils in a cerebrospinal fluid image by utilizing a gray-level co-occurrence matrix.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Immunologically active polypeptide
ActiveUS9816989B2Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAnimals/human peptidesAutoimmune conditionAntiendomysial antibodies
Disclosed are immunomodulatory polypeptides that elicit an unusual induced cytokine profile, compositions comprising such polypeptides, compositions comprising antibodies that specifically bind to such polypeptides, and methods of using the same, including in cancer treatment, in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, in organ transplantation and for reducing graft rejection, for promoting fertility, and for identifying a neutrophil subset and / or other cellular subset including by flow cytometry. Pharmaceutical compositions and kits, and treatment methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CDRES PHARMA LLC
Neutrophil inhibitors
Compositions enriched for Neutrophil Inhibitory Factor which inhibit neutrophil activity including adhesion to vascular endothelial cells are provided. Also provided are recombinant Neutrophil Inhibitory Factors which also which inhibit neutrophil activity. Such compositions may comprise a glycoprotein isolated from nematodes. These compositions and recombinant Neutrophil Inhibitory Factors are useful in the therapy of conditions which involve abnormal or undesired inflammatory responses.
Owner:DENDREON PHARMA LLC
Bi-specific affinity reagents for cell-lineage-specific tnf-alpha neutralisation
ActiveUS20150284460A1Strong specificityProlong half-life in vivoBiocideBacteriaCell lineageAntibody fragments
The invention relates to isolated bispecific affinity reagents, such as antibodies or antibody fragments that bind TNFα and a marker molecule for macrophages and / or neutrophils. The affinity reagents of the invention enable pathogenic sub-populations of TNFα to be neutralised, whilst protective sub-populations of TNFα are not affected.
Owner:DEUT RHEUMA FORSCHUNGSZENT BERLIN
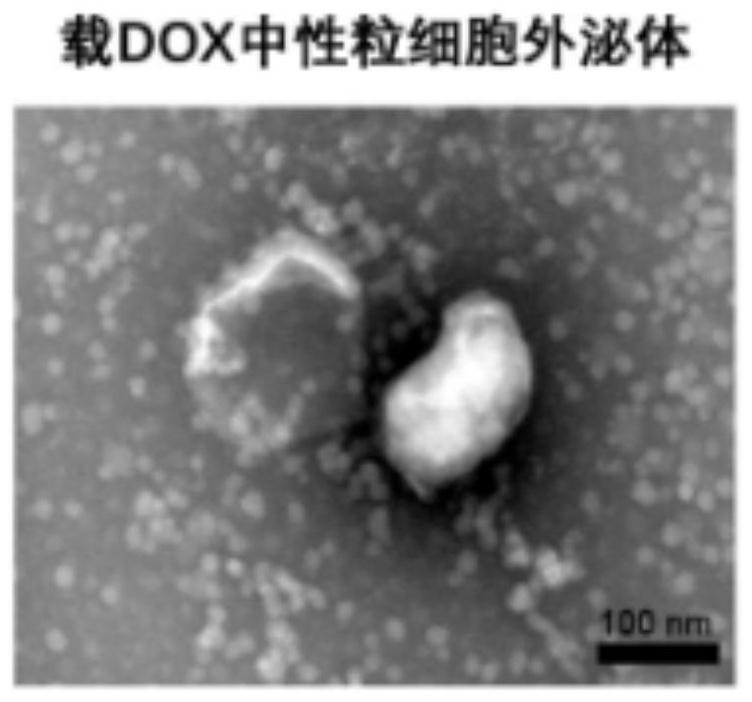
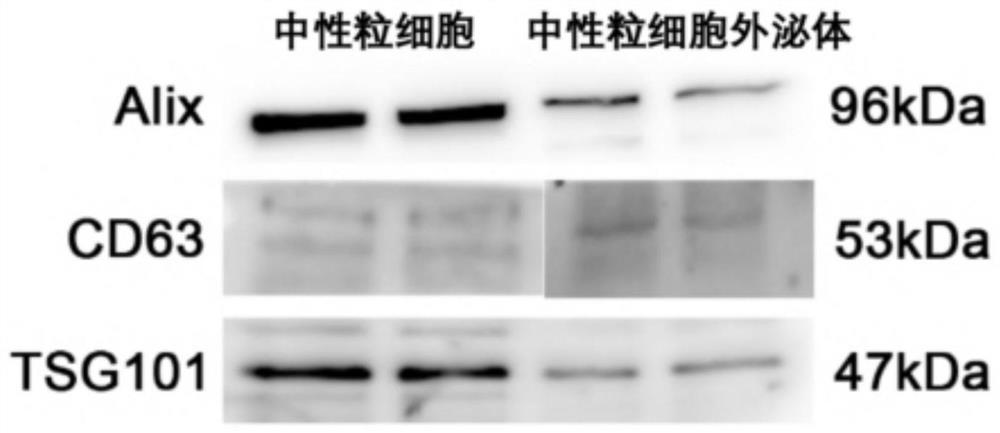
Neutrophil-like nano drug delivery system as well as preparation method and application thereof
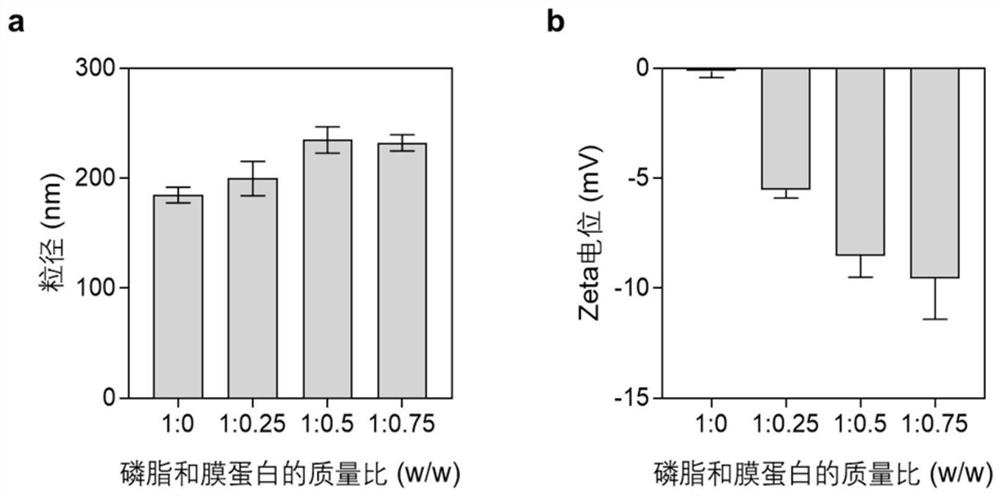
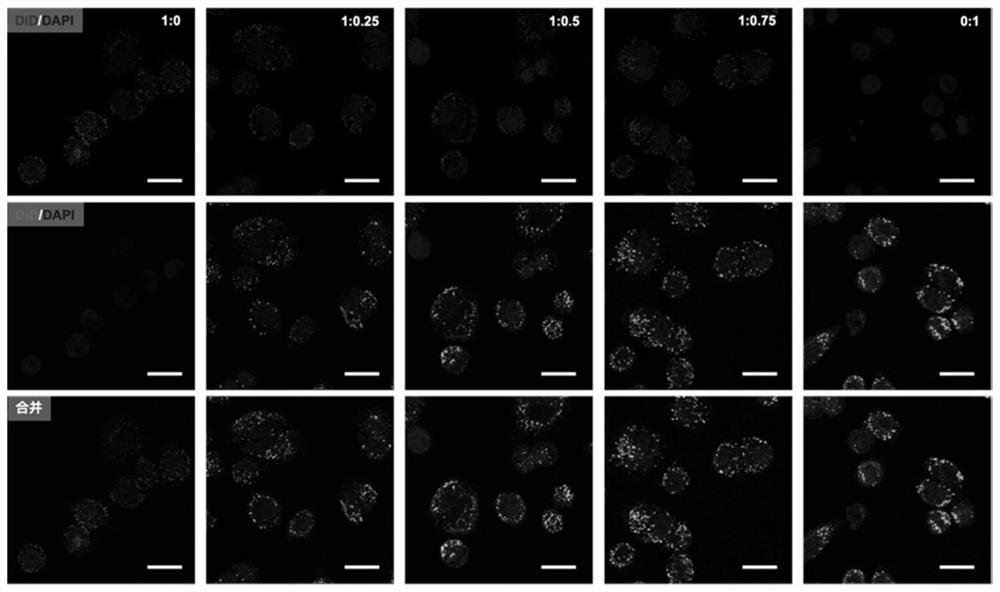
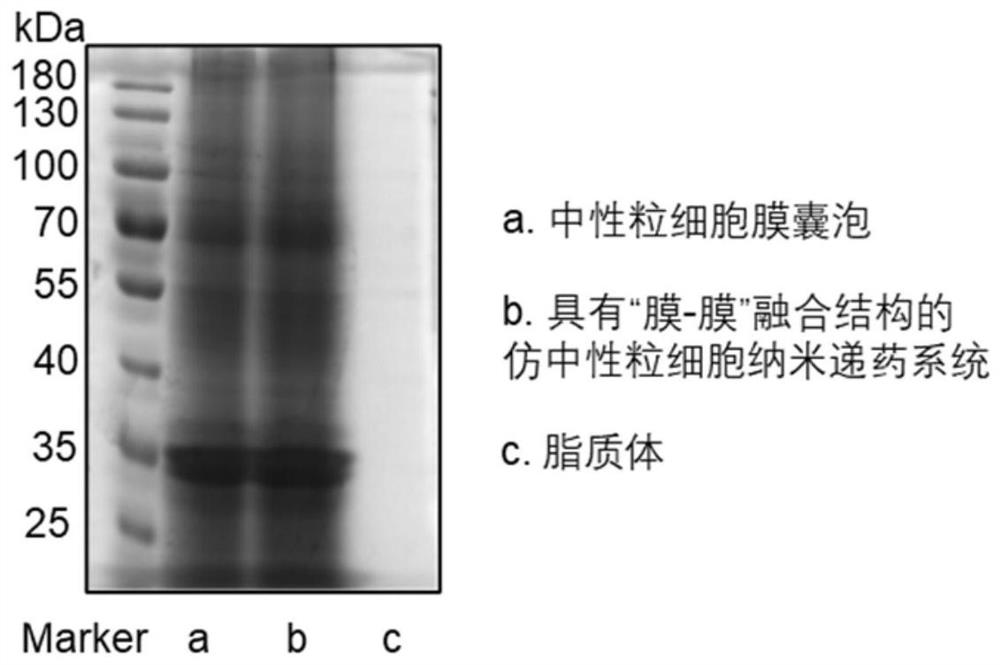
PendingCN113952461AEasy to prepareConditions are easy to controlAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderLipofectaminePhospholipid
The invention discloses a neutrophil-like nano drug delivery system, which has a phospholipid bilayer structure and is prepared by interactive fusion of an activated neutrophil membrane stimulated by a stimulating factor and phospholipid molecules, and the particle size of the nano drug delivery system is 100-300nm. The invention further discloses a preparation method and application of the neutrophil-like nano drug delivery system. According to the neutrophil-like nano drug delivery system with the membrane-membrane fusion structure, the advantages of the liposome and the cell carrier are fully combined, the respective defects of the liposome and the cell carrier are avoided, the liposome is used for loading drugs to overcome the defect that the cell carrier is difficult to load drugs, the active targeting ability of the liposome is endowed by the activated-state neutrophil membrane, the combination of the liposome and the cell carrier is beneficial to realizing accurate delivery of the drug to the inflammation part, can improve the treatment effect, can reduce the toxic and side effects, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Application of Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton as neutrophil modulator
The invention relates to application of a Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton as a neutrophil modulator. The present application provides a neutrophil modulator, which comprises a component derived from the cell wall of Nocardia rubra, and which can modulate the chemotactic function, phagocytosis function, and bactericidal function (reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, degranulation formation) of neutrophil. The neutrophil regulator disclosed by the invention can also improve the local immune microenvironment of a chronic infection wound.
Owner:LIAONING GREATEST BIO-PHARM CO LTD
Blood-brain barrier penetrating drug delivery system as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114642736AHave biological propertiesHas good biological propertiesCell dissociation methodsOrganic active ingredientsPharmacologyDelivery system
The invention relates to a blood-brain barrier penetrating drug delivery system as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The blood-brain barrier penetrating drug delivery system comprises a neutrophil exosome and a drug entrapped in the neutrophil exosome, the medicine is a medicine for treating central nervous system diseases. The invention constructs a neutrophil exosome drug-loading delivery system with good biocompatibility, and the drug-loading system has biological characteristics similar to that of neutrophil, can efficiently penetrate through a blood-brain barrier, effectively respond to inflammation, and target an inflammation site, so that the drug-loading system has a good application prospect. The compound is a drug carrier with great application prospect for treating glioma and other central nervous system diseases. The invention provides a new strategy with a transformation application prospect for non-invasive inflammatory microenvironment targeted drug delivery of glioma and other central nervous system diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of traditional Chinese medicine composition in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating coronavirus complicated with lung injury
InactiveCN111803543AIncrease percentageImprove the level ofAntiviralsRespiratory disorderPulmonary InjuryCD8
The invention discloses application of a traditional Chinese medicine composition in preparation of a medicine for preventing and treating novel coronavirus complicated with lung injury. The intervention effect of the traditional Chinese medicine composition on novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) is screened, and a clinical experiment result shows that the traditional Chinese medicine composition has agood effect of inhibiting lung injury and lung fibrosis caused by novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). The traditional Chinese medicine composition can improve the levels of albumin, lymphocyte, lymphocyte percentage, neutrophil and CD8 cells and reduce the levels of C reactive protein and lactate dehydrogenase, the novel coronavirus complicated with lung injury can be treated in an assisted manner, and a recovery rate can be improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG LEIYUNSHANG PHARM CO LTD
Visual detection method for tumor metastasis related neutrophils
The invention discloses a visual detection method for tumor metastasis related neutrophils. The visual detection method specifically comprises the following steps of 1) preparing novel tumor metastasis related neutrophils, 2) preparing tumor cells, 3) preparing a visual device, 4) preparing a fluid, 5) preparing a recording device, 6) searching an optimal visual field, and 7) recording tumor metastasis related neutrophil capture circulating tumor cells. The in-vivo fluid condition of tumor cells captured by novel tumor metastasis related neutrophils can be simulated by utilizing existing equipment in a laboratory, visual detection is carried out, high-end precious equipment does not need to be specially purchased, and the method can be popularized and used in an experimental platform.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
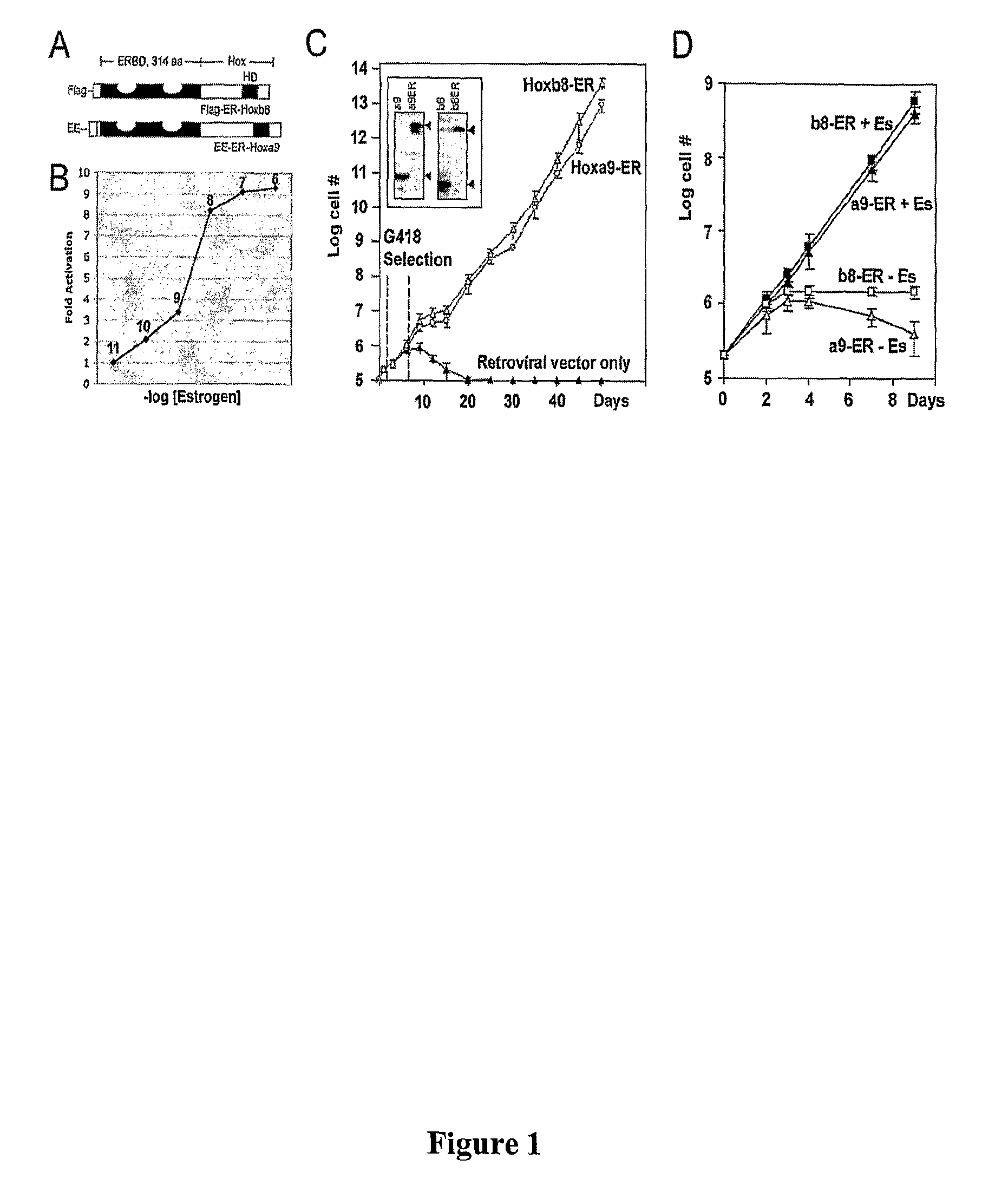
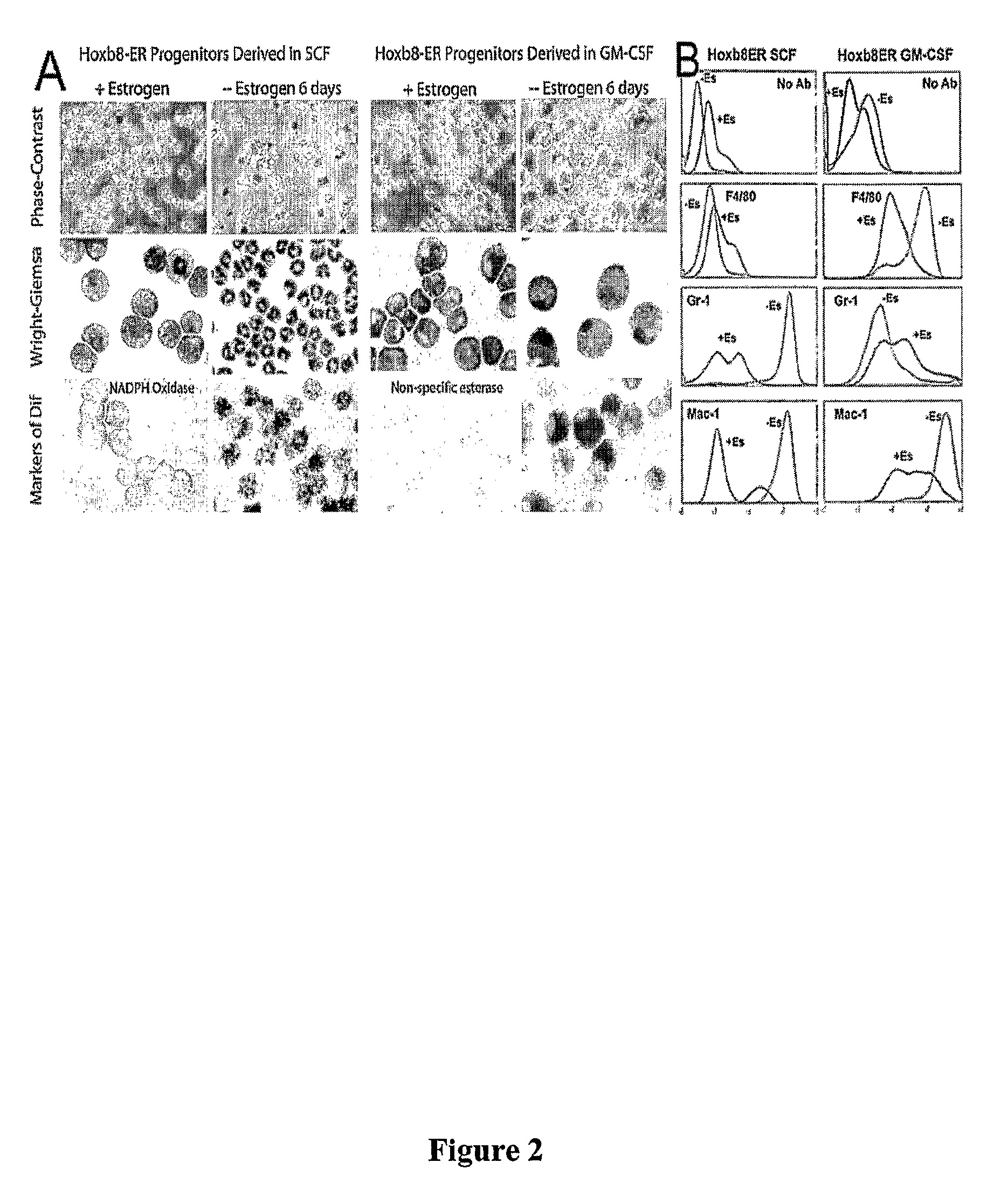
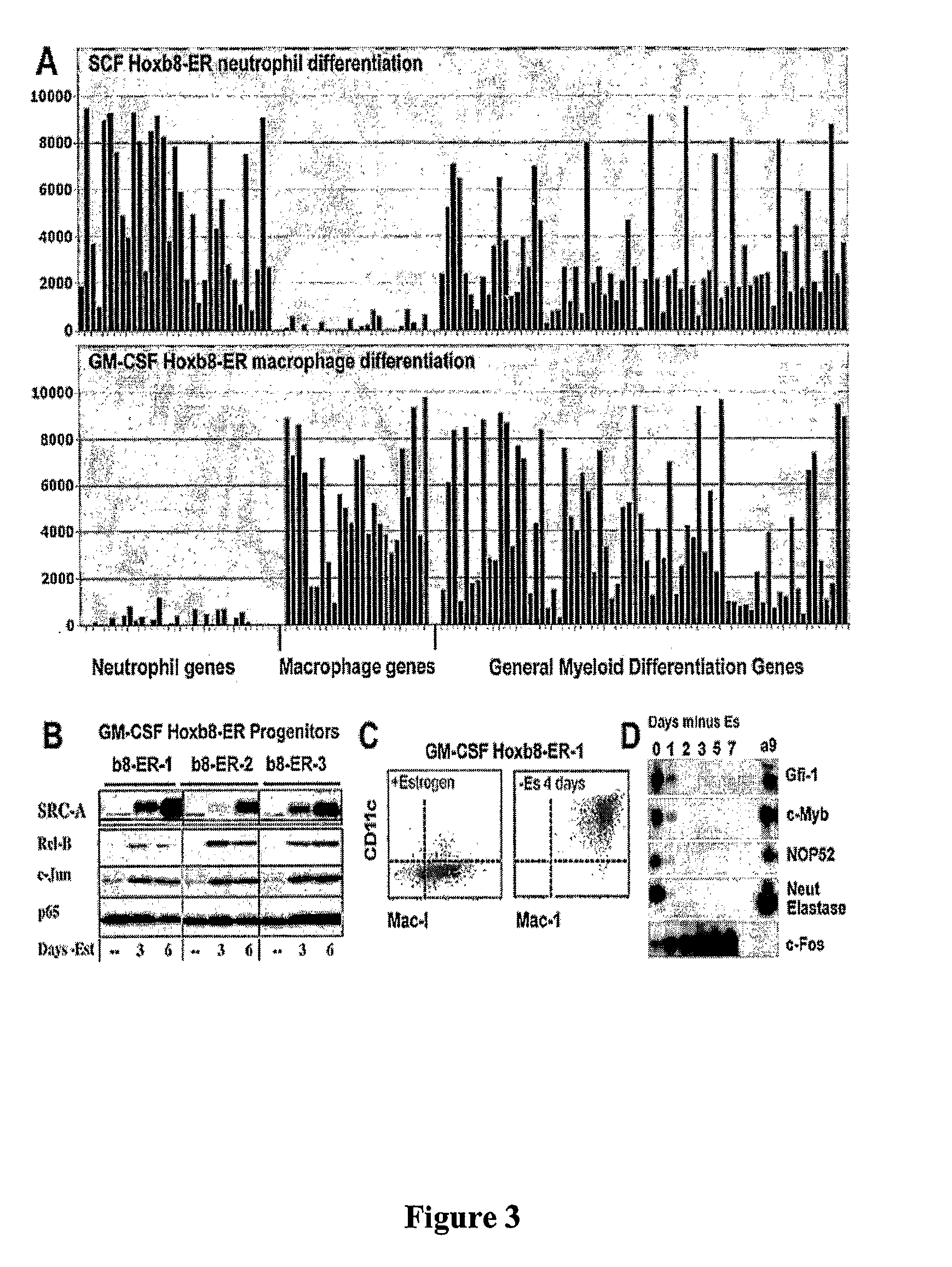
Derivation of unlimited quantities of neutrophils or monocyte/dendritic cells
A method to generate unlimited numbers of macrophage / dendritic cells or neutrophils from mice, using conditional Hox oncoproteins is disclosed. The invention further includes the establishment of a system to investigate immune responses to microorganisms or diseases involving chronic inflammation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Anti-tumor composition based on nano-silver material and application of anti-tumor composition
ActiveCN112604003AGood curative effectHigh biosecurityInorganic active ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsTumor therapyTumor cells
The invention discloses an anti-tumor composition based on a nano-silver material and application of the anti-tumor composition. The anti-tumor composition comprises a drug A and a drug B, wherein the drug A is attenuated salmonella, and the drug B is sialic acid modified nano-silver. The drug A and the drug B are combined for use and can be used for preparing medicines for treating tumors. Attenuated salmonella in the anti-tumor composition is planted in a tumor site in a targeted mode, sialic acid modified nano-silver is targeted to neutrophils, and efficient targeted delivery to the tumor site is achieved under the recruitment effect of salmonella; the nano-silver reaching the tumor site can be used for enhancing the curative effect of salmonella by directly killing tumor cells and removing neutrophils, and the biological safety of bacterial treatment is improved by removing salmonella. The anti-tumor composition can solve the key bottleneck problem of salmonella in clinical application, and efficient and safe tumor treatment based on salmonella is achieved.
Owner:湖南航天天麓新材料检测有限责任公司
Recombinant chimeric protein of neutrophil inhibitory factor and hirugen, and pharmaceutical composition thereof
ActiveUS20100150860A1Good curative effectGood behaviorBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmacologyNeutrophilic cell
Provided is a chimeric protein comprising neutrophil inhibitory factor, the peptide FRRP specially recognizing the thrombin active site and hirugen. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition comprising the chimeric protein, which can be used for treating or preventing cerebral injury and cerebral edema, inhibiting platelet aggregation etc.
Owner:SHANDONG NEWTIME PHARMA +1
Medicine for promoting tissue cell regeneration
PendingCN114569596APromote activation migrationPromote healingAntipyreticAnalgesicsWhite blood cellPharmaceutical drug
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, and provides a medicine for promoting tissue regeneration. The medicine for promoting tissue regeneration comprises PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the PBT. The medicine for promoting tissue regeneration, provided by the invention, has the beneficial effects that at an injured part, PBT migrates white blood cells to the injured or infected part and promotes neutrophil to activate and migrate to the injured part in vivo, so that the healing of a matrix wound is obviously stimulated and promoted.
Owner:QC BIO-TECH(SHENZHEN) CO LTD
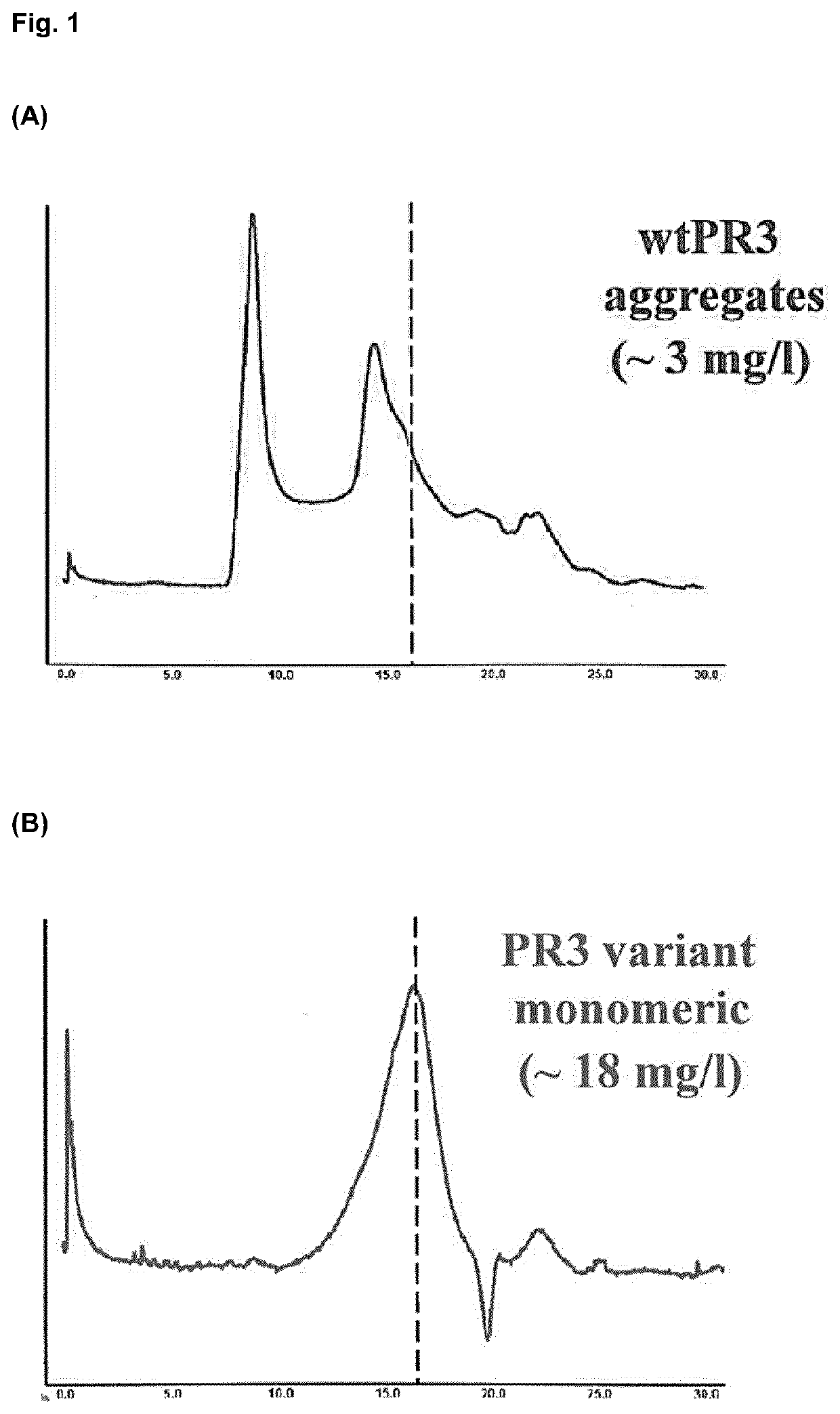
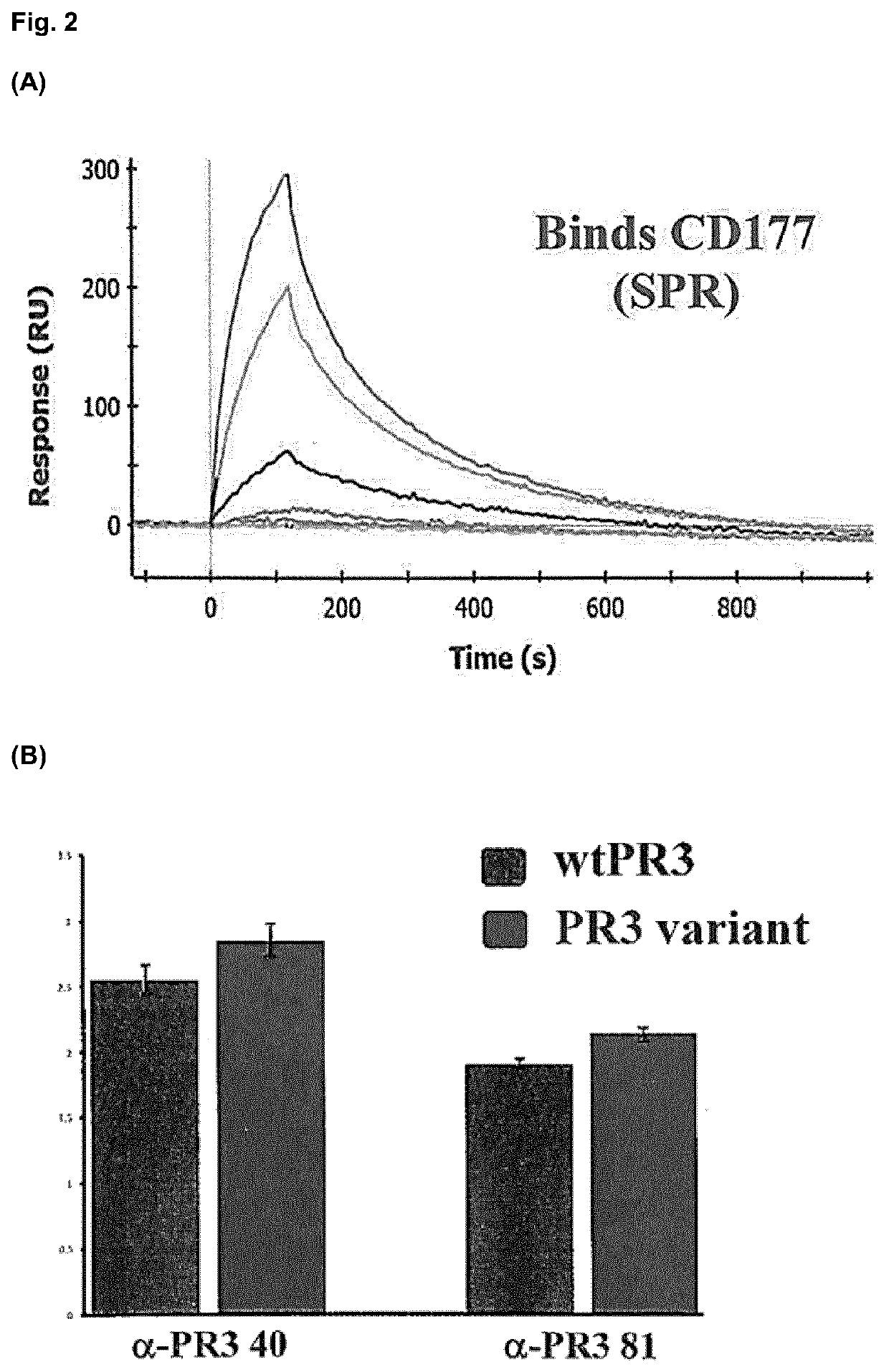
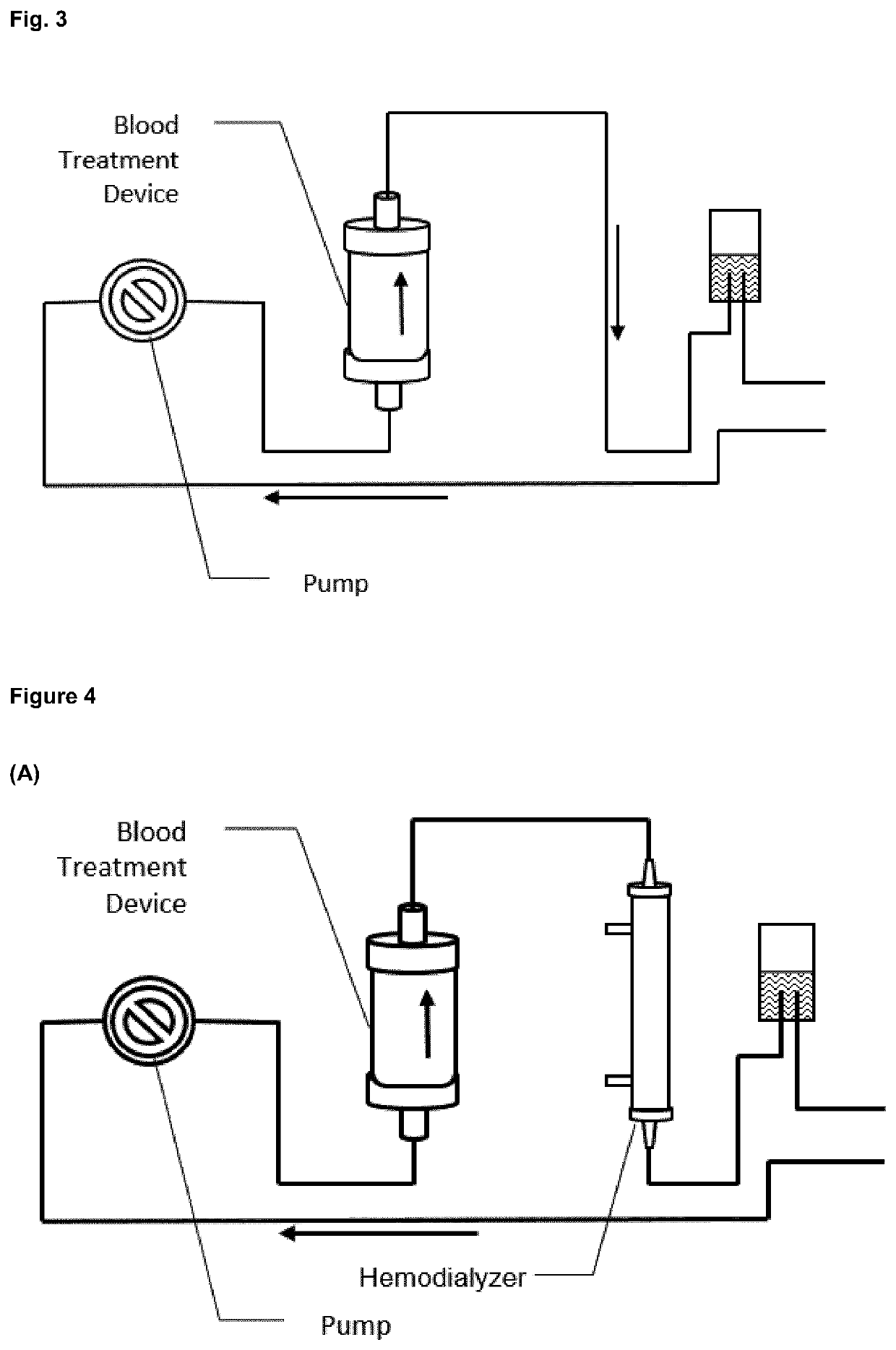
Extracorporeal devices for methods for treating diseases associated with Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies
PendingUS20220088279A1Reduced aggregation behaviorReduce oligomerizationPeptide/protein ingredientsHaemofiltrationDiseaseBlood treatments
The invention relates to a blood treatment device configured to remove anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs) from the blood or blood plasma of a person in need thereof in an extracorporeal blood circuit, wherein the device comprises a matrix, and wherein said matrix comprises a monomeric form of proteinase 3 (PR3). The invention further relates to an extra-corporeal blood circuit comprising a blood treatment device of the invention and to the blood treatment device for use as a medicament or to methods of treating a medical condition associated with ANCA.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com