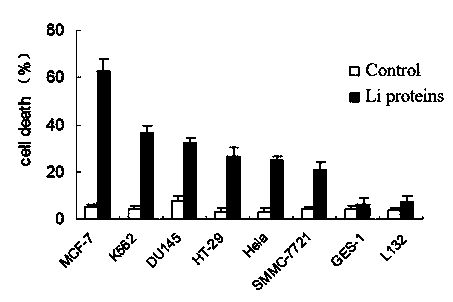Patents
Literature
90 results about "Lamprey" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are an ancient extant lineage of jawless fish of the order Petromyzontiformes, placed in the superclass Cyclostomata. The adult lamprey may be characterized by a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth. The common name "lamprey" is probably derived from Latin lampetra, which may mean "stone licker" (lambere "to lick" + petra "stone"), though the etymology is uncertain. The plural form lamprey is sometimes seen.
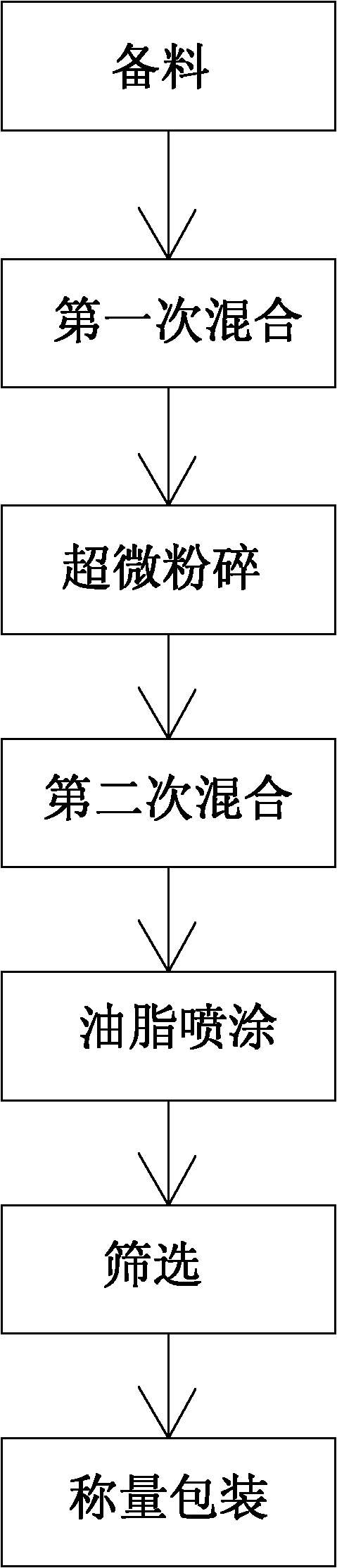
Powder compound feed for adult Japanese eels
InactiveCN101978858ALow costAdequate nutritional needsClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffYeastLamprey
The invention discloses a powder compound feed for adult Japanese eels. The feed comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 52.5 to 60.0 percent of steam-dried fish meal, 24.0 to 26.0 percent of pre-gelatinized starch, 7.0 to 11.5 percent of extruded soybean, 0.5 to 1.5 percent of fish oil, 2.0 to 4.0 percent of beer yeast, 1.0 to 2.0 percent of mineral, 0.5 to 1.0 percent of monocalcium phosphate, 0.3 percent of choline chloride and 0.2 percent of multi-vitamin. The feed can supply sufficient nutrition at an adult Japanese eel breeding stage and eel breeding cost is lowered.
Owner:福建天马饲料有限公司
Eel feed
InactiveCN101874564AModerate proportionDelicious meatAnimal feeding stuffCod liver oilAnimal science
The invention relates to an eel feed. The eel feed consists of the following components in percentage by weight: 30 to 55 percent of mussel powder, 8 to 15 percent of corn protein powder, 2 to 4 percent of milk powder, 7 to 10 percent of chicken blood powder, 1 to 4 percent of duck blood powder, 4 to 7 percent of sorghum protein powder, 10 to 20 percent of cabbage worm powder, 1 to 2 percent of mineral additive, 2 to 5 percent of vinasse, 3 to 7 percent of cod liver oil and 1 to 2 percent of vitamin blending agent. The method for preparing the eel feed comprises the following steps of: pouring the components into a blender in a certain ratio to mix and stir uniformly; adding quantitative grease and water into the mixture; stirring the mixture into a sticky dough shape; and feeding the eel after sieving the mixture by using a 60-mesh sieve.
Owner:孙秀美
Cultivating method of sinocyclocheilus grahami seedling
InactiveCN101822230AImprove survival rateIncrease growth rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaCarpWater quality
The invention relates to a cultivating method of a sinocyclocheilus grahami seedling, belonging to the technical field of fish culture. The cultivating method comprises the steps of the cultivation of fish fries growing mouths in rich water, artificial cultivation of fish fries, the rearing of fish fries at middle and rear stages and pest control. In the cultivation of fish fries growing mouths in rich water, a temporarily-cultivating pond is arranged in a tunnel, bait for fish fries growing mouths is chlamydomonas and rotatoria cultivated in rich water and the fish fries are cultivated at water temperature of 15 DEG C for 10-12 days. In the artificial cultivation of fish fries, the fish fries are cultivated by eel powder feed with the protein content of 40 percent for 40 days. The feed in the fish fries at middle and rear stages is carp crushed feed with the protein content of 39 percent. In the pest control, the water quality and the conditions of fish bodies are detected every three days, 50-80ml / mu of povidone iodine for controlling bacterial infection and 50-50ml / mu of rotatoria one-time removal (ammonium ethylene-bis-dithiocarbamate) for controlling balantidiasis are splashed every 15 days. The invention can effectively improve the survival rate and the growth speed of inocyclocheilus grahami seedlings, is simple and convenient, and is beneficial to being popularized and generalized. Bacterial.
Owner:云南省水产技术推广站
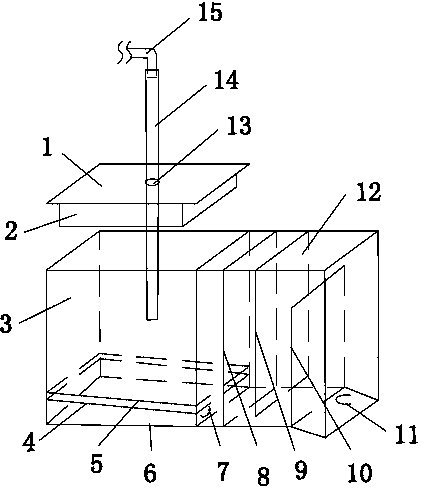
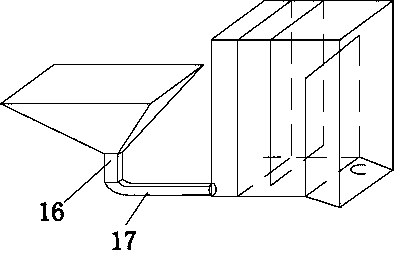
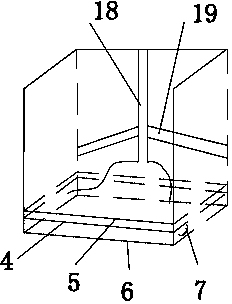
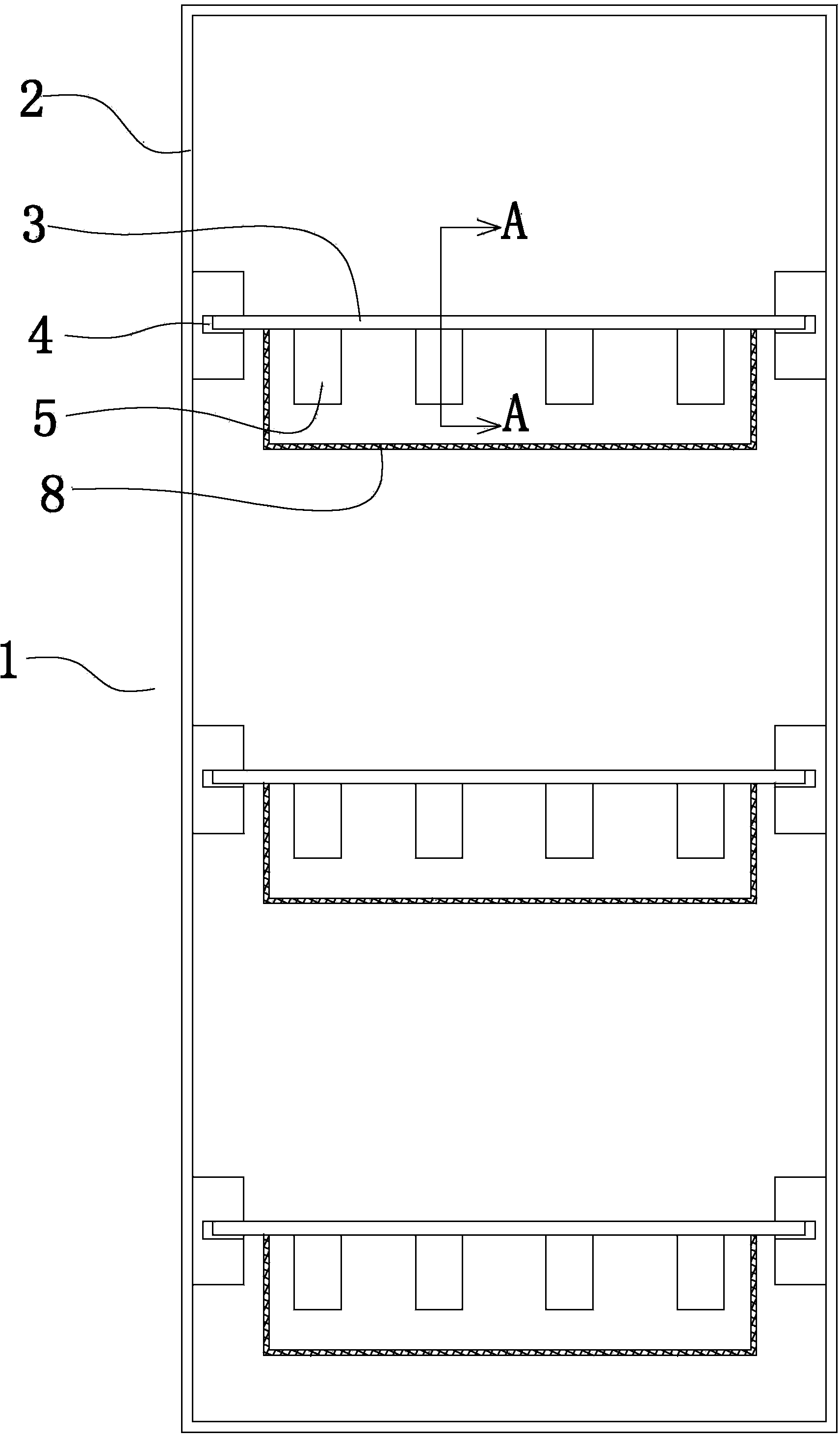
Eel breeding pond
InactiveCN104255633AWater level remains constantPromote generationPisciculture and aquariaLampreyWater level
The invention relates to an eel breeding pond and belongs to the technical field of breeding equipment. The eel breeding pond comprises a breeding pond body formed by pouring concrete, a cover plate and a water injection connector. The water injection connector is arranged over the culture pond body and used for injecting water into the culture pond body through a water injection pipe. The bottom of the breeding pond body is provided with a first drain outlet in connection with a rear breeding pond of the breeding pond. The inner surface of the bottom of the breeding pond body is provided with a rock ballast layer and a yellow sand layer. An escape prevention net, a first gate and a second gate are sequentially arranged in the rear breeding pond from one side of the first drain outlet. One side of the bottom of the rear breeding pond, which is close to the second gate, is provided with a second drain outlet. A feeding device for feeding eel is also arranged in the breeding pond body. Therefore, the eel breeding pond has the functions of escape prevention, eel catching easiness and water injection and drainage convenience, is easy to feed, can maintain a constant water level in long term, provides a good living environment for eel, and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
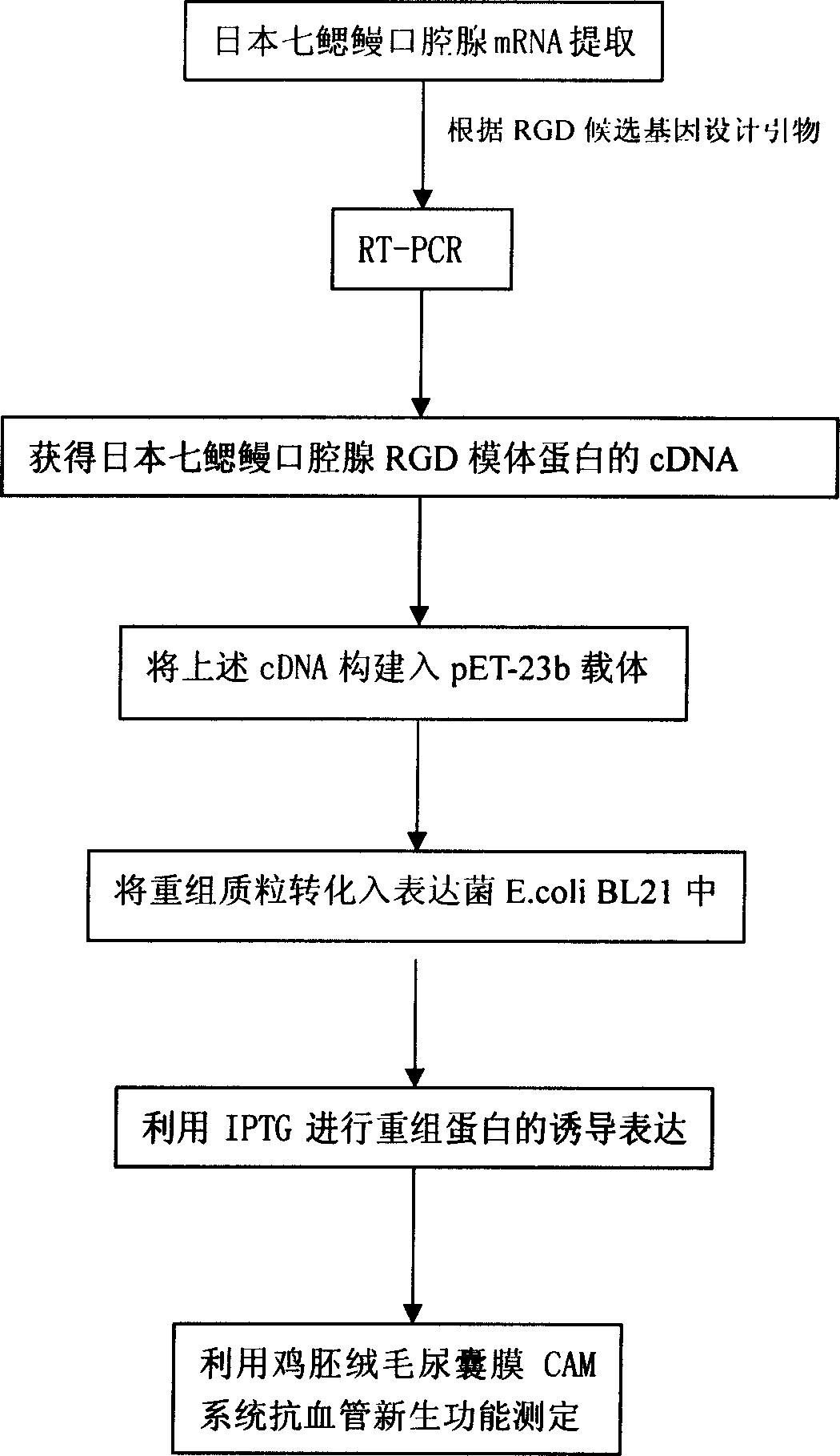
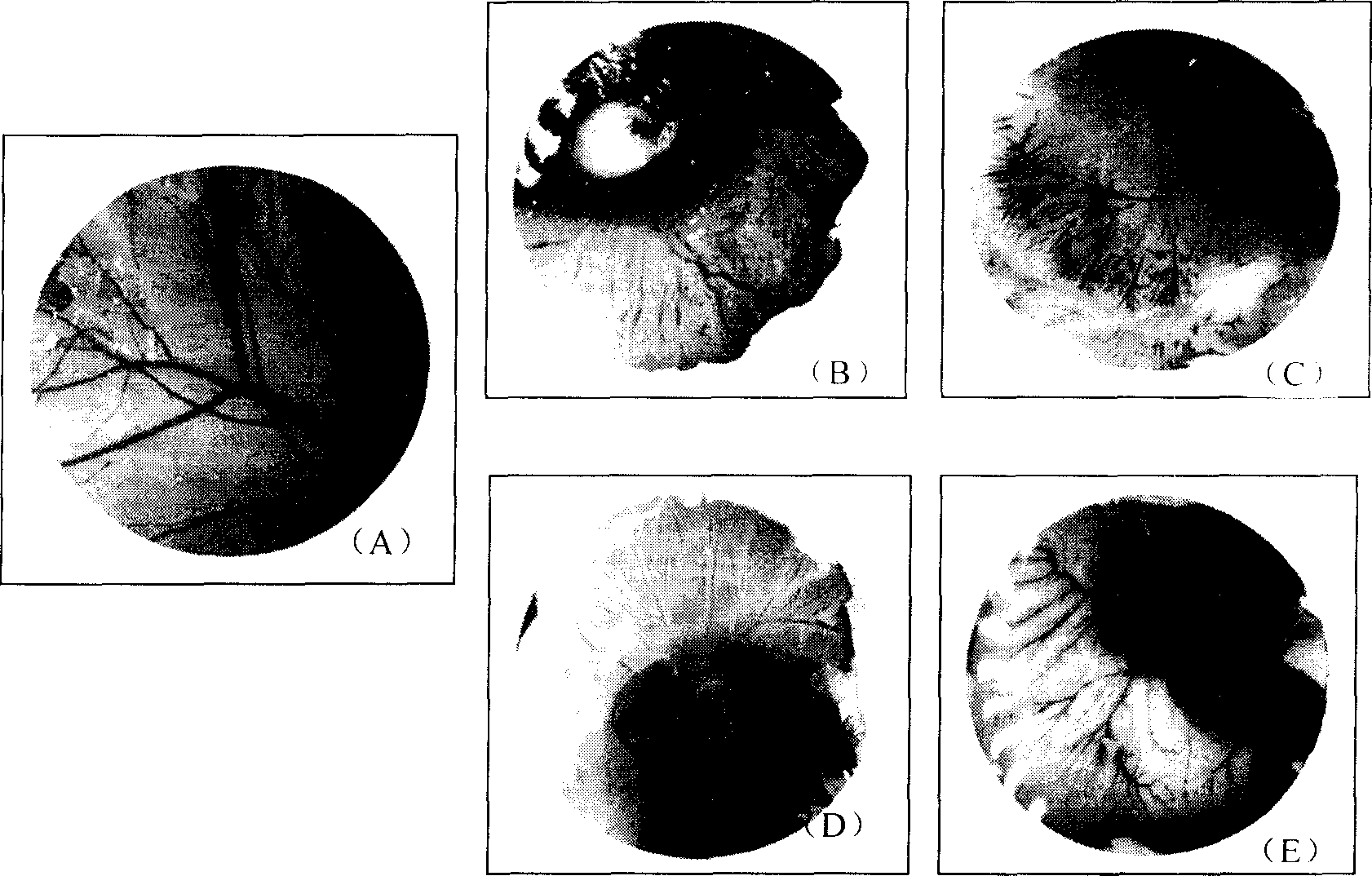
Gene clone and expression of RGD die body protein of oral gland in Japan lamprey possessing function for anti tumour
InactiveCN1760362AReduced number of blood vesselsPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationVascular endotheliumBlood vessel
The gene clone and expression of Japonese lampreyí»s oral gland model proteins RGD with antineoplastic action are disclosed. Three cDNA sequences with said model proteins RGD and their clones, the protein sequence and its expression in engineered bacteria, and the action of proteins RGD in closing the signal transfer channel to suppress the vascular neogenesis and tumor cell reproduction for antineoplastic purpose are also disclosed.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Expanded pelleted feed of grown eel fishes without pollution
ActiveCN101040658AGuaranteed normal growthImprove uniformityFood processingClimate change adaptationYeastFeed conversion ratio
The invention discloses a nuisance-free bulked granulated compound feed for adult eels, which comprises steam heated fish meal 45-55%, flour 18-25%, soybean waste 5-15%, bulked soybean 1-10%, fish oil 2-6%, brewer's yeast powder 2-6%, minerals 1-3%, choline chloride 0.3-1%, and vitamins for eels 0.2%. The feed has a higher conversion rate.
Owner:福建天马饲料有限公司
Expanded pelleted feed for black eel fishes without pollution
ActiveCN101040657AGuaranteed normal growthImprove uniformityMetabolism disorderFood processingYeastFeed conversion ratio
The invention discloses a nuisance-free bulked granulated compound feed for eels, which comprises steam heated fish meal 55-63%, flour 20-25%, soybean waste 2%-10%, bulked soybean 1-5%, fish oil 2-4%, brewer's yeast 2-5%, minerals 1-3%, choline chloride 0.3-1%, and vitamins for eels 0.2%. The feed has a higher conversion rate.
Owner:FUJIAN TIANMA TECH GRP
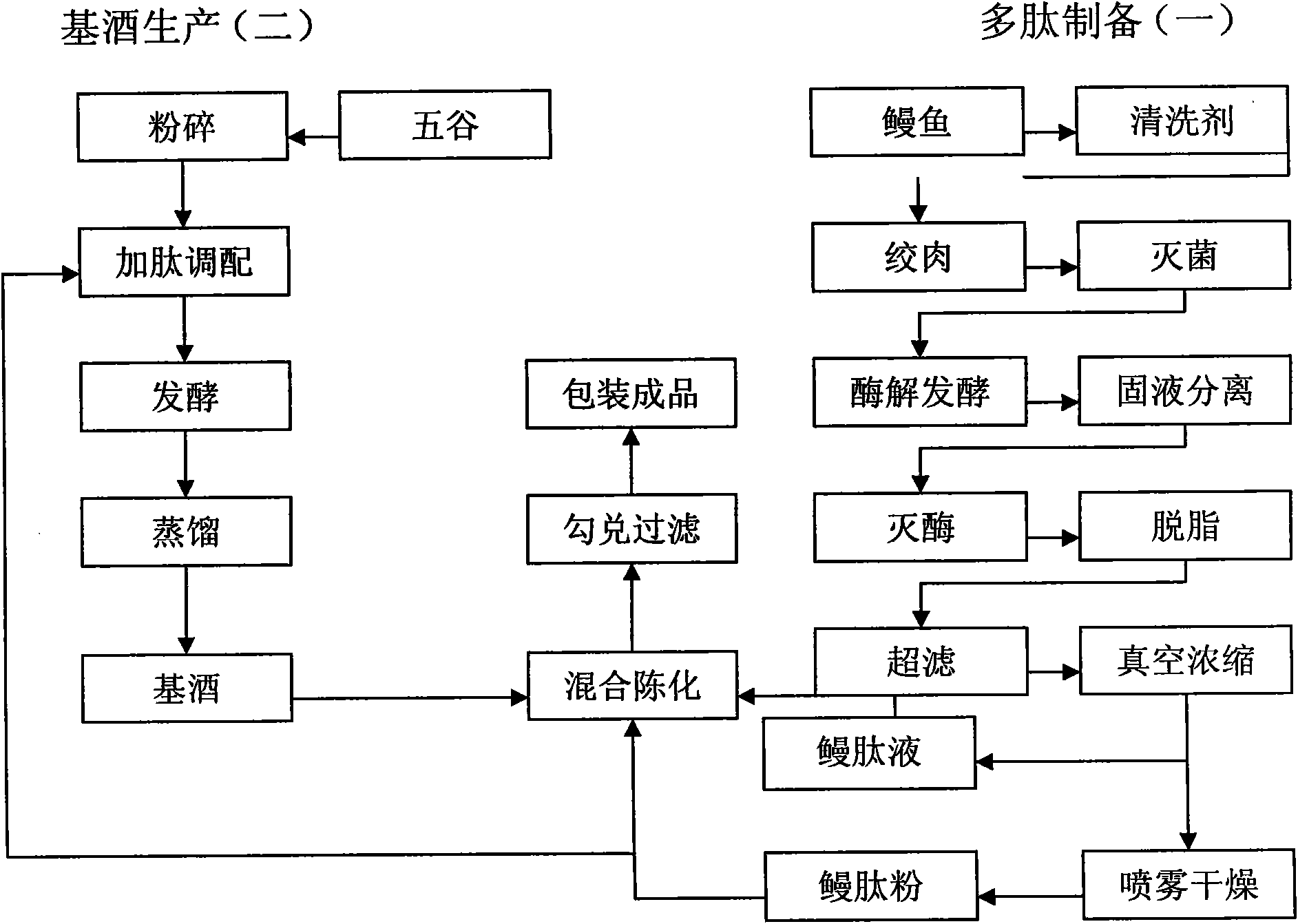
Method for preparing eel polypeptide wine
InactiveCN101857830AFast absorptionCycle fastAlcoholic beverage preparationFermentationCombined methodOrganism
The invention discloses a method for preparing eel polypeptide wine. The method is characterized by ensuring the characteristics of stable polypeptide content, no precipitates, no repetition, adjustable alcohol content and large suitable population of the wine by a twice-adding method of adding polypeptide dry powder through base wine fermentation and adding polypeptide concentrated solution through blending. By the combined method of modern biological engineering technology and the traditional brewing processes, the eel polypeptide wine prepared by the method has a strong, pure and mild mouthfeel, special eel aroma and taste and golden and gleaming color. Ethanol accelerates polypeptide activities, promotes the fast absorption of nutrition elements of unblended wine and enters an organism for circulation use, so that a peptide wine product has the effects of fast supplying nutrition, removing fatigue, stimulating the circulation of blood, removing dampness, dispelling cold and the like and can fast remove peculiar smell so as to be a natural health-care nutrition drink.
Owner:福建省乾龙生物工程有限公司
Combined tool for processing sea eel or finless eel
ActiveCN103976000AAffect online operationInhibit sheddingFish threading devicesPoultry/fish slaughtering/stunningLampreyFinless eel
The invention discloses a combined tool for processing sea eel or finless eel. The invention aims to provide a combined tool which is convenient and quick in operation, low in cost and fit for killing a small amount of sea eel or finless eel in the places, such as home, restaurants and hotels. The combined tool comprises a sea eel or finless eel automatic loading device, a shaping elastic sleeve and a cutter, wherein the sea eel or finless eel automatic loading device comprises a storage box with an opening at the upper end and a plurality of vertical insert plates which are arranged in the storage box and can be taken out of the storage box; a plurality of loaders are respectively arranged on the vertical insert plates; mesh enclosures are respectively arranged on one side of each of the vertical insert plates; the loaders on the same vertical insert plate are all located in the corresponding mesh enclosures; each of the loaders comprises an inducing sleeve, a pin, a dragging line, a trigger rod, a spring steel sheet and a bait bag; the spring steel sheet is arranged right under the inducing sleeve; the bait bag is arranged in the inducing sleeve; one end of the inducing sleeve is fixed on a side wall of each of the vertical insert plates; penetrating through holes are respectively arranged on the side walls of the vertical insert plates corresponding to the inducing sleeve.
Owner:MARINE FISHERIES RES INST OF ZHEJIANG
Method for artificial hastening spawning of yellow porgy
An artificial echolic method for golden tai includes such steps as choosing two years old golden tai, culturing ever year under a certain condition, feeding zazor clam, young squid, the sex gland of squid, or eel plus VE and VC, exchanging water by 1 / 3 every day, and injecting the prolan after injecting anaesthetic four times at intervals of 10 days. Said prolan is sequentially luliberin A3 for the first injection, and the second injection, and the luliberin A2 another component for the third and the fourth injections.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Indoor high-density breeding method of current-year fingerlings of scatophagus argus
ActiveCN108323458AImprove the survival rate of breedingUniform sizeClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaLampreyHigh density
The invention relates to the field of aquaculture, in particular to an indoor high-density breeding method of current-year fingerlings of scatophagus argus. The indoor high-density breeding method consists of breeding preparation, fingerling pulling net counting, fingerling transportation and delivery, bait management, water quality management and pulling net capture and adopts an indoor cement pool for high-density breeding of the current-year fingerlings of the scatophagus argus; aquaculture water is estuary brackish water, artificially-bred fingerlings that are converted to eel feed are transported to the indoor cement pool, the specification body length is 1.3-1.5 cm, and the breeding density is 300-400 / m<2>; the eel feed is fed to the fingerlings with a respective body length of lessthan 3 cm, and floating pellet feed is fed to the fingerlings with a respective body length of 3 cm; during breeding, sewage suction and bottom cleaning are performed on time, and water change and pool turnover are performed timely; as for the current-year fingerlings with a respective specification body length of more than 4-5 cm, the pulling net capture can be performed to transfer to the pool for breeding. The indoor high-density breeding method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the survival rate after indoor high-density breeding for 181 days is 80-85 percent, and the technical blank of indoor intensive and large-scale production of the current-year fingerlings is filled up.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES RES INST
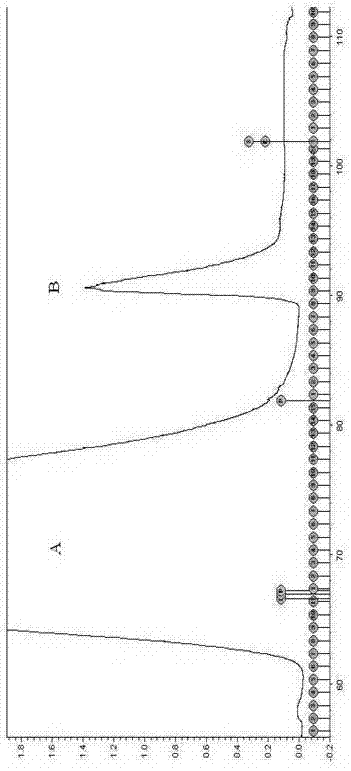
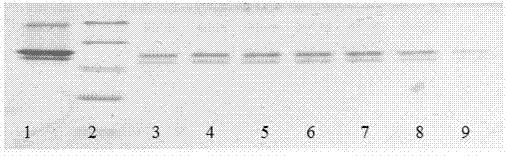
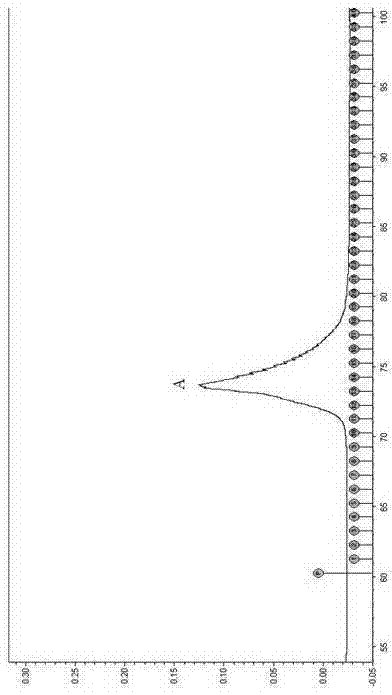
Liproteins, preparation method and application of liproteins in preparing medicament for preventing and treating tumor diseases
ActiveCN103554242APeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsAbnormal tissue growthHeterologous
The invention discloses liproteins, a preparation method and an application of liproteins in preparing a medicament for preventing and treating tumor diseases. The liproteins are pure natural proteins which are separated and purified from a cell culture fluid of lamprey corpuscle, is named Liproteins, has a Jacalin_like domain and a Pore-formingtoxin_like domain, and can be synthesized through expression of a heterologous expression system to form recombinant protein of liproteins. The liproteins have a specific killing function of tumor cells, does not destroy normal cells, and does not have side effect to human bodies.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Granulated eel compound feed
InactiveCN101791066APromote growthImprove productivityAnimal feeding stuffTransformation efficiencySaccharomyces
The invention disclose a granulated eel compound feed which is prepared by puffing the following components and then sieving by a 40-meshed sieve: 42-50% of fishmeal, 10-15% of shrimp powder, 10-15% of corn flour, 10-15% of flour, 10-15% of soybean meal, 5-10% beer yeast, and the balance vitamins and minerals for eel. The eel compound feed of the invention has balanced nutrition, low cost, high transformation efficiency and stable quality, eel can grow well after eating the feed, and the yeast can protect eel from eel viruses, reduce occurrence of diseases, and improve eel yield.
Owner:大丰绿食源水产养殖有限公司
Larval crab cultivating pond and the cultivating method
InactiveCN101040606AImprove survival rateReduce cannibalismClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaLampreyImproved survival
The invention relates to a Scylla serrata seed cultivating pool and relative method, in particular to a method for improving survival rate and growing seed Scylla serrata quickly. the invention comprises a main pool and a seed pool, wherein the bottom of th main pool is provided with a slope inclined along a water outlet, and a sand layer, the sand layer is provided with at least one groove extended from the high part to the lower part of the bottom of the main pool to be collected into the water outlet, the seed pool is arranged under the water outlet with a network box inside. The water specific weight is 1.006-1.015 while the seed cultivating density is 2000-3000n / m2, while the water is exchanged each day and the forge is fish slurry, shellfish meat, or the like to be fed for at least four times and 2-3 times of seed weight, and the whole cultivation is aerated continuously.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Indoor cement pond culturing method of artificially bred sebastiscus marmoratus fingerling
ActiveCN107027663AImprove water qualityRemove in timeClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenile fishCement
Provided is an indoor cement pond culturing method of artificially bred sebastiscus marmoratus fingerling. The method is characterized in that in May to June every year, the specification of artificially bred sebastiscus marmoratus juvenile fishes reaches 2 cm to 4 cm, domestication of salinity and bait is carried out, the salt reducing speed is 2% / d, the final breeding salinity is kept at 11% to 15%, domestication bait of the juvenile fishes is sea eel feed, and more than 90% of the juvenile fishes take mixed feed; when the feed scrambling phenomenon occurs, one-age fingerling is cultured and cultured to November to December, and when the water temperature is below 15 DEG C, sebastiscus marmoratus is transferred into an indoor cement pond for overwintering culture; the water temperature of culture water is raised to 15 DEG C or above in next spring, the sebastiscus marmoratus overwintering fingerling gets into a two-age fingerling culture stage, and the fingerling is cultured till overwintering. The survival rate of the sebastiscus marmoratus can reach 72% to 82%, the overwintering survival rate is 90% or above, operation is easy and convenient, and popularization is easy.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES RES INST
Raising method for promoting quick growth of young loaches
InactiveCN101715741APromote rapid growthImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseLamprey
The invention relates to a raising method for promoting quick growth of young loaches. The raising of young loaches is divided into 2 stages which are a 0.3 to 3cm body length stage and a 3 to 5cm body length stage respectively, wherein at the 0.3 to 3cm body length stage, soybean milk and young eel feed, of which the content of crude proteins is 47 percent are mixed in a ratio of 1 to 5 and then used for feeding the young loaches; and at the 3 to 5cm body length stage, the noturus flavipinnis feed of which the content of crude proteins is 32 percent and the snakehead feed of which the content of crude proteins is 44 percent are mixed in a ratio of 2 to 1 and then used for feeding the young loaches. The raising method can promote the quick growth of the young loaches, lower the risk of contracting a disease, and improve survival rate of the young loaches.
Owner:常先苗
Preparation method of affinity chromatography purification tag-free genetic recombinant lamprey Lj-RGD3 protein
InactiveCN103694330AEasy to operateImprove purification ratePeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesLampreyMicrobiology
The invention discloses a preparation method of an affinity chromatography purification tag-free genetic recombinant lamprey Lj-RGD3 protein rLj-RGD3(Tag<->). The preparation method has simple processes and a high purification rate. According to the preparation method, a recombinant expression vector pET23b-RGD3(Tag<->) without any purification tags is constructed; the recombinant plasmid is transferred into expression bacteria and a genetic recombinant protein is expressed; and through metal-chelating ion affinity chromatography, cation exchange and dialysis, the lamprey Lj-RGD3 genetic recombinant protein without any affinity chromatography purification tags is prepared, is named as rLj-RGD3(Tag<->) protein and has protein purity greater than or equal to 99%.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Sea eel small molecular peptide extracted from sea eel bones and extraction method thereof
InactiveCN105506043AMeet the needs of useMaintain stabilityFermentationLampreyAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to a method for extracting sea eel small molecular active peptide from sea eel bones. The method comprises the following steps of 1, sea eel bone processing, 2, low-temperature smashing, 3, cell dissolution processing, 4, biological enzymolysis processing and 5 postprocessing; the ratio of the obtained sea eel small molecular peptide with the molecular weight being 0-480 d is 88.5% or more; the sea eel small molecular peptide is applicable to a peptide for diagnosis, a peptide vaccine, an antibacterial activity peptide, a cell factor simulation peptide, a cell factor simulation peptide, an antiviral peptide or an anti-tumor peptide and a peptide health care product.
Owner:潘爱国
Live eel bait hooking device
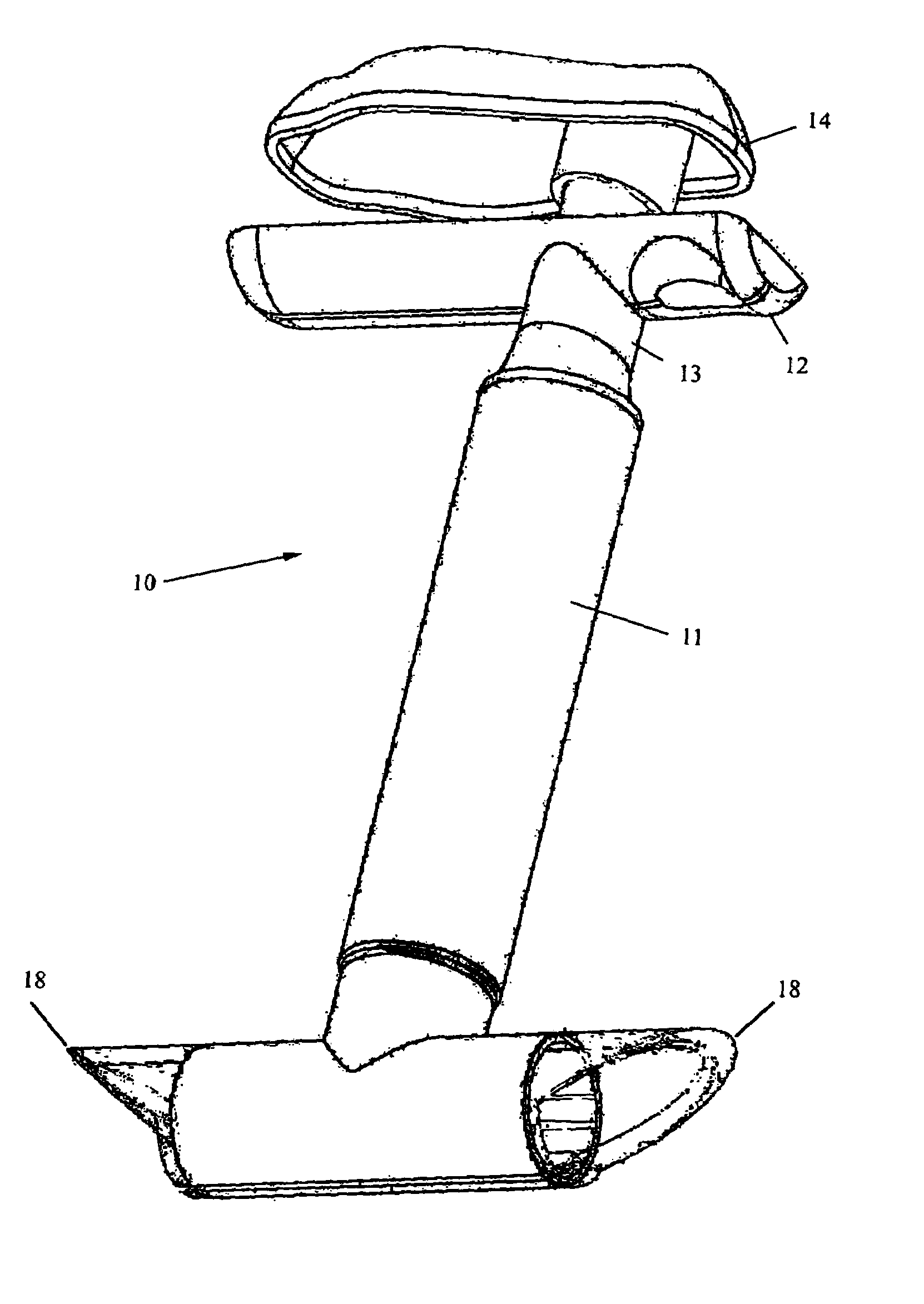
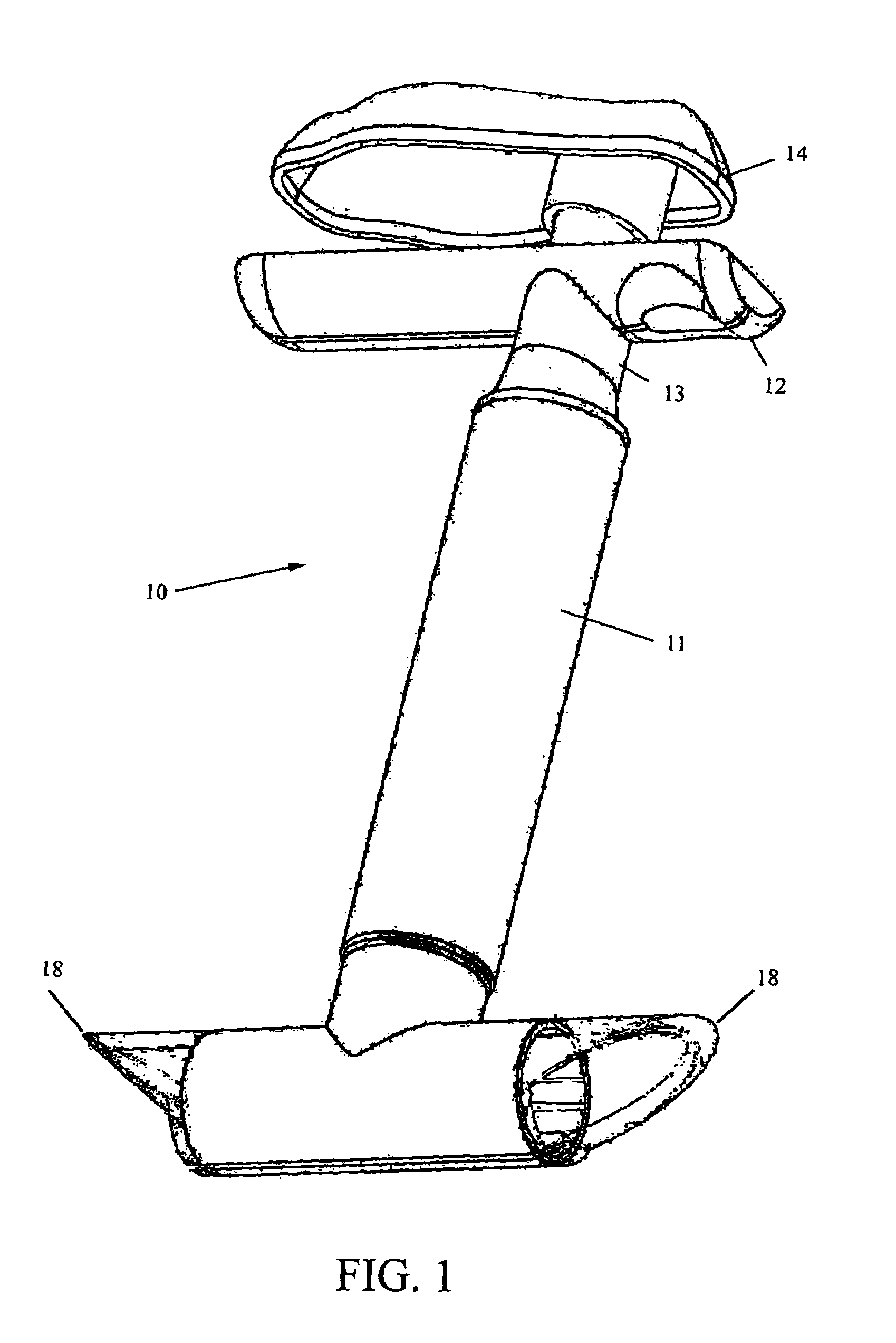
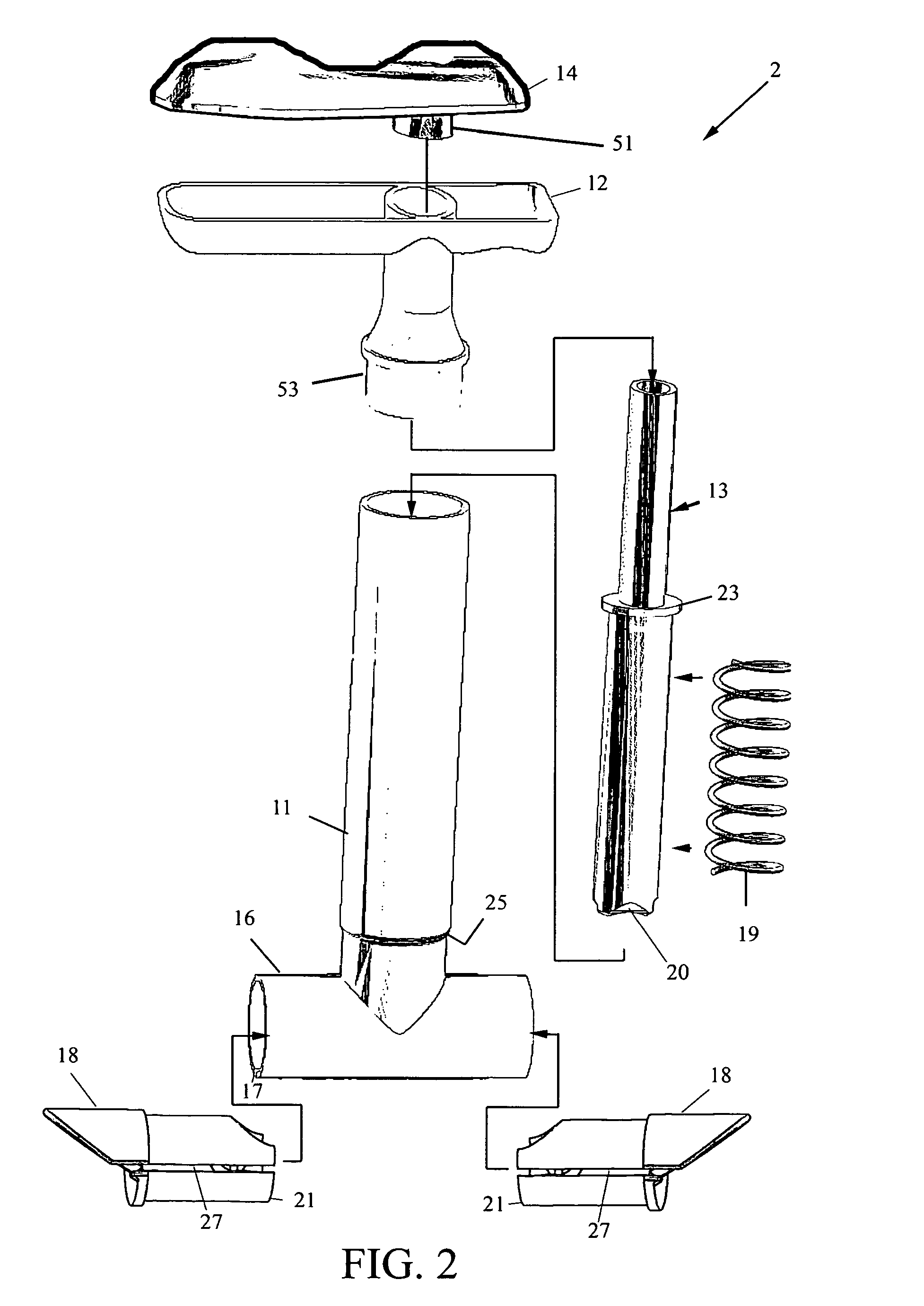
A live eel hook-insertion device. A hand-operated unit is disclosed that generally comprises a T-handle / trigger driving a spring-mounted plunger through a housing, an open-ended eel nesting tube at one end of the housing and defined by a lateral notch, and a distal yoke on the plunger for immobilizing an eel within the nesting tube. The T-handle trigger is actuated to trap the eel, whereupon a hook can be easily inserted into the eel. The nesting tube is further defined by a lengthwise notch to allow extraction of fishing line if the eel backs out of the nesting tube with hook attached. In use, the device is inserted into a bait well full of eels and the nesting tube is placed flat against the bottom. One eel will enter the nesting tube, whereupon the yoke is distended to trap the eel against the floor of the nesting tube. A hook with attached fishing line is inserted through the notch of the nesting tube and the eel is thereby hooked. A stationery hook-insertion device is also disclosed, and this comprises a hopper formed with a drain hole and an external neck at the drain hole, an articulated mounting bracket for the hopper, a tubular chute connected to the neck of the hopper and protruding downward therefrom, and a constricted yoke at the distal end of the tubular chute for immobilizing an eel inside said tubular chute with a portion of the eel protruding outward through the yoke for hook insertion. The eels tend to slide through the hole in the hopper and down the chute, extending its lips out of the chute for hooking the eel. Both disclosed embodiments eliminate the need to chase, catch, handle, or untangle live eels thus making this whole process of baiting them quick, clean, and easy.
Owner:FREBURGER JR ANTHONY
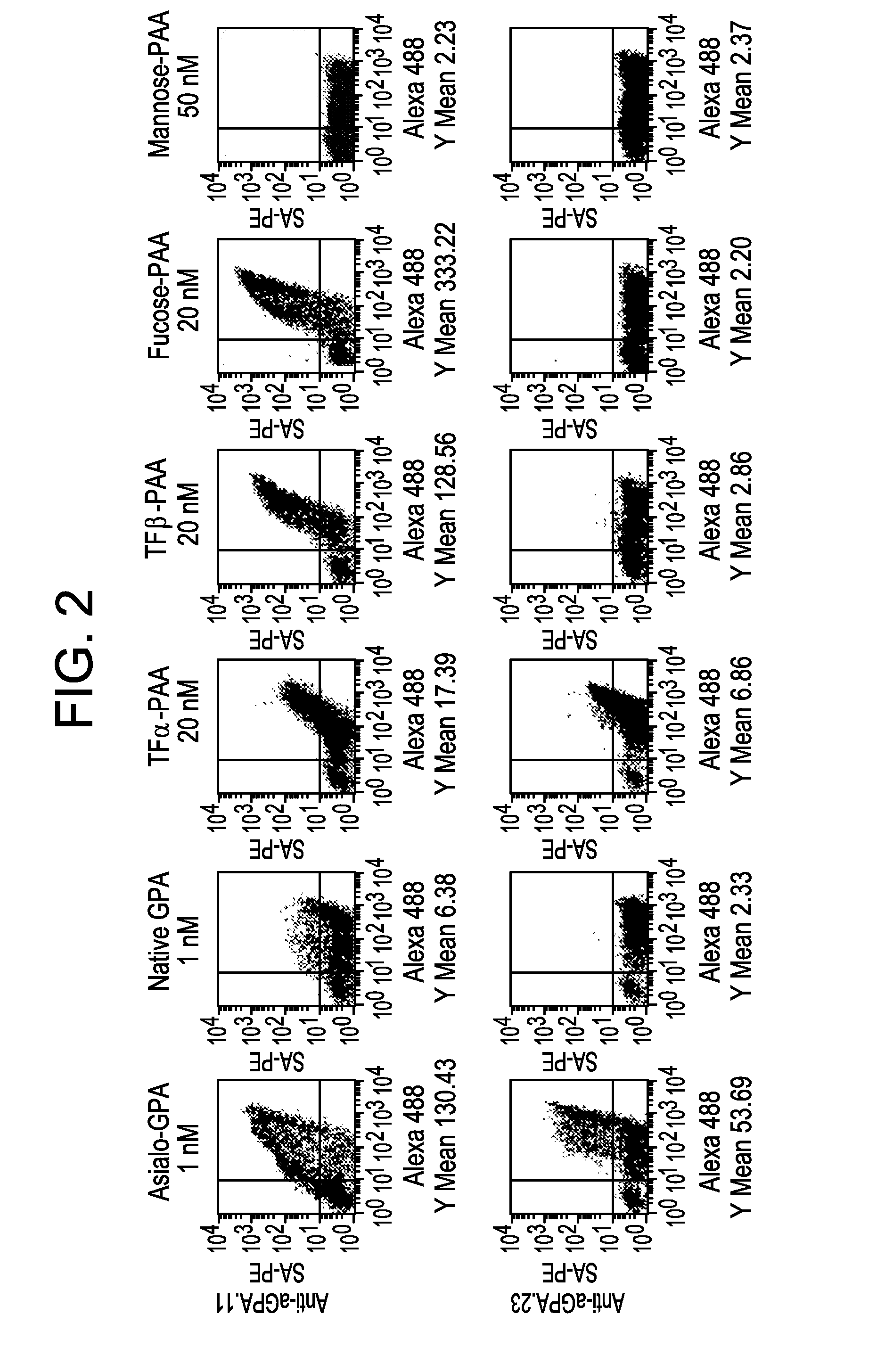
Lambodies with high affinity and selectivity for glycans and uses therefor
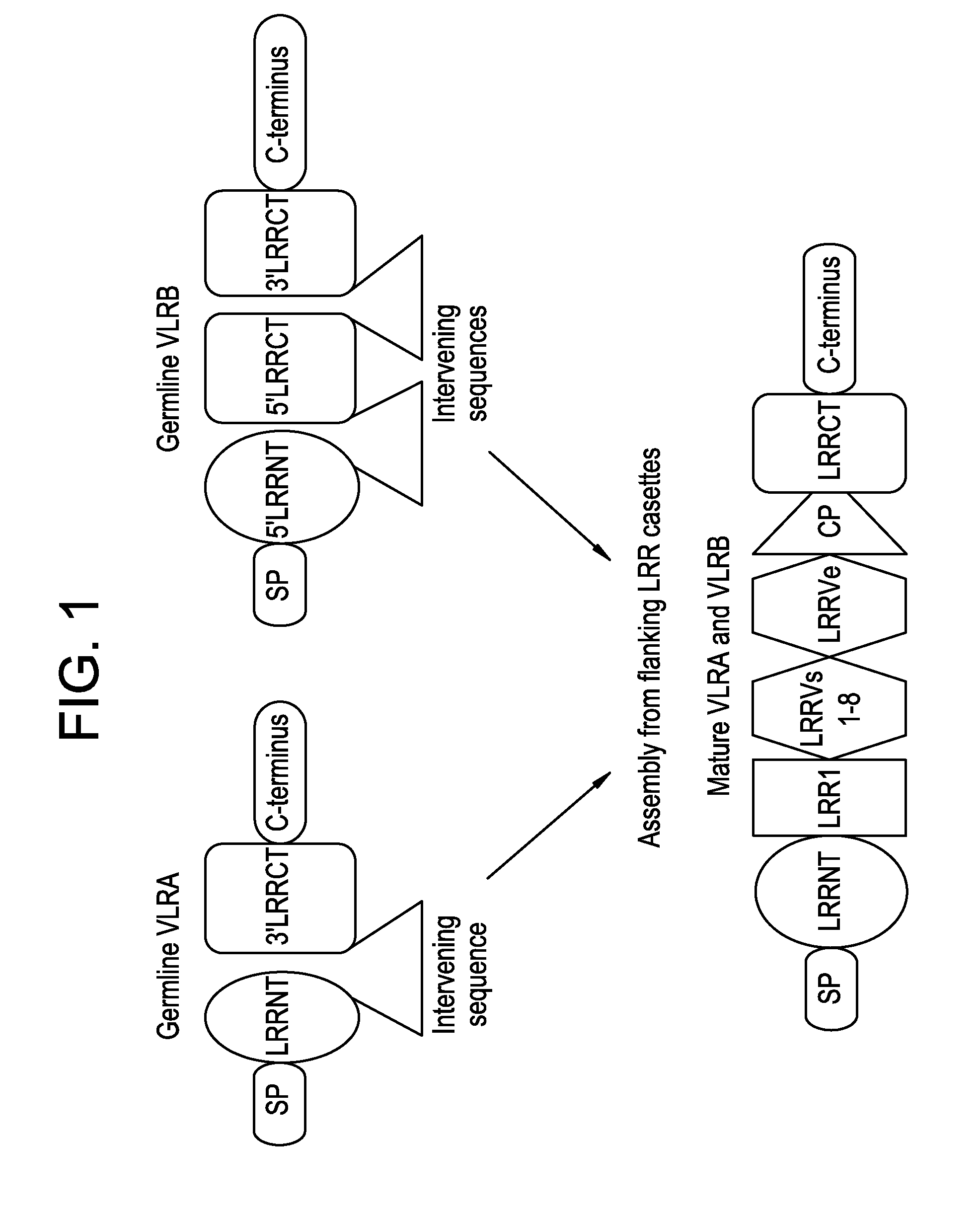
The invention relates to dimeric proteins comprised of subunits having (i) recombinant lamprey variable lymphocyte receptor (VLR) diversity regions linked to (ii) multimerization domains. The dimeric proteins exhibit binding specificity for glycosylated antigens, and they may be used in methods of detecting or isolating glycans from a sample, and in methods of disease diagnosis, prognosis, progression monitoring, treatment, and imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Gene clone of and expression Japan lamprey oral cavity gland KGD model protein possessing anti thrombotic action
A gene clone and expression of the oral gland KGD pattern protein of Japanese lamprey with anti-thrombosis is disclosed. Its cDNA sequence and clone, its relative protein sequence, its expression in colibacillus and Piohia yeast, its combination with the glucoprotein gpó�b / IIIa on cell membrane of platelet to suppress the platelet coagulation, and its application in developing the anti-thrombosis medicines are disclosed.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for inducing artificial ovulation and spawning of fresh-water eels
ActiveCN105377025AShorten ovulation periodPrevent degradationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaIntraperitoneal routeSeawater
The present invention relates to a method for inducing artificial ovulation and spawning of fresh-water eels, wherein a feminization inducing material (e.g., 17beta -Estradiol) for inducing feminization is fed into a culturing bath in which brood fish as an object of artificial ovulation are cultured, for a predetermined period of time, and when the ovulation induction period has come, a flathead mullet pituitary extract (FPE) of flathead mullet, which are fish in rivers and broad streams, as an ovulation inducing agent is added in the culturing bath, thereby promoting artificial ovulation even without applying an administration manner using intraperitoneal injection. Preferably, according to the present invention, the ovulation and spawning of the brood fish can be induced by selectively setting the conditions of fresh water, brackish water, and seawater for culture water of the culturing bath, feeding a feminization inducing material for inducing complete feminization of the fresh-water eel brood fish into the culturing bath at the fresh water condition of the culture water, performing a pretreatment procedure for the feminization, setting the seawater condition of the culture water, and then feeding the ovulation inducing agent into the culture water.
Owner:GOOGOL HLDG
Technology for breeding marble goby
InactiveCN101697713AReduce ammonia nitrogen contentGrow fastClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaLampreyFresh fish
The invention relates to a technology for breeding fish, in particular to a technology for breeding marble goby, which belongs to the technical field of aquiculture. The technology comprises maintenance of the pond, throwing and feeding of breeding baits, and the like. The field pond is used for cultivating hyacinth and narcissus, thereby reducing the content of ammonia nitrogen in pond water and keeping the water quality and the water temperature stable; and fish slurry mixed by iced fresh fish or eels is fed as the bait, thereby accelerating the growth of fries and providing the market with a byproduct which has the advantages of delicious flavor, high safety and reliability.
Owner:阎莉
Technology for cultivating takifugu flavidus summer fingerlings in cement pond of simple plastic greenhouse
ActiveCN103026990AShorten the timeTime stretchedClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater qualityOrder copepoda
The invention discloses a technology for cultivating takifugu flavidus summer fingerlings in a cement pond of a simple plastic greenhouse. The cement pond is adopted, and an arch-shaped ring top is formed above the cement pond. The technology is characterized in that: a dimmable shading film covers on the arch-shaped ring top; the air density in the cement pond is 1-1.5 pieces per square meter; the stocking sizes are 10-12 millimeters in full lengths per fingerling; the stocking density is 1,000-1,500 fingerlings per square meter; the water level is 70 centimeters during stocking; 20 centimeters of fresh water is injected every day from the second day, the cement pond is full of water four days later, and 50 percent of water is changed every other day from the fifth day; after 10-15 days of cultivation, bait scraps and fish excrement are cleared; the water quality indexes are that: the salinity of sea water is 0.8-1.2 percent, the water temperature is 25-28 DEG C, the dissolved oxygen is over 5 mg / L, and the pH is 7.5-8.5; medium-sized cladocerans and copepods are fed at an earlier stage, and large frozen fairy shrimps are fed at a middle stage; and after the full lengths of fingerlings are up to 30 millimeters, a compound feed is fed instead of the frozen fairy shrimps, and an eel feed is fed completely after 3-4 days of transition.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
River eel green culturing method
InactiveCN105145429AIncrease productionEnhance physical fitnessClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaLampreyNatural food
The invention discloses a river eel culturing method comprising the following steps of ground processing, preprocessing forage sorting and feeding and daily management. With the above method, pond culturing output can be increased; natural foods are employed for the culture, so product is green and safe and taste can be remained; and river eel quality can be increased and diseases can be prevented.
Owner:SUZHOU CITY XIANGCHENG DISTRICT YANGCHENGHU TOWN JIANMEI AQUATIC PROD ECOLOGICAL CULTURE PROFESSIONAL COOP
Aquaculture process for South American eel larvae
InactiveCN104663540AOptimizing cleaning optimization schemeEasy to disinfectClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPotassium permanganateAquaculture
The invention aims to provide an aquaculture process for South American eel larvae. The aquaculture process includes cleaning aquaculture ponds, and controlling the water temperatures and the salinity of the eel fry ponds. The aquaculture ponds are soaked or cleaned by the aid of dry quicklime powder, bleaching powder, potassium permanganate, clear water and the like; the water temperatures and the salinity of the aquaculture ponds are controlled in such modes that temperature difference of the ground are regulated, water is blended, salt is added into the water at specified steps, the water is diluted at specified steps and the like. The aquaculture process has the advantages that cleaning optimization schemes implemented before the aquaculture ponds are utilized are optimized by means of exploration, and methods for removing cement alkali are improved; aquaculture pond sterilization modes are optimized; the growth speeds of the eel larvae are increased, eel deformity can be prevented, and the death rates in larva aquaculture periods can be decreased; eel larva releasing modes and salinity regulation modes are modified, and accordingly death of the eel larvae due to temperature or salinity problems in releasing procedures further can be reduced.
Owner:陈宏
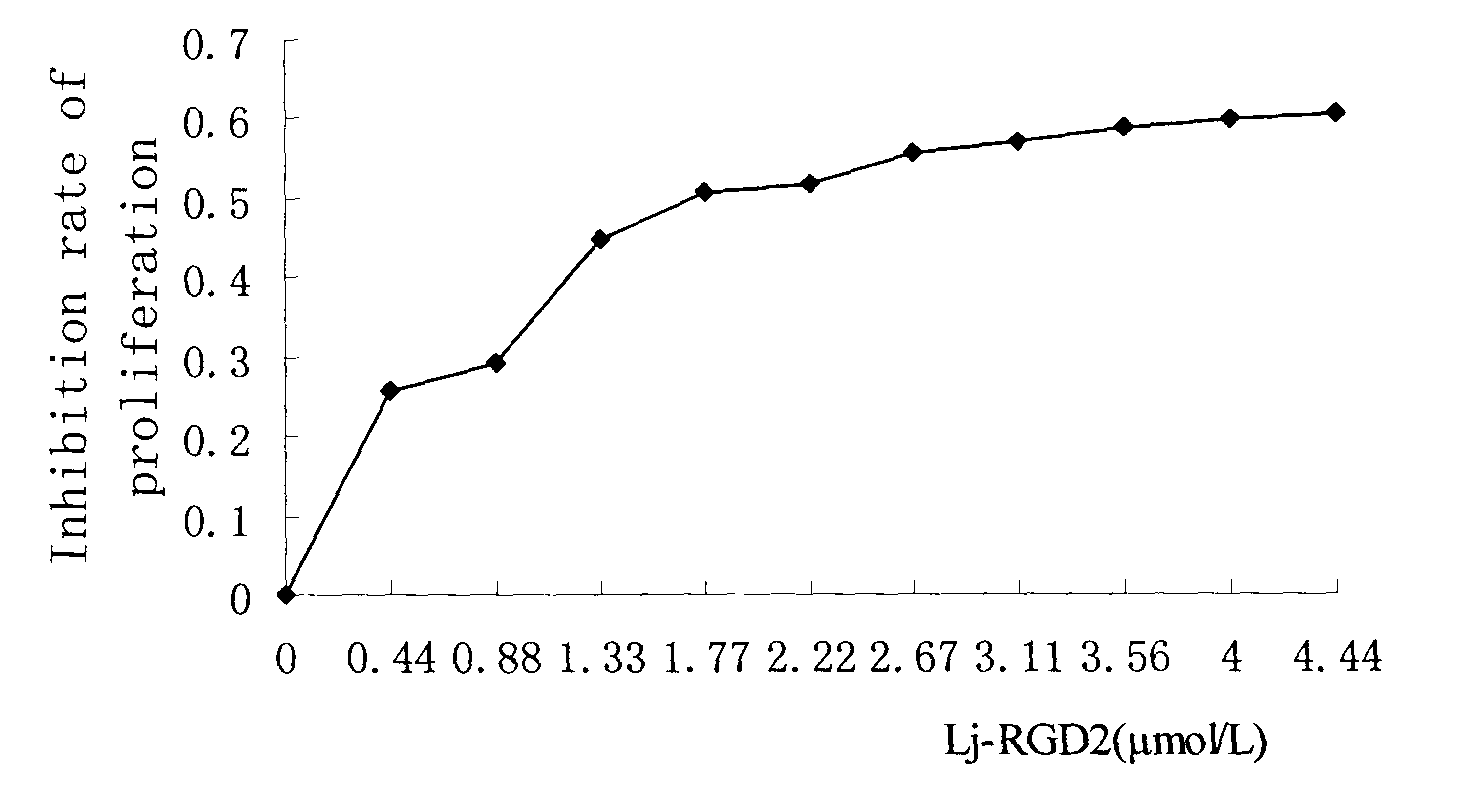
Application of lamprey Lj-RGD2 in preparation of anti-angiogenesis antitumour drug
InactiveCN103173453AReduce in quantityPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationVascular endotheliumBlood vessel
The invention provides an application of lamprey Lj-RGD2 in preparation of an anti-angiogenesis antitumour drug, belongs to the biotechnology field and relates to gene cloning and protein expression of RGD die body protein Lj-RGD2 in an oral cavity gland of lamprey in Japan, a strong-effect function of Lj-RGD2 for inhibiting angiogenesis by inhibiting a signal transduction pathway of integrin highly expressed on the surface of new vascular endothelial cells and an application of the lamprey Lj-RGD2 as an angiogenesis inhibitor in preparation of antitumour drugs.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Ecological cultivation method of fugu flavidus intercropping barracuda parental fish
InactiveCN104982354AImprove water qualityMake full use of spaceClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBroodstockWater source
An ecological cultivation method of fugu flavidus intercropping barracuda parental fish is characterized in that barracudas are released to prepare parental fish in winter; an outdoor earth pond is provided with an aerator of 1.5 Kw at every 3 to 5 mu; the pond is disinfected by quick lime before the barracudas are released; water is injected into the pond a week later and the water source is natural seawater; after ten days of injecting the water, two-year-old barracudas are released to prepare parental fish as backup; the density is within the range of 20 to 30 tails per mu without feeding fish meal; in spring, the water temperature of the outdoor earth pond is risen to 14 to 15 DEG C; two-year-old fugu flavidus fingerlings that live through winter are released into the outdoor earth pond; the density is within the range of 800 to 1000 tails per mu; the fugu flavidus fingerlings are fed with baits twice a day; the daily bait-feeding amount is 3 to 8 percent of the weight of each of the fugu flavidus fingerlings; the baits are eel feeding stuff; the next bait-feeding amount is regulated timely according to the ingestion situation; the water is changed once every two weeks; from mid to late of November, the fugu flavidus fingerlings are started to be caught into a greenhouse for living through winter; and the barracudas are kept in the pond to early January and the pond is dried for catching the barracudas when the temperature is relatively low.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES RES INST +1
Feed formula for eel fries
InactiveCN104705515AEnhance immune functionSuitable for long-term feedingAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseSucrose
The invention discloses a feed formula for eel fries. The feed formula comprises the following components in parts by weight: 3-12 parts of roots of woods Greenstar, 4-12 parts of a soybean oil, 3-12 parts of earthworm powder, 3-9 parts of cinnamon powder, 5-15 parts of cane sugar, 5-10 parts of rice flour, 5-20 parts of powder of shrimps and crab shells, 5-15 parts of coptis chinensis powder, 3-15 parts of duck blood powder, 4-12 parts of a fish oil, 4-12 parts of sweet potato powder, 2-6 parts of phospholipid powder, 3-9 parts of peanut meals, and 3-12 parts of liver powder. The feed formula disclosed by the invention can enhance the immune function of eels, and can improve the capabilities of disease prevention and disease resistance of the eels; the feed formula is reasonable in compound ratio and rich in nutriments, and is suitable for feeding eel fries in freshwater fish ponds or captive fish ponds in sea areas for a long time.
Owner:MINGGUANG YONGYAN AQUATIC FOOD
Wild adult exopalaemon modestus training method
ActiveCN102440203AImprove the living environmentImprove domestication effectClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffPhototaxisWater quality
The invention discloses a wild adult exopalaemon modestus training method. In the invention, according to the ecological habits of the exopalaemon modestus, the good living environment is provided for the exopalaemon modestus, and the exopalaemon modestus is subjected to feed training in a quantifying manner at the fixed position after the hunger stimulation, and is induced to eat particle feed by eel feed with higher protein content and more soft texture, so that the possibility that the fresh animal bait minced fillet, viscera and the like pollute water can be avoided. In the training process, the ratio of the eel feed to the particle feed is adjusted gradually, finally the exopalaemon modestus only eats the particle feed, simultaneously, the feeding time in the morning is deferred to the proper time section, so that the various inconveniences caused by the night feeding can be avoided. In the training, due the comprehensive methods such as gradual temperature raising, addition of hiding devices, arrangement of a bait table for observation, utilization of phototaxis and the like, the good training effect is obtained, the training success rate achieves 90%; and after 40-60 days, the trained adult exopalaemon modestus broods the baby exopalaemon modestus successfully, and the brooding time is reduced by 10-20 days compared with the time of the exopalaemon modestus brooded in natural water.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com