Biological 3D printing method for large tissues
A 3D printing and tissue technology, applied in the field of 3D bioprinting of large tissue, can solve the problems of flow channel effectiveness, cumbersome operation, structural collapse, etc., achieve good biocompatibility, ensure survival rate, and solve the effect of collapse
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] refer to figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment provides a bio-3D printing method of a large tissue, comprising the following steps:
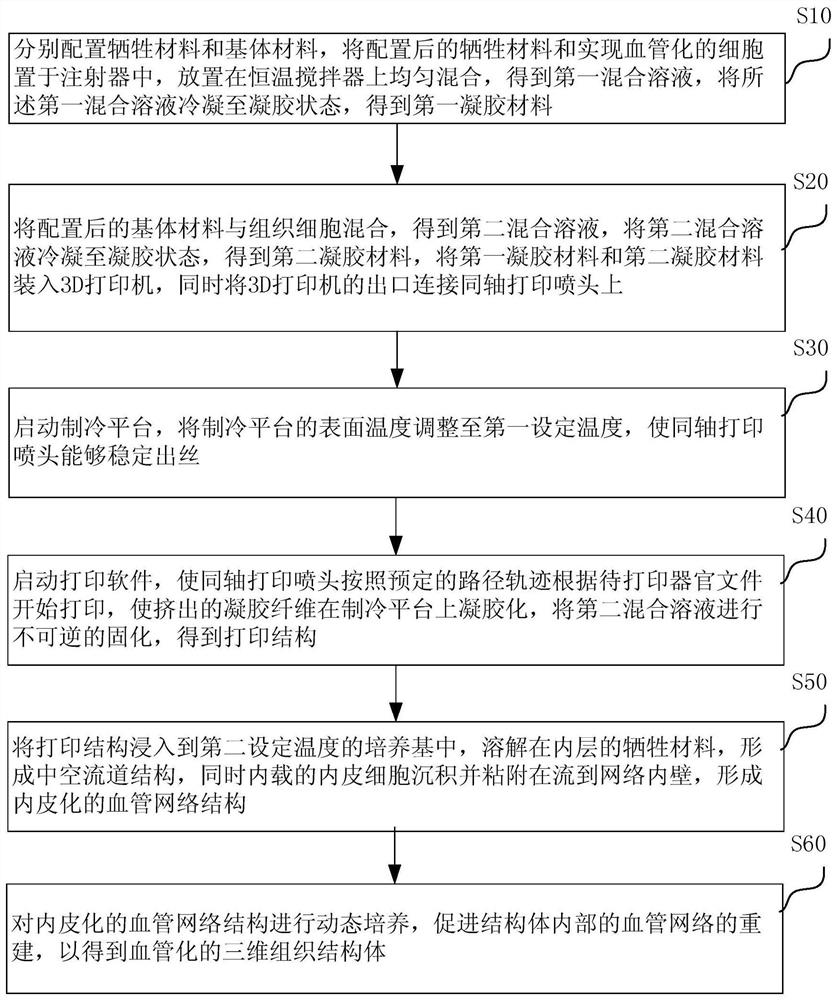
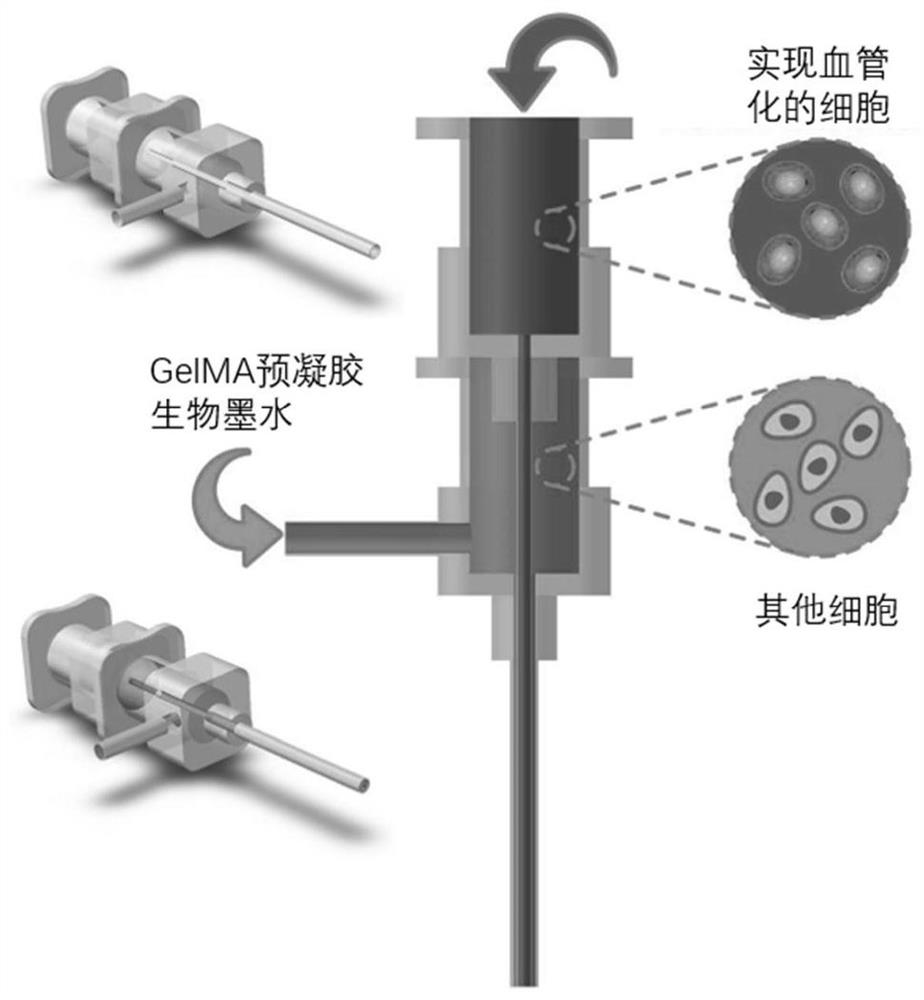
[0041] S10, prepare the sacrificial material and the matrix material respectively, put the prepared sacrificial material and cells that realize vascularization (such as endothelial cells, cells that can be induced to differentiate into endothelial tissue) into a syringe, and place them on a constant temperature stirrer for uniform mixing , to obtain a first mixed solution, and condense the first mixed solution to a gel state to obtain a first gel material.
[0042] The aforementioned sacrificial material may include gelatin and other materials with good biocompatibility, printability, and easy removal. The above-mentioned matrix material may include GelMA (methacrylic anhydride gelatin) and other materials with good biocompatibility, printability, stability and non-deformation characteristics.
[0043] Specifically, the sacrificial ...
Embodiment 2
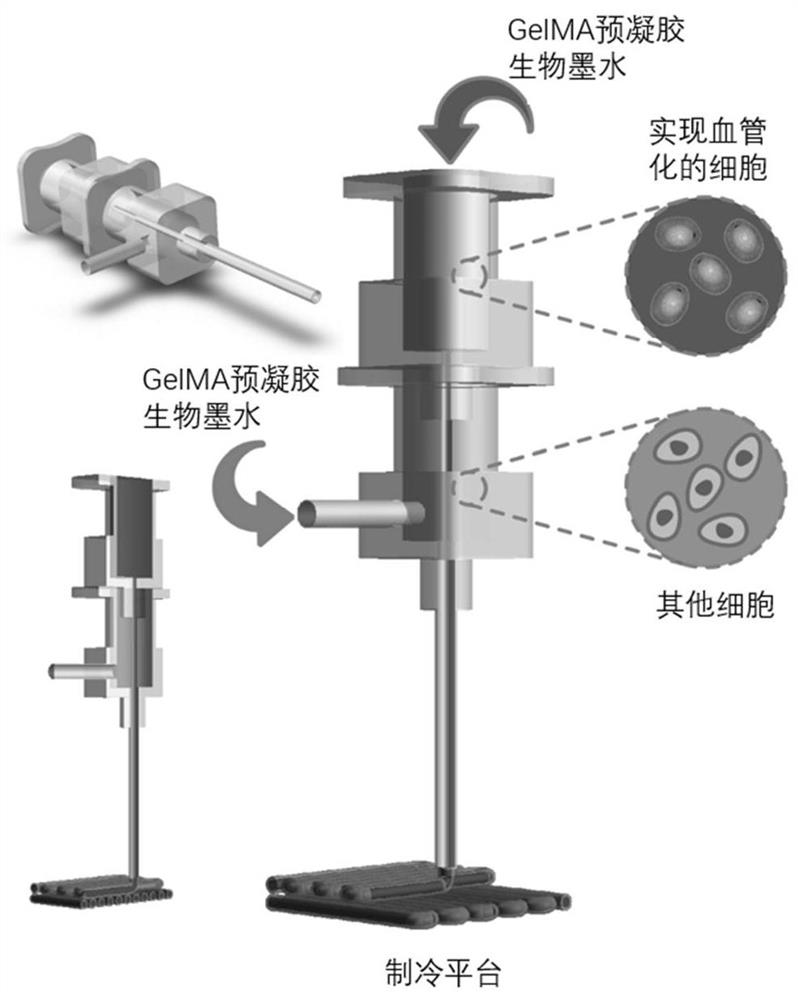
[0079] In this embodiment 2, the devices involved in the execution of the bio-3D printing method of the above-mentioned bulk tissue may include: a bio-3D printer with a motor module of the three coordinate axes of XYZ controlled; coaxial printing nozzles, external nozzles The inner diameter is up to 3mm, and the inner diameter of the inner nozzle is up to 0.5mm; a cooling platform with real-time temperature control; a syringe pump system with controllable flow rate.
[0080] Specifically, the device for realizing the bio-3D printing method of the above-mentioned bulk tissue may include: a printing system and a refrigeration system. The above printing system can refer to figure 2 As shown, the motor is an ordinary two-phase four-wire stepping motor, which passes through the motor base of the module coaxially. The two are fixedly connected by four screws, and the limit switch is fixed on the motor base of the module on the motor side by two screws. , used to realize positionin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com