Taking-out system for urinary system stent
A urinary system and catheter technology, which is applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of stent type limitation, increase the difficulty of surgery, and sensitization, and achieve the effect of accurate stent removal process, increase the success rate of surgery, and reduce the difficulty of surgery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
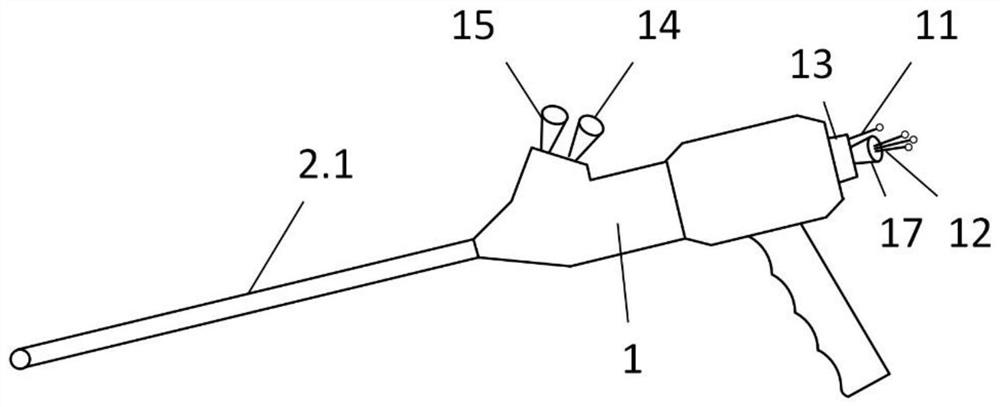
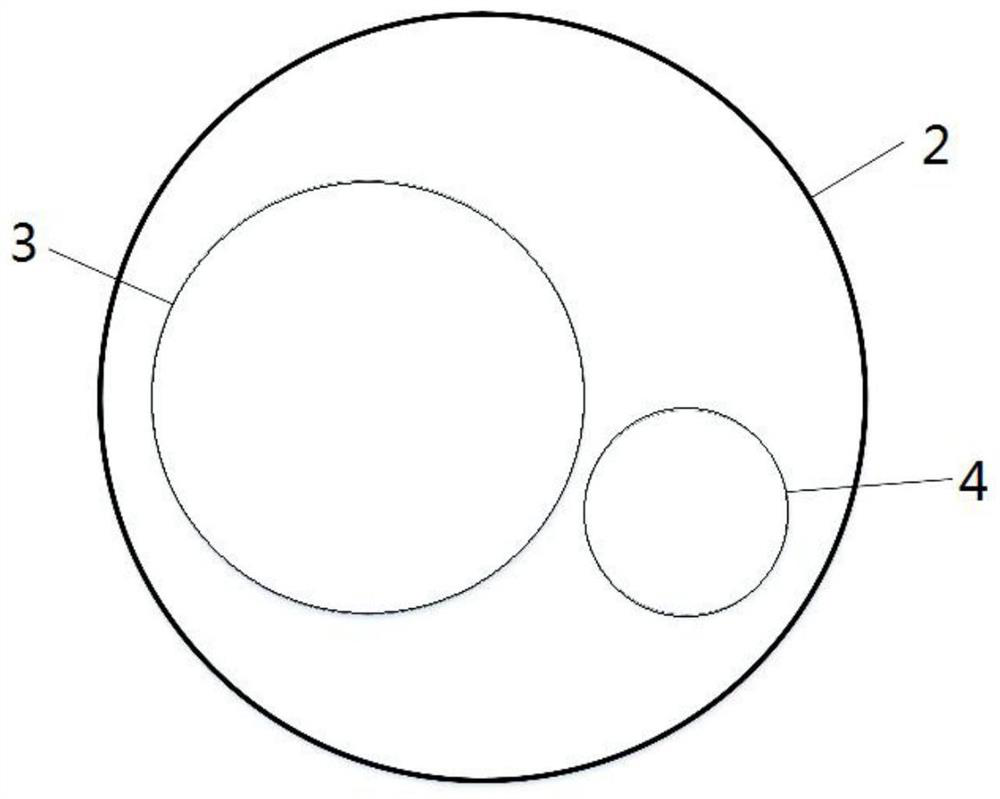
[0059] Patients implanted with bladder neck stents had to have the stents removed due to problems such as stent displacement and recurrent stenosis. During the bladder neck stent removal operation, the stent removal channel 3 assembled with the distal catheter protection tube 8 (the distal catheter 7 has been assembled) and the proximal catheter 6 passes through the operation channel reserved on the external operation handle 1 as a whole, and It is fixed with the operating handle outside the body, and the front end is placed in the channel 2 of the working sleeve inside the body. The operation adopts retrograde insertion and extraction. One person holds the operating handle 1 to perform the water injection operation to flush out the obstructed tissue, and at the same time adjusts the imaging system to observe the operation position in real time, and guides the extraction system to the end of the stent. After the other person adjusts the stent take-out channel 3 and reaches th...
Embodiment 2
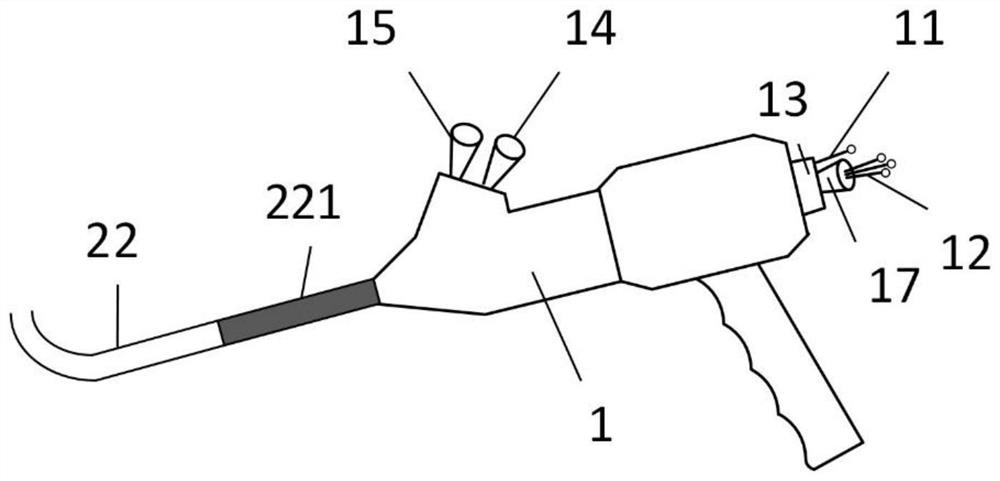
[0061] Ureteral stents are the most difficult to remove among urinary stents. Metal ureteral stents (Uventa TM ) is a three-layer structure of nickel-titanium alloy mesh-polytetrafluoroethylene film-nickel-titanium alloy mesh. When this kind of bracket is taken out, one person holds the operating handle 1 to perform the water injection operation, and guides the removal system to the end of the bracket. The other person adjusts the proximal catheter joint 11 on the extracorporeal operating handle 1, moves the anchor buckle 162 at the end of the proximal catheter 6, and fixes it with the metal edge at the end of the bracket. Adjust the anchor buckle 161 at the end of the distal catheter 7 and fix it with the metal edge of the stent head. Adjust the distal catheter protection tube 8 to the head of the stent, and adjust the position of the proximal catheter 6 outward. After the stent is detached from the ureteral tissue, reversely adjust the knob 17 to detach the distal cathete...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Nickel-free austenitic stainless steel ureteral stent design structure as follows Figure 11 shown. When this kind of bracket is taken out, one person holds the operating handle 1 to perform the water injection operation, and guides the removal system to the end of the bracket. The other person adjusts the proximal catheter joint 11 on the extracorporeal operating handle 1, moves the anchor buckle 162 at the end of the proximal catheter 6, and fixes it with the metal edge at the end of the bracket. Adjust the anchor buckle 161 at the end of the distal catheter 7 and fix it with the metal edge of the stent head. Adjust the distal catheter protection tube 8 to the head of the stent, and adjust the position of the proximal catheter 6 outward. After the stent is detached from the ureteral tissue, reversely adjust the knob 17 to detach the distal catheter protection tube 8 from the stent, and at the same time adjust the distal catheter 7 to detach it from the stent, and con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com