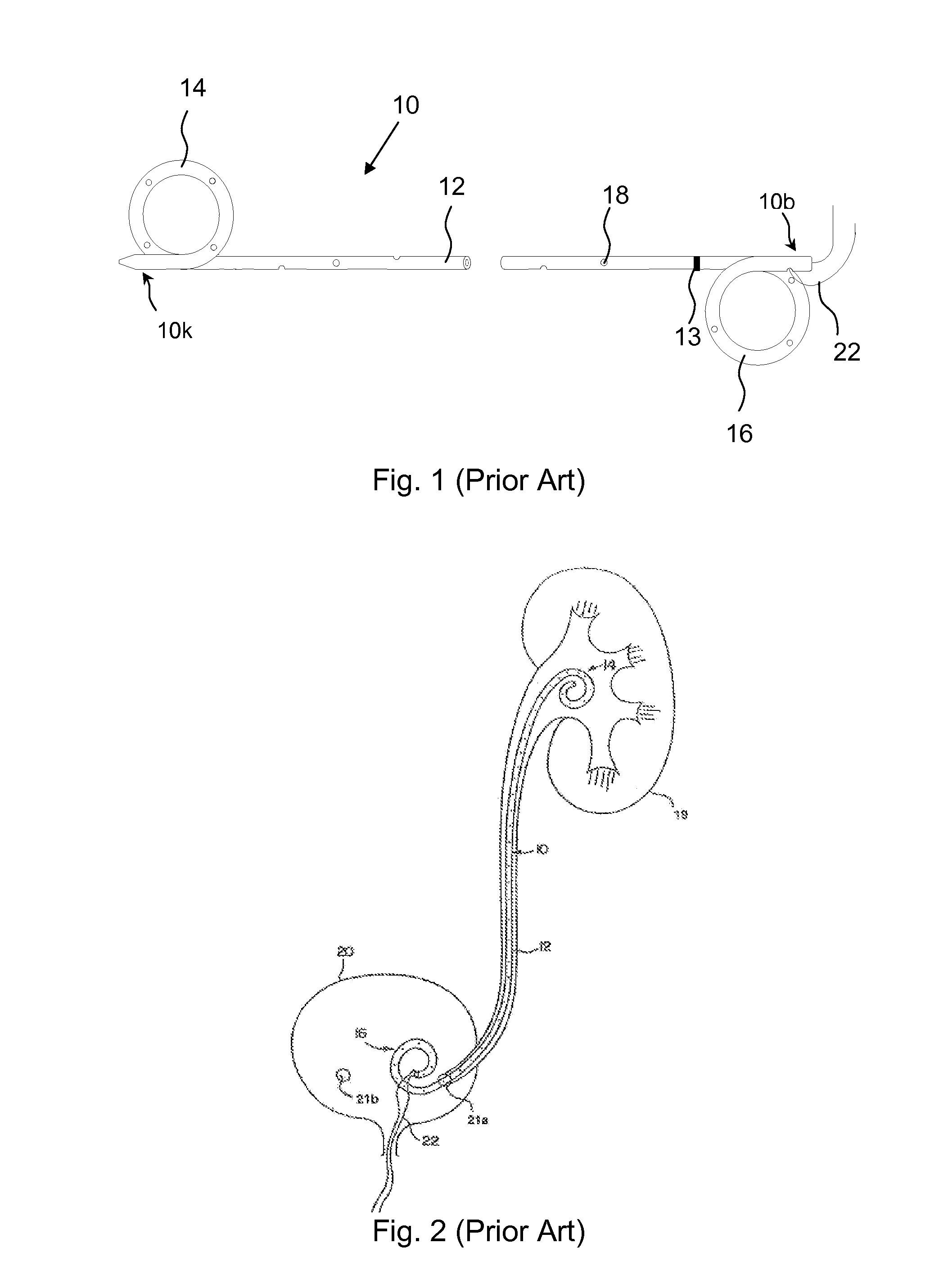
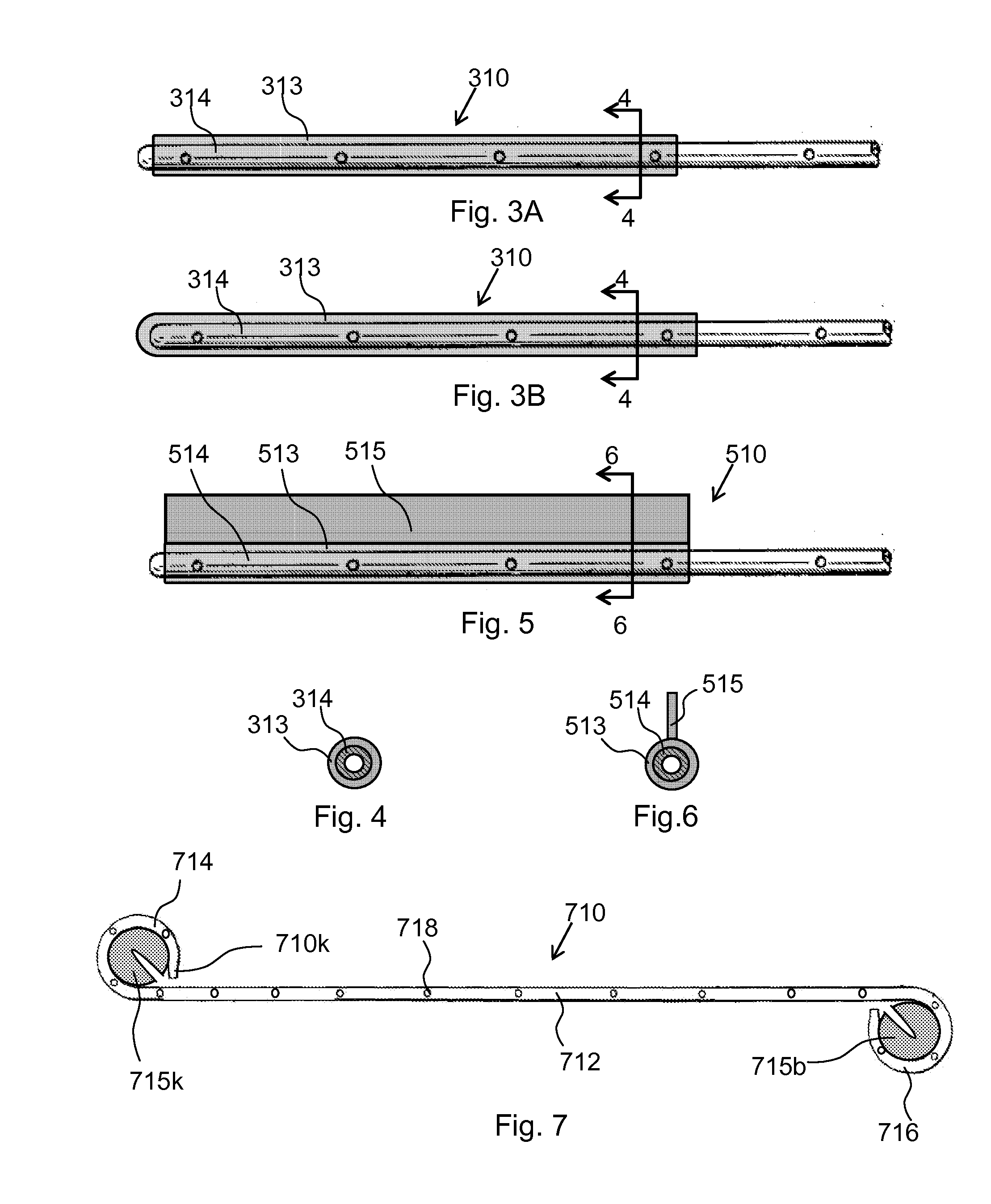
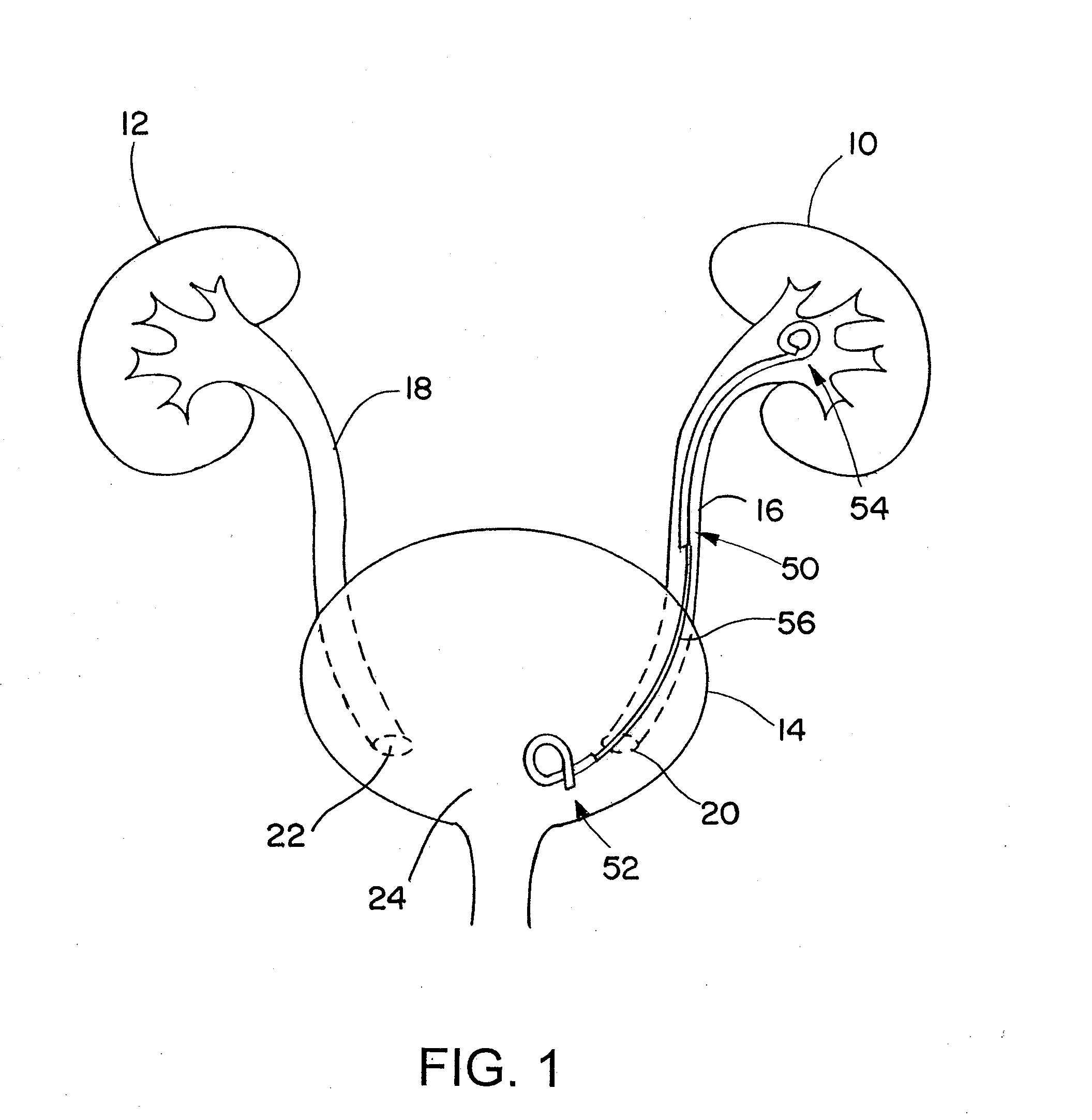
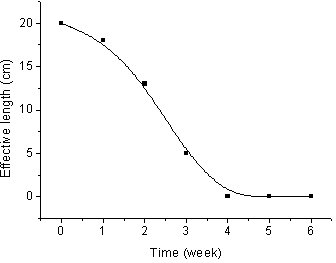
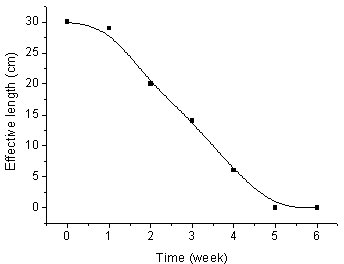
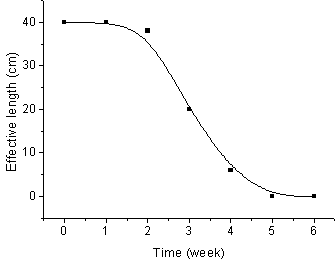
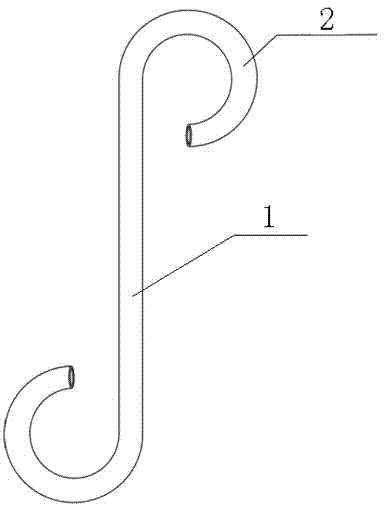
Patents
Literature
183 results about "Ureteral stents" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
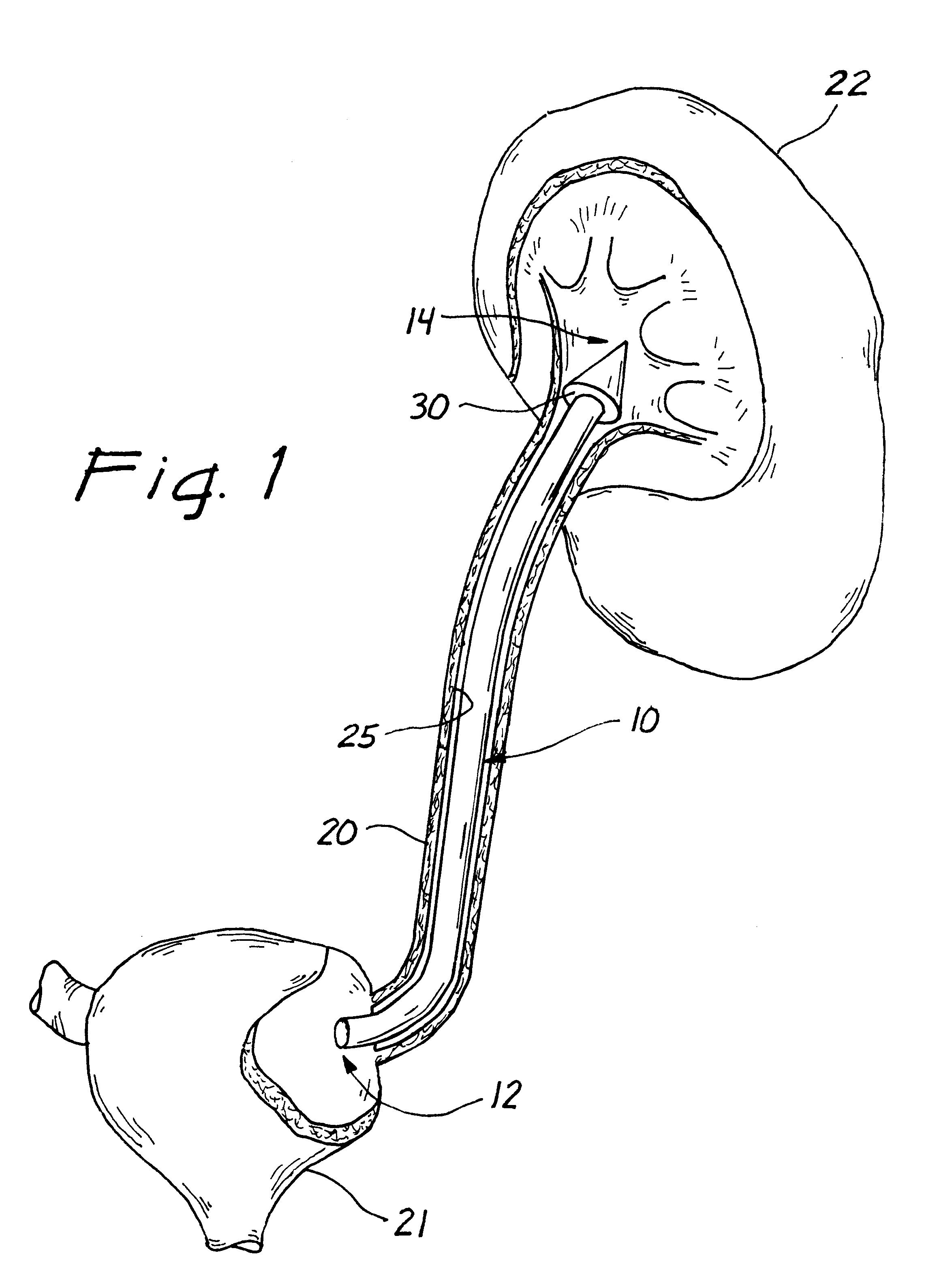
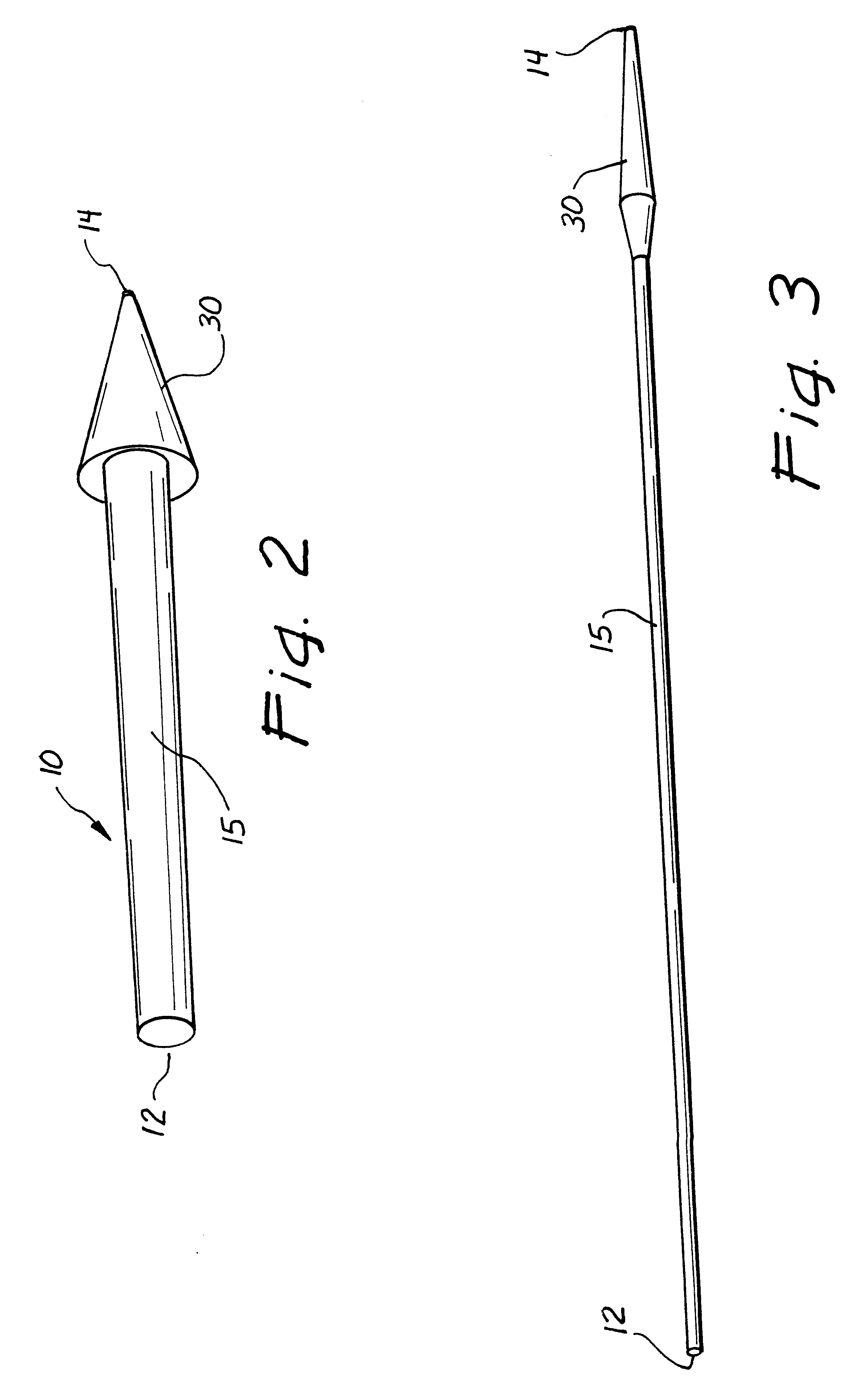
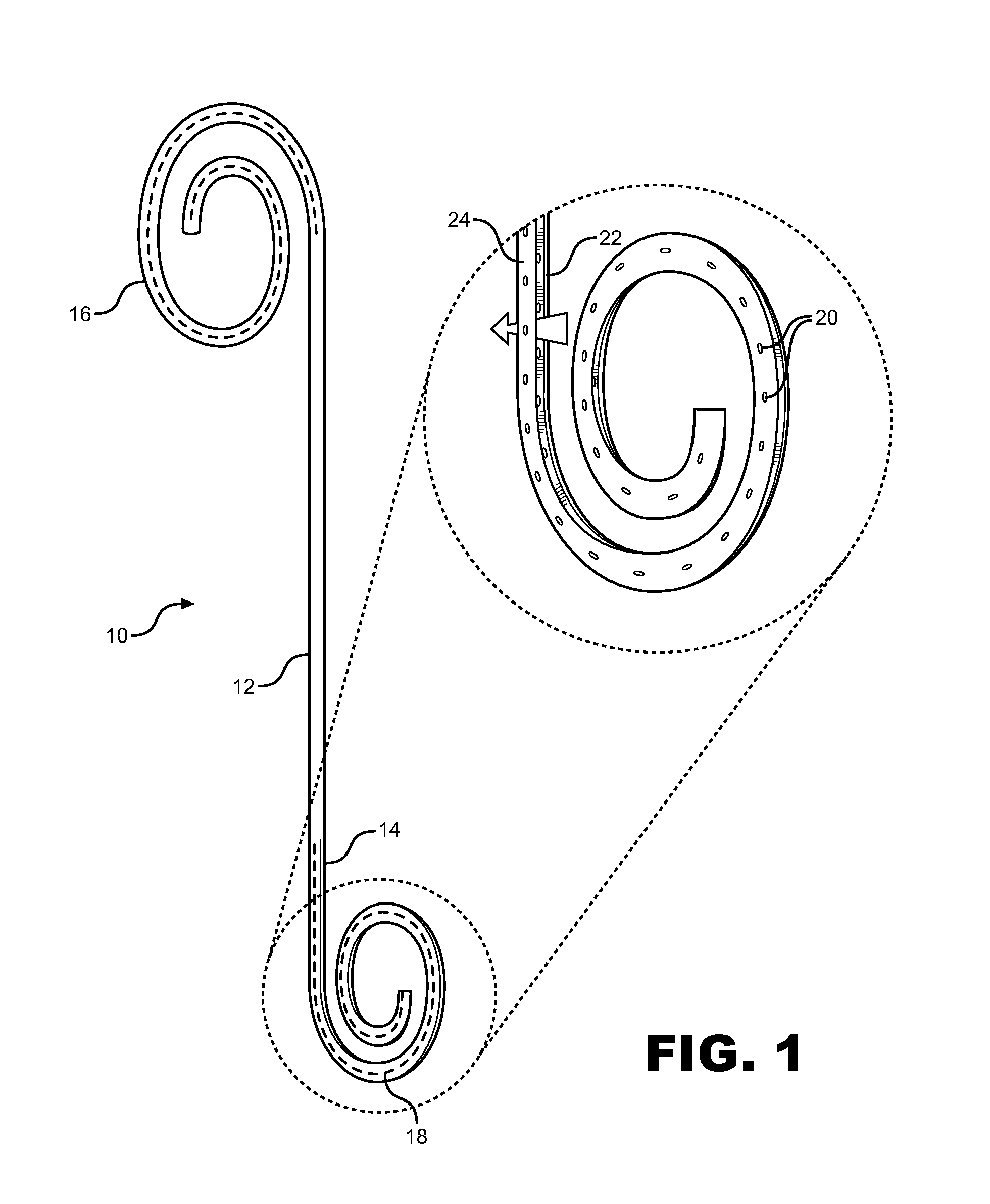
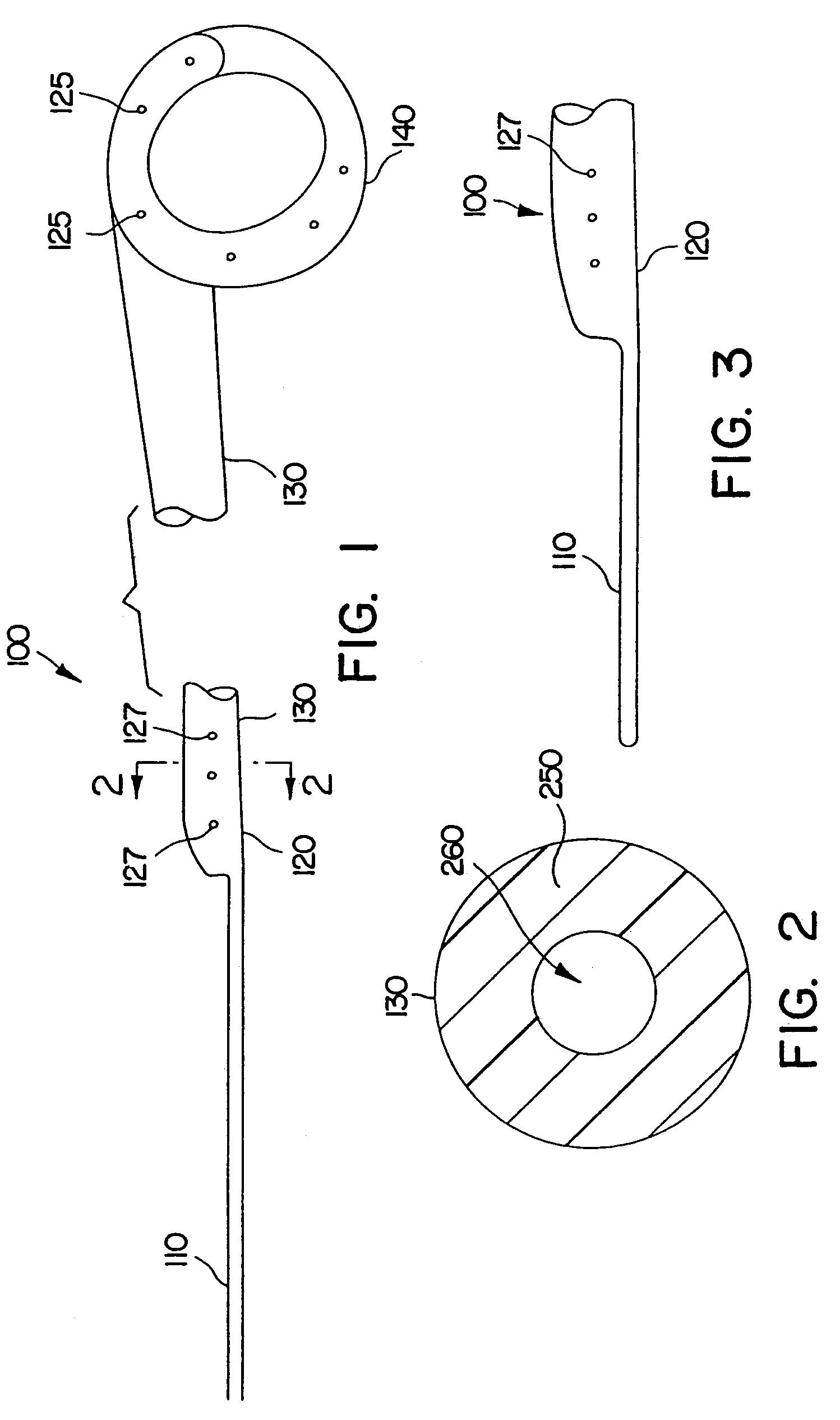
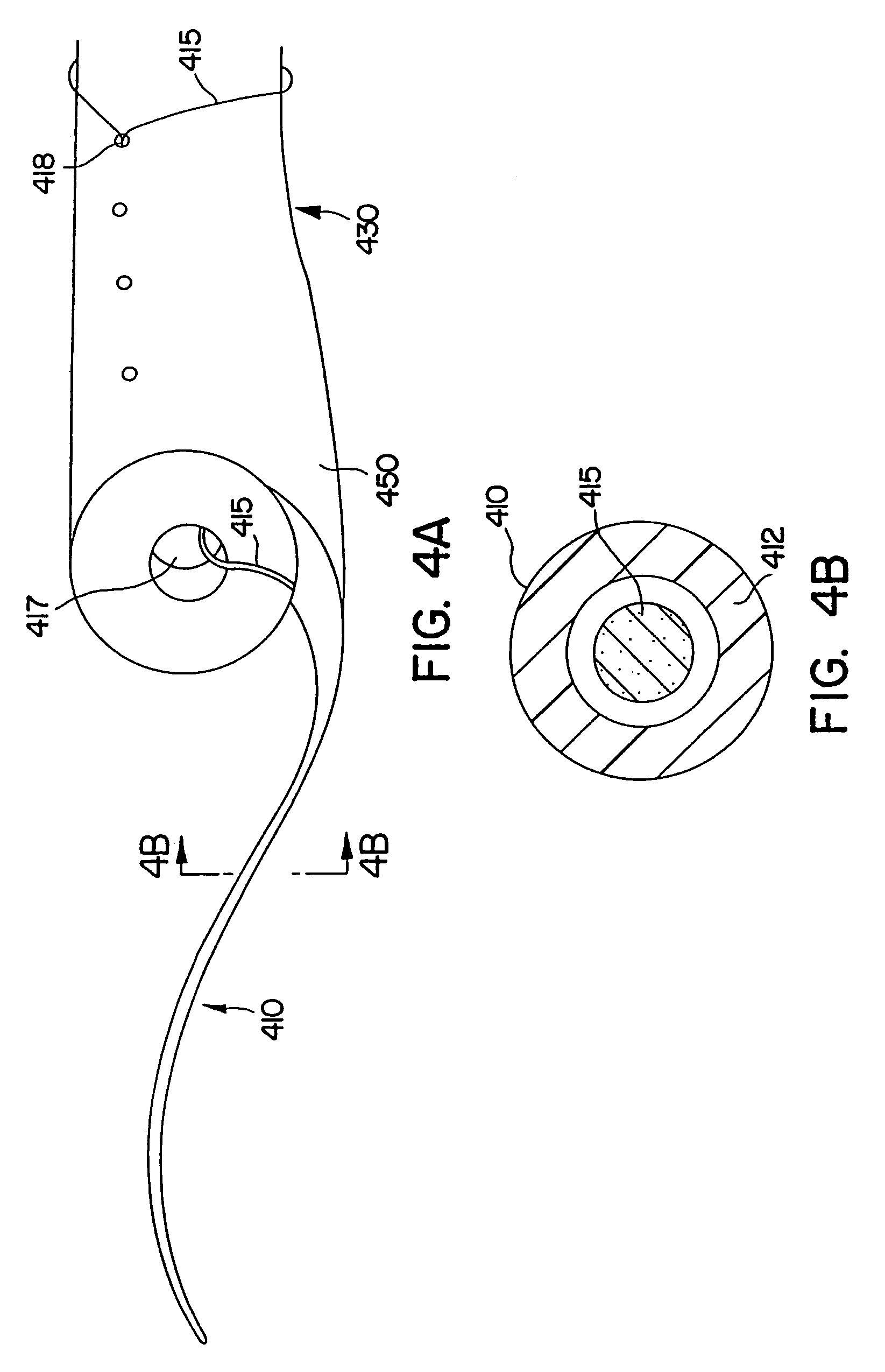
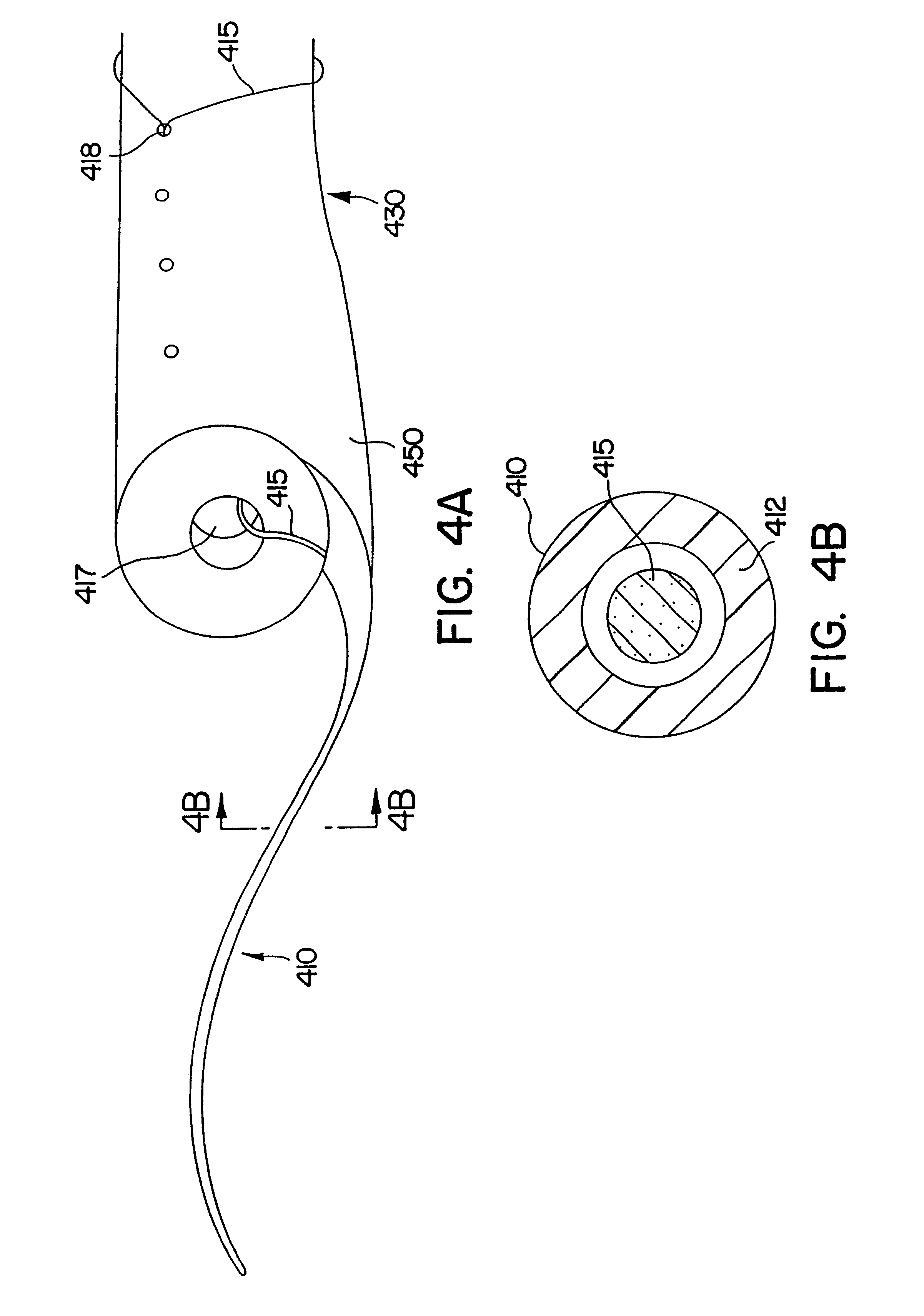
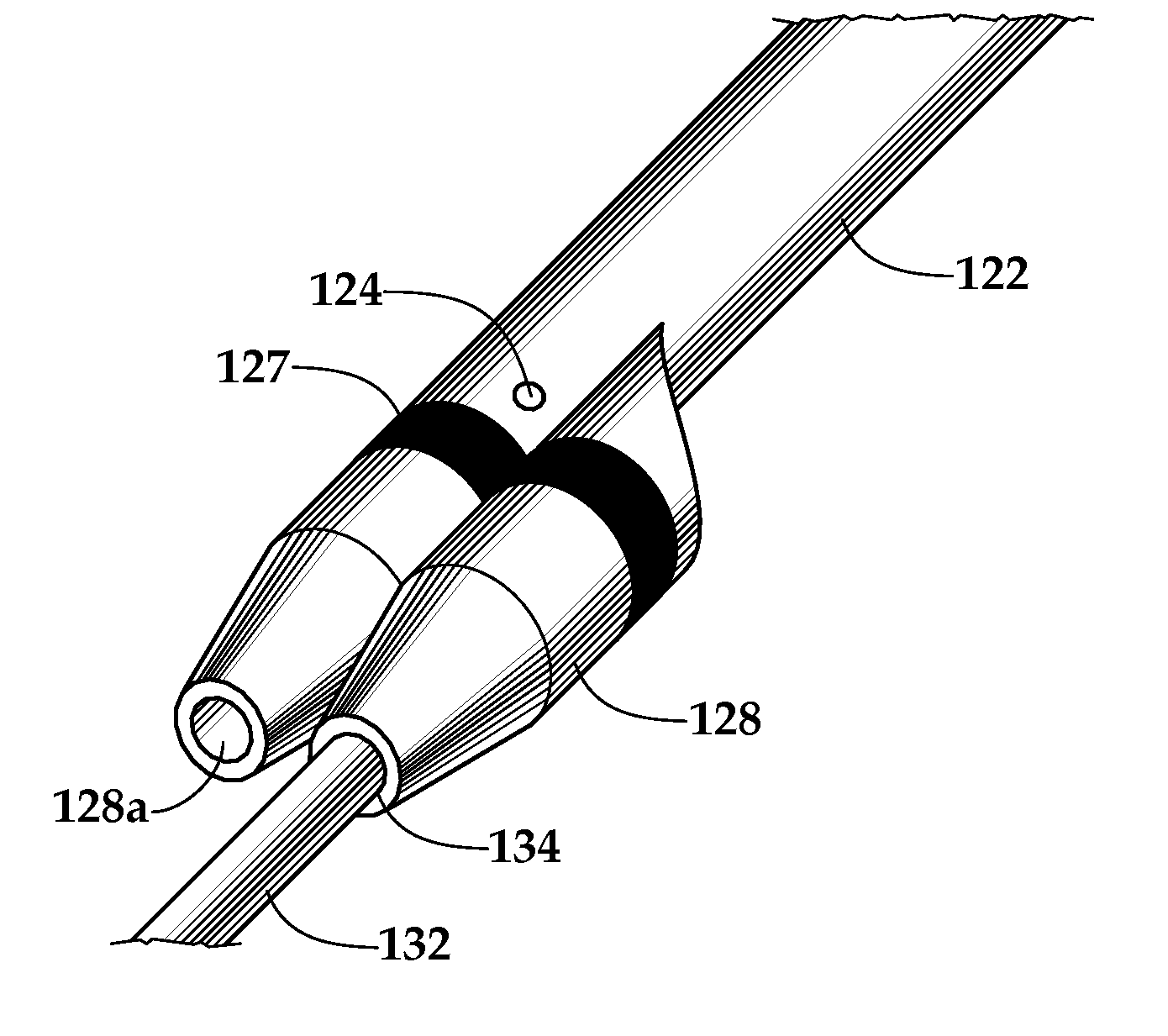
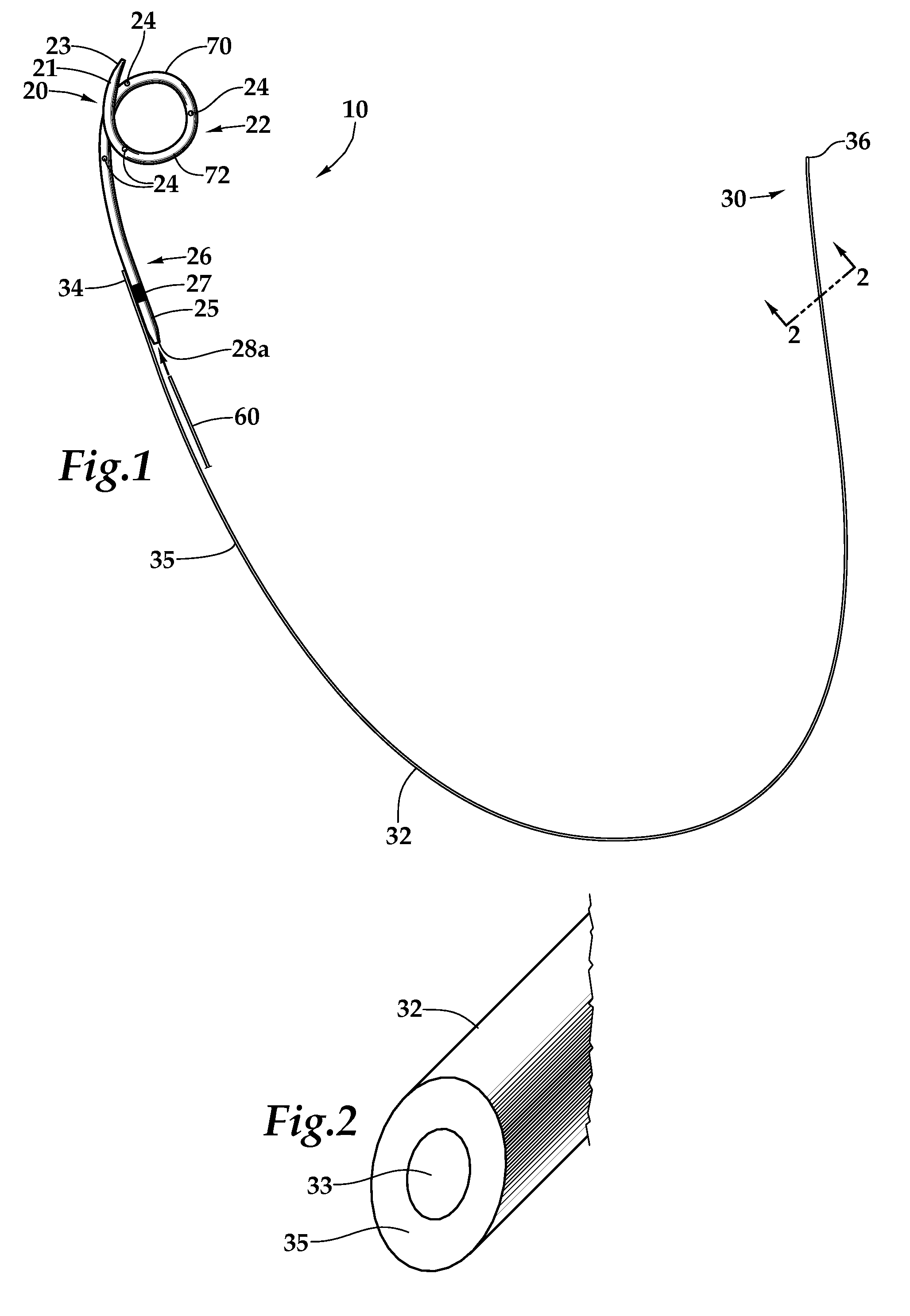
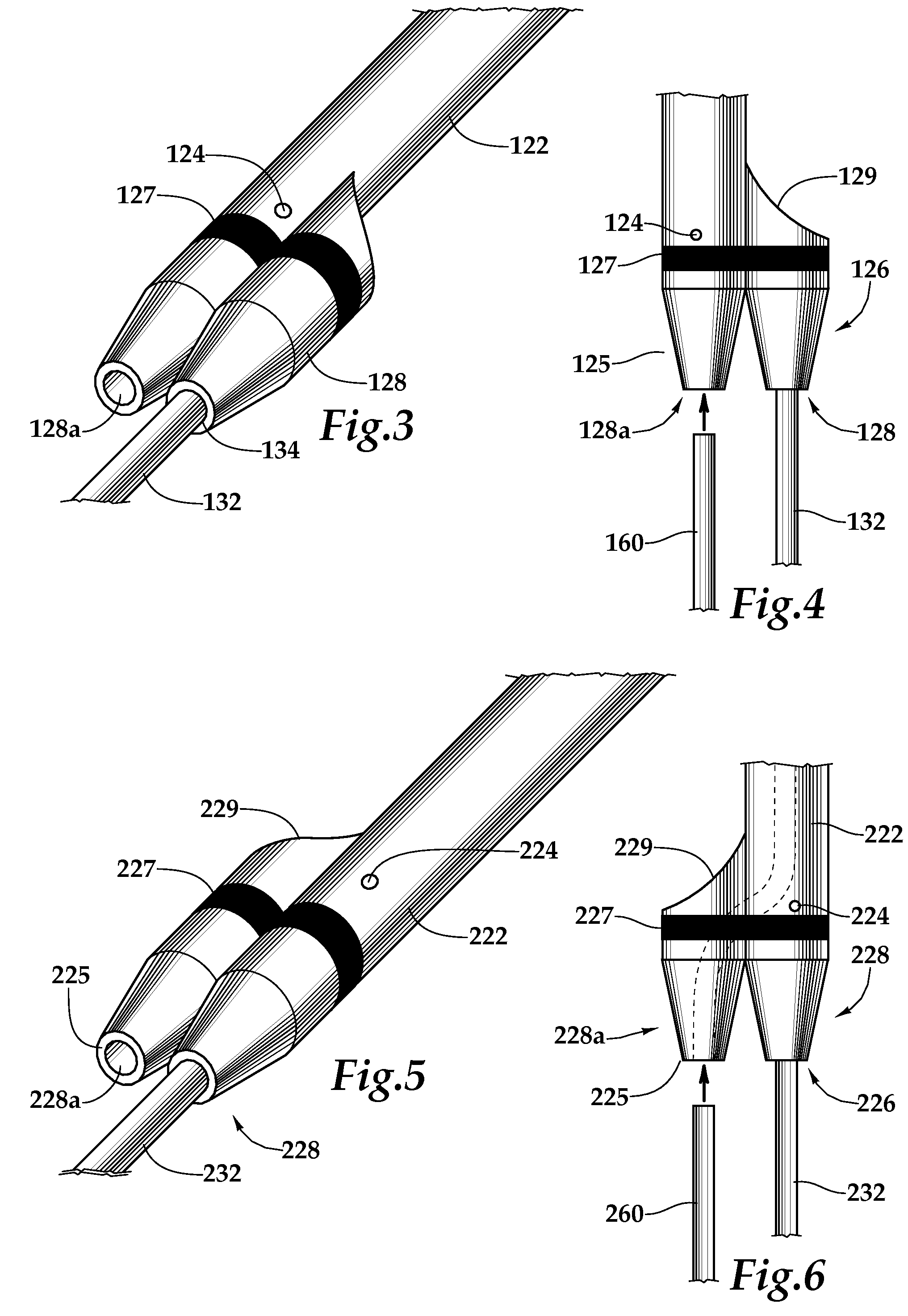
Ureteral stent system apparatus and method
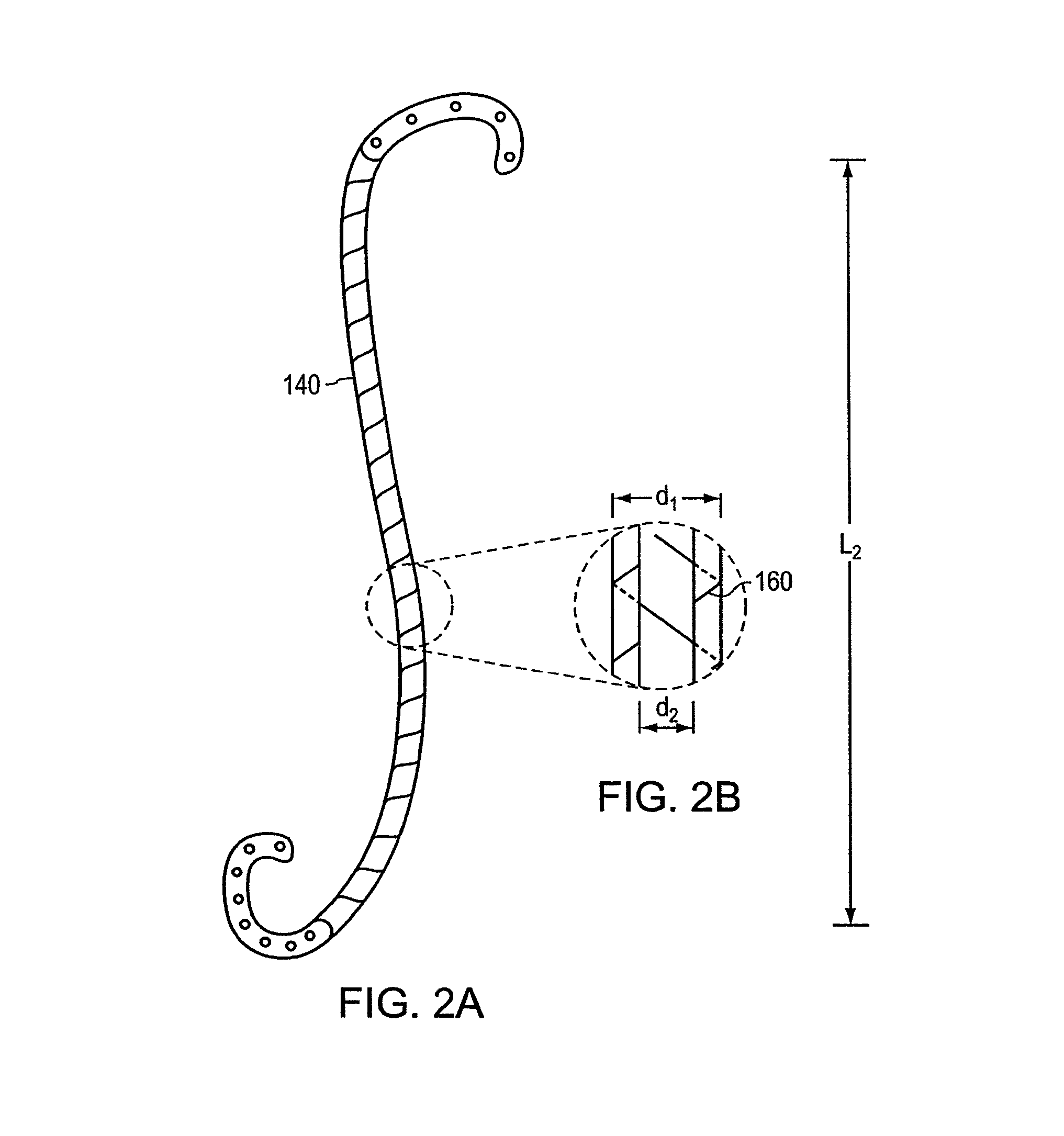
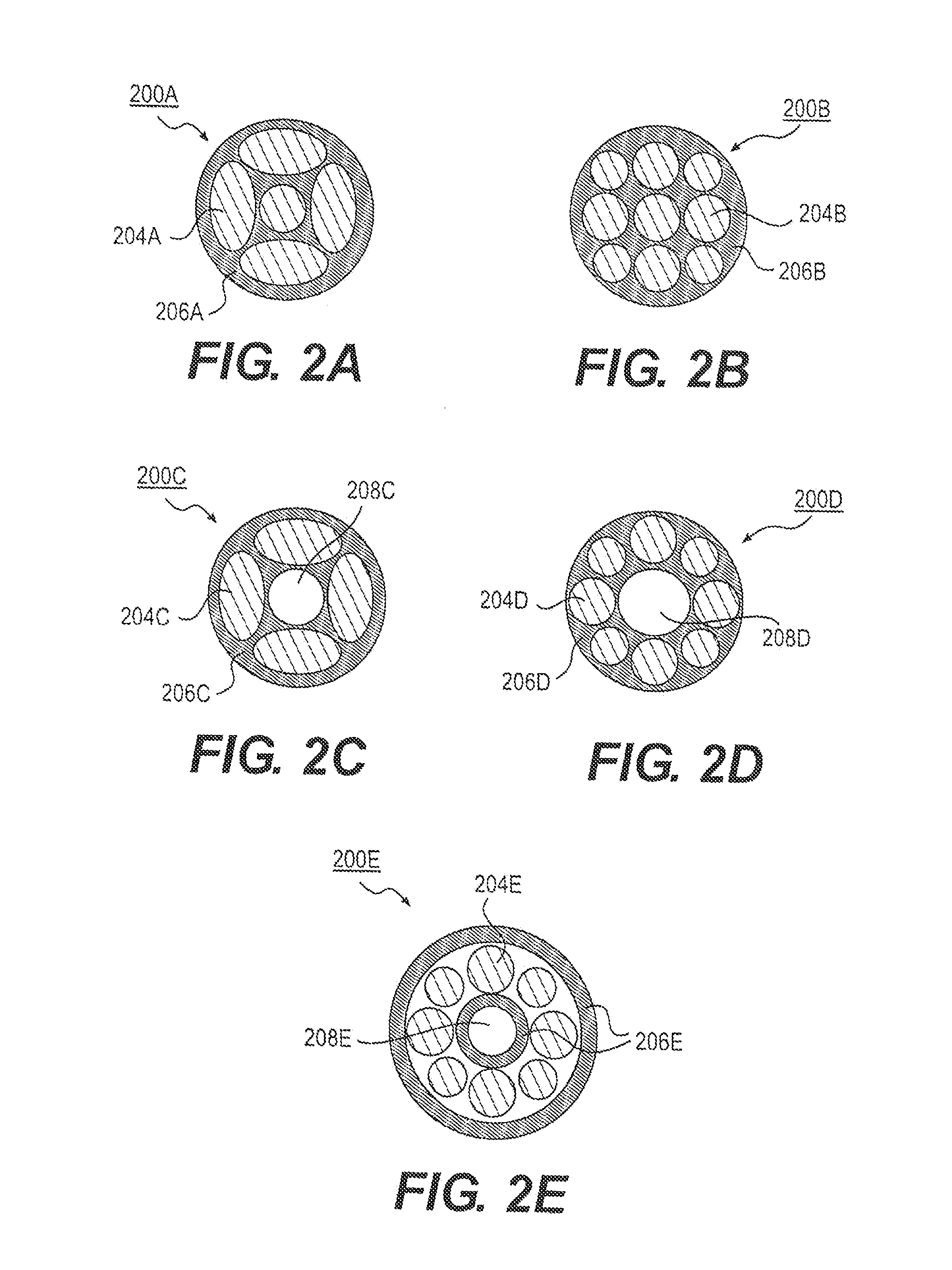
A stent having an elongate tubular configuration is formed of a plurality of elongate elements interwoven or braided to form a tubular configuration. The elements may be relatively strong and rigid, but movable relative to each other within the weave or braid in order to provide the stent with generally soft characteristics. The elements may be formed of different materials, such as an absorbent material permitting the stent to be doped with materials such as drugs and chemicals. Even the absorbency can be controlled and varied to provide a predetermined time-release of the absorbent.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Ureteral stent configured for improved patient comfort and aftercare
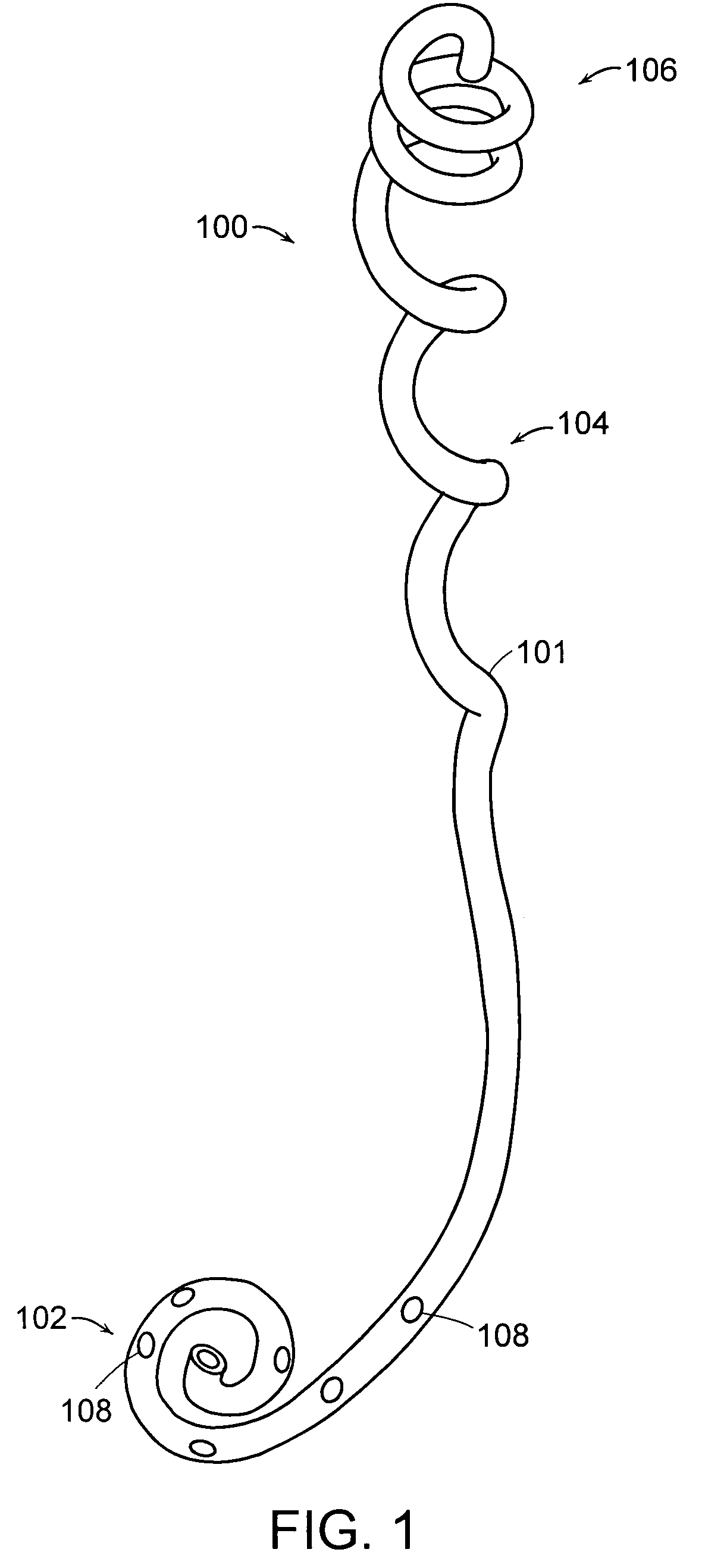
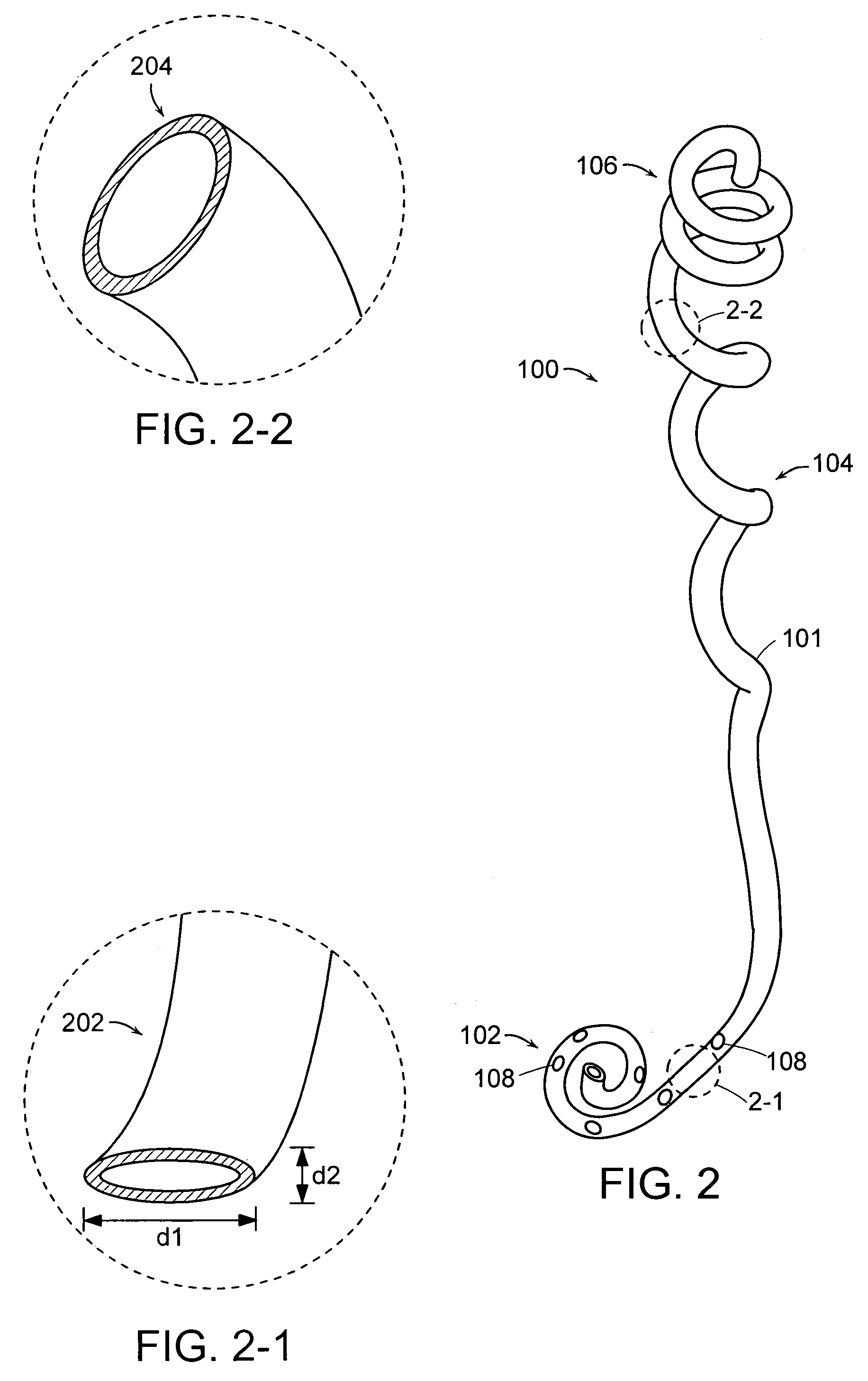
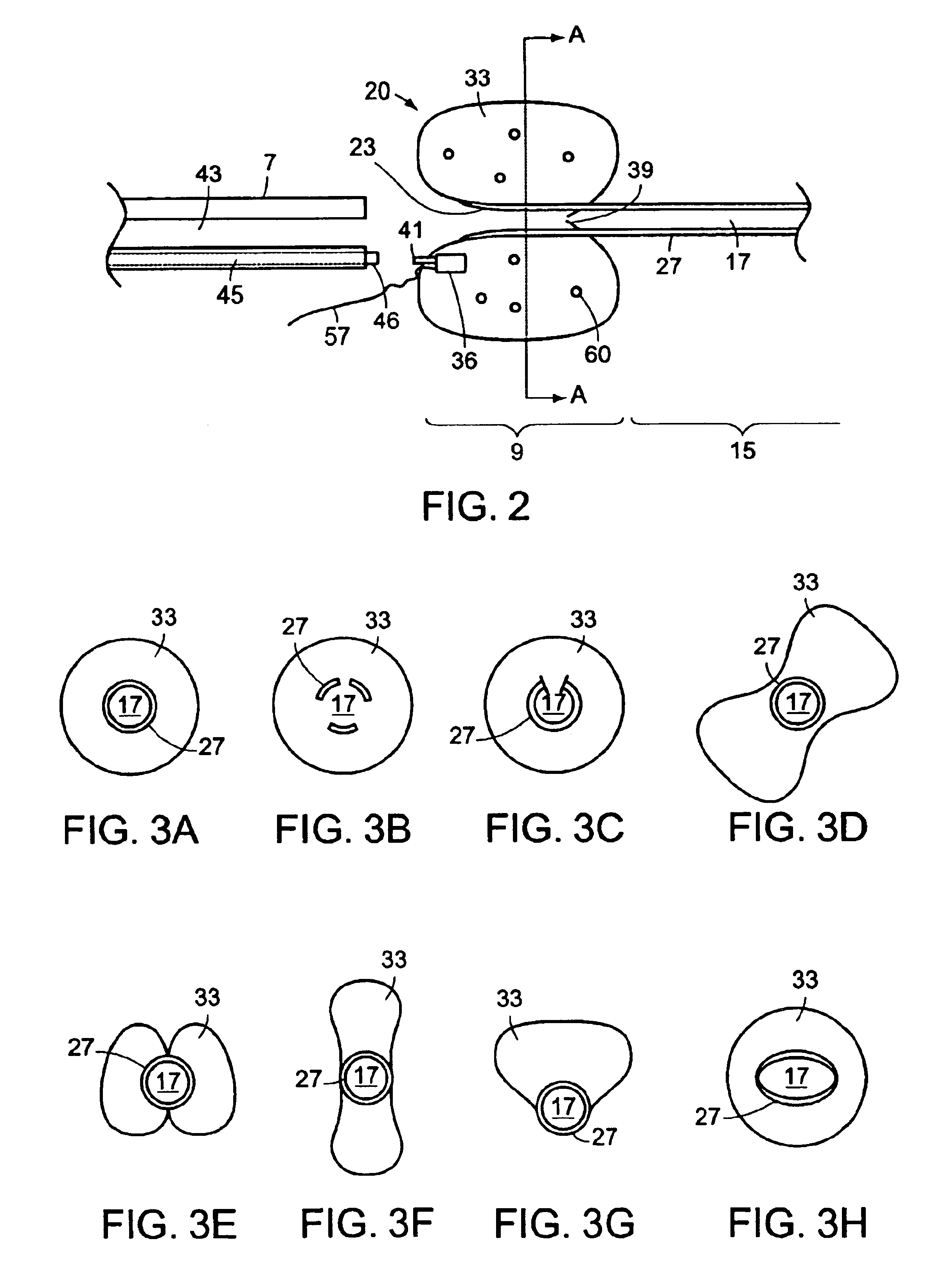
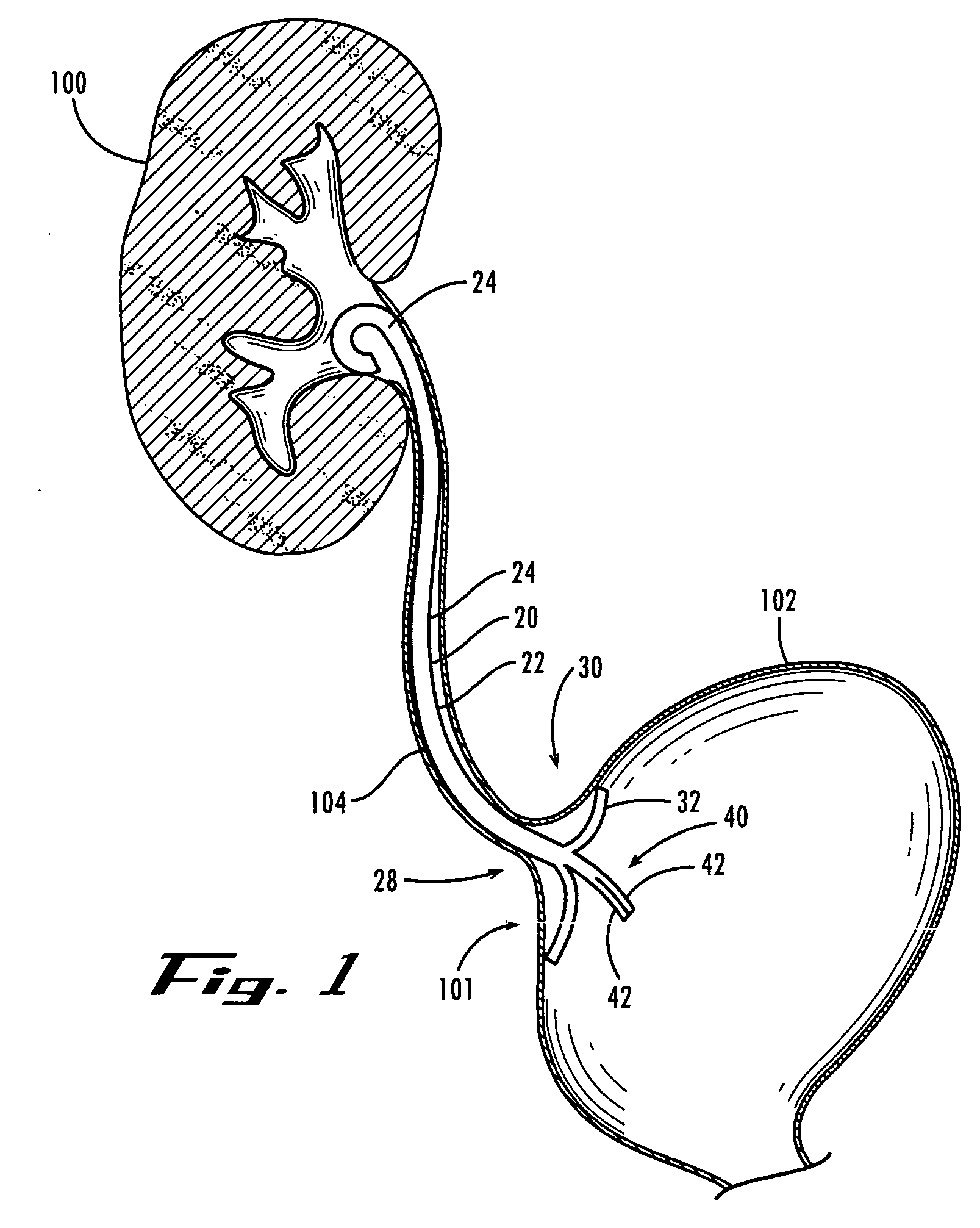
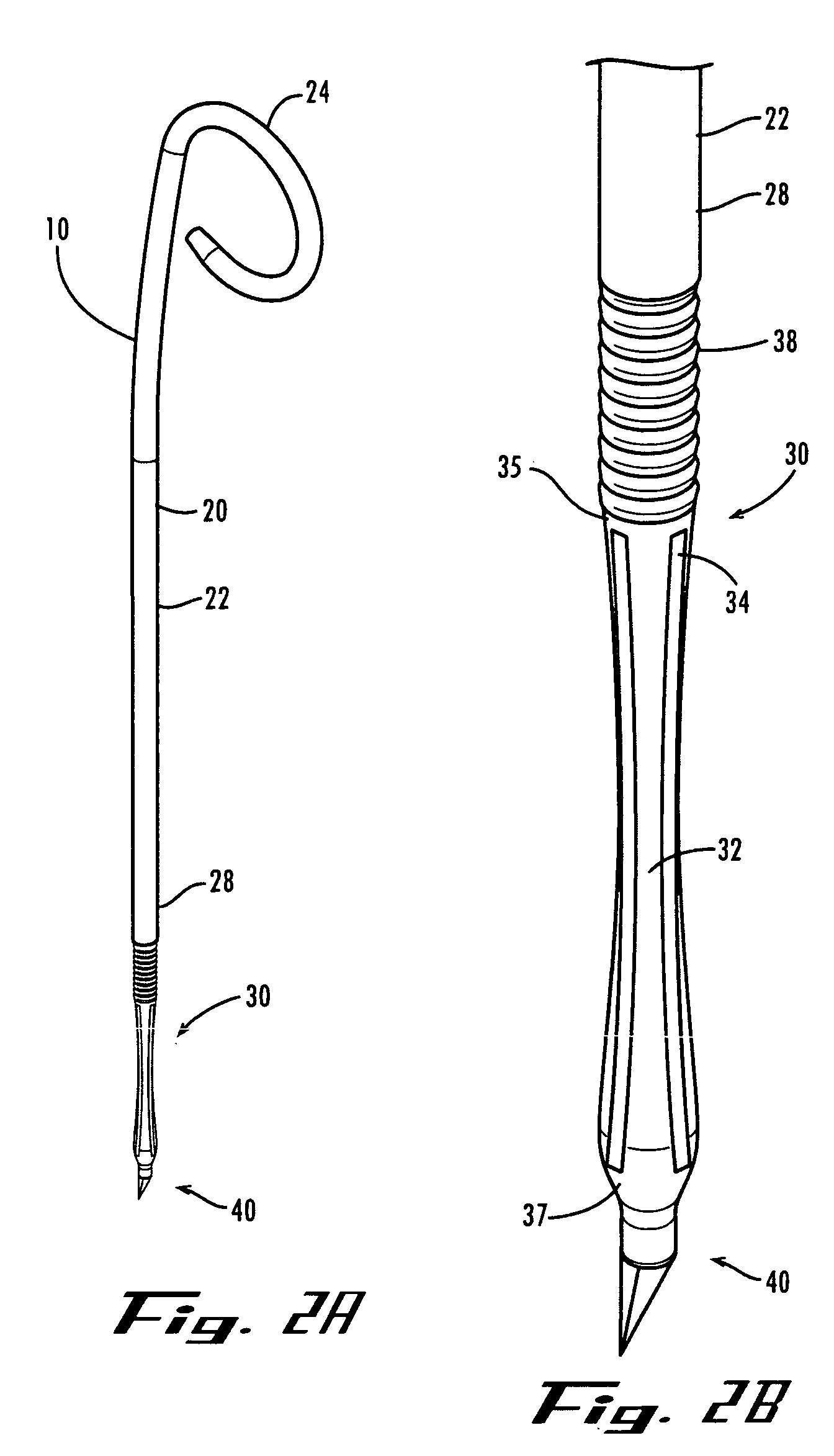
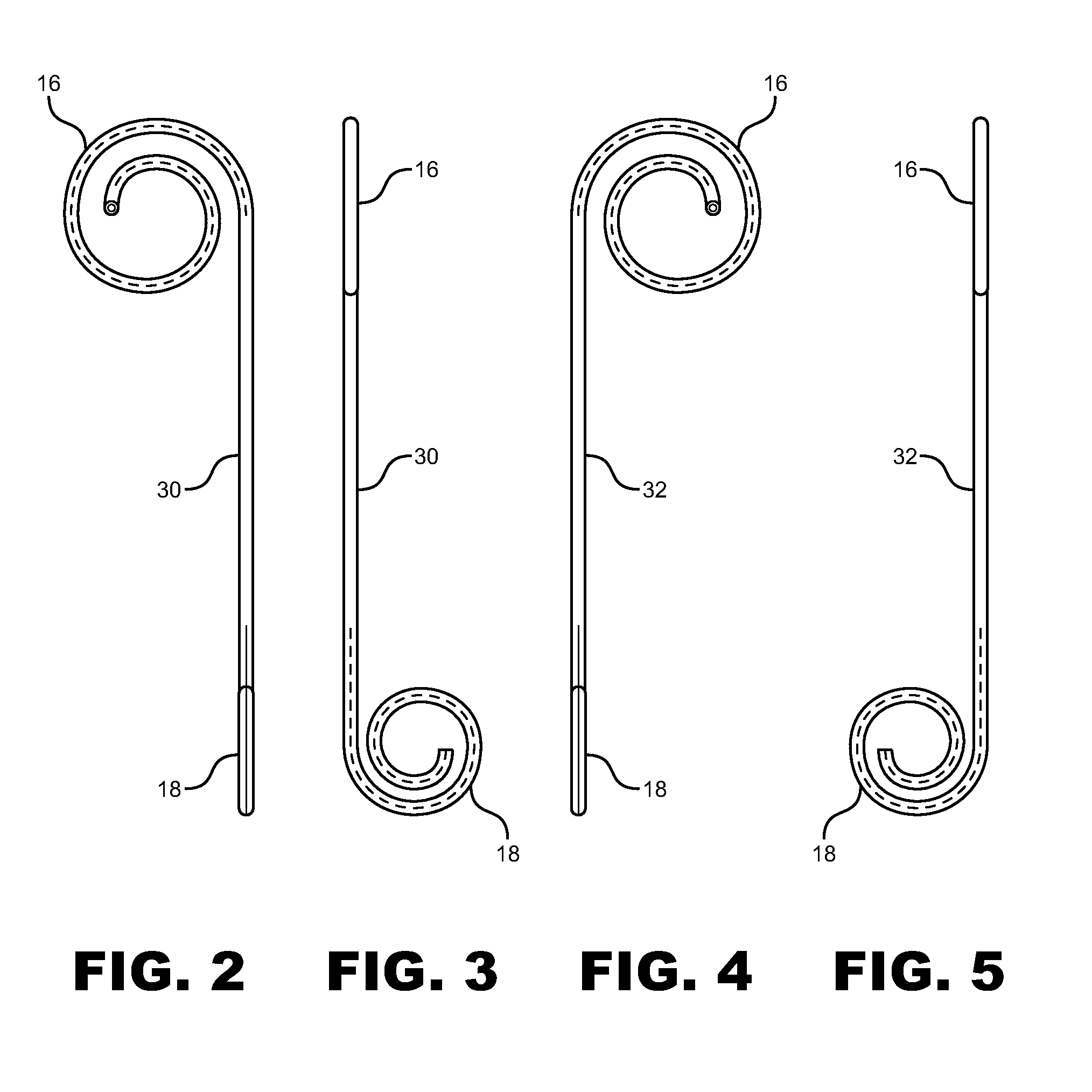
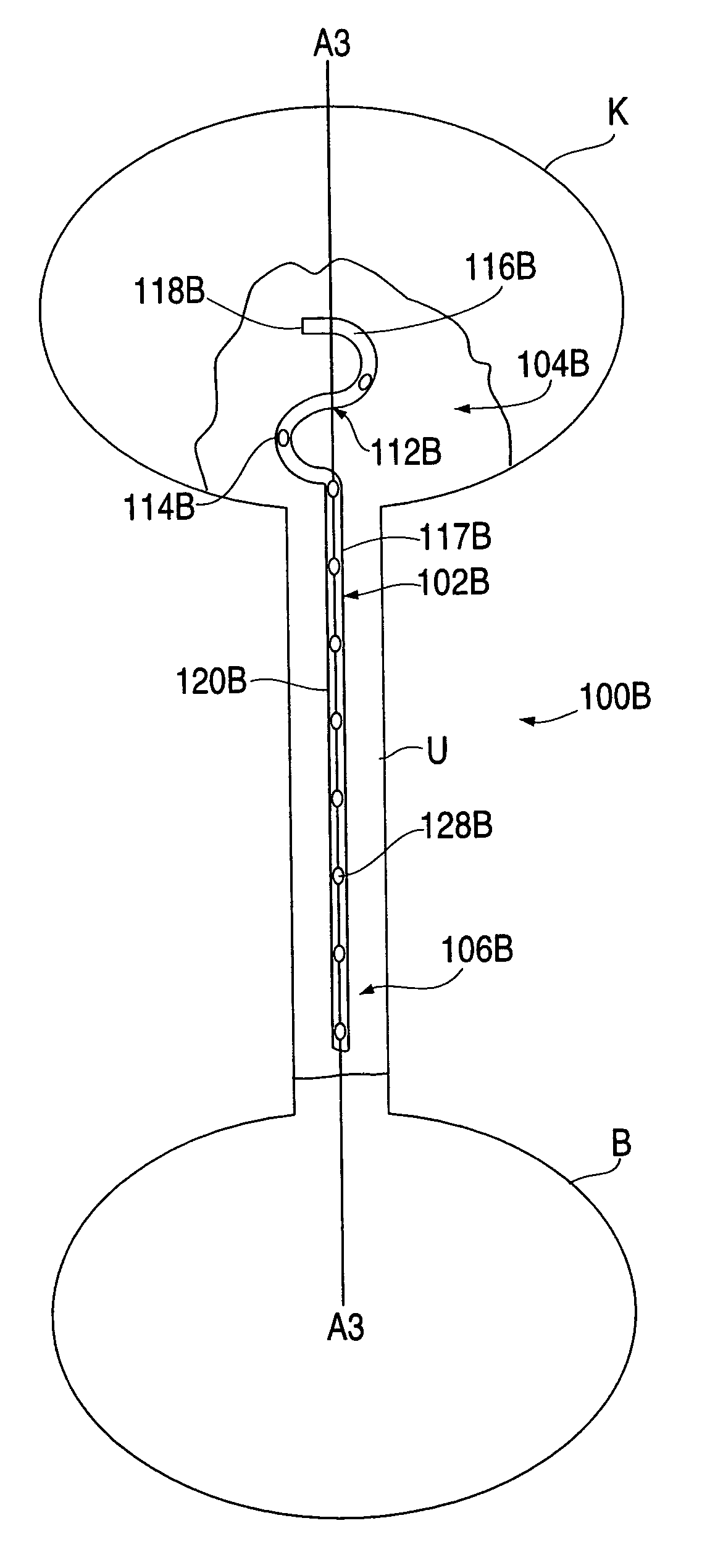
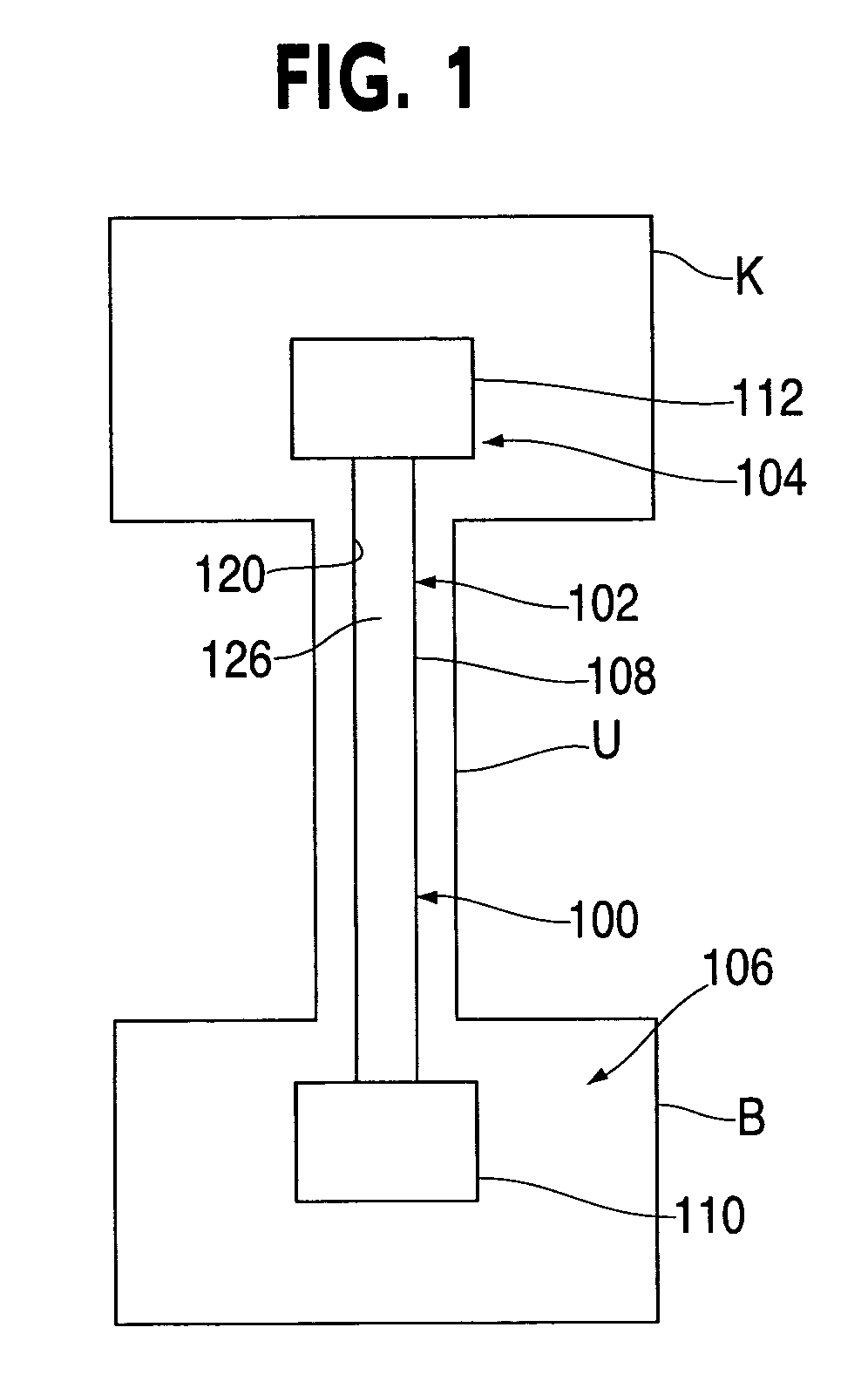
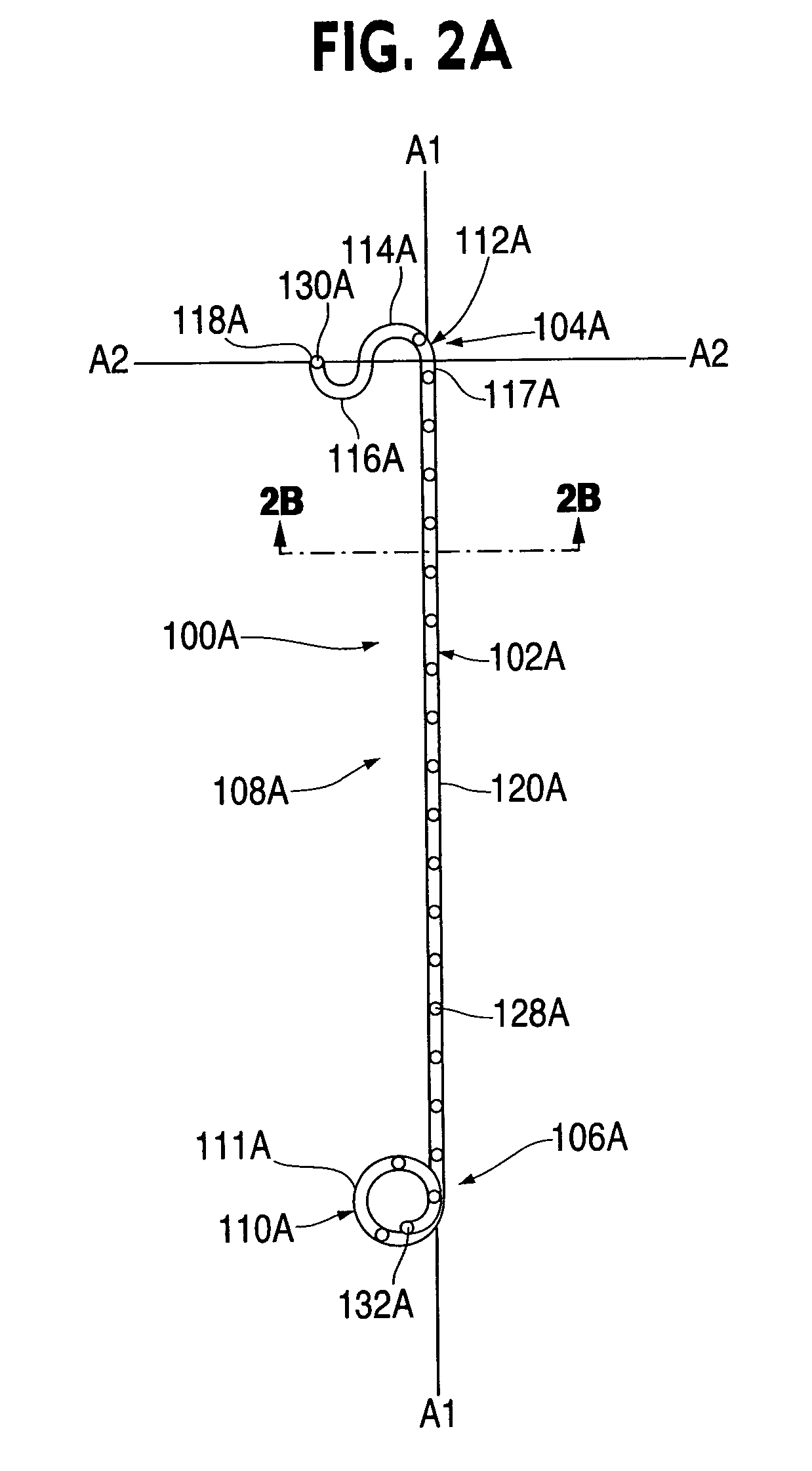
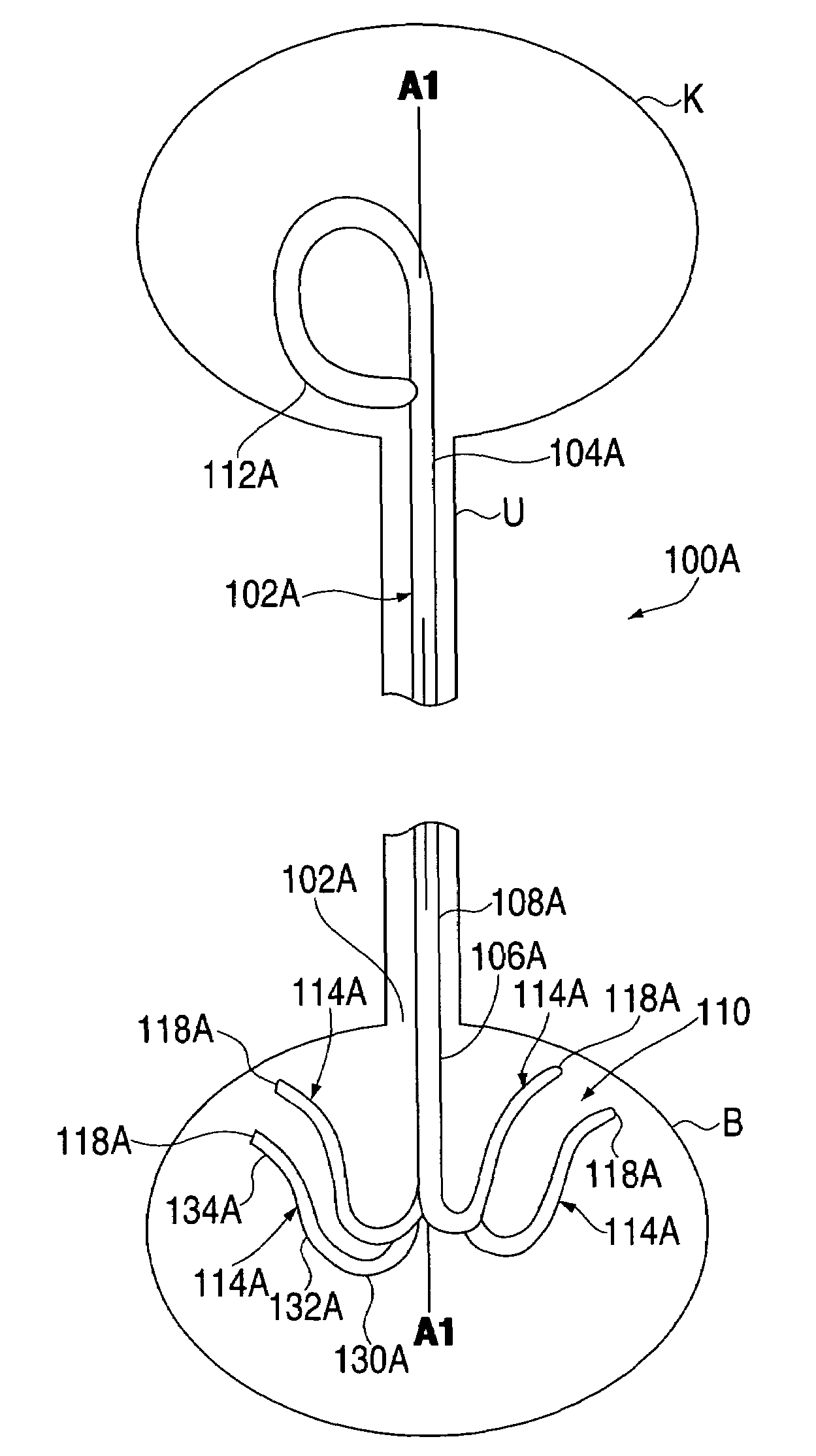
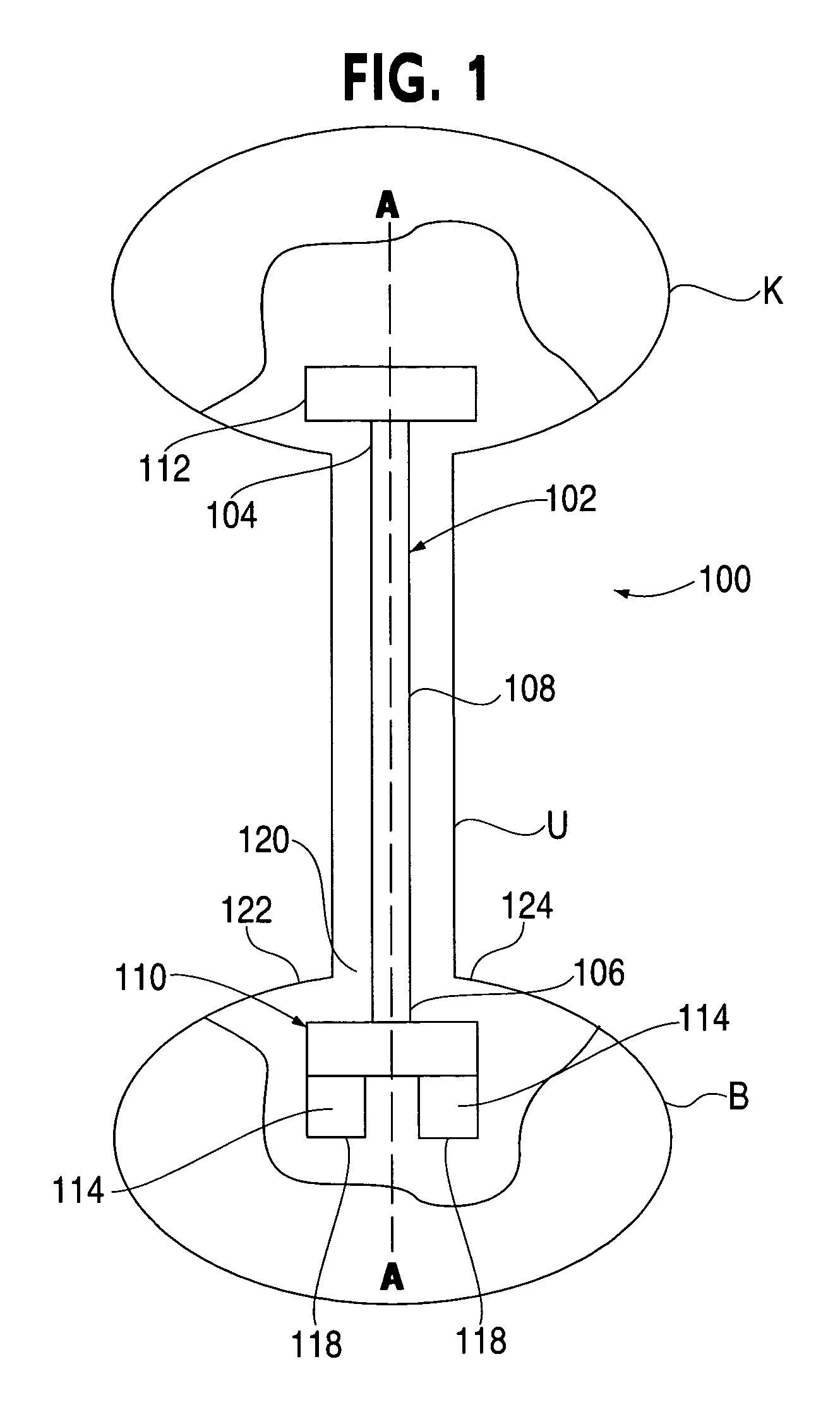
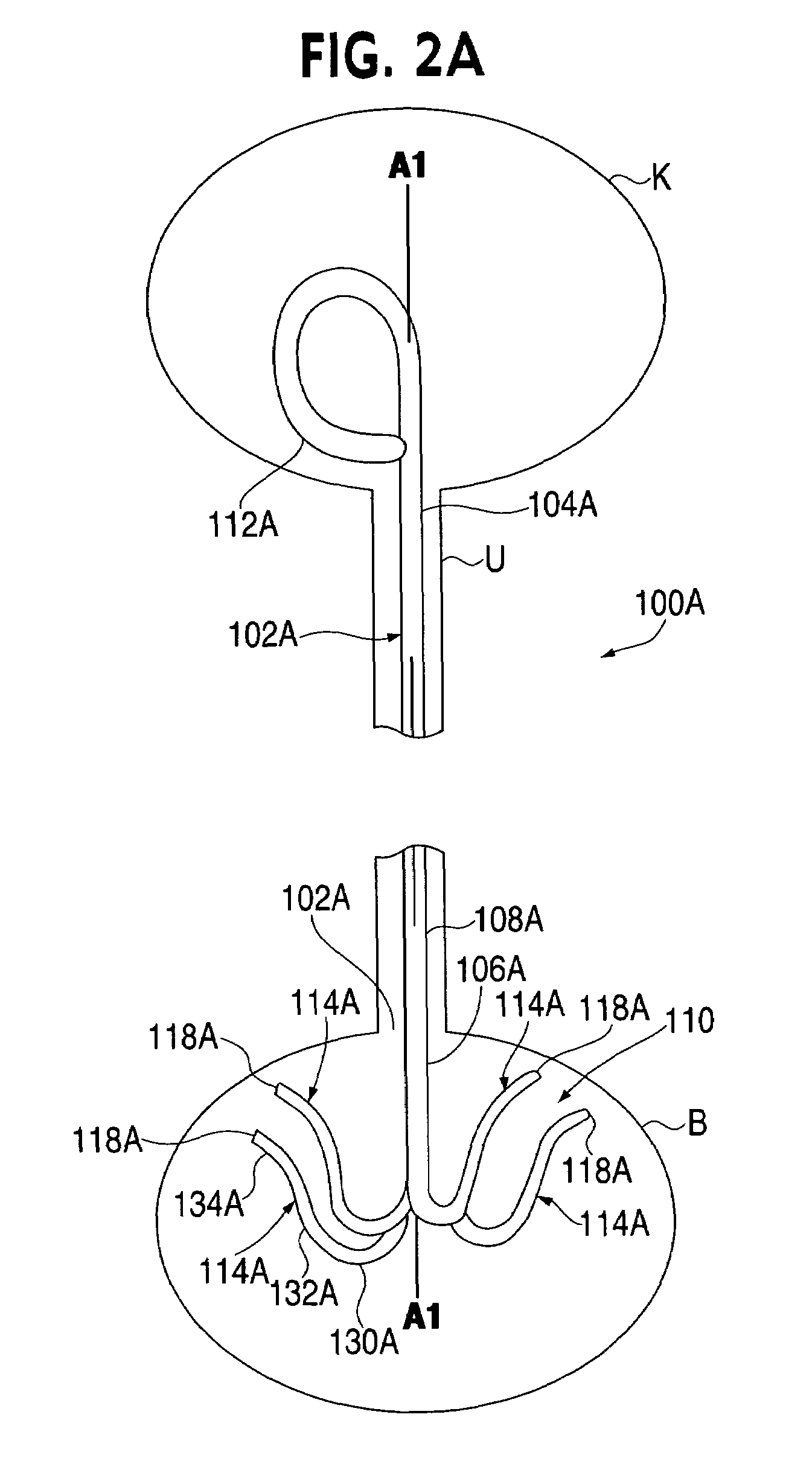
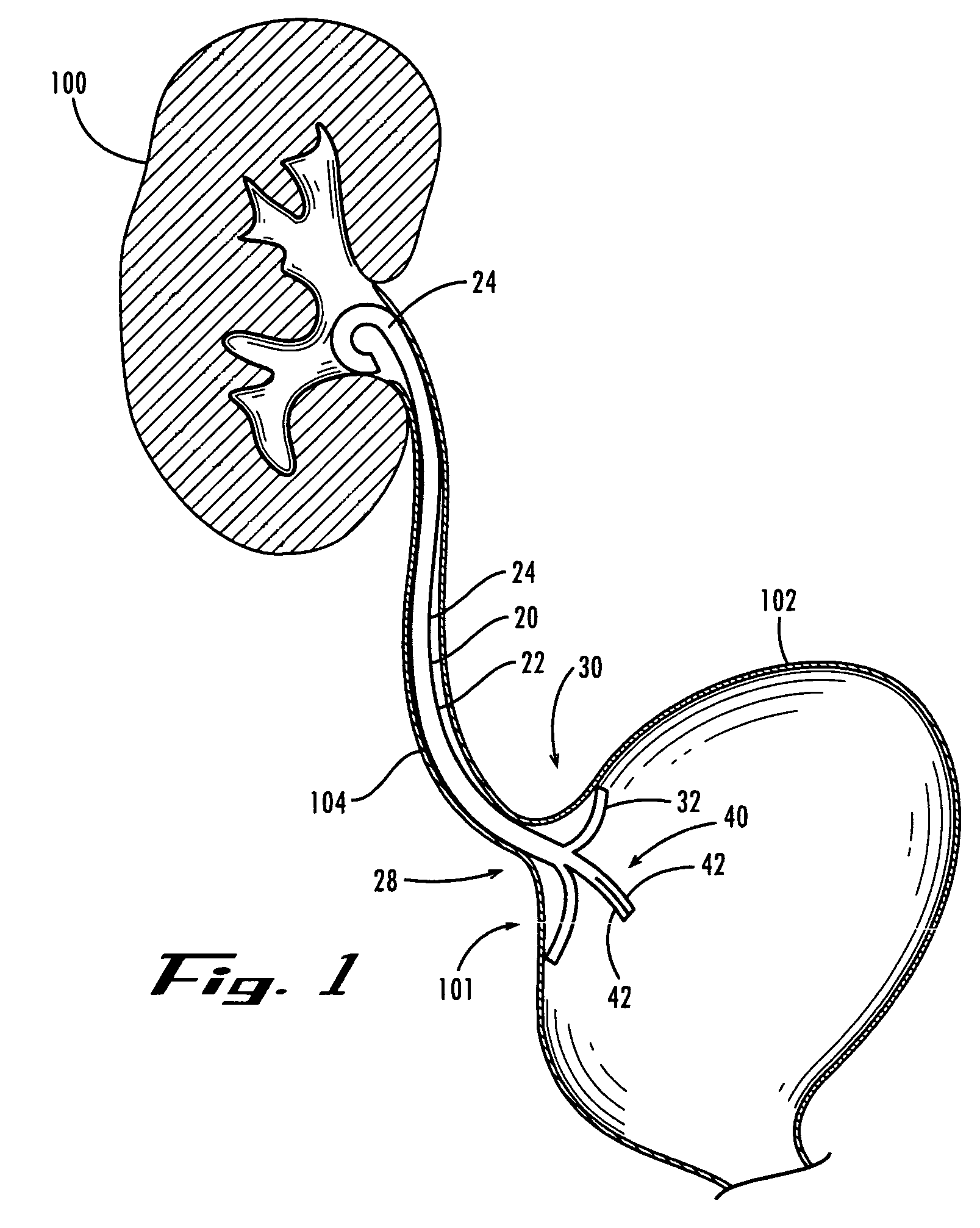
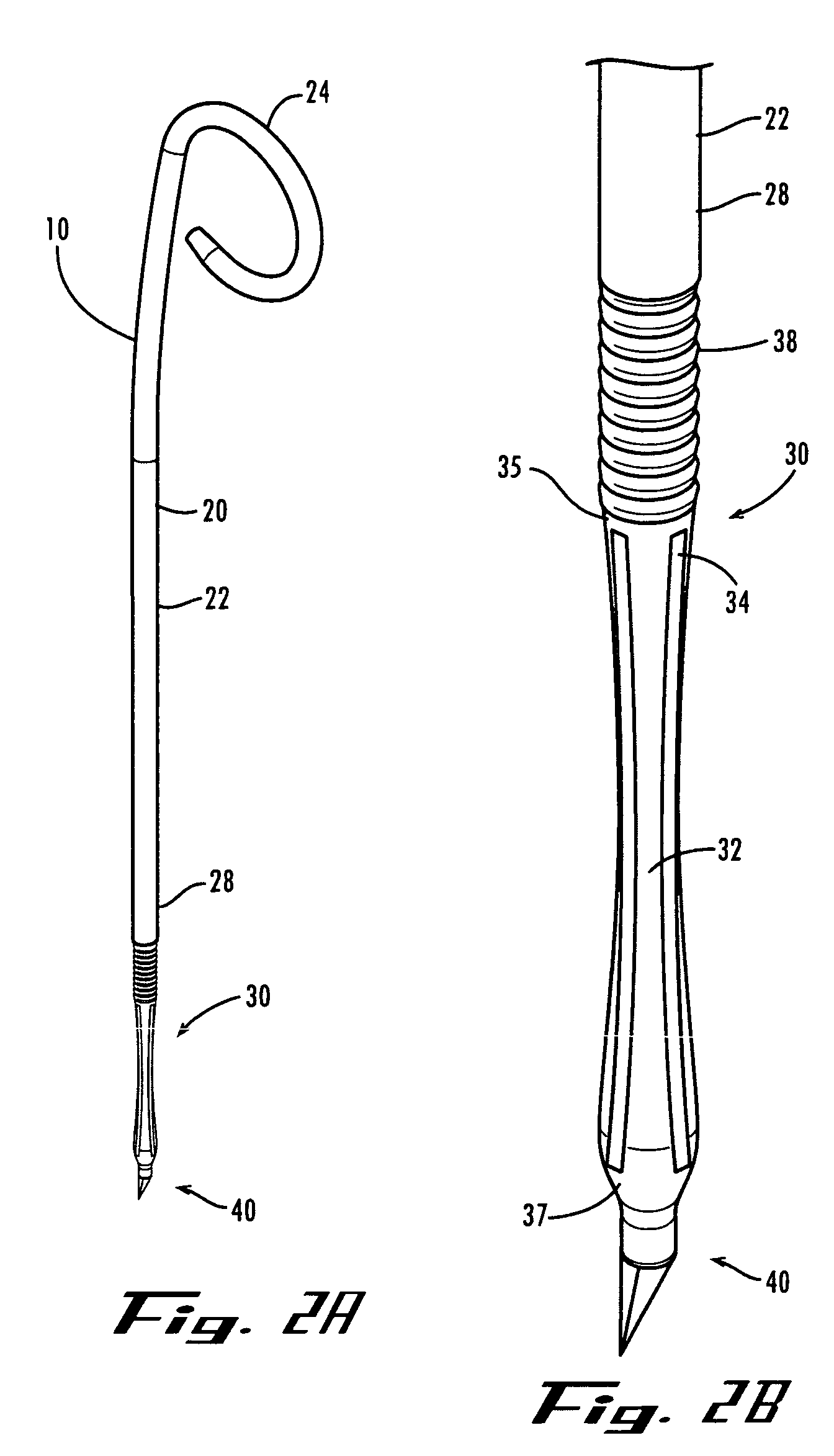
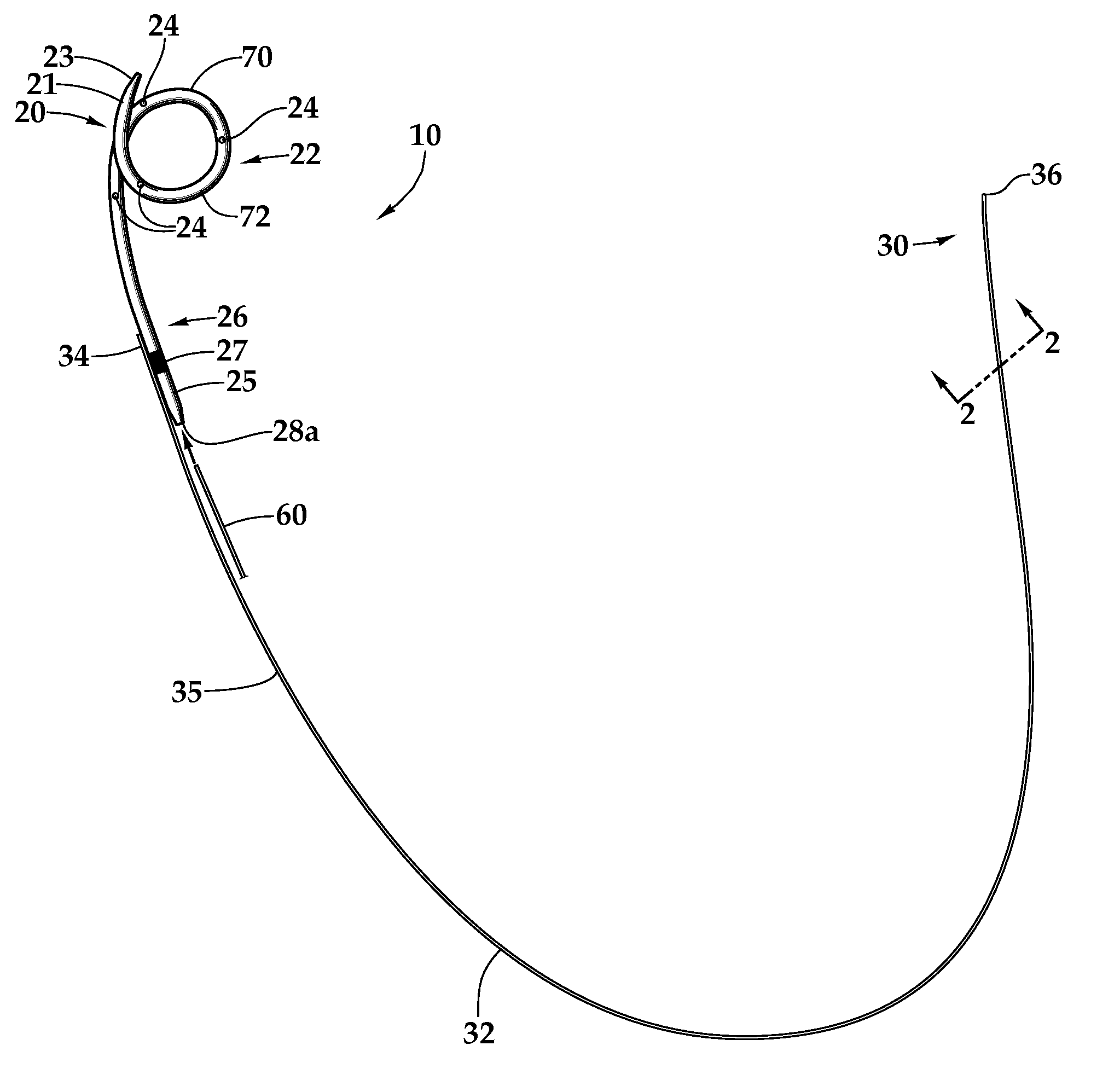
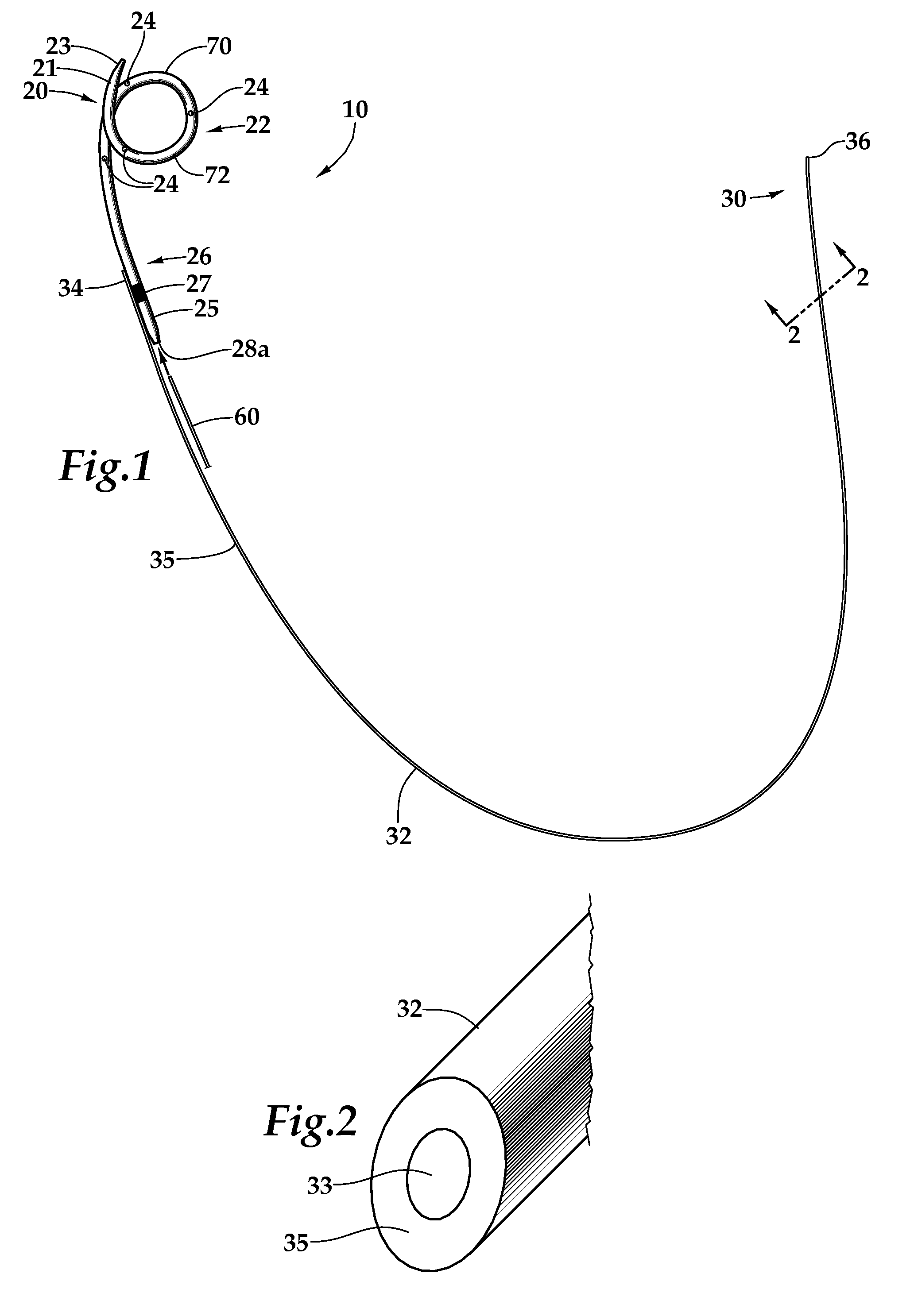
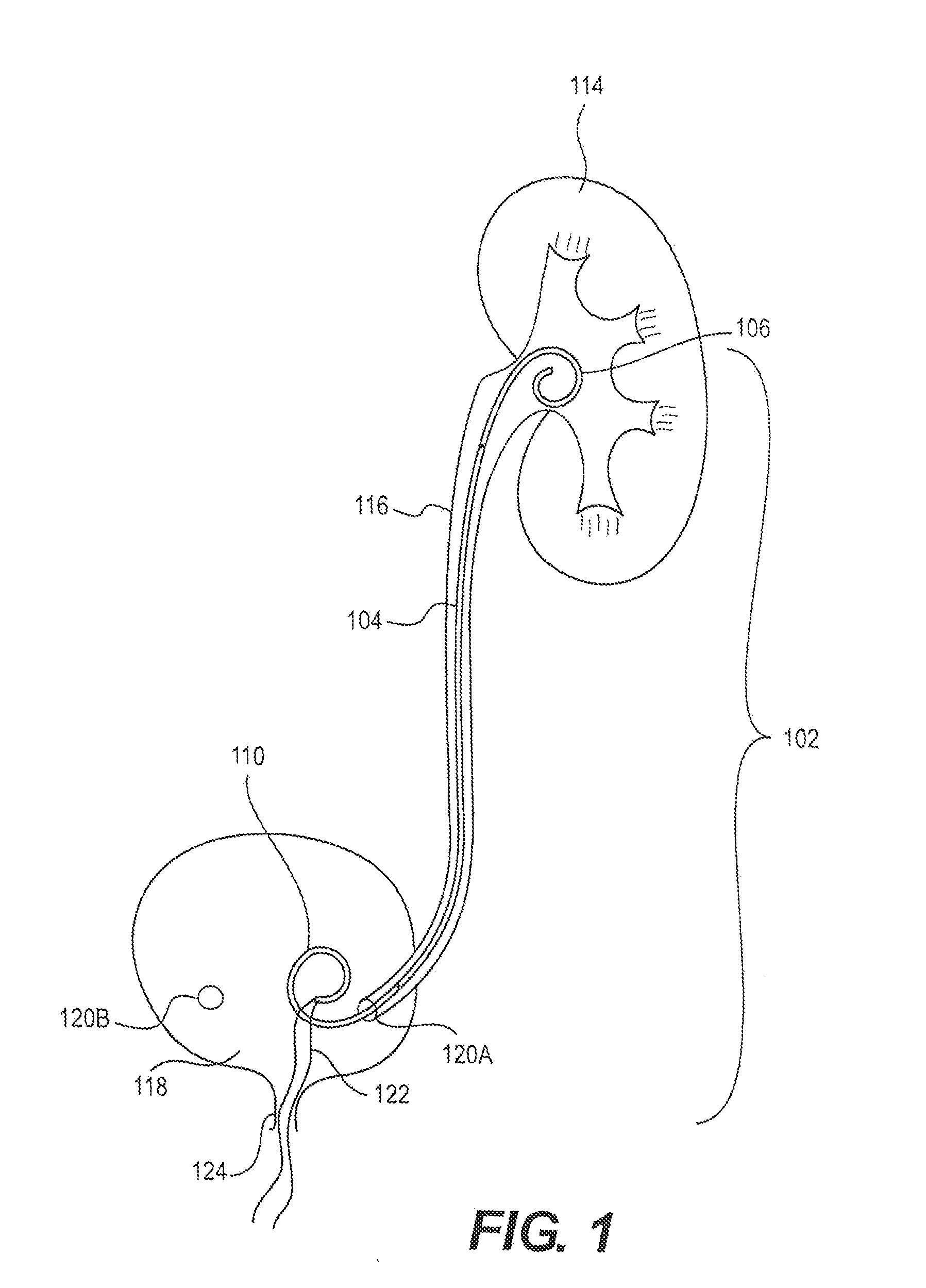
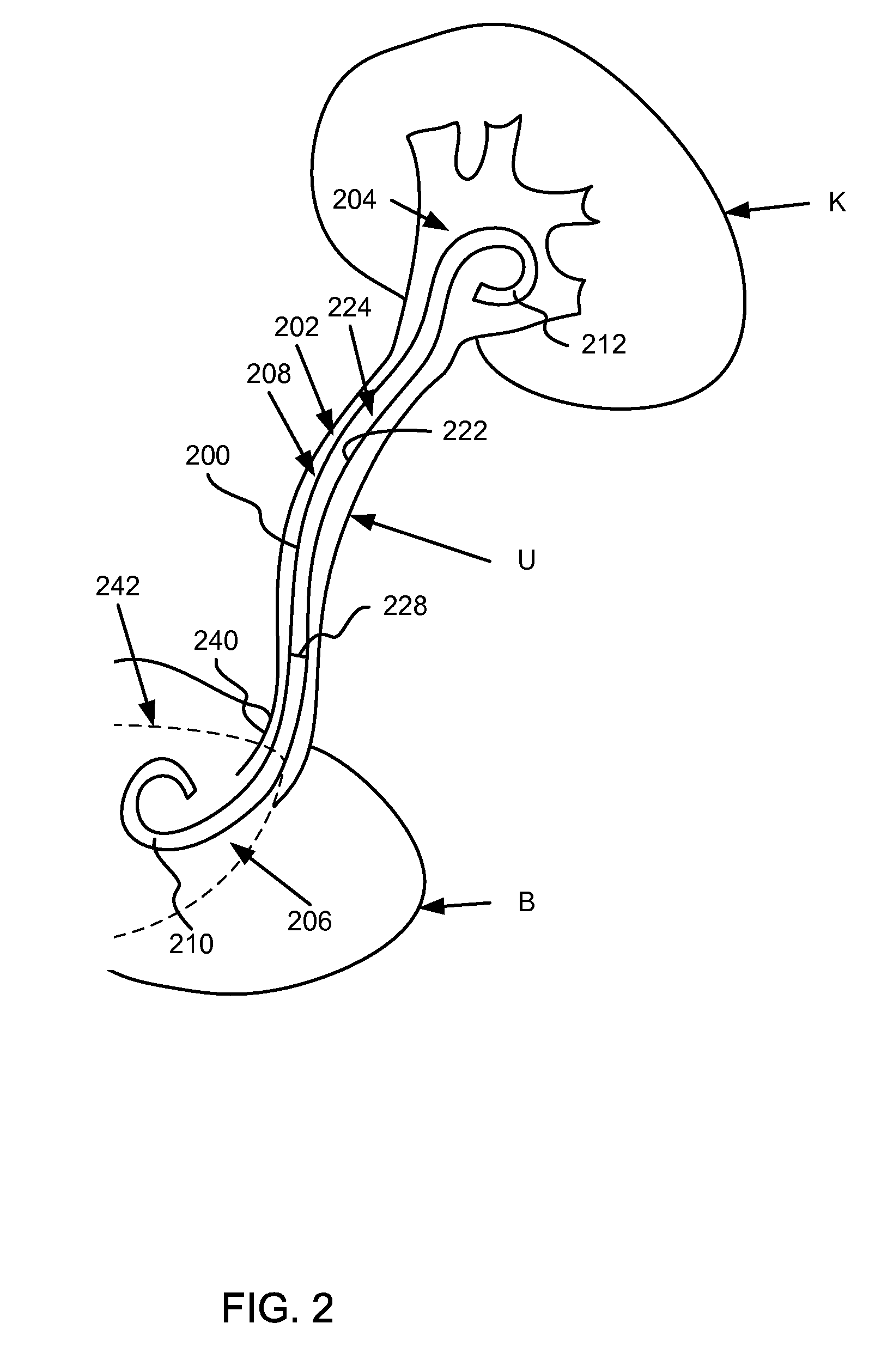
A ureteral stent is configured for improved patient comfort and aftercare. The stent can have one or more of the following features: a distal portion with a somewhat flattened, non-circular cross-section that provides reduced irritation and elimination of urine reflux; a proximal portion with a helical coil shape that allows self-anchoring of the stent below the kidney; and a portion along the body of the stent having a coil shape that allows self-adjustment of the stent with ureteral movement.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Ureteral stent with end-effector and related methods
InactiveUS6949125B2Decreased fluid retentionMinimizing patient discomfortBalloon catheterSurgeryUrethraControl release
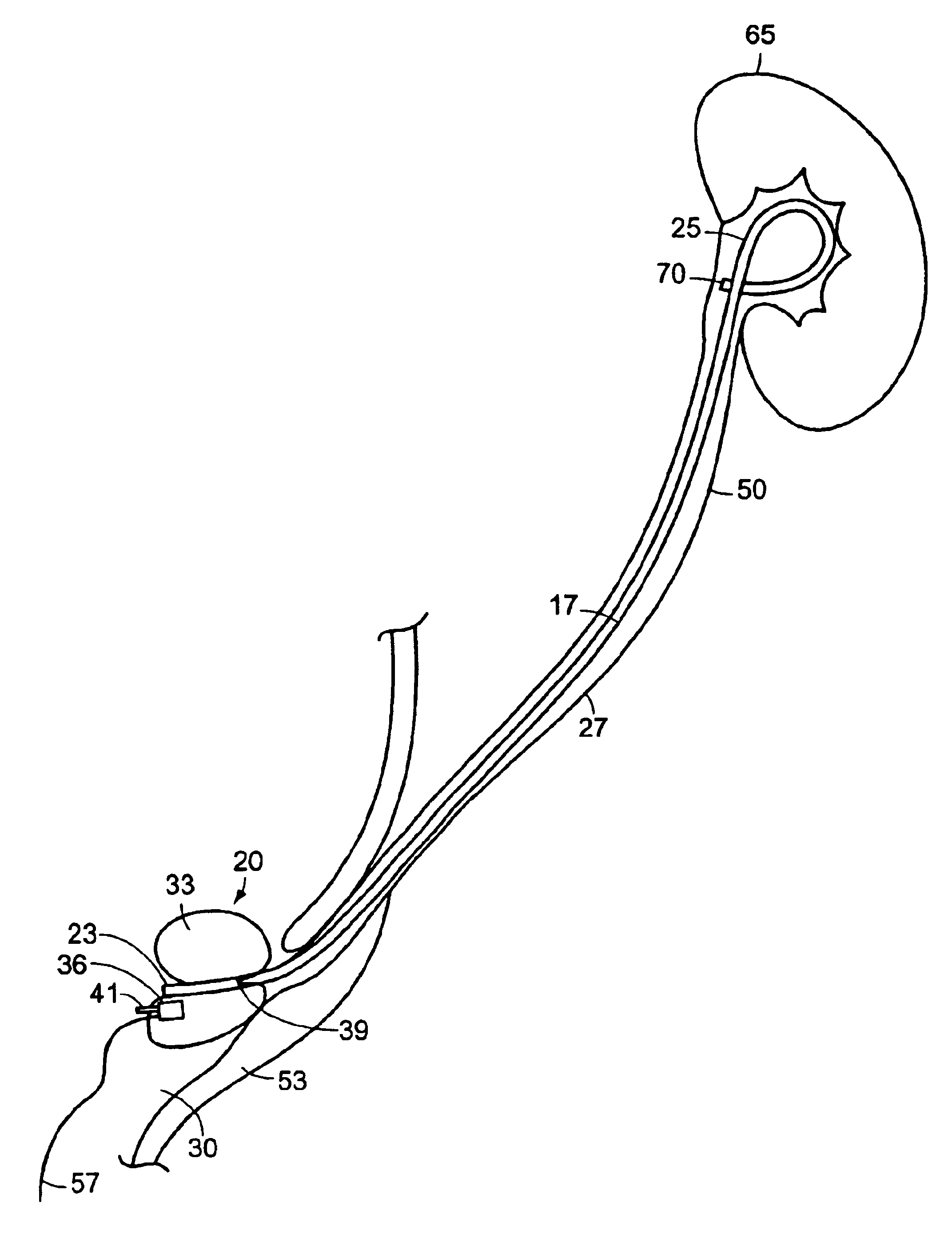
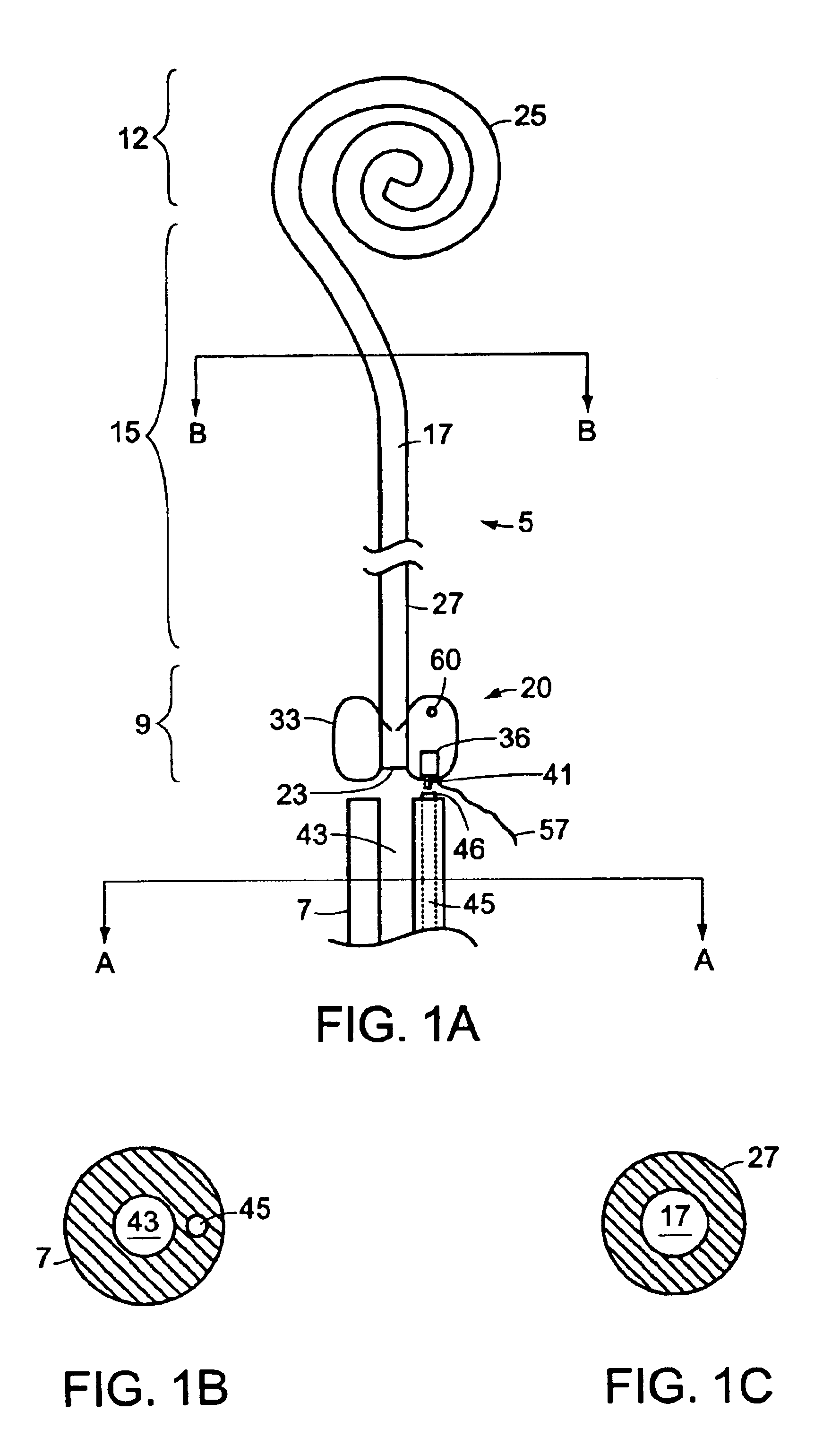
A system and related methods for maintaining the patentcy of the ureter comprising a pusher tube having a pusher tube lumen and an inflate lumen disposed within a wall of the pusher tube and a urinary stent having a proximal and distal portions with an elongated body portion therebetween configured to fit the ureter of the patient and defining a lumen. The system further includes an end-effector that may comprise an inflatable balloon positioned at the proximal portion of the urinary stent for retaining the proximal portion in the urinary bladder. At the distal portion, a retention end-piece is positioned for retaining the distal portion of the stent in the renal pelvis. The end-effector and the retention end-piece of the stent maintain the elongated body portion in situ. The end-effector may also include an inflatable balloon and may contain pharmaceutical or biologic agents for controlled release into the bladder.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Ureteral stent
A ureteral stent comprising an elongated tubular member having a body portion and opposed distal end portion and proximal end portion, the elongated tubular member defining a lumen therein; a retention disk comprising a plurality of generally axial, spaced-apart collapsable struts interconnected with a membrane to form a generalized tube with a retention disk lumen therein, the retention disk lumen in fluid communication with the lumen of the body portion, the struts and the membrane couple to the body portion proximal end at a retention disk distal end and terminate at a retention disk proximal end, each strut having a widthwise folding hinge substantially dividing the length of the strut, the struts adapted to have an expanded state wherein the struts are unfolded and substantially straight, as well as a free-resting state wherein each strut folds in upon itself at the folding hinge to form an inverted umbrella-like disk-shaped configuration; and a valve, wherein the inverted umbrella-like configuration provides a conformal shape to the ureteral orifice.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
Ureteral stent with axial and radial variability
A device is provided that includes an implantable conduit with first and second ends and a first retainer coupled to the first end by a first joint. A second retainer is coupled to the second end by a second joint, wherein the first and second joints are each configured to allow movement of the implantable conduit relative to the respective first and second retainers.
Owner:VANCE PROD INC D B A COOK UROLOGICAL INC
Ureteral stent with conforming retention structure
A ureteral stent includes an elongate member defining an axis and having a proximal end portion and a distal end portion. A first extension member and a second extension member extend from the proximal end portion and each include a first portion, a second portion, a third portion and an end portion. In an unconstrained configuration, the first portion is arcuate and extends away from the axis, the second portion extends from the first portion in a distal direction, and the third portion extends from the second portion in a direction away from the axis. In the unconstrained configuration, the end portions of the first and second extension members are spaced apart from each other sufficiently, and the first extension member and the second extension member are sufficiently rigid, to collectively help retain at least a portion of the ureteral stent within a bladder of a patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
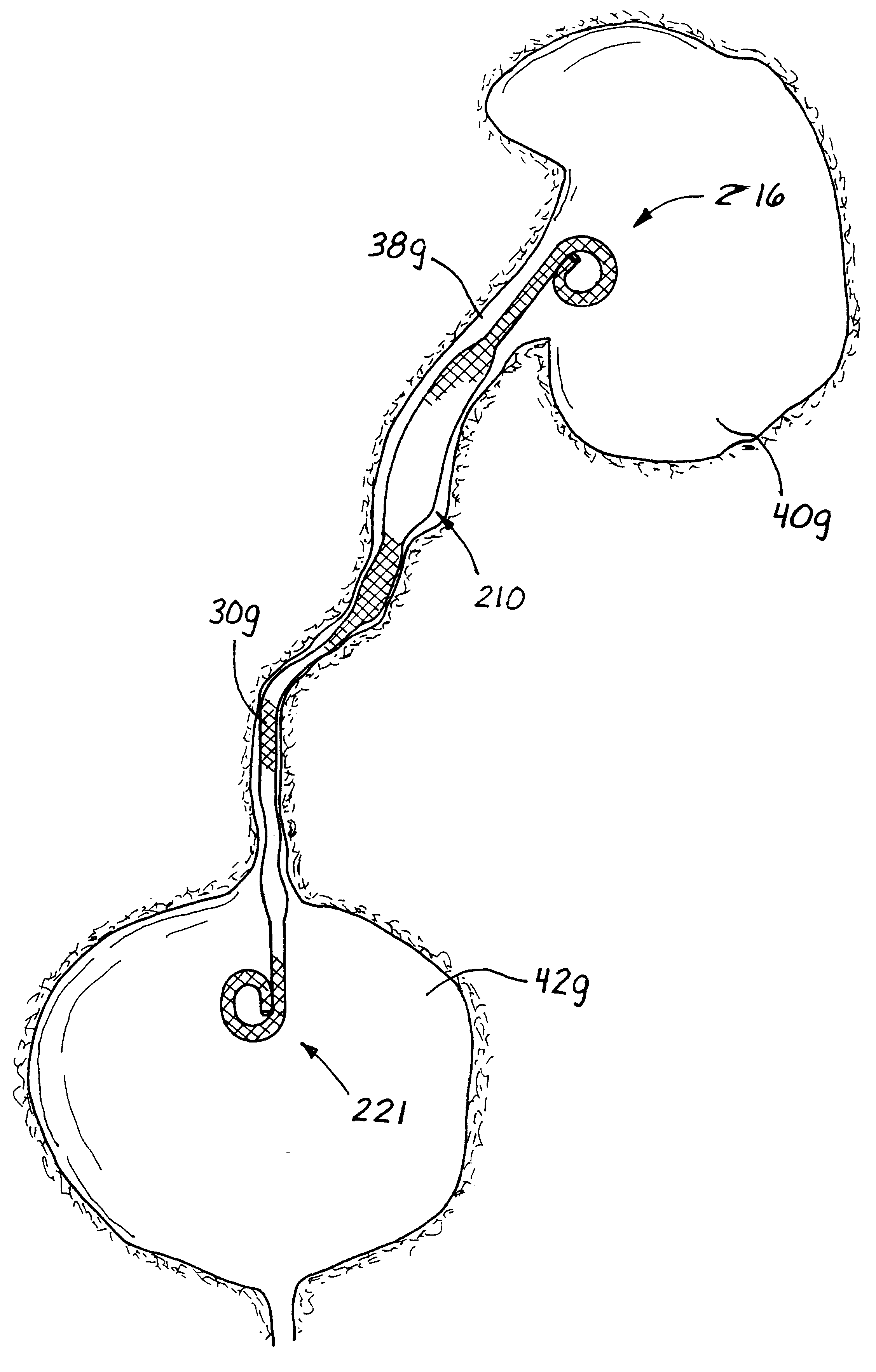
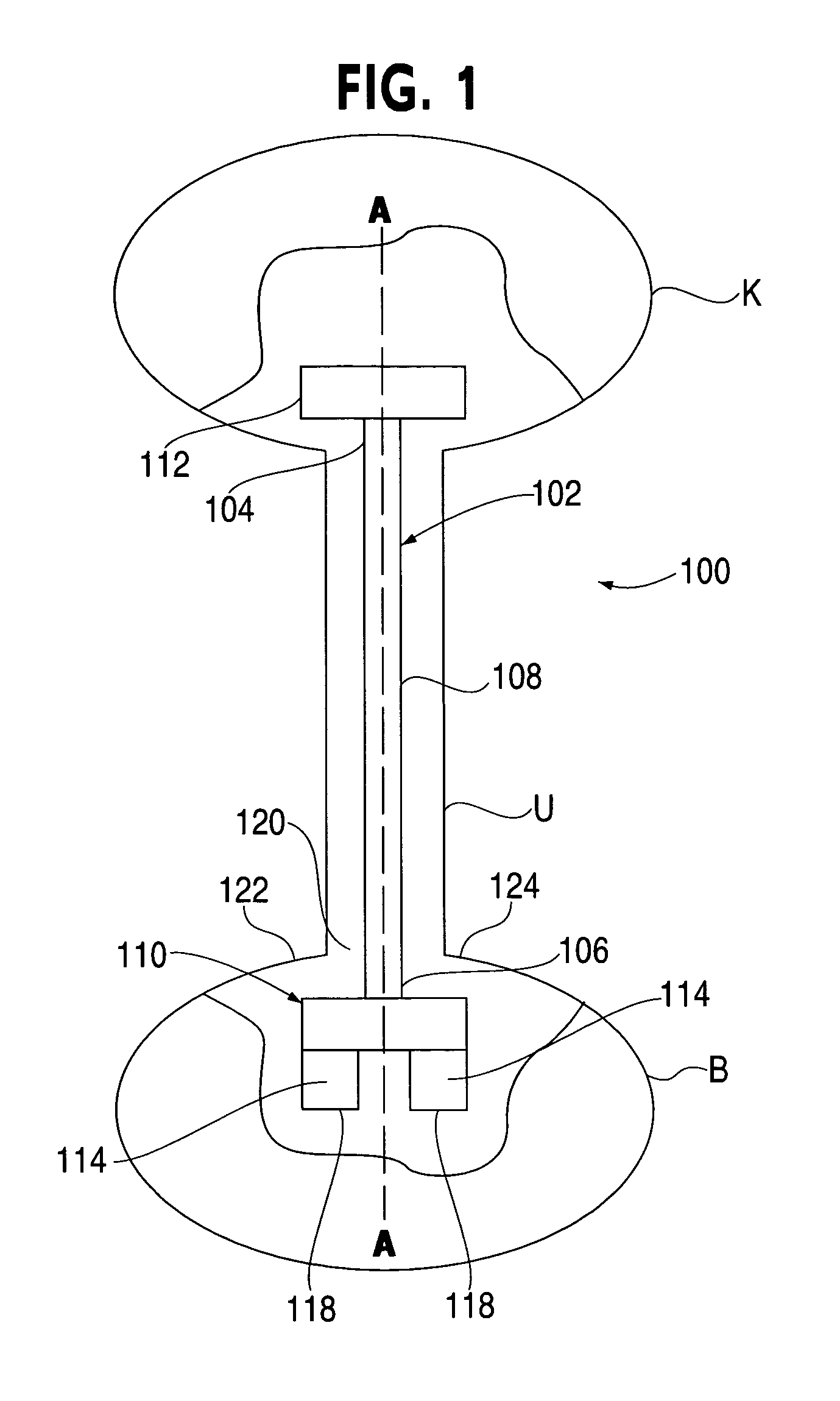
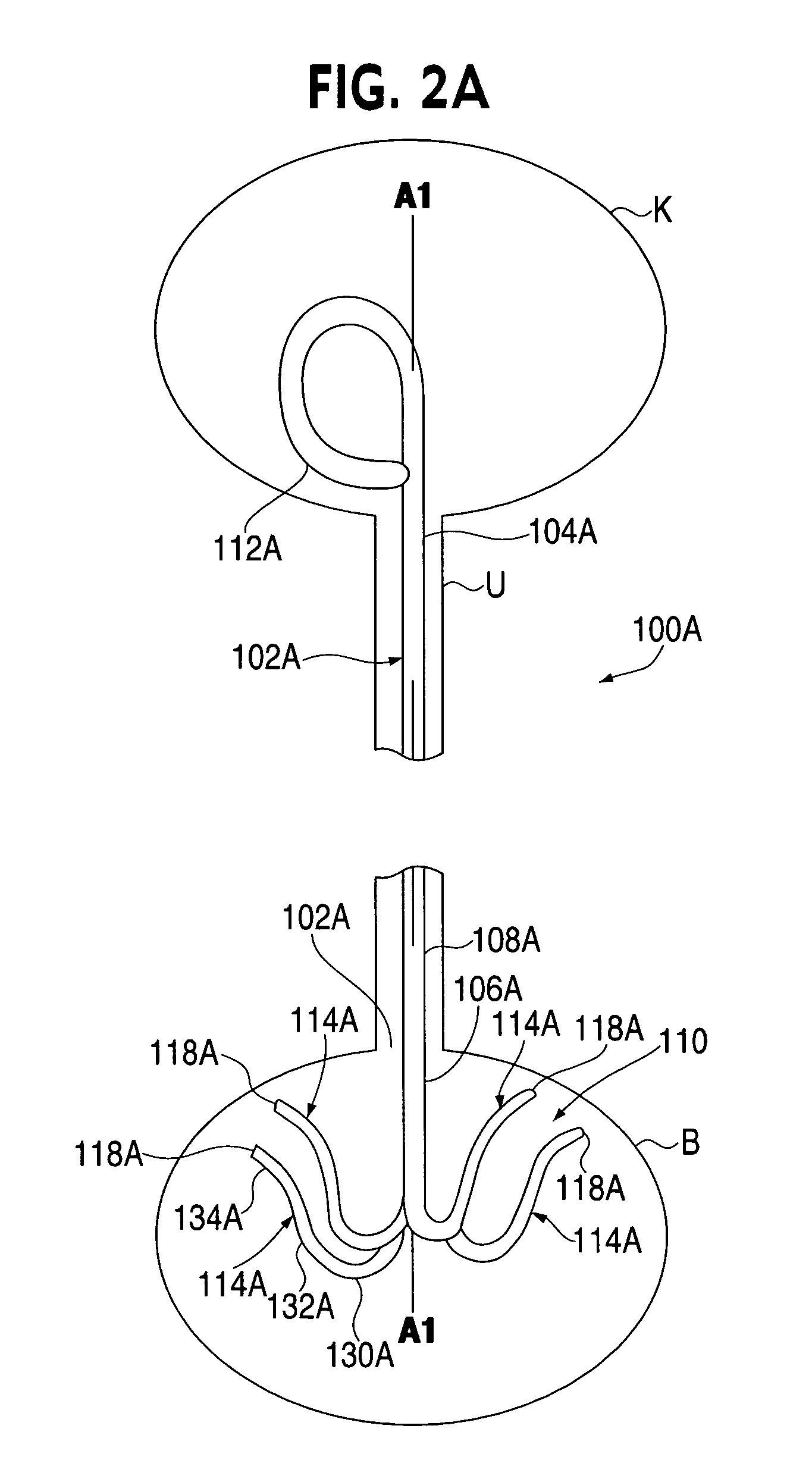
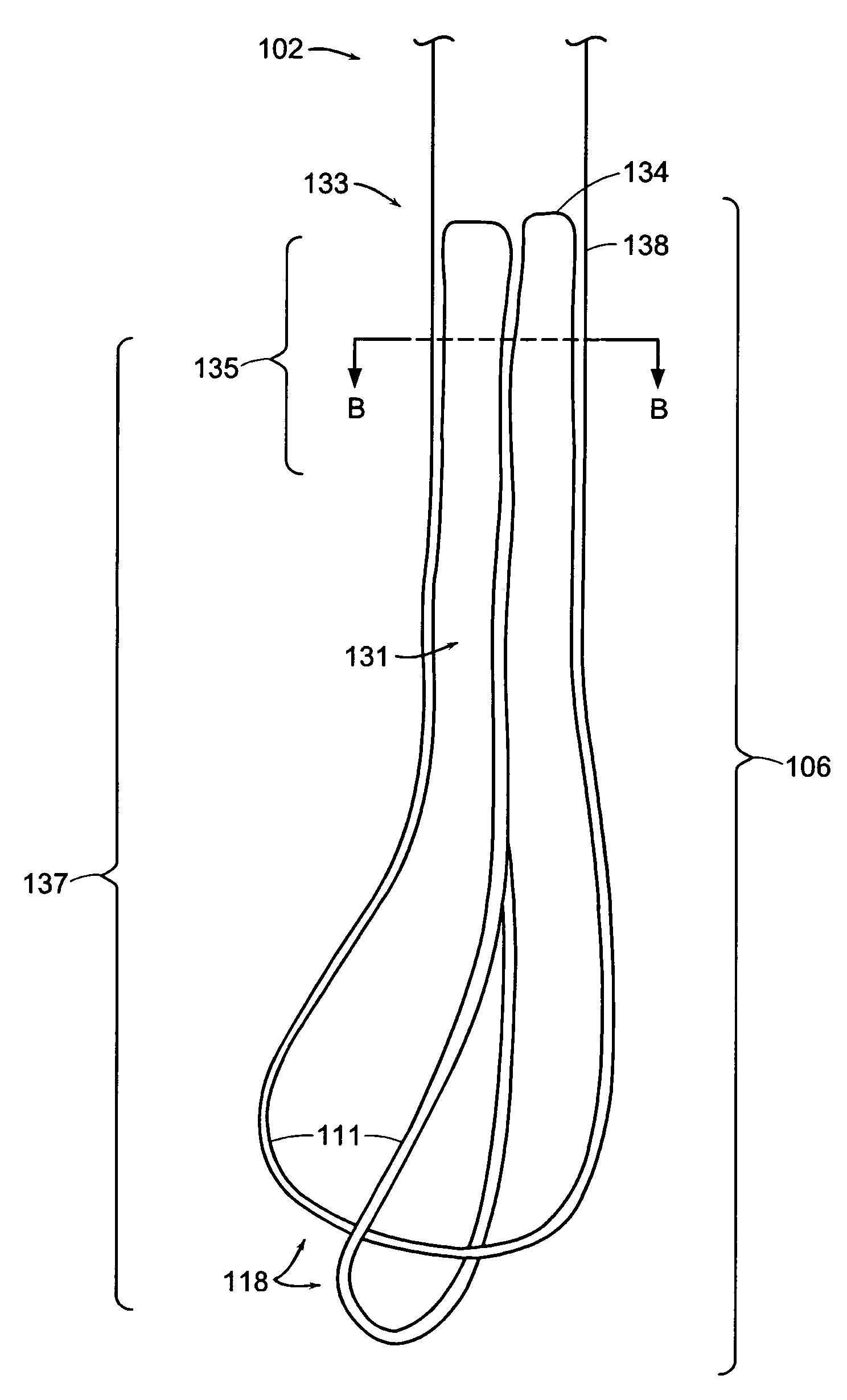
Anti-Refluxive and Trigone Sparing Internal Ureteral Stent
ActiveUS20120053700A1Reduction and elimination of refluxImprove comfortWound drainsTubular organ implantsInsertion stentRenal segment
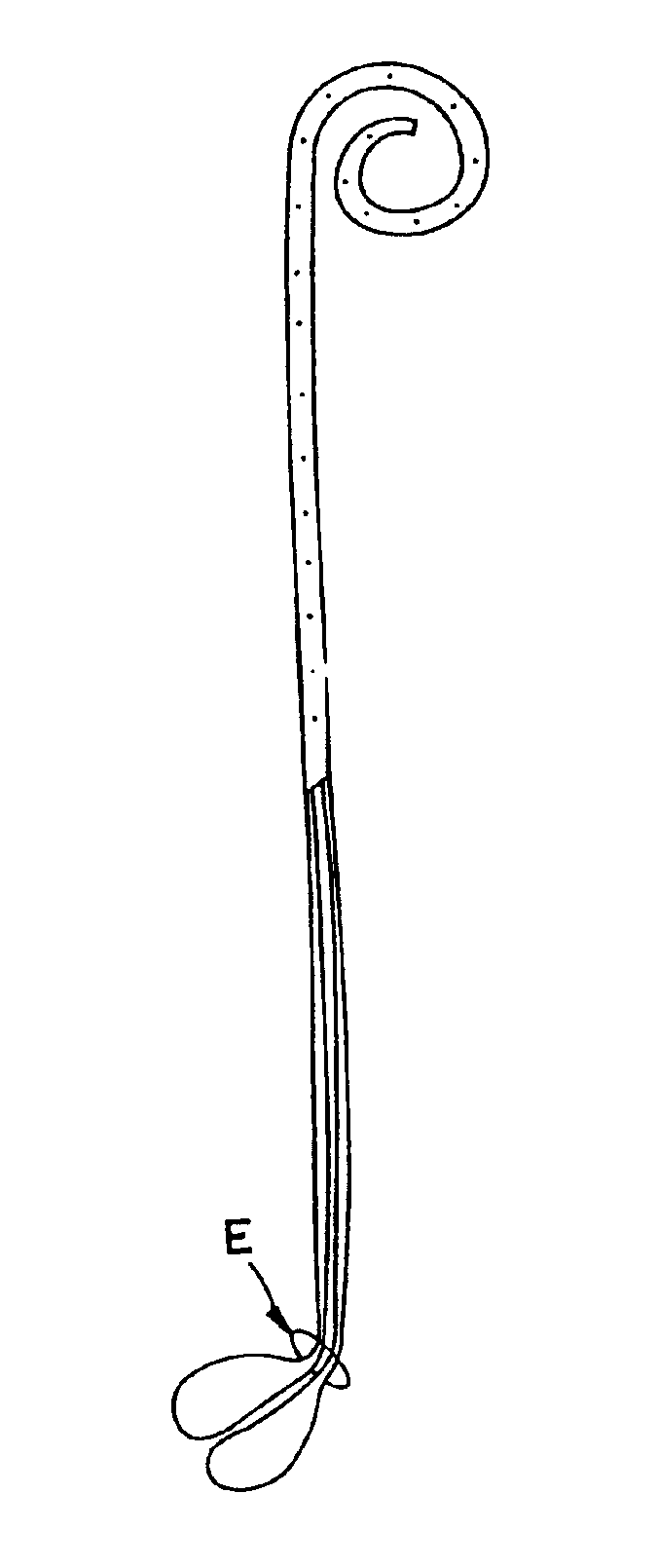
A ureteral stent has an elongated body connecting a coiled, renal segment to a coiled, bladder end segment. In one embodiment of the present invention, the coiled, bladder end segment and a lower, intramural segment of the elongated body are provided as a first flap and a second flap. The lower, intramural segment is of such length as to extend through a patient's intramural ureteral, preferably 2-4 cm. In another embodiment of the present invention, the coiled, renal segment is provided in a first plane and the coiled, bladder end segment is provided in a second plane such that the first plane and the second plane are transverse with respect to one another.
Owner:RICKNER THOMAS W
Ureteral stent with small bladder tail(s)
InactiveUS6945950B2Decreases patient discomfortInhibit migrationUrinary bladderStentsInsertion stentLeft ureter
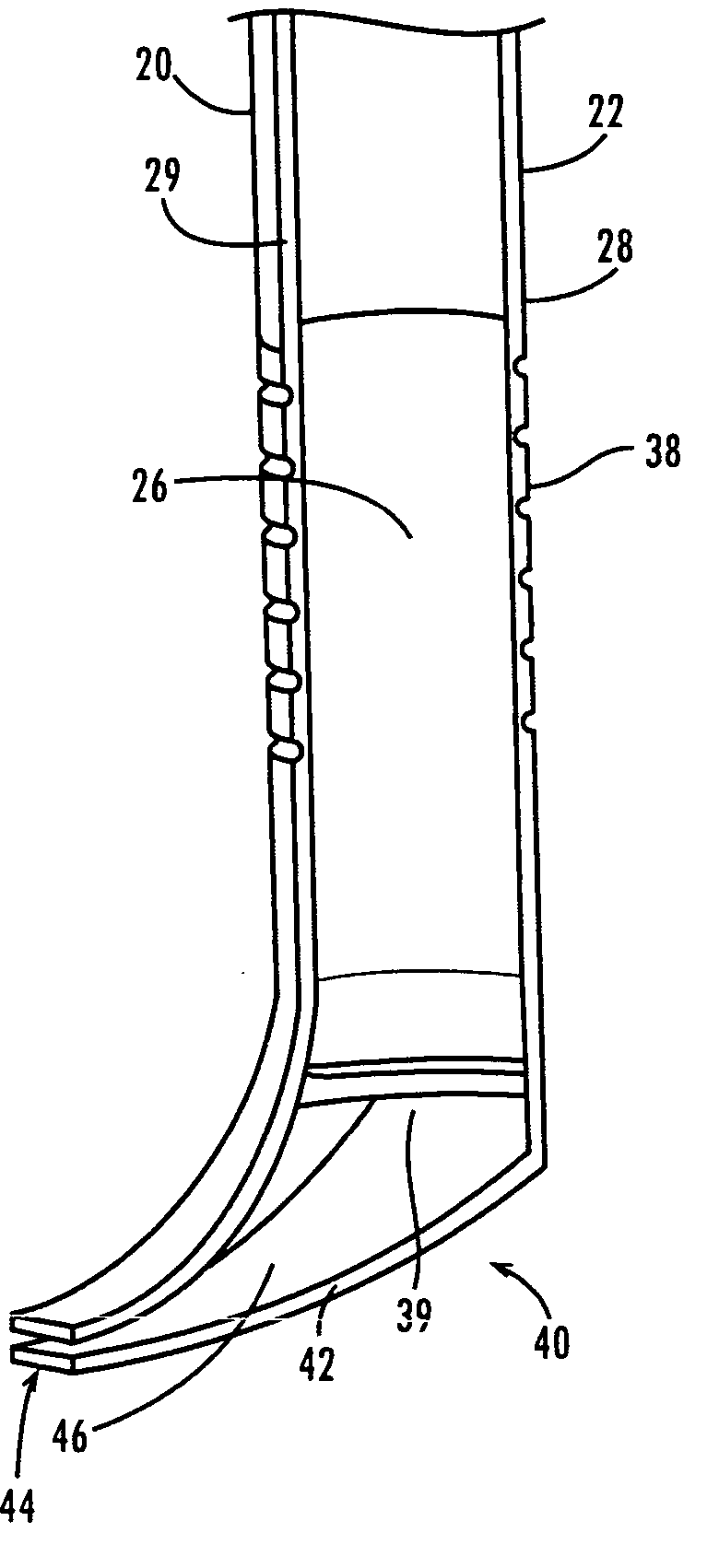
A ureteral stent for assisting movement of urine along a patient's ureter and into the patient's bladder. The stent includes an elongated tubular segment extending toward the bladder from a kidney end region for placement in the renal cavity to a bladder end region. A central lumen connects at least one opening at the first end region to at least one opening in the bladder end region. Thin flexible tail(s) are attached to the bladder end region of the tubular segment at a point outside the bladder so as to receive urine from the opening in the bladder end region and to transport urine from there across the ureter / bladder junction and into the bladder. The tails include an elongated external urine-transport surface configured to transport urine. The transporting surface(s) are configured to extend along at least part of the ureter, across the ureter / bladder junction, and into the bladder.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC +1
Ureteral stent
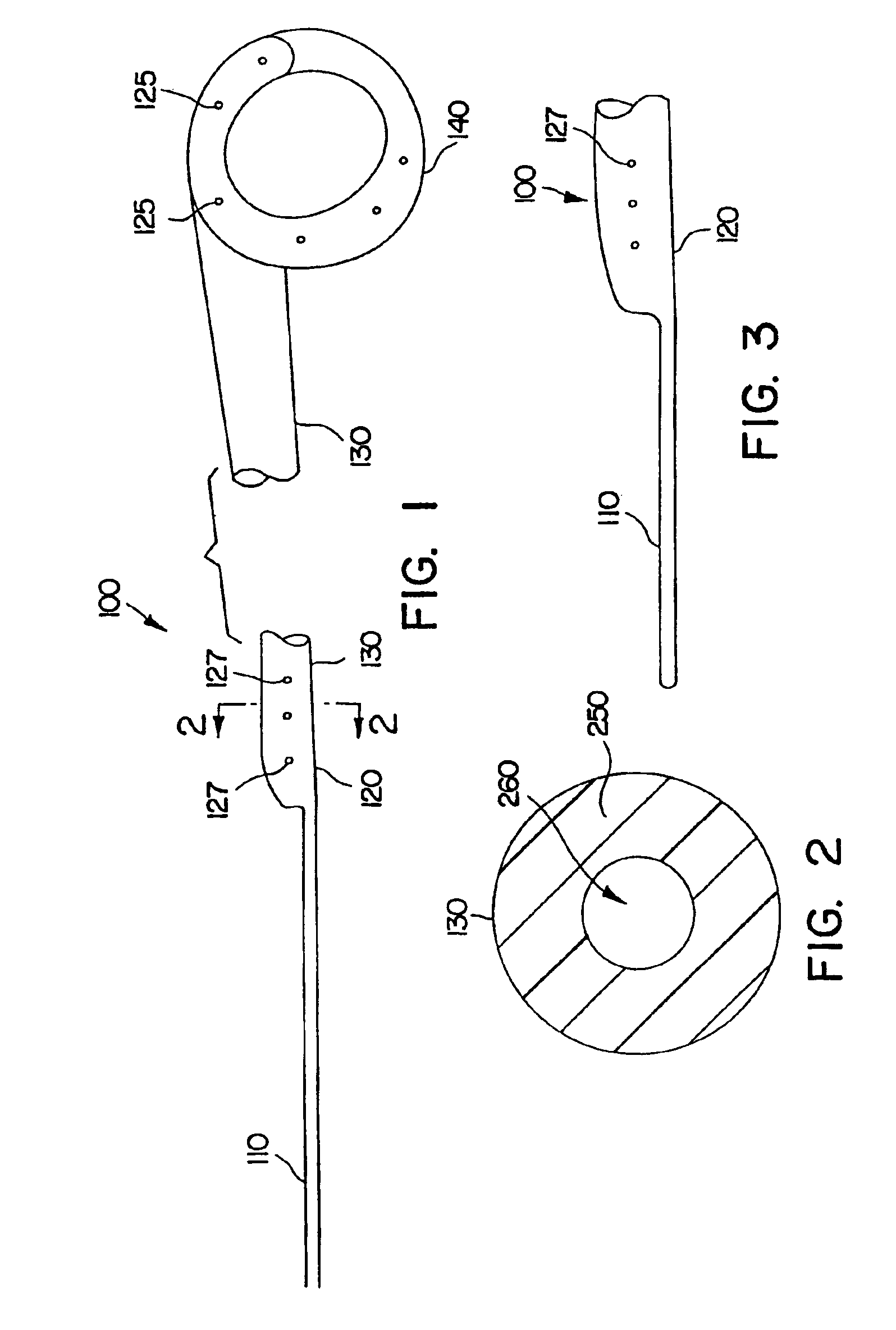
A ureteral stent assembly includes an elongate member having a distal end portion for placement within a kidney of a patient and a proximal end portion for placement in at least one of a ureter of the patient and a bladder of the patient. The distal end portion has a retention portion configured to help retain at least a portion of the elongate member in the kidney of the patient. The elongate member is configured to be passed through the ureter of the patient from the kidney to the bladder to remove the elongate member from the patient. In one embodiment, the retention portion is configured such that a distal tip of the distal end portion of the ureteral stent is spaced from a sidewall of the ureter when the elongate member is passed through the ureter of the patient to remove the elongate member from the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Ureteral stent with conforming retention structure
A ureteral stent includes an elongate member defining an axis and having a proximal end portion and a distal end portion. A first extension member and a second extension member extend from the proximal end portion and each include a first portion, a second portion, a third portion and an end portion. In an unconstrained configuration, the first portion is arcuate and extends away from the axis, the second portion extends from the first portion in a distal direction, and the third portion extends from the second portion in a direction away from the axis. In the unconstrained configuration, the end portions of the first and second extension members are spaced apart from each other sufficiently, and the first extension member and the second extension member are sufficiently rigid, to collectively help retain at least a portion of the ureteral stent within a bladder of a patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method of disposing a linearly expandable ureteral stent within a patient
A method includes placing a ureteral stent on an insertion tool. The ureteral stent includes an elongate member having a distal end coupled to a distal retention member. The elongate member includes a solid spring wire having a plurality of coils defining a lumen. A first portion of the insertion tool is disposed within the lumen, and the distal retention member, which has a nominally curved shape, is disposed about a second portion of the insertion tool such that the distal retention member is substantially linear. The insertion tool is inserted into the body of the patient and the ureteral stent is moved along the insertion tool such that at least a portion of the distal retention member is disposed within the kidney and a portion of the elongate member is disposed within the ureter.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
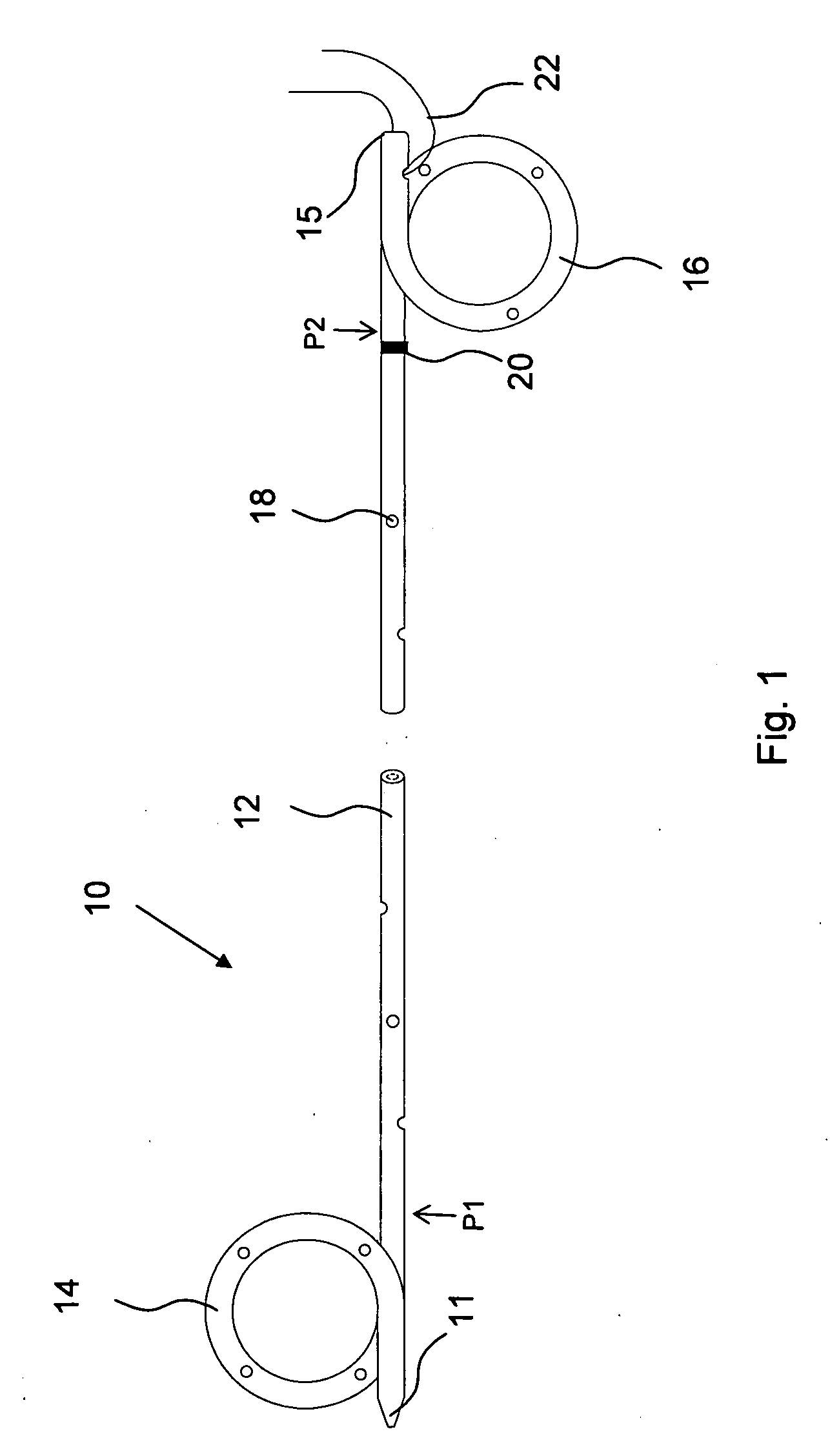
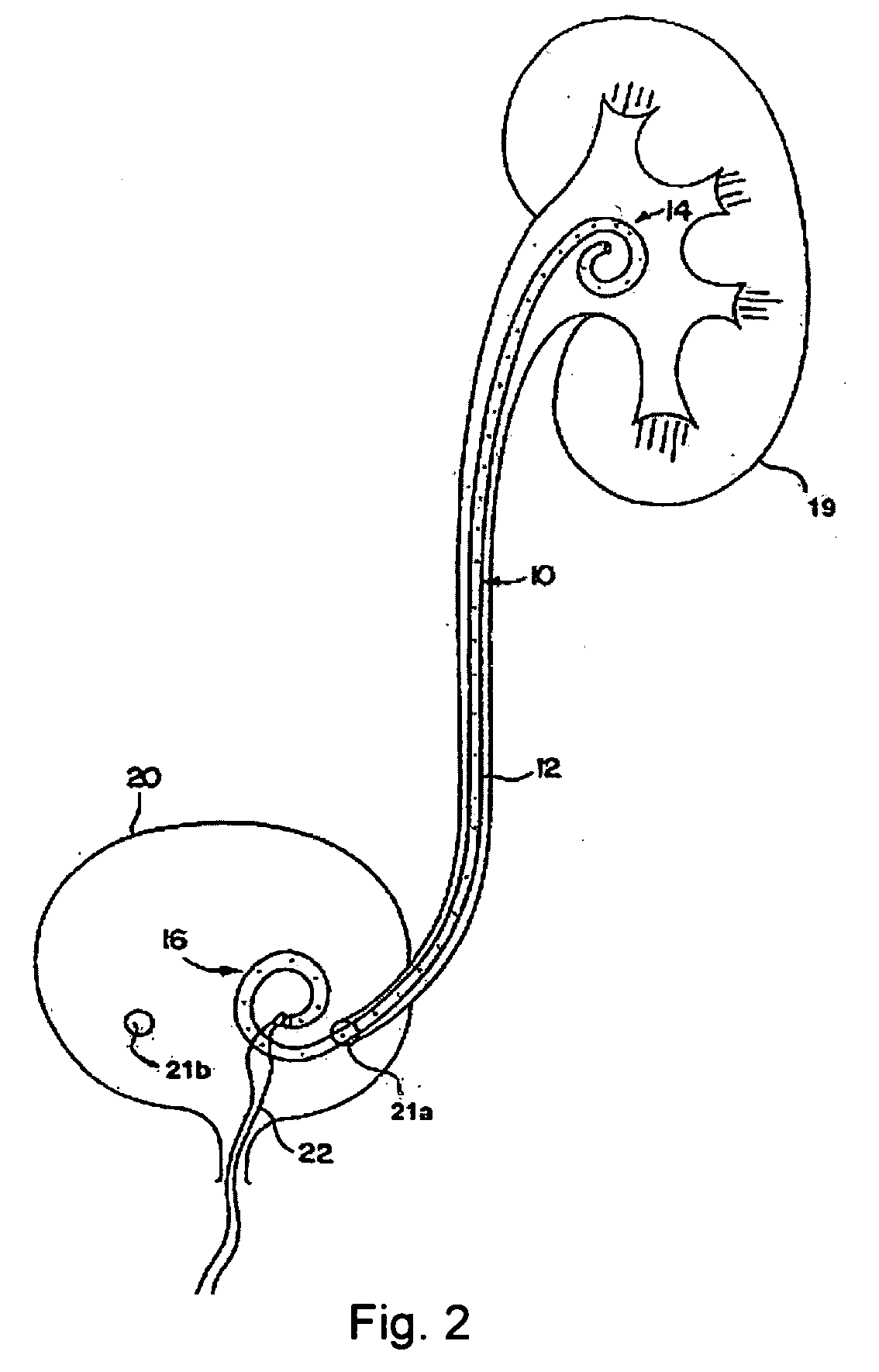
Precision stent positioner
A positioner is provided that is able to precisely position a stent, such as a ureteral stent, by using an anatomical landmark, such as a ureteral orifice. The positioner is placed over a wire guide and advanced until the proximal portion of the stent abuts a stent-stop. The positioner and stent are together pushed until the positioner reaches the ureteral orifice. The stent can be deployed and the positioner can be removed leaving the stent correctly positioned within the kidney and bladder.
Owner:VANCE PROD INC D B A COOK UROLOGICAL INC
Ureteral stent with end-effector
InactiveUS8007540B2Less irritatingReduce retentionBalloon catheterEar treatmentUrethraControl release
A system and related methods for maintaining the patentcy of the ureter comprising a pusher tube having a pusher tube lumen and an inflate lumen disposed within a wall of the pusher tube and a urinary stent having a proximal and distal portions with an elongated body portion therebetween configured to fit the ureter of the patient and defining a lumen. The system further includes an end-effector that may comprise an inflatable balloon positioned at the proximal portion of the urinary stent for retaining the proximal portion in the urinary bladder. At the distal portion, a retention end-piece is positioned for retaining the distal portion of the stent in the renal pelvis. The end-effector and the retention end-piece of the stent maintain the elongated body portion in situ. The end-effector may also include an inflatable balloon and may contain pharmaceutical or biologic agents for controlled release into the bladder.
Owner:BOSTON SCIENTIFIC SCIMED INC
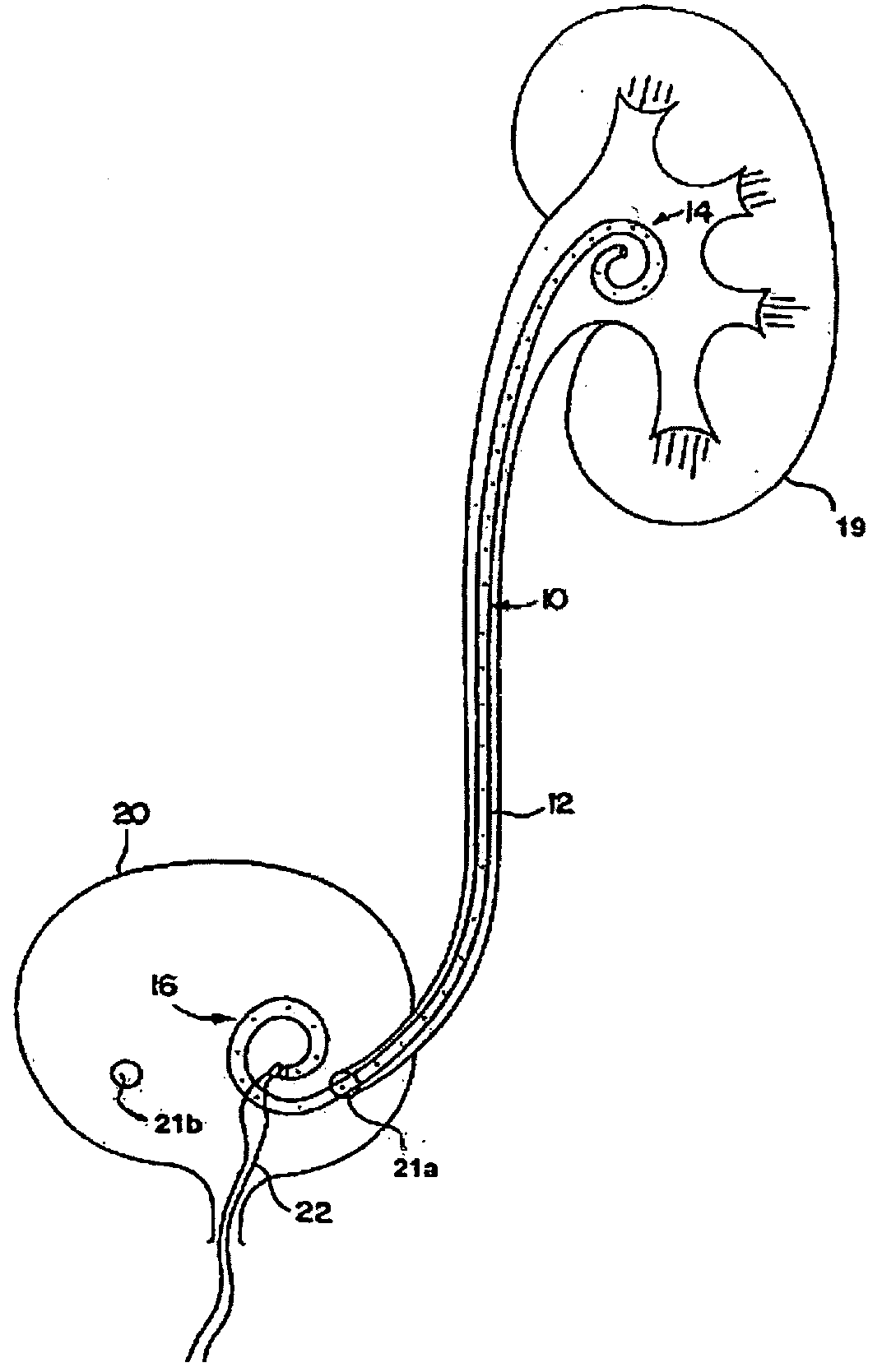
Ureteral stent for improved patient comfort
A ureteral stent for assisting the movement of urine along a patient's ureter and into the patient's bladder. The stent includes an elongated tubular segment extending toward the bladder from a kidney end region for placement in the renal cavity to a bladder end region. A central lumen connects at least one opening at the first end region to at least one opening in the bladder end region. Thin flexible tail(s) are attached to the bladder end region of the tubular segment at a point outside the bladder so as to receive urine from the opening in the bladder end region of the tubular segment and to transport urine from there across the ureter / bladder junction and into the bladder. The tails include an elongated external urine-transport surface sized and configured to transport urine along the ureter. The urine transporting surface(s) are sized and configured to extend along at least part of the ureter, across the ureter / bladder junction, and from there into the bladder. In some embodiments, the distal region includes a tubular body with a lumen in fluid communication with an interstitial area defined by one or more flexible filaments of the proximal region forming at least one loop.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Ureteral stent
A ureteral stent comprising an elongated tubular member having a body portion and opposed distal end portion and proximal end portion, the elongated tubular member defining a lumen therein; a retention disk comprising a plurality of generally axial, spaced-apart collapsable struts interconnected with a membrane to form a generalized tube with a retention disk lumen therein, the retention disk lumen in fluid communication with the lumen of the body portion, the struts and the membrane couple to the body portion proximal end at a retention disk distal end and terminate at a retention disk proximal end, each strut having a widthwise folding hinge substantially dividing the length of the strut, the struts adapted to have an expanded state wherein the struts are unfolded and substantially straight, as well as a free-resting state wherein each strut folds in upon itself at the folding hinge to form an inverted umbrella-like disk-shaped configuration; and a valve, wherein the inverted umbrella-like configuration provides a conformal shape to the ureteral orifice.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
Medical device with tail(s) for assisting flow of urine
InactiveUS6849069B1Decrease patient discomfortDecreases patient discomfortUrinary bladderStentsInsertion stentLeft ureter
A ureteral stent for assisting movement of urine along a patient's ureter and into the patient's bladder. The stent includes an elongated tubular segment extending toward the bladder from a kidney end region for placement in the renal cavity to a bladder end region. A central lumen connects at least one opening at the first end region to at least one opening in the bladder end region. Thin flexible tail(s) are attached to the bladder end region of the tubular segment at a point outside the bladder so as to receive urine from the opening in the bladder end region of the tubular segment and to transport urine from there across the ureter / bladder junction and into the bladder. The tails include an elongated external urine-transport surface sized and configured to transport urine along the ureter. The urine transporting surface(s) are sized and configured to extend along at least part of the ureter, across the ureter / bladder junction, and from there into the bladder.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP
Ureteral stents for release of urologically beneficial agents
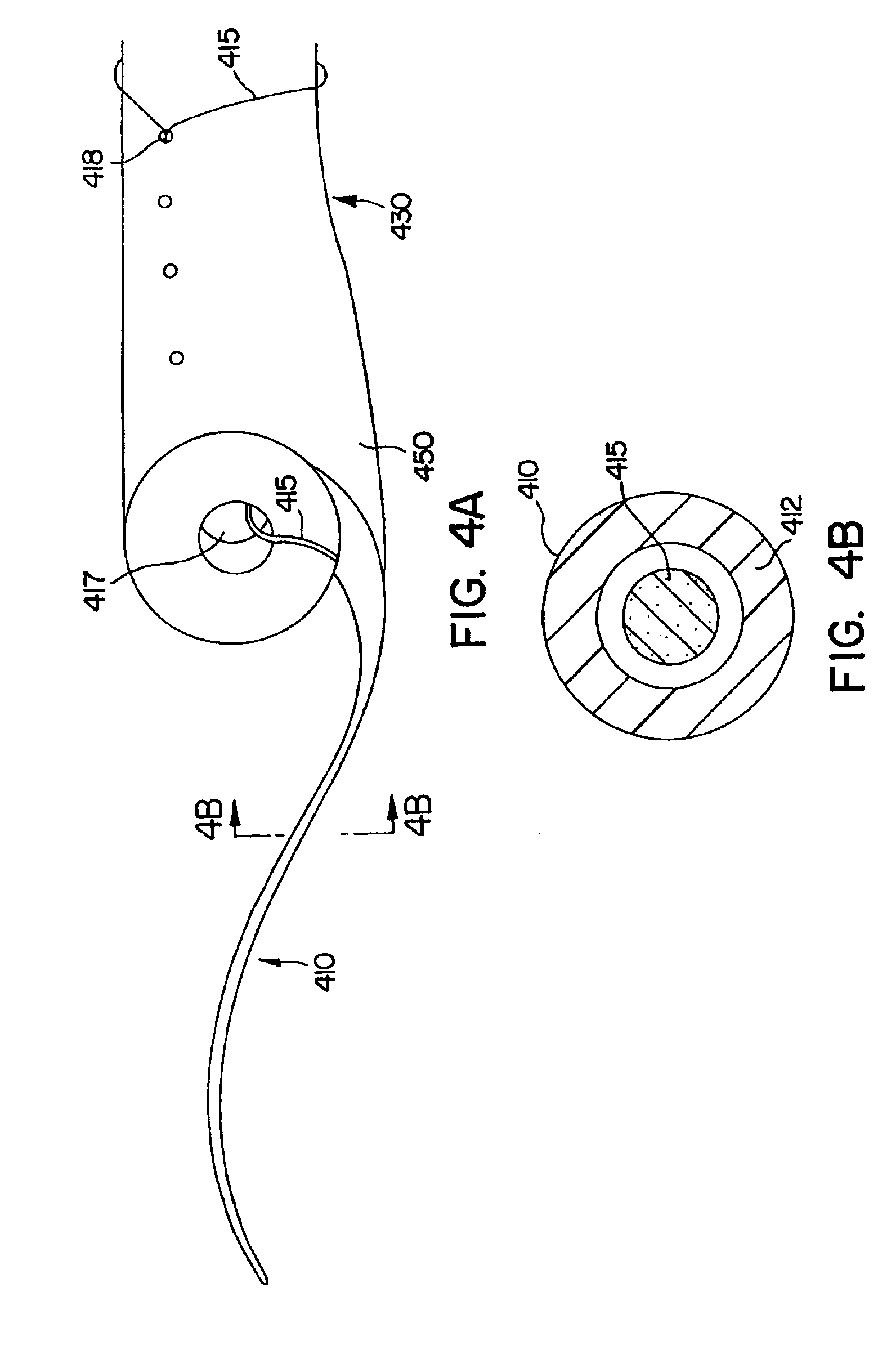
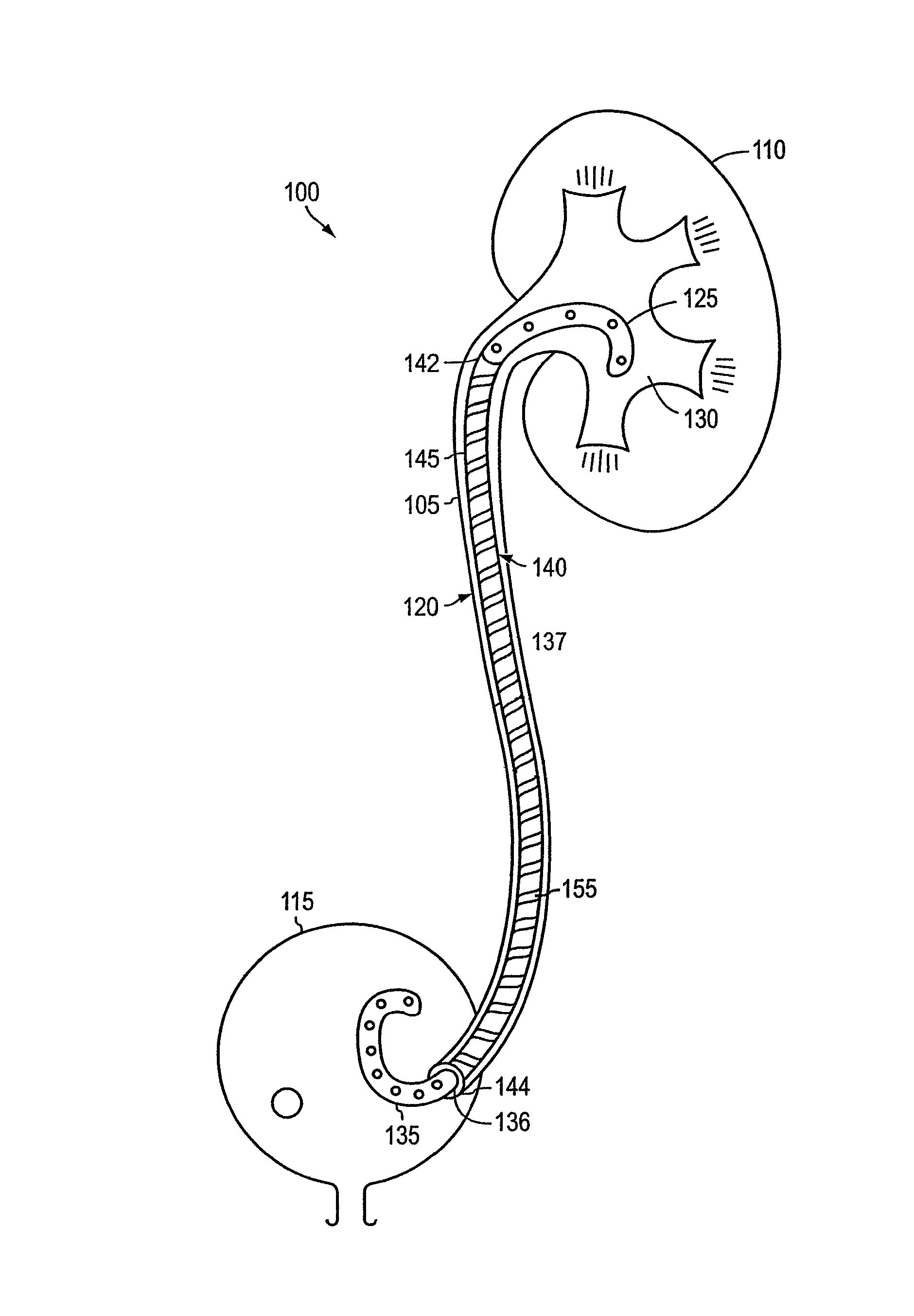
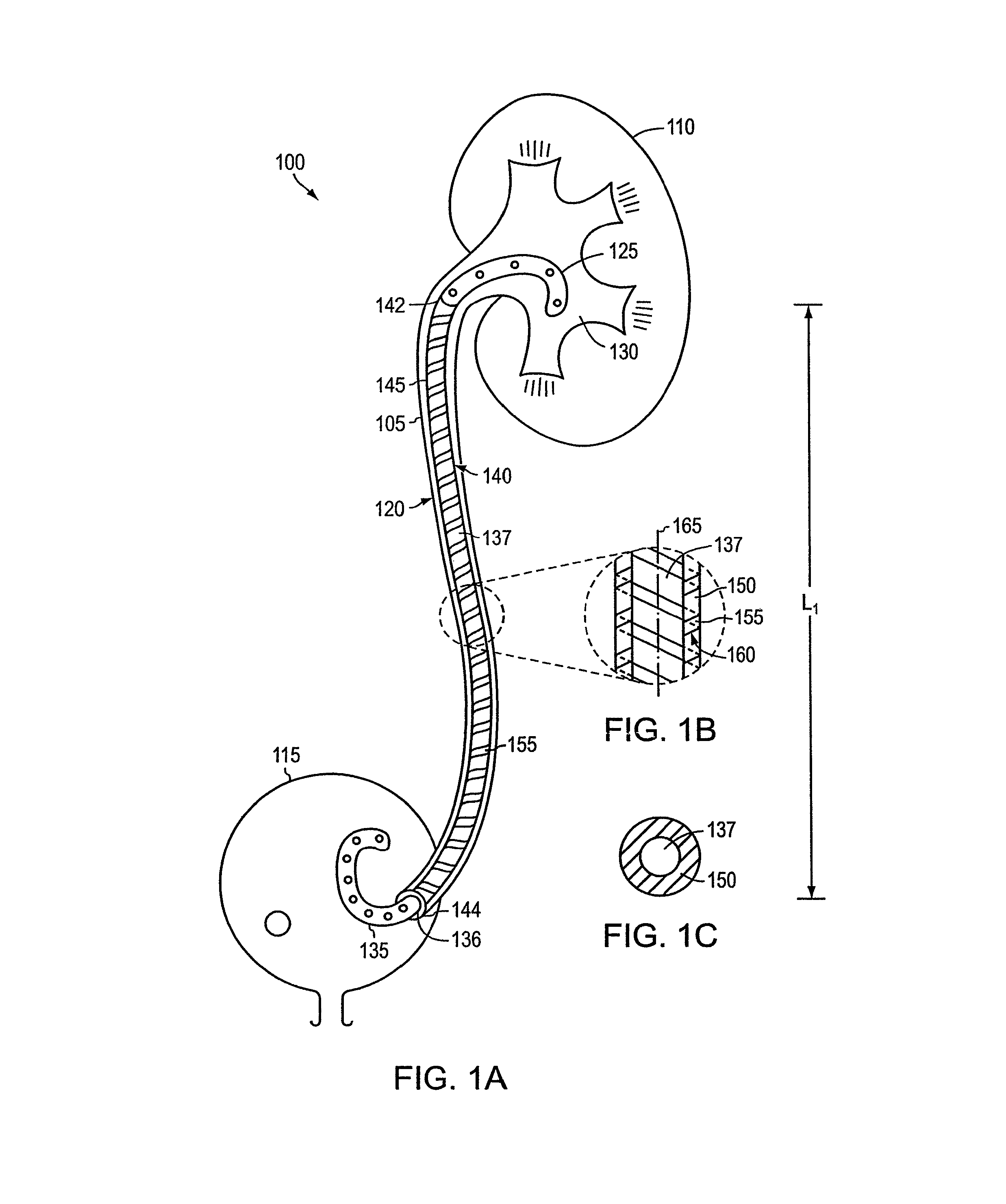
According to one aspect of the invention, ureteral stents are provided that comprise an elongated stent body and a urologically beneficial agent. The elongated stent body comprises a kidney portion adapted to occupy the kidney of a subject upon implantation, a ureter portion adapted to occupy the ureter of a subject upon implantation, and a bladder portion adapted to occupy the bladder of a subject upon implantation. The ureteral stents of the invention are adapted to release the urologically beneficial agent into the subject. Moreover, the amount of urologically beneficial agent that is released varies along the length of the stent. Other aspects of the invention pertain to methods of forming such stents and methods of using such stents.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Ureteral Stent
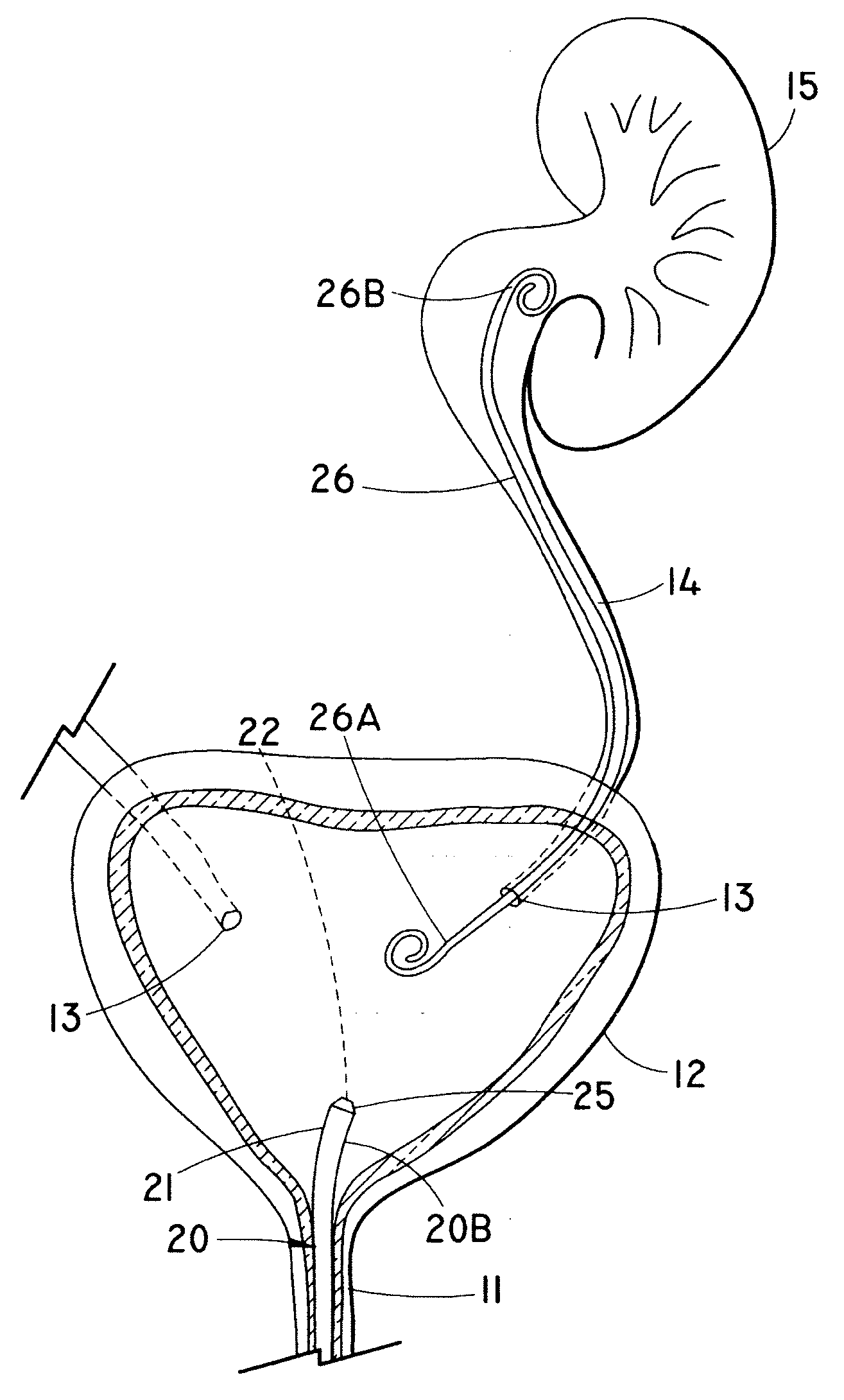
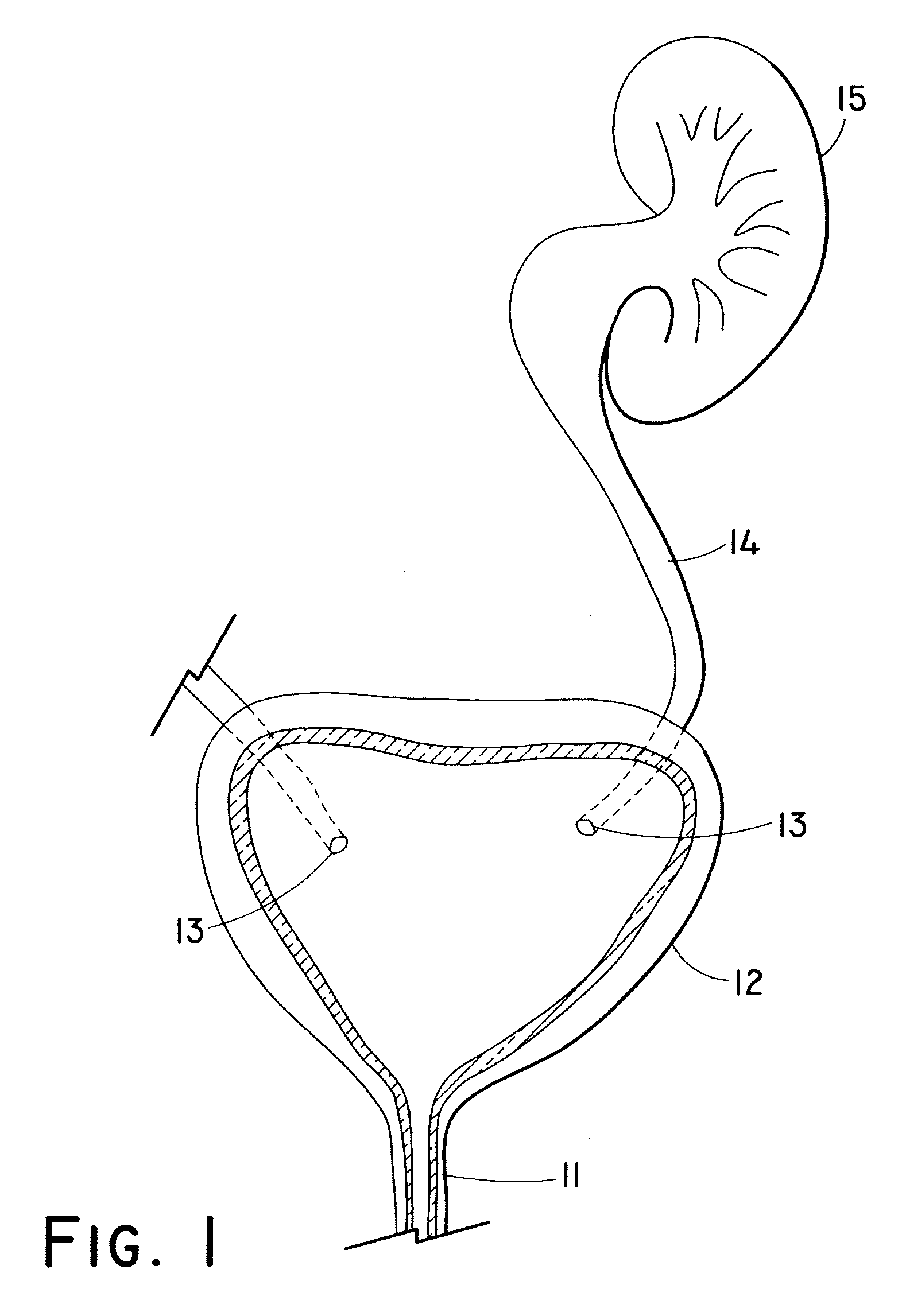
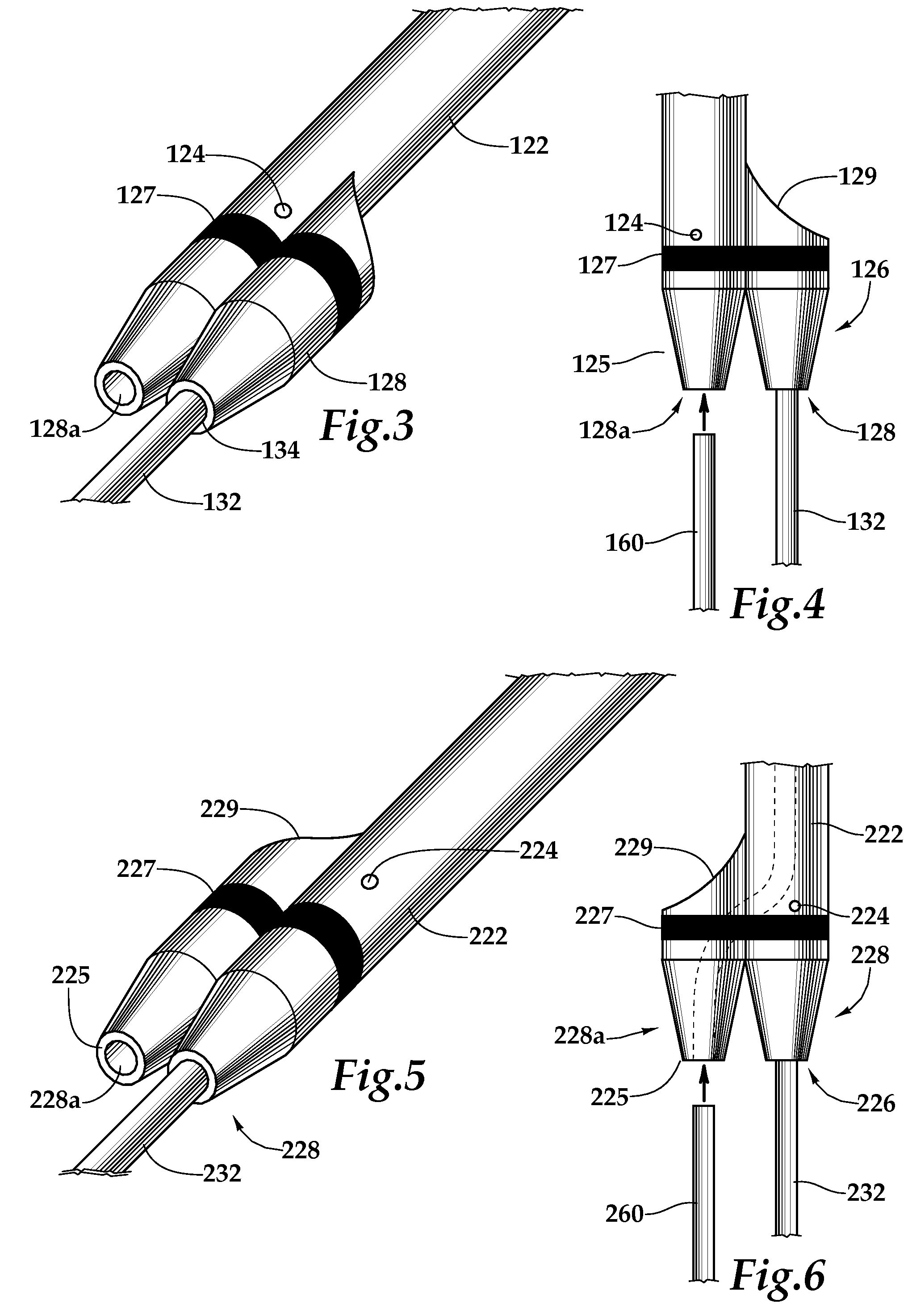
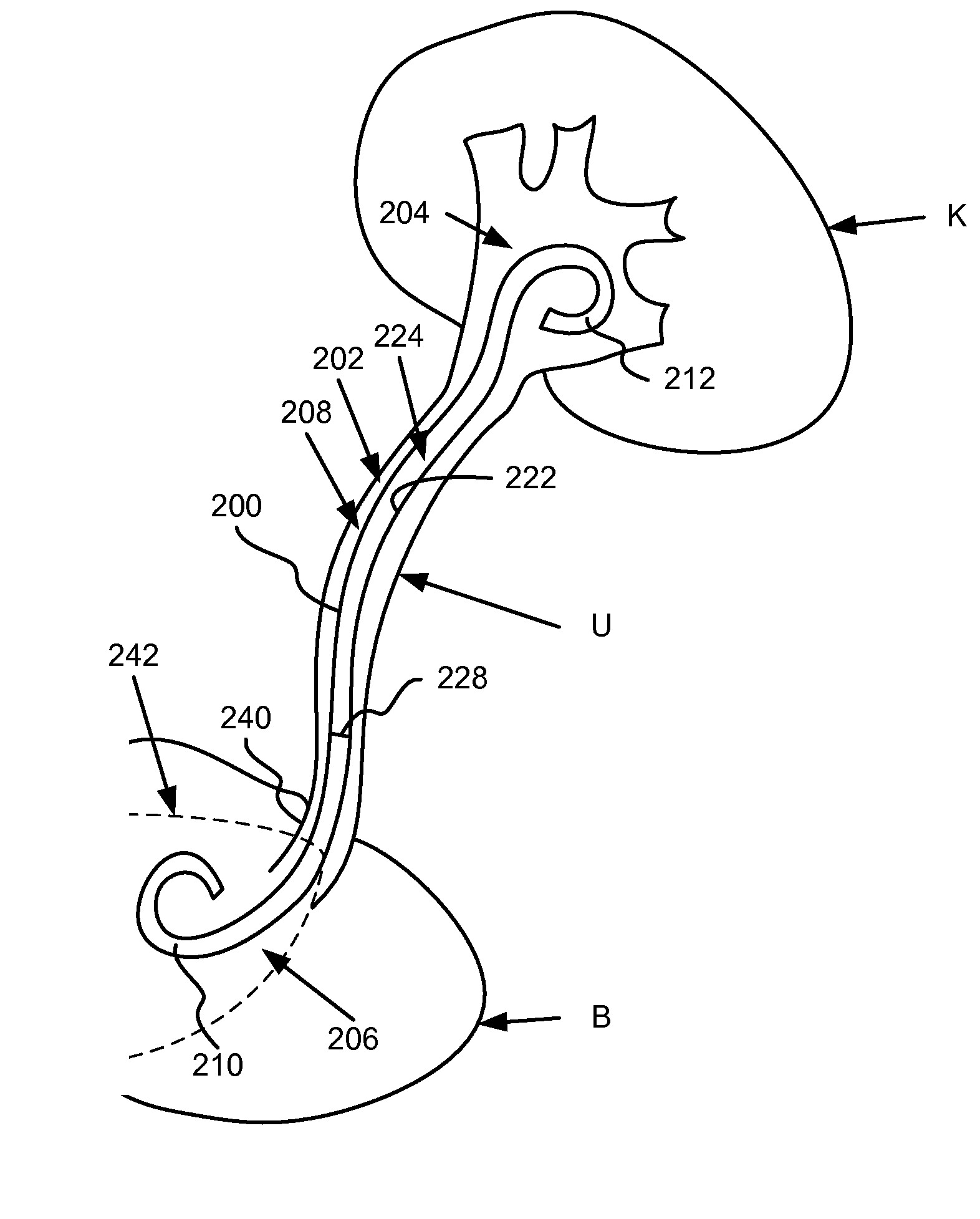
A ureteral stent comprising a short renal coil made of a pliable material and a wick portion made of a material having a hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity different from that of the renal coil and extending from a ureteropelvic junction to a bladder so as to assist in the transfer of urine out of a kidney and into the bladder and to improve patient comfort. Due to increased hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity, wick may be significantly smaller in diameter than renal coil, resulting in less reflux of urine into the kidney and further decreasing patient discomfort. The stent may further comprise one or more couplers between the renal coil and wick portion, such as clamps, couplers, sutures, adhesives or receiving ends of the renal coil, and the wick portion may further comprise a sheath surrounding an elastic core to prevent kinking and enhance the ability of the wick portion to move with the patient. A novel method of ureteral stent placement is also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Ureteral stent with drug-releasing structure
According to one aspect of the present disclosure, ureteral stents are provided that comprise an elongated stent body, at least one deployable retention structure, and at least one sleeve and / or sheet of drug-releasing material. In various embodiments, at least one sleeve and / or sheet of drug-releasing material is deployed concurrently with the deployment of at least one deployable retention structure. The ureteral stents of the present disclosure are adapted to release the urologically beneficial drug into a subject.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
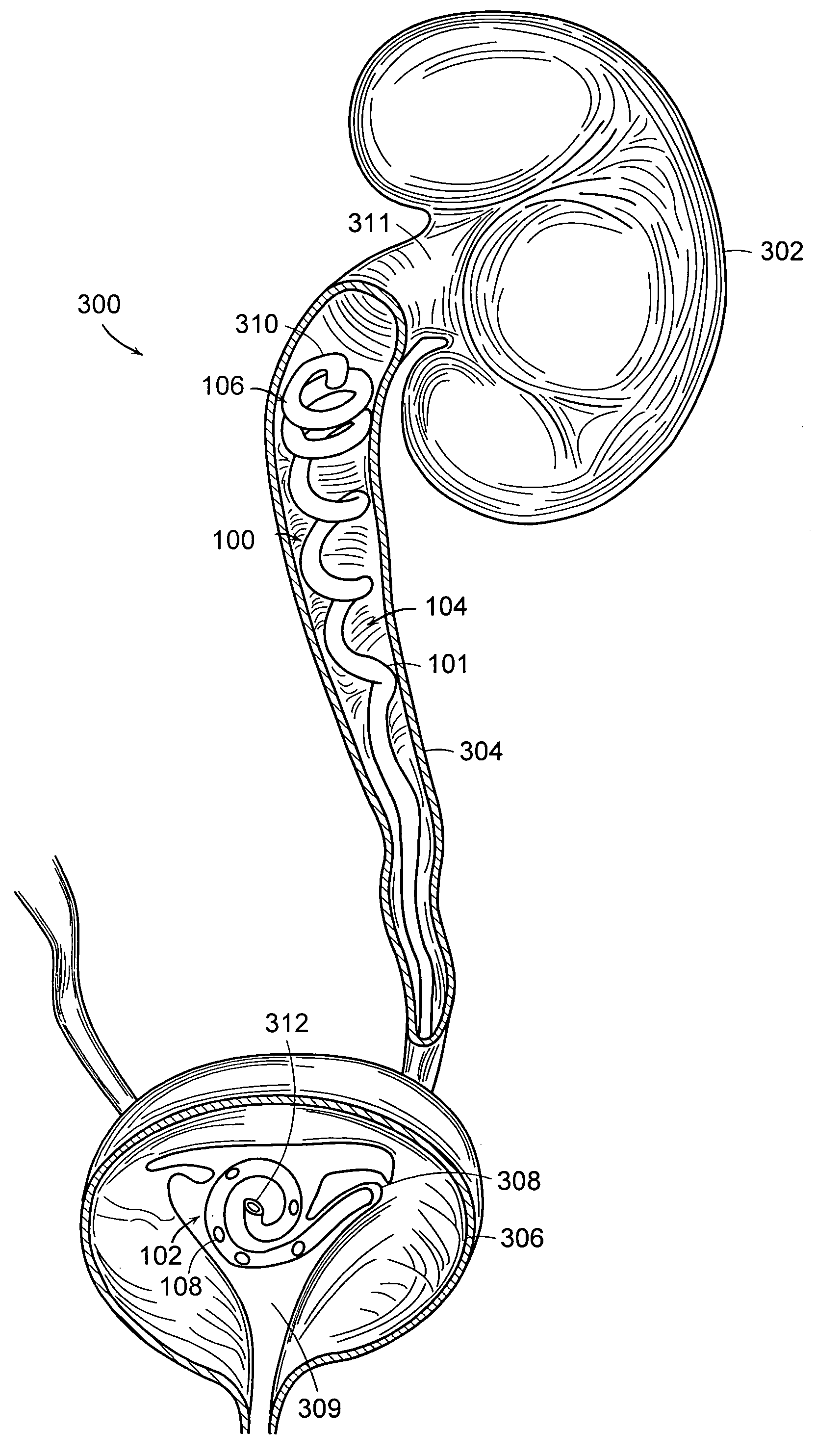
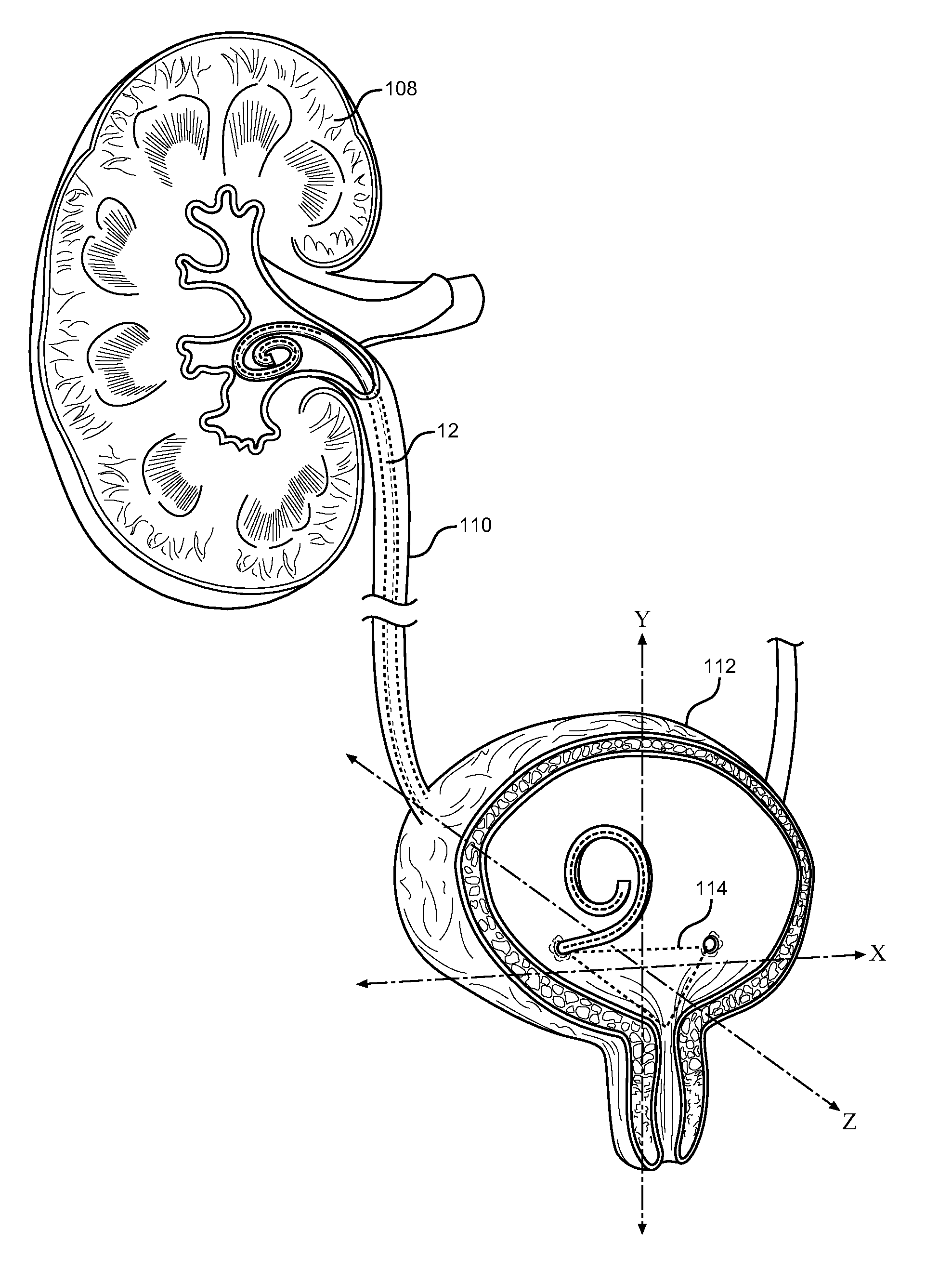
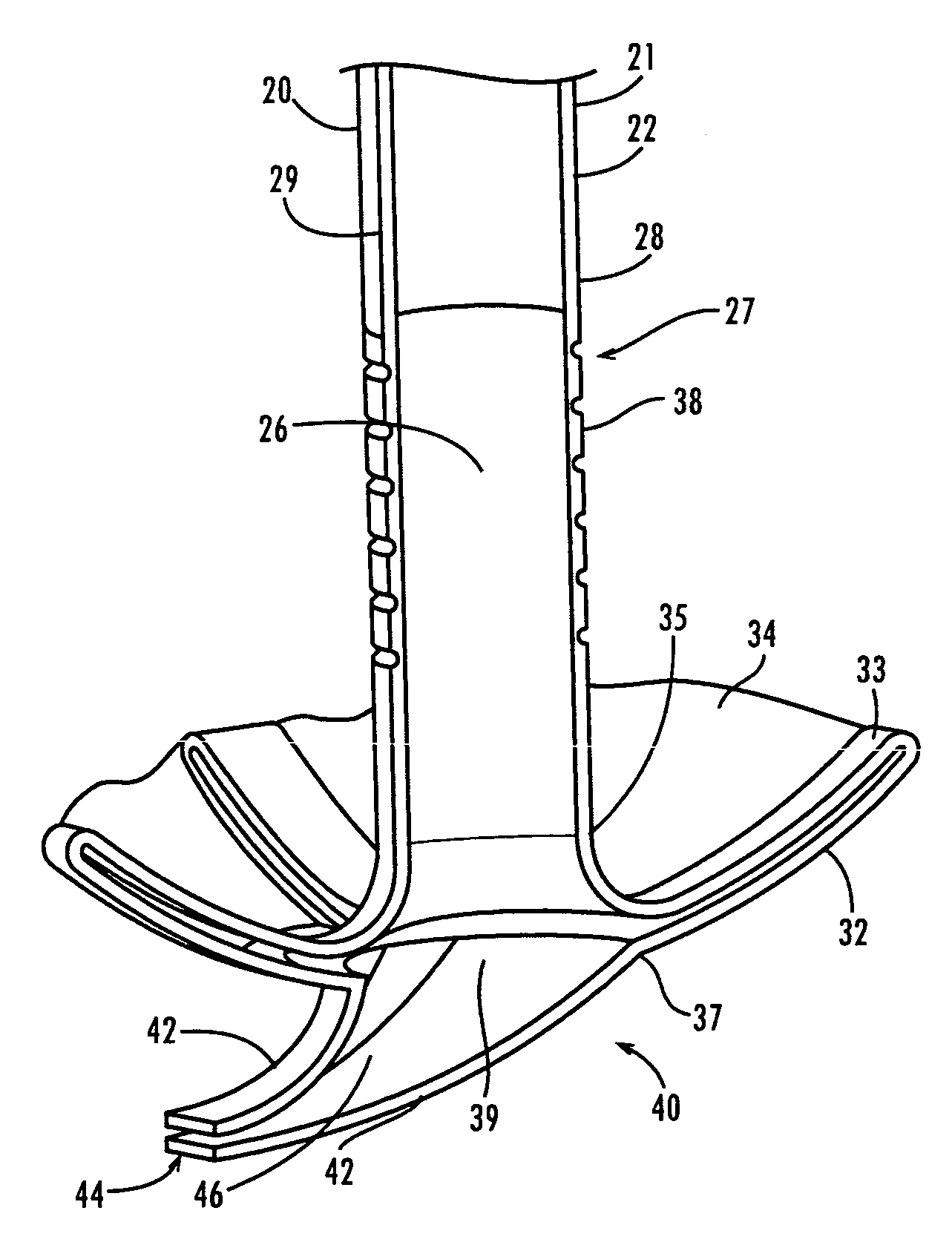
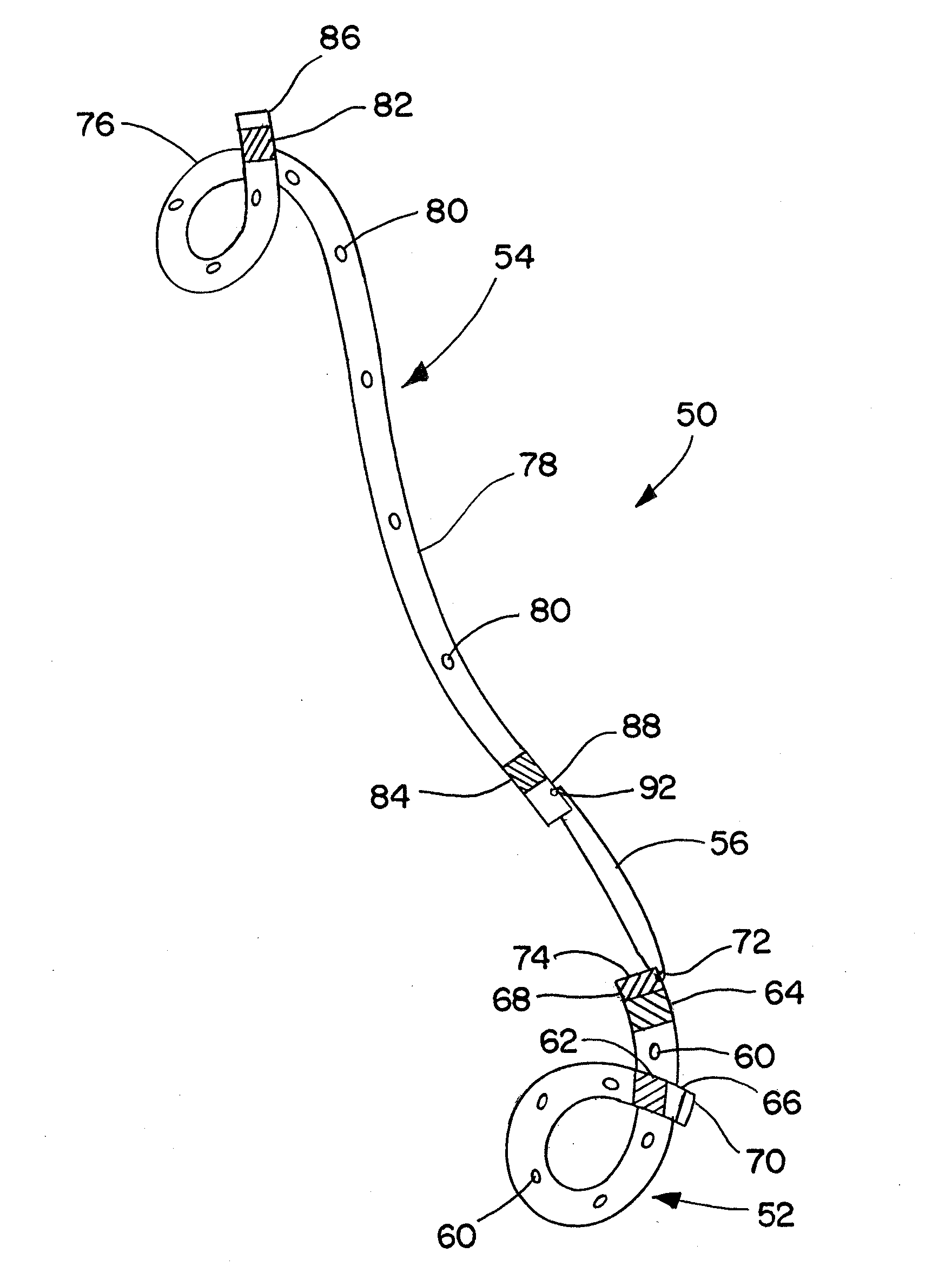
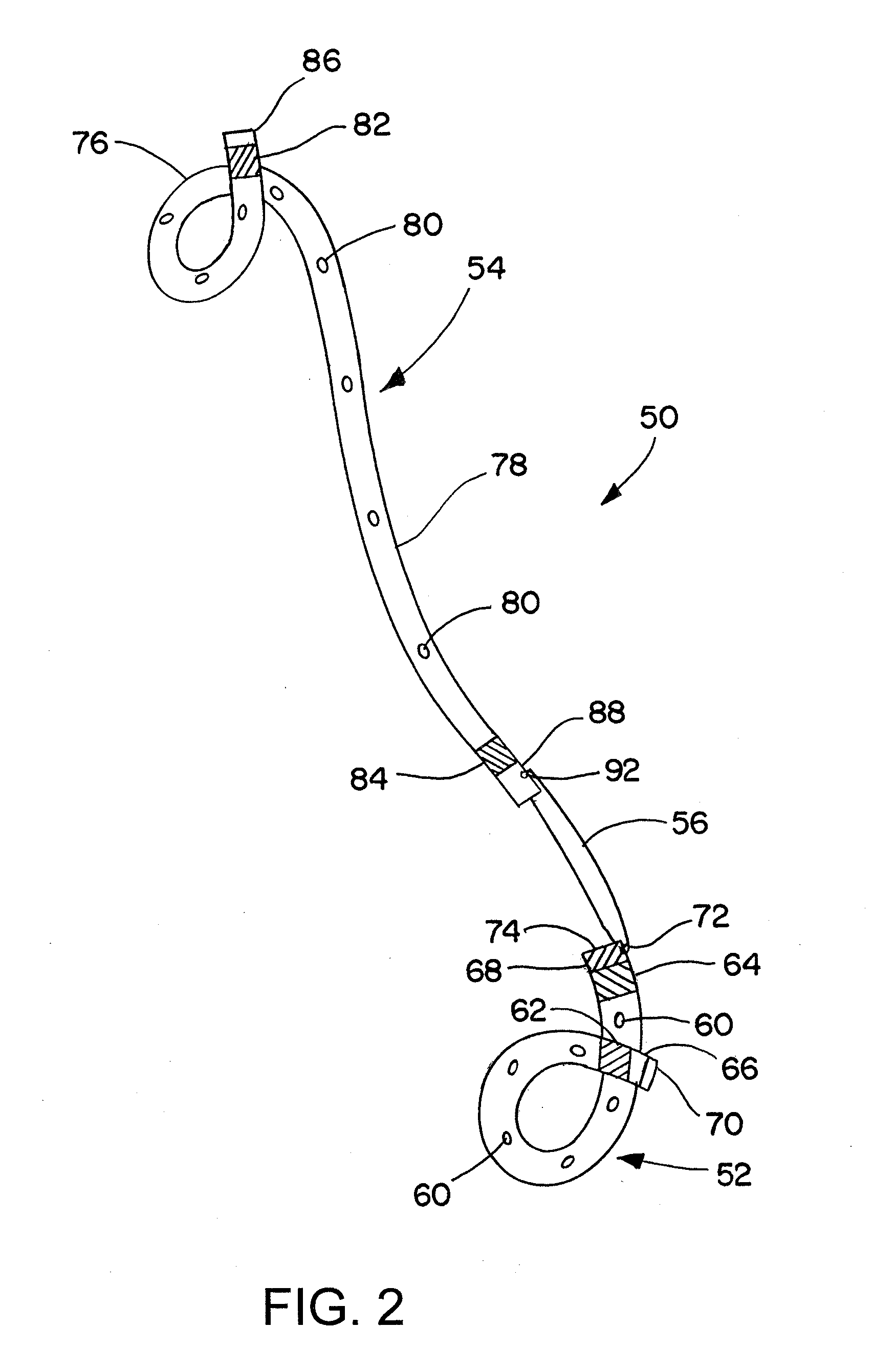
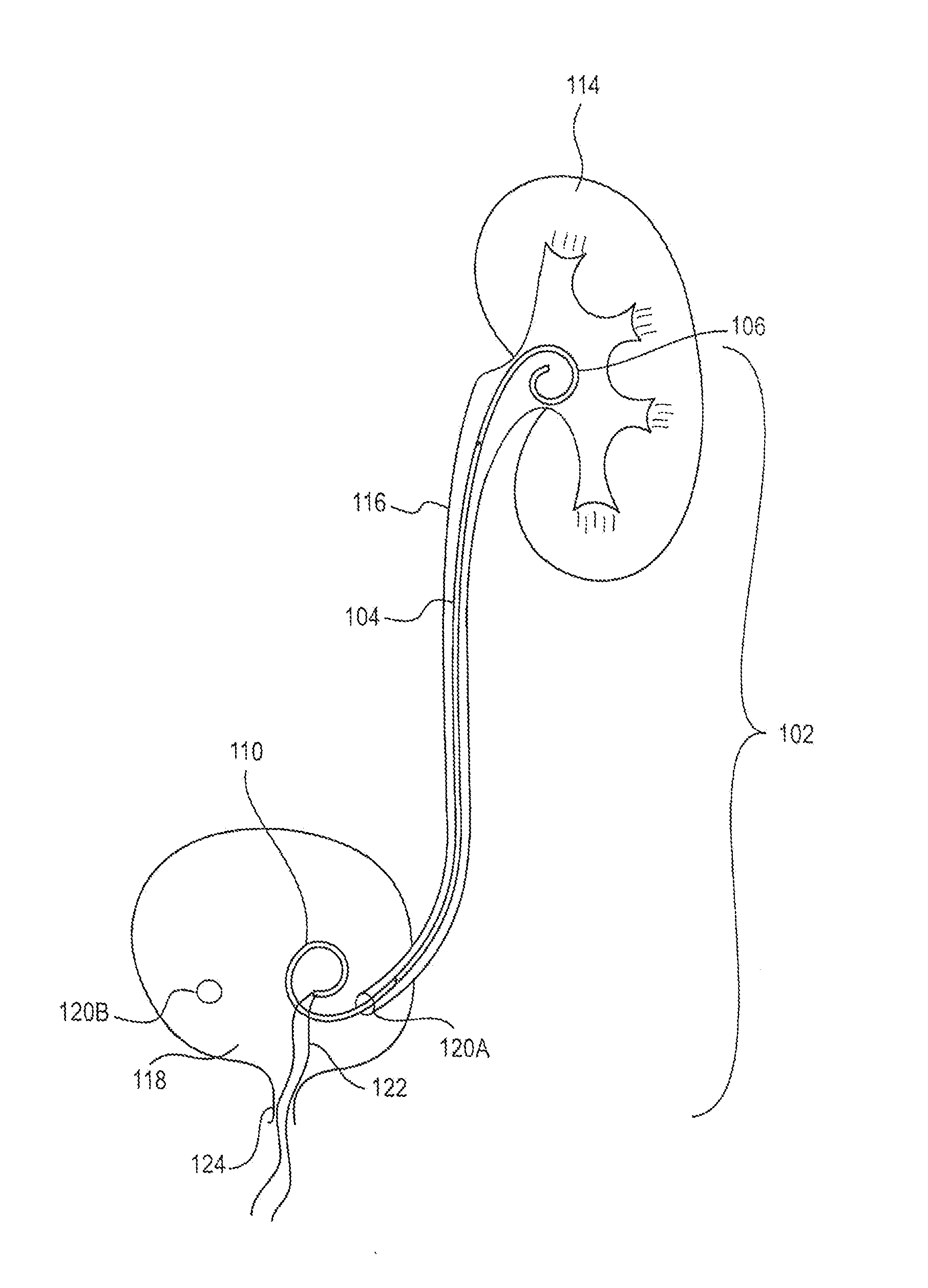
Ureteral stent for placement in a kidney and bladder
Provided is a ureteral stent (=50) including a bladder portion (=52) positioned in a bladder of a patient, a kidney portion (=54) positioned in a kidney and ureteral passageway of the patient, and one or more tethers (=56) coupling the bladder portion to the kidney portion. The ureteral stent allows urine to pass around a blockage, and allows a ureter orifice connecting the ureteral passageway to the bladder to move between a compressed state and an uncompressed state to prevent or minimize urinary reflux, flank pain, blood in the urine, etc., while allowing the bladder portion to move freely in the bladder to prevent the bladder portion from irritating the trigone muscle.
Owner:UNIV HOSPITALS HEALTH SYST
Ureteral stent with end-effector and related methods
InactiveUS20060015190A1Less irritatingReduce retentionStentsBalloon catheterControl releaseInsertion stent
A system and related methods for maintaining the patentcy of the ureter comprising a pusher tube having a pusher tube lumen and an inflate lumen disposed within a wall of the pusher tube and a urinary stent having a proximal and distal portions with an elongated body portion therebetween configured to fit the ureter of the patient and defining a lumen. The system further includes an end-effector that may comprise an inflatable balloon positioned at the proximal portion of the urinary stent for retaining the proximal portion in the urinary bladder. At the distal portion, a retention end-piece is positioned for retaining the distal portion of the stent in the renal pelvis. The end-effector and the retention end-piece of the stent maintain the elongated body portion in situ. The end-effector may also include an inflatable balloon and may contain pharmaceutical or biologic agents for controlled release into the bladder.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
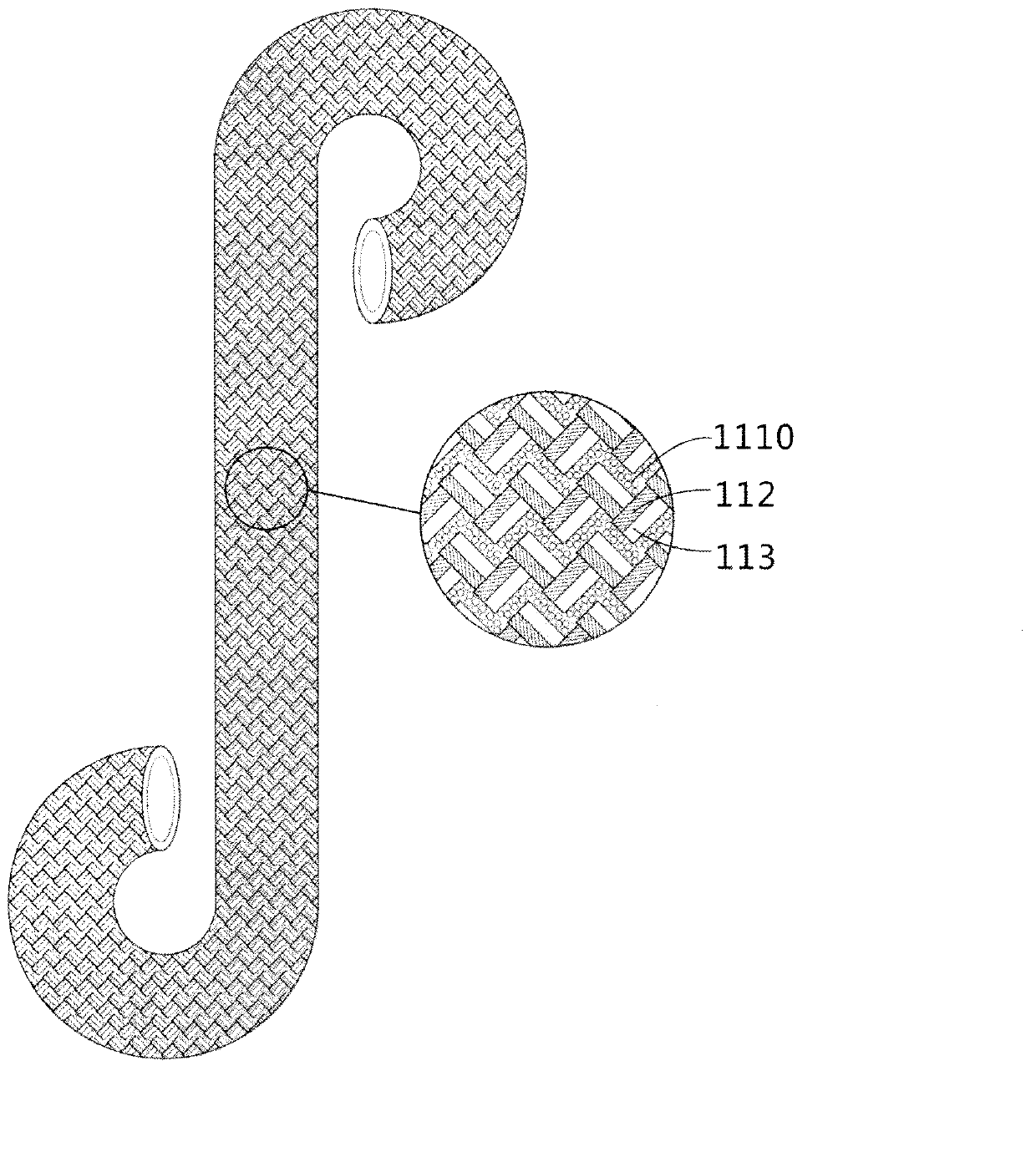
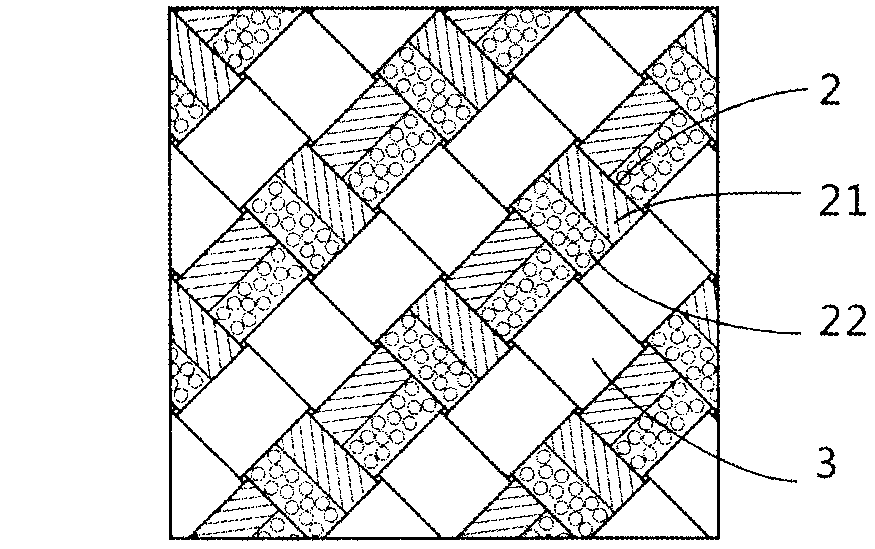
Textile multicomponent enhancement structure-gradually degradable ureteral stent tube and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a textile multicomponent enhancement structure-gradually gradable ureteral stent tube and a preparation method thereof. The textile-based ureteral stent tube is characterized by comprising a film phase and a fiber phase containing different components, wherein the film phase and the fiber phase are mutually mixed, the mechanical property is enhanced, and the two phases are gradually degraded. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: weaving at least two degradable fibrous raw materials with different melting temperatures on a core mold by a weaving structure mixed by different configuration, and melting the components with low melting point in the tube wall fiber materials into film by virtue of temperature in a thermal treatment technology, so that the other fiber components in the tube wall can be tightly and evenly combined to enhance the tube wall of the weaving tube. The ureteral stent tube is simple to prepare, has the excellent axial tensile property and flexibility of a fiber stent, and the excellent mechanical supporting performance of a film material stent tube, and can realize the gradual degraded steps of the film and the fiber successively; and a degradation product is less than 0.1mm<3>.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Degradable double-layer compound ureteral stent tube
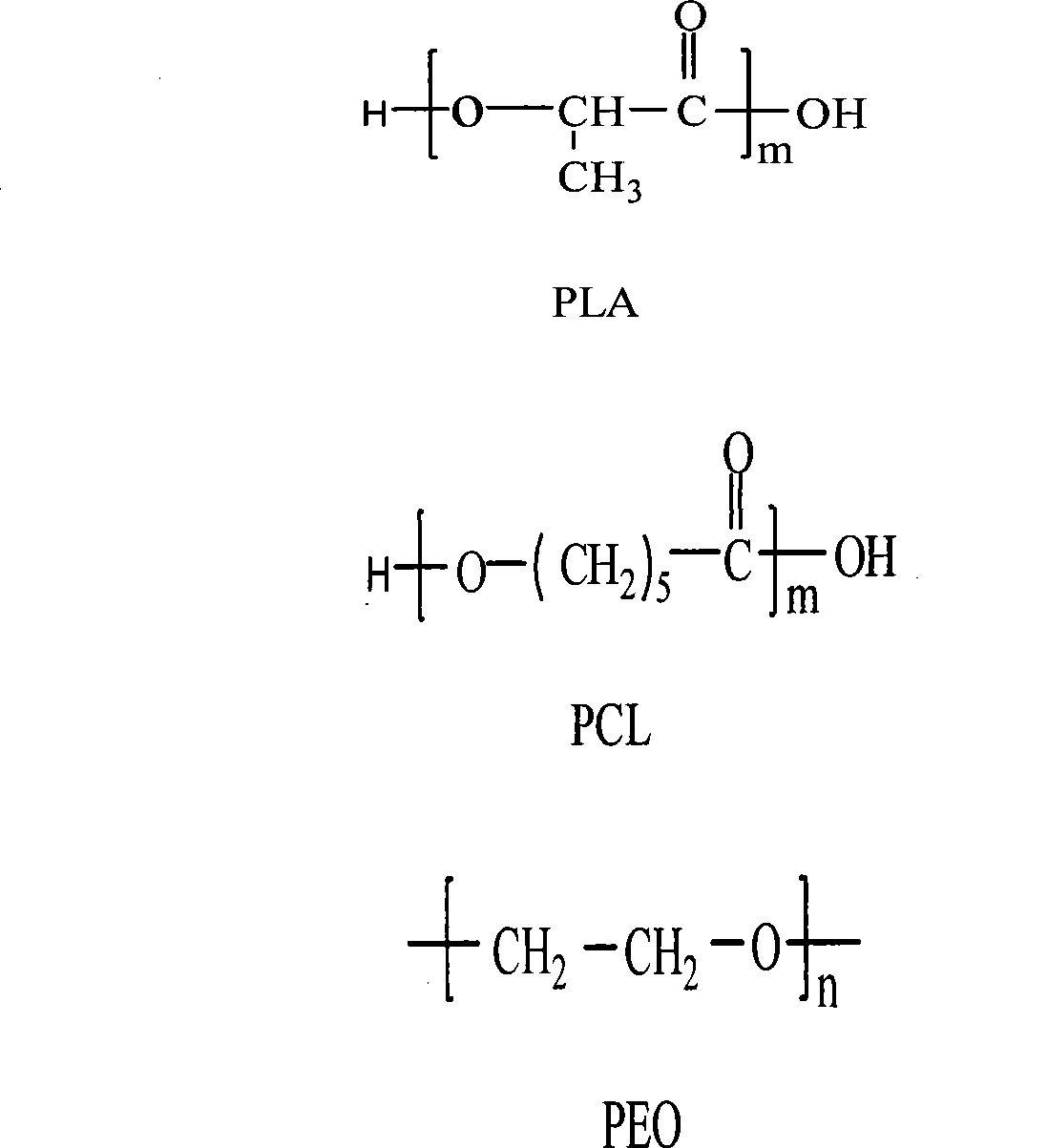
The invention discloses a ureteral stent tube made of a degradable material. The stent tube is a double-layer compound tube, the inner layer is constituted by a L-lactide / epsilon-caprolactone copolymer (PLLCA) elastomer material, and the weight average molecular weight of an L-lactide / epsilon-caprolactone copolymer is 0.1-0.8 million, wherein an epsilon-caprolactone unit accounts for 15%-25% in the copolymer, an L-lactide unit accounts for 75%-85%, and a layer of poly-1,4-dioxanone (PPDO) is uniformly covered on the outer layer of the ureteral stent tube. The viscosity average molecular weight is 0.1-0.5 million. The ureteral stent tube has the advantages of being good in biocompatibility, being capable of realizing self-degradation, being capable of being degraded and excreted from a body without drawing the tube, and reducing suffering and economic burden of a patient.
Owner:ZHEJIANG APELOA JIAYUAN BIOMEDICAL MATERIAL +1
Ureteral stent
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Stents and methods of use thereof
Medical devices such as ureteral stents, and methods of use thereof are disclosed. The medical device may include an elongate member configured to be implanted within a patient's body, wherein the elongate member includes an outermost diameter and a plurality of support members disposed within a biodegradable matrix. Degradation of the biodegradable material may result in a reduction of size of the medical device. Some or all of the support members, such as at least two of the support members, may be arranged non-concentrically.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Stent with soluble bladder retention member
Ureteral stents having at least a portion of a proximal end of the ureteral stent constructed with a material that dissolves after being exposed to a bodily fluid for a period of time are disclosed herein. At least a portion of the proximal end portion of the elongate member includes a dissolving portion configured to dissolve in response to being exposed to a bodily fluid for a period of time. The elongate member also includes a non-dissolving portion that includes the entire retention member of the distal end portion and is substantially stable in the bodily fluid of the urinary tract of the patient. In some embodiments, a medial portion of the ureteral stent is also constructed with one or more dissolving materials. In some implementations, the proximal and / or the medial portions of the ureteral stent are constructed using various combinations of dissolving and non-dissolving materials.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
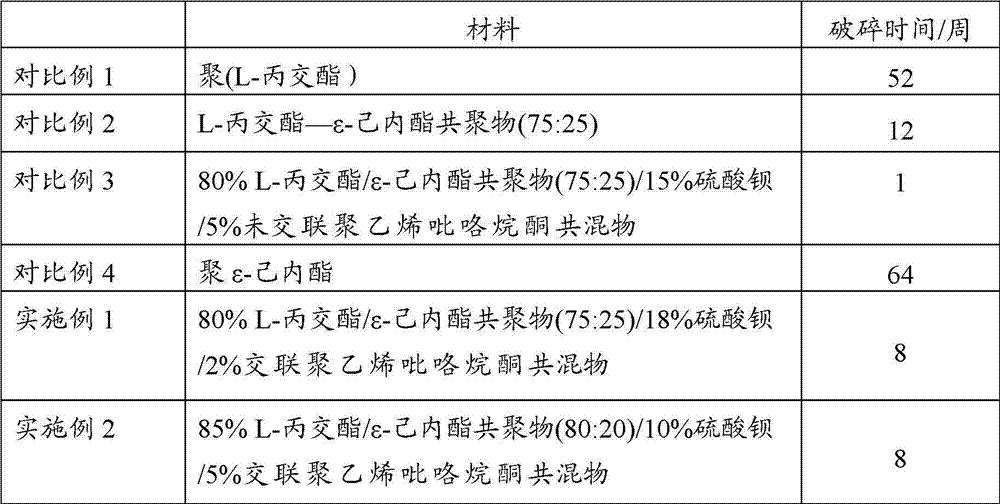
Composite material for making degradable ureteral stent and application thereof
ActiveCN103041454AIncreased degradation rateAvoid cloggingStentsSurgeryBiocompatibility TestingCross-linked polyethylene
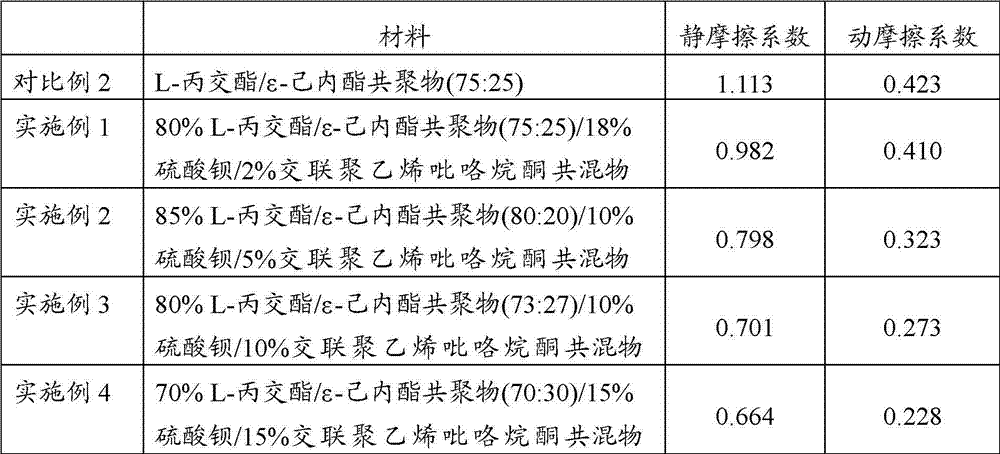
The invention provides a kind of composite material for making a degradable ureteral stent, comprising: 60-98% by weight of L-lactide / Epsilon-caprolactone copolymer, and 2-40% by weight of polyvinylpolypyrrolidone. The L-lactide / Epsilon-caprolactone copolymer in the composite material is elastomeric material with good biocompatibility, and the polyvinylpolypyrrolidone can reduce a surface friction coefficient of the prepared degradable ureteral stent, and simultaneously raises the degradation speed of the degradable ureteral stent. The invention also discloses a degradable ureteral stent prepared by the composite material. The degradable ureteral stent has good biocompatibility, is easy to degrade, and can be used in an operation in urinary surgery.
Owner:ZHEJIANG APELOA JIAYUAN BIOMEDICAL MATERIAL +2
Ureteric branches support and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101422634AReduce coefficient of frictionEasy to implantStentsSurgeryMedicineUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a ureter bracket and a preparing method thereof; the ureter bracket uses biodegradable macromolecules as raw materials and is prepared through a dip forming method. In the method, a mould coated with parting medium on the surface is inserted into solution or meltwater of the biodegradable macromolecules for repeatedly dipping and film forming so as to get the ureter bracket. The degradable ureter bracket is characterized by various sizes, degradation rates and mechanical strengths, which can be compounded with various medicines or developers; furthermore, the ureter bracket can be applied in medical field and satisfy various requirements of clinical application. The method is characterized by simple operating process and mild operating conditions.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
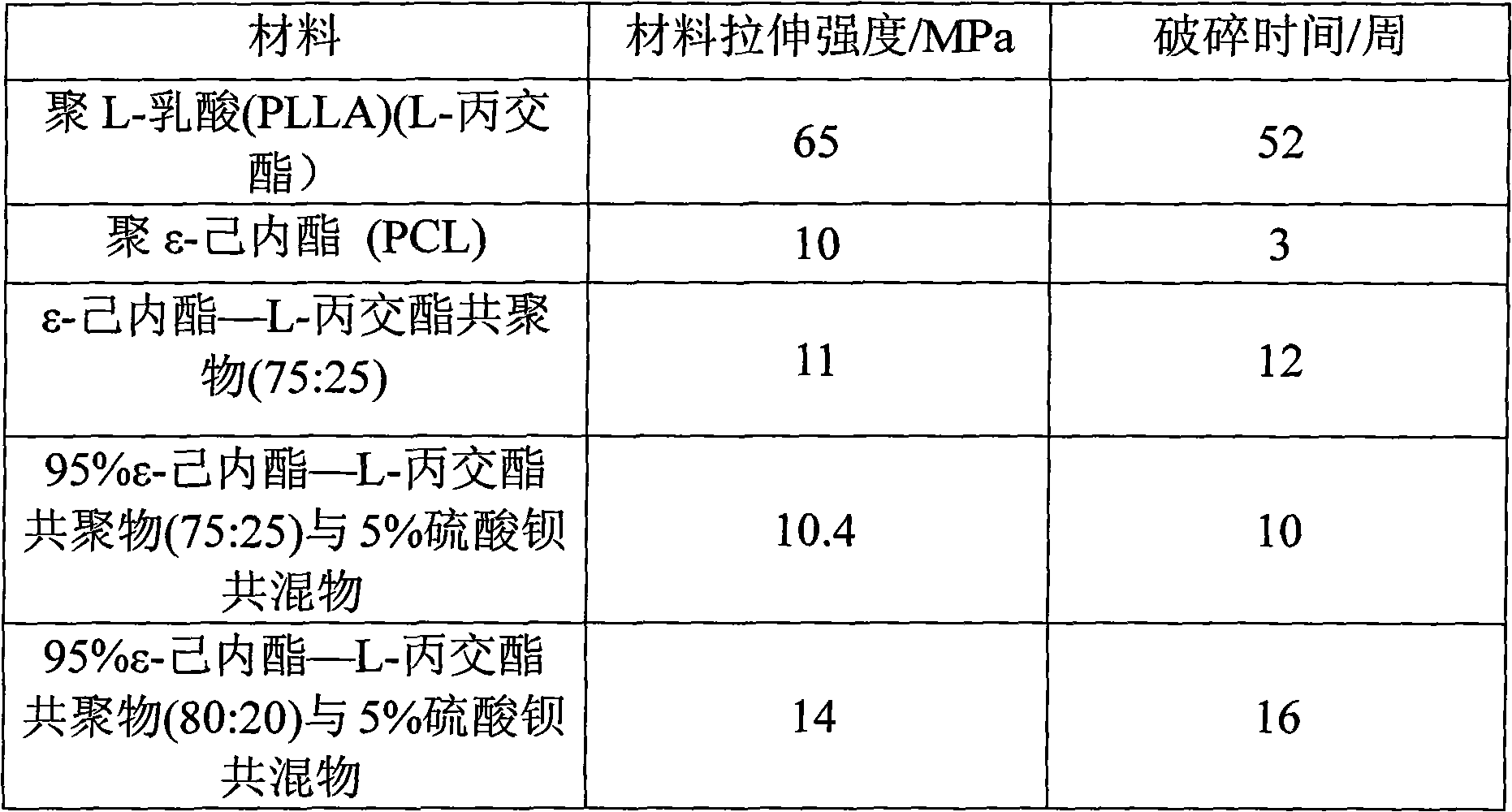
Gradient degradable polymeric material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103374208AIdeal degradation timeGood biocompatibilitySuture equipmentsStentsPolyesterPolymer science
A polymer material capable of gradient degradation. The polymer material is formed by at least two types of aliphatic polyesters having different degradation velocities, the aliphatic polyesters being arranged in an ascending order or descending order of the degradation velocities and fused together. The polymer material may be manufactured as thread materials, barrier materials, tube materials, and controlled drug release carriers, which specifically comprise sutures, medical dressings, adhesion prevention material, hemostasis material, guided tissue regeneration barriers, tissue repair materials, enhancement surgical meshes, drug carriers, cartilage tissue culture scaffolds, scaffolds, and especially urethral scaffolds.
Owner:山东省新征程工业科技有限公司
Gradually degradable braided ureteral stent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102266594AControllable and procedural degradation processReduce complicationsSurgeryCatheterYarnBiochemical engineering
The invention relates to a gradually degradable woven ureter scaffold tube and a preparation method thereof. The woven ureter scaffold tube comprises a tube body. The woven ureter scaffold tube is characterized in that: the tube body is woven by using at least two fiber raw materials with different degradation rates. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: making the at least two fiber raw materials with different degradation rates into yarns, weaving the obtained yarns on a first core die by adopting a rhombic structure on a 16 to 32-spindle weaving machine to form a woven tube, stripping the woven tube from the first core die to form the tube body after heat setting, performing secondary heat setting, and coating the tube body by using chitosan to make the tail end of the annular structure. According to the woven ureter scaffold tube, gradient degradation can be realized, the degradation time is controllable, the degraded product is smaller than 1mm<3>, the structure is fixed, and the mechanical property is good.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com