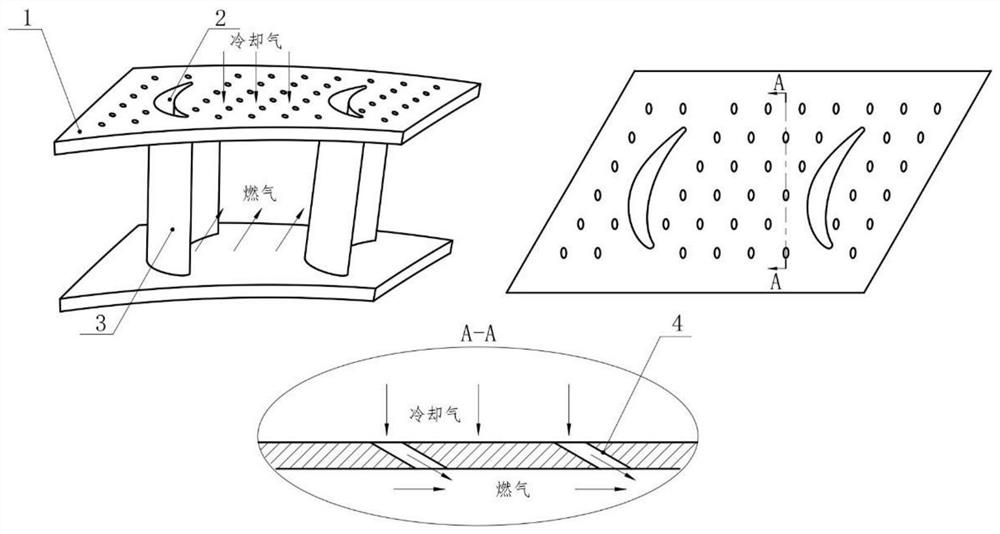
Turbine blade branch net type cooling structure
A technology for cooling structure and turbine blades, which is applied in the direction of supporting components of blades, engine components, machines/engines, etc. It can solve the problems of small heat exchange area and cooling efficiency that cannot meet high thrust-to-weight ratio aeroengines, etc., to achieve increased cooling area, The effect of improving the heat exchange capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
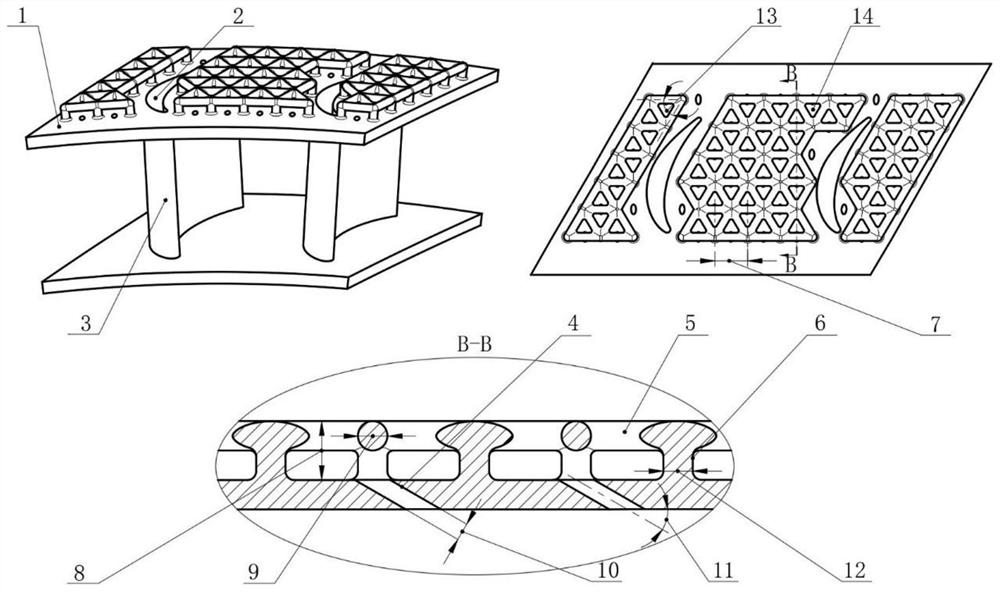
[0031] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of a turbine guide vane with a branched cooling structure provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the branch network cooling structure of this embodiment is composed of two parts: a cylindrical support structure and a network connection structure. The cylindrical support structure in the branch-network cooling structure is perpendicular to the outer surface of the turbine guide blade edge plate, and the mesh connection structure is approximately parallel to the outer surface of the edge plate.
[0032] The cylindrical support structure in the branch network cooling structure is defined by the diameter φD 1 The cylinders of =1 mm are arranged in an equilateral triangle, each cylinder is located at the vertices of the equilateral triangle, and the side length of the equilateral triangle is the distance L=3mm between two adjacent cylinders.
[0033] The network connection structure in the branch netw...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A turbine guide vane with a branch-network cooling structure, the cylindrical support structure in the branch-network cooling structure is defined by the diameter φD 1 = 2mm columns, arranged in a regular triangle, each column is located at the apex of the regular triangle, the side length of the regular triangle is the distance between two adjacent columns L = 5mm, the typical value can be 4mm.
[0037] The network connection structure in the branch network cooling structure is determined by the diameter φD 2 = 2mm column, the total height of the branch network cooling structure H = 3mm, the diameter of the air film hole φd = 0.8mm, the angle ∠A between the axis of the air film hole and the outer surface of the edge plate 2 = 40°. The ratio of the diameter of the gas film pores to the network connection is in the range of 0.8.
Embodiment 3
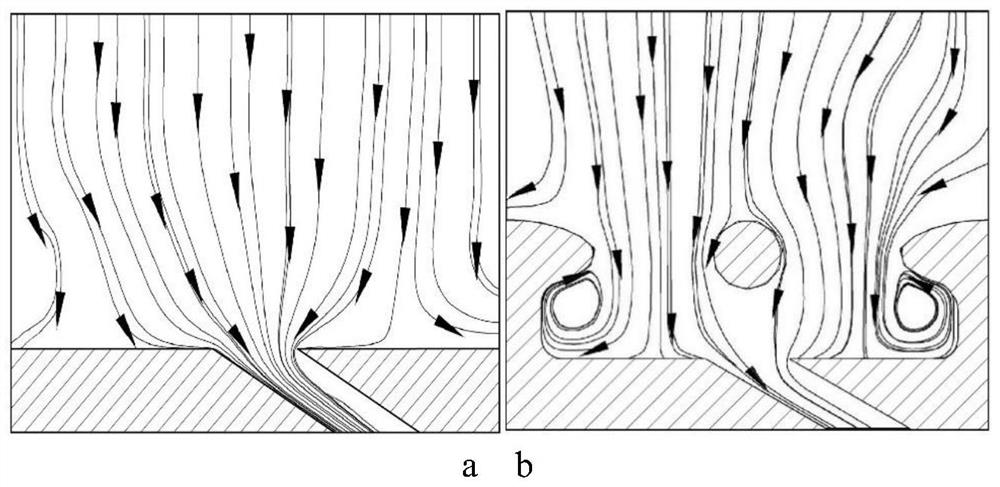
[0039] In the layout of the air film hole, a mode with less flow resistance can be adopted, that is, the cooling air inlet is arranged directly under the triangular mesh, as shown in Image 6 shown. Compared with the first embodiment, although this form reduces the cooling air flow distance and the cooling effect is reduced, it also reduces the flow resistance and loss, and also has the advantage of being easy to observe the clogging of the orifice. Therefore, the position of the air film hole can be reasonably arranged according to different working conditions and the cooling requirements of different positions of the edge plate under the condition that the size of the branch network structure remains unchanged, so as to maximize the utilization of cooling air.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com