SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker for identifying high-risk groups with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and kit and application thereof
A marker and nasopharyngeal carcinoma technology, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and oncology, to improve early diagnosis rate, reduce mortality rate, and improve positive predictive value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1 Genome-wide association analysis to determine new genetic susceptibility loci for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
[0058] In this example, the genome-wide association study and analysis of the population in the high-incidence area of nasopharyngeal carcinoma was carried out, and the SNP sites significantly related to the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma were initially screened out, and further external verification was carried out in an independent population, and finally the SNP sites associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma were identified. SNP sites associated with risk of disease (P-8 ). The specific experimental method is as follows:
[0059] 1. Establish a unified standard specimen bank and database
[0060] For 6,828 nasopharyngeal cancer patients and 10,473 healthy controls, systematically collect complete demographic data and clinical data, collect blood, saliva or oropharyngeal swab samples that meet the standards according to standard operating procedu...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2 Establishment of polygenic genetic risk score model and detection kit for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
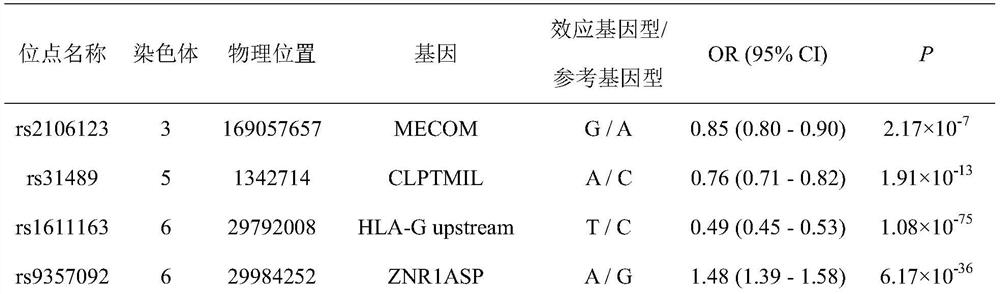
[0076] This example combines the 8 new SNPs (rs1867277, rs226241, rs3131875, rs1611163, rs9357092, rs2596506, rs2844484, rs9268644) obtained in Example 1, and other 6 SNPs (rs2106123, rs31489, rs259650) associated with the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma , rs2251830, rs6475604, rs9507124), through statistical analysis of data, a polygenic genetic risk score model for nasopharyngeal carcinoma and a detection kit were established. The specific experimental methods are as follows:
[0077] 1. Establishment and validation of a polygenic genetic risk score model for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
[0078] According to the GWAS study, we not only found 8 new SNPs associated with the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, but also verified 6 SNPs associated with the incidence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. In order to further study the effect of the comprehensive index c...
Embodiment 3
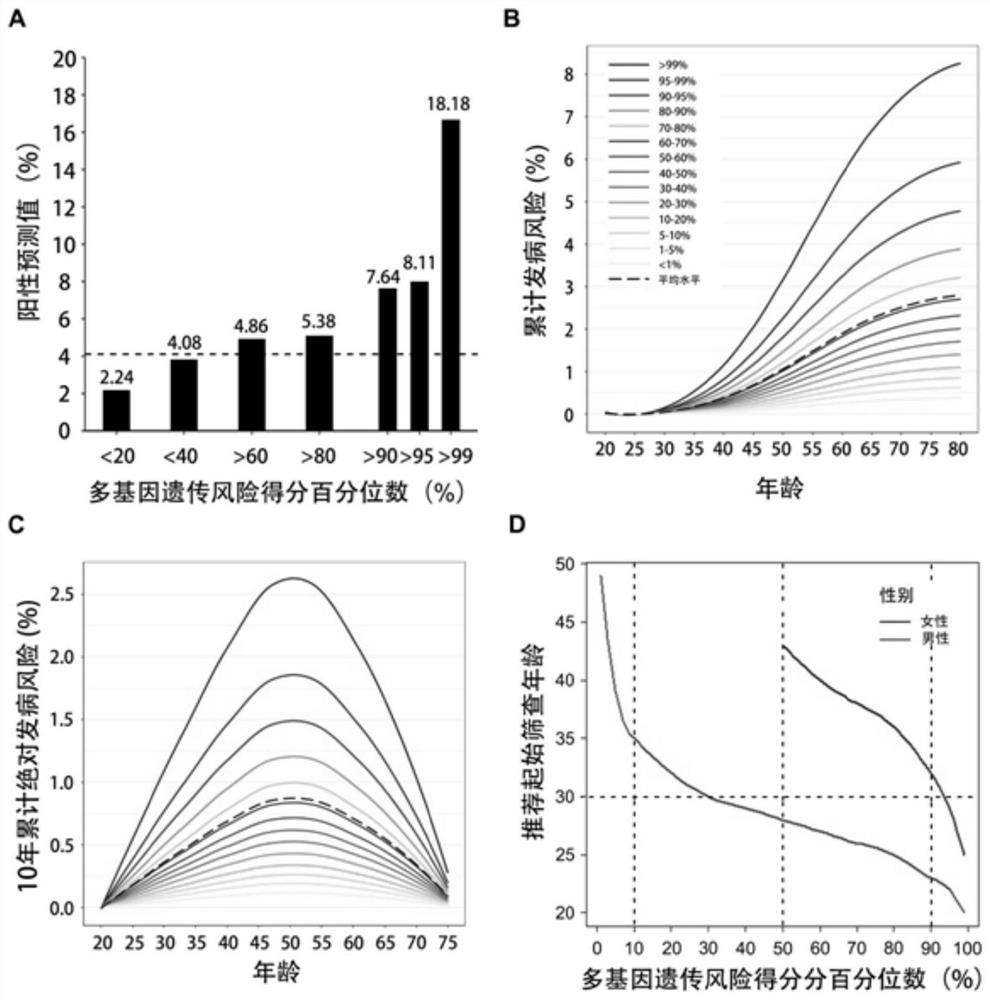
[0136] Example 3 High-risk individuals for nasopharyngeal carcinoma can be effectively identified based on the polygenic genetic risk score for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
[0137] Using the polygenic genetic risk score model and the kit constructed in Example 2, we tested the polygenic risk score for the population.
[0138] The distribution of polygenic risk scores can be obtained according to the scores of polygenic inheritance scores, see Table 2 for details.
[0139] Table 2 Score distribution of polygenic risk score
[0140]
[0141]
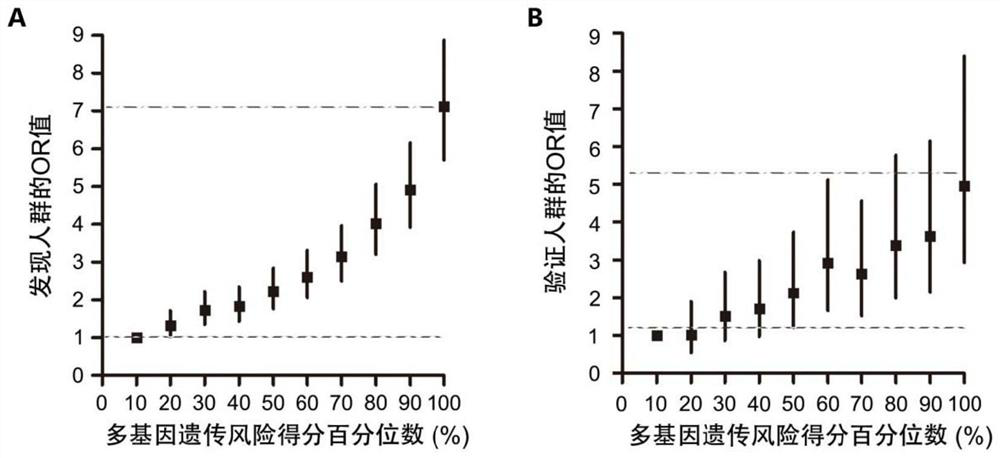
[0142] The dose-effect relationship between polygenic risk score and nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk figure 1 As shown, PRS can effectively identify high-risk groups of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, that is, with the increase of PRS, the risk of developing nasopharyngeal carcinoma gradually increases, and there is a significant dose-effect relationship. Such as figure 1 As shown in (A) in the figure, in the establishment population of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com