Preparation method of polytetrafluoroethylene ultra-thin filament
A PTFE, slender technology, applied in filament/thread forming, one-component halogenated hydrocarbon artificial filament, textile and papermaking, etc., can solve the problem of low shrinkage, easy broken filaments, PTFE Vinyl fibers are prone to burrs and other problems, and achieve the effects of stable elongation at break, improved tensile strength, and low thermal shrinkage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
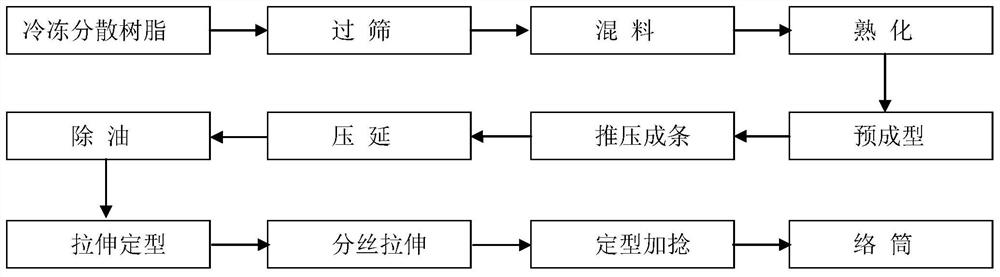
[0050] The preparation method of the polytetrafluoroethylene ultrafine filament described in the present embodiment 1 is made up of the following steps:
[0051] (1) Store the polytetrafluoroethylene dispersed particles in a low-temperature environment for a period of time, and mix them with additive oil in proportion after screening to obtain a polytetrafluoroethylene mixture treated with low-temperature oil, and seal it after screening again spare;
[0052] (2) maturing the polytetrafluoroethylene mixture prepared in step (1) in a high-temperature environment, and then compression molding;
[0053] (3) placing the polytetrafluoroethylene mixture molded in step (2) in a pushing die cavity with a compression ratio of 260 to push and continuously extrude the strip to obtain a polytetrafluoroethylene strip;
[0054] (4) Feed the polytetrafluoroethylene strip through the guide plate into the calender to extrude the film, and the film is degreased through heat treatment;
[0055...
Embodiment 2
[0074] The preparation method of the polytetrafluoroethylene ultrafine filament described in the present embodiment 2 is made up of the following steps:
[0075] (1) Store the polytetrafluoroethylene dispersed particles in a low-temperature environment for a period of time, and mix them with additive oil in proportion after screening to obtain a polytetrafluoroethylene mixture treated with low-temperature oil, and seal it after screening again spare;
[0076] (2) maturing the polytetrafluoroethylene mixture prepared in step (1) in a high-temperature environment, and then compression molding;
[0077] (3) placing the polytetrafluoroethylene mixture molded in step (2) in a pushing die cavity with a compression ratio of 260 to push and continuously extrude the strip to obtain a polytetrafluoroethylene strip;
[0078] (4) Feed the polytetrafluoroethylene strip through the guide plate into the calender to extrude the film, and the film is degreased through heat treatment;
[0079...
Embodiment 3
[0098] The preparation method of the polytetrafluoroethylene ultrafine filament described in the present embodiment 3 is made up of the following steps:
[0099] (1) Store the polytetrafluoroethylene dispersed particles in a low-temperature environment for a period of time, and mix them with additive oil in proportion after screening to obtain a polytetrafluoroethylene mixture treated with low-temperature oil, and seal it after screening again spare;
[0100] (2) maturing the polytetrafluoroethylene mixture prepared in step (1) in a high-temperature environment, and then compression molding;
[0101] (3) placing the polytetrafluoroethylene mixture molded in step (2) in a pushing die cavity with a compression ratio of 260 to push and continuously extrude the strip to obtain a polytetrafluoroethylene strip;
[0102] (4) Feed the polytetrafluoroethylene strip through the guide plate into the calender to extrude the film, and the film is degreased through heat treatment;
[0103...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com