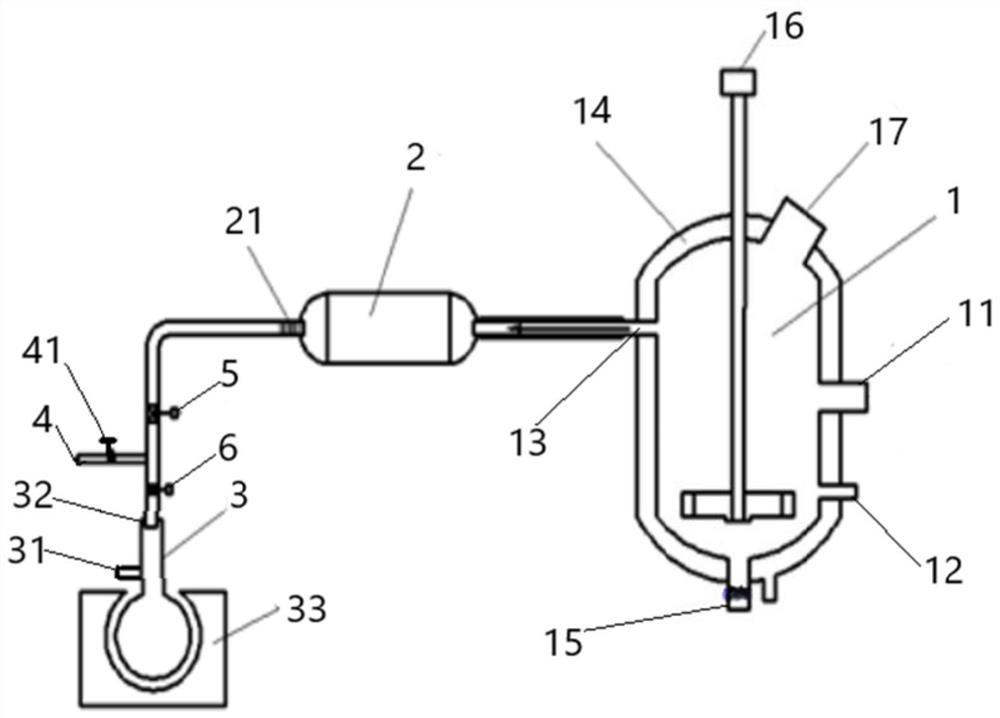
Device and method for preparing gallium chloride
A technology of gallium chloride and ammonium chloride, applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, chemical/physical/physical chemical processes, etc., can solve the problem of low gas utilization rate, high degree of gas dryness, hydrogen chloride gas or chlorine gas Safety hazards and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Use high-purity reagents (that is, the purity is not less than 99.99%, the same below) for raw material preparation, put ammonium chloride and gallium into the reaction kettle at a molar ratio of 6:1, pass a protective gas for a period of time, and remove the reaction kettle The air in the air; the reactor is heated to about 350°C to decompose the ammonium chloride into ammonia and hydrogen chloride, and fully react the generated hydrogen chloride with metal gallium to form gaseous gallium chloride;
[0046] Then, the temperature of the reactor is controlled at 220° C., so that the ammonium chloride generated by the reaction of ammonia gas and excess hydrogen chloride is recrystallized to form solid ammonium chloride, and the gallium chloride is kept in a gaseous state;
[0047] Introduce protective gas through the second protective gas inlet to replace the sealed container, and use a vacuum tube to vacuumize the sealed container; after vacuuming the sealed container, cl...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Use high-purity reagents (that is, the purity is not less than 99.99%, the same below) for raw material preparation, put ammonium chloride and gallium in a molar ratio of 5:1 into the reaction kettle, pass a protective gas for a period of time, and remove the reaction kettle The air in the air; the reactor is heated to about 360°C to decompose ammonium chloride into ammonia and hydrogen chloride, and fully react the generated hydrogen chloride with metal gallium to form gaseous gallium chloride;
[0050] Then the temperature of the reactor is controlled at 240°C, so that the ammonium chloride generated by the reaction of ammonia and excess hydrogen chloride is recrystallized to form solid ammonium chloride and precipitated, and the gallium chloride is kept in a gaseous state;
[0051] Introduce protective gas through the second protective gas inlet to replace the sealed container, and use a vacuum tube to vacuumize the sealed container; after vacuuming the sealed contain...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Use high-purity reagents (that is, the purity is not less than 99.99%, the same below) for raw material preparation, put ammonium chloride and gallium in a molar ratio of 7:1 into the reactor, pass a period of protective gas, and remove the reactor The air in the air; the reactor is heated to about 400°C to decompose the ammonium chloride into ammonia and hydrogen chloride, and fully react the generated hydrogen chloride with metal gallium to form gaseous gallium chloride;
[0054] Then the temperature of the reactor is controlled at 250°C, so that the ammonium chloride generated by the reaction of ammonia and excess hydrogen chloride is recrystallized to form solid ammonium chloride and precipitates, and the gallium chloride is kept in a gaseous state;
[0055] Introduce protective gas through the second protective gas inlet to replace the sealed container, and use a vacuum tube to vacuumize the sealed container; after vacuuming the sealed container, close the first val...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com