Hydrophobic charge-induced chromatography optimal ligand density prediction method
A hydrophobic charge and prediction method technology, applied in the field of chromatographic separation, can solve the problems of expensive ligands and difficult fixation, and achieve the effect of optimizing the development process, reducing workload, and avoiding a large amount of ligand density optimization work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
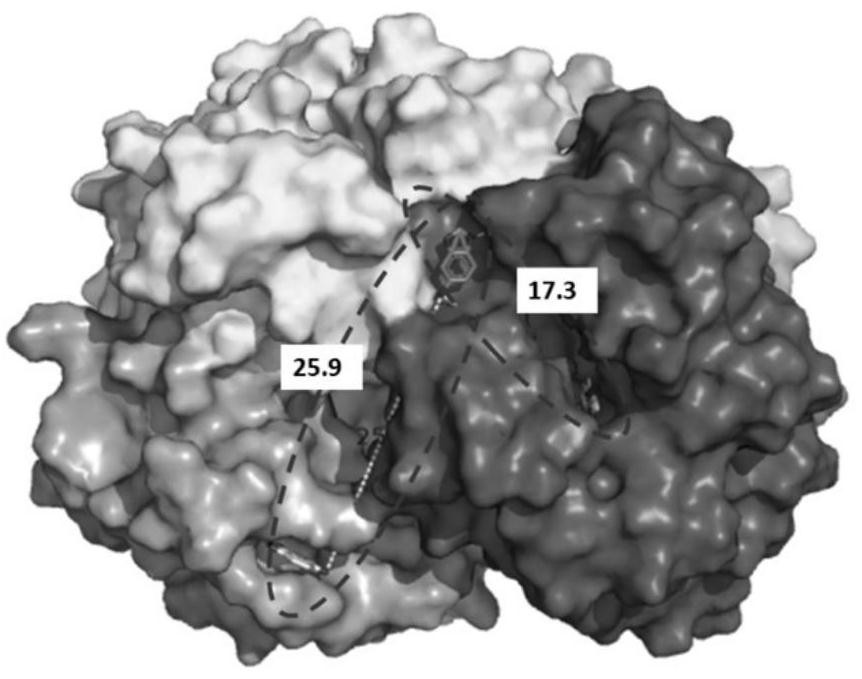
[0038] Obtain the three-dimensional structure data of bovine hemoglobin (2qss) from the RCSB PDB database, and use AutoDock (version 1.5.6) molecular docking software to analyze the recognition site of 5-aminobenzimidazole on the surface of bovine hemoglobin, based on the following principles: 1) The ligand is located in The surface of the protein is convenient for mutual contact; 2) The interaction force between the ligand and the protein is large; 3) The distance between the ligand recognition sites is small; 4) There is no obvious protein protrusion structure between the ligand recognition sites. Based on this, the optimal ligand group was determined, and the distances were determined by the distance measurement function module in the Pymol software as
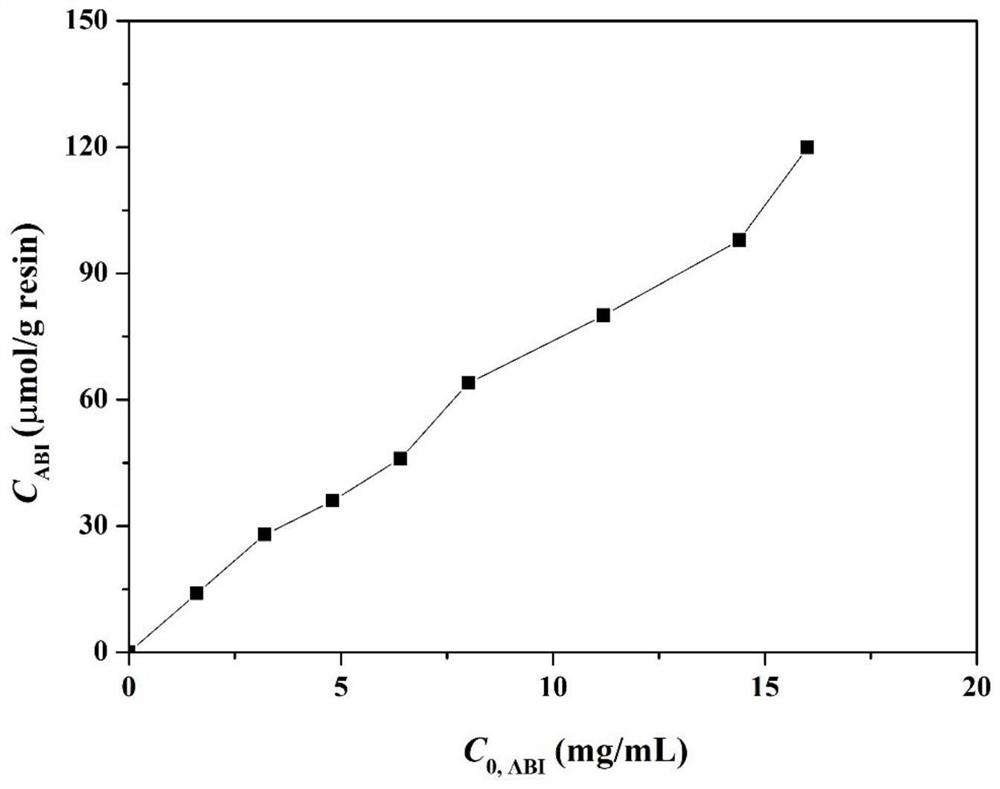
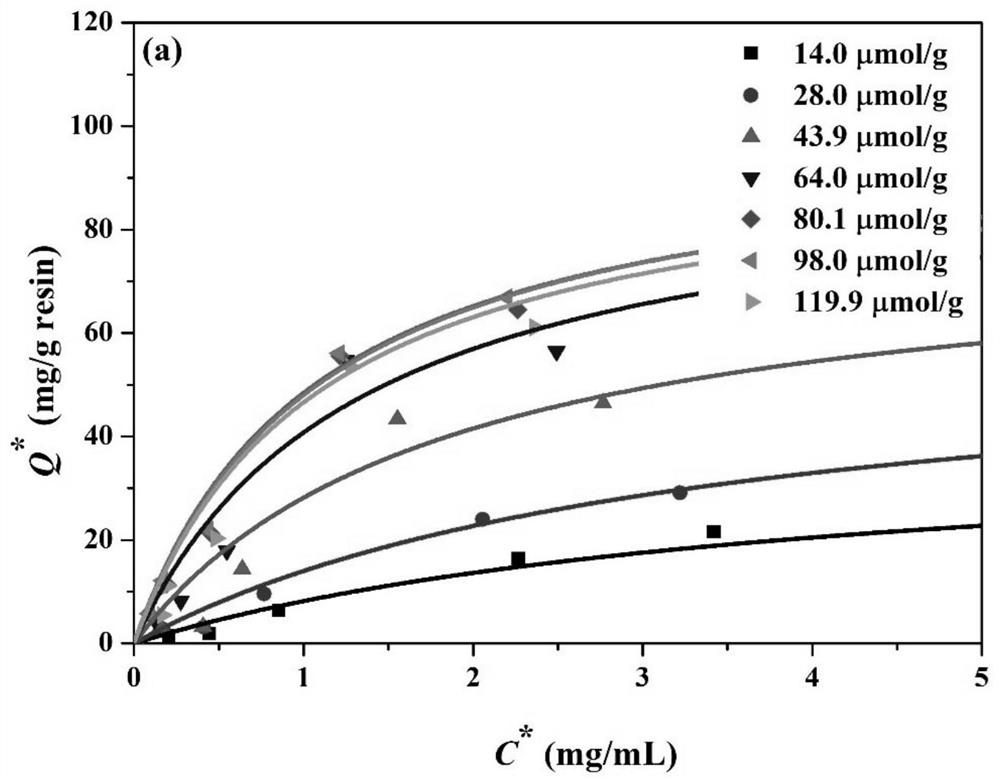
[0039] Take 10g of 4% agarose gel microspheres, measure the matrix pore structure parameters, and obtain a specific surface area of 200m 2 / g. According to the ligand spacing and the specific surface area of microsph...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The three-dimensional structure data of bovine hemoglobin (2qss) was obtained from the RCSB PDB database, and the molecular docking software was used to analyze the recognition site of 5-aminobendazole on the surface of bovine hemoglobin, based on the following principles: 1) The ligands are located on the surface of the protein, which is convenient for mutual contact; 2) The interaction between the ligand and the protein is strong; 3) The distance between the ligand recognition sites is small; 4) There is no obvious protein protrusion structure between the ligand recognition sites. According to this, the optimal ligand spacing is determined as
[0044] Take 10g of 3.5% agarose gel microspheres, measure the matrix pore structure parameters, and obtain a specific surface area of 170m 2 / g. According to the distance between the ligands, the optimal density range is predicted to be 42-94 μmol / g. The microspheres were placed in a 100mL Erlenmeyer flask, 7mL of allyl b...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The three-dimensional structure data of bovine hemoglobin (2qss) was obtained from the RCSB PDB database, and the molecular docking software was used to analyze the recognition site of 5-aminobendazole on the surface of bovine hemoglobin, based on the following principles: 1) The ligands are located on the surface of the protein, which is convenient for mutual contact; 2) The interaction between the ligand and the protein is strong; 3) The distance between the ligand recognition sites is small; 4) There is no obvious protein protrusion structure between the ligand recognition sites. According to this, the optimal ligand spacing is determined as
[0047] Take 10g of 6% agarose gel microspheres, measure the matrix pore structure parameters, and obtain a specific surface area of 250m 2 / g. According to the distance between the ligands, the optimal density range is predicted to be 62-139 μmol / g. The microspheres were placed in a 100mL Erlenmeyer flask, 7mL of allyl br...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com