Heat treatment method for reducing residual stress of forgings
A heat treatment method and residual stress technology, applied in the field of forging, can solve the problems of increasing the number of pick and place forgings, easily generating thermal stress, and difficult to accurately control the temperature, etc., and achieve the effect of simplifying the heat treatment process, reducing the temperature difference of the cross section, and ensuring synchronous cooling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
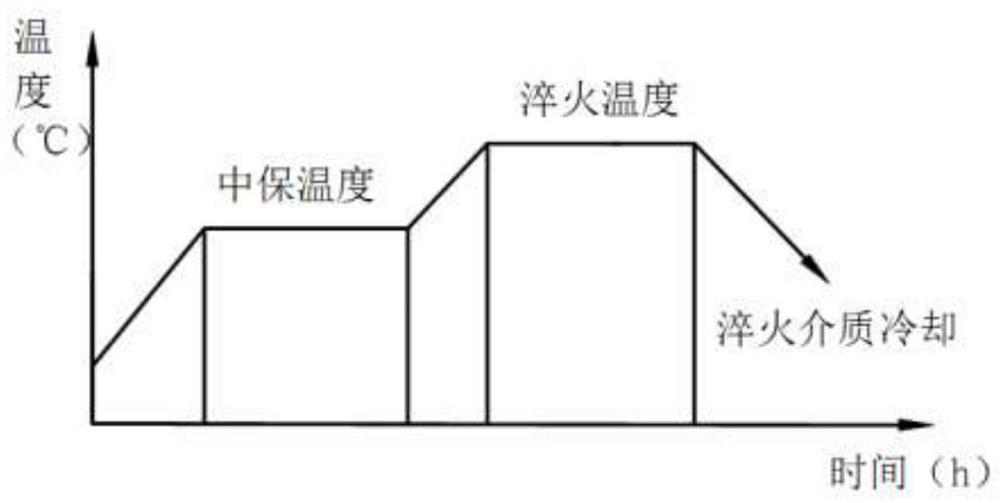
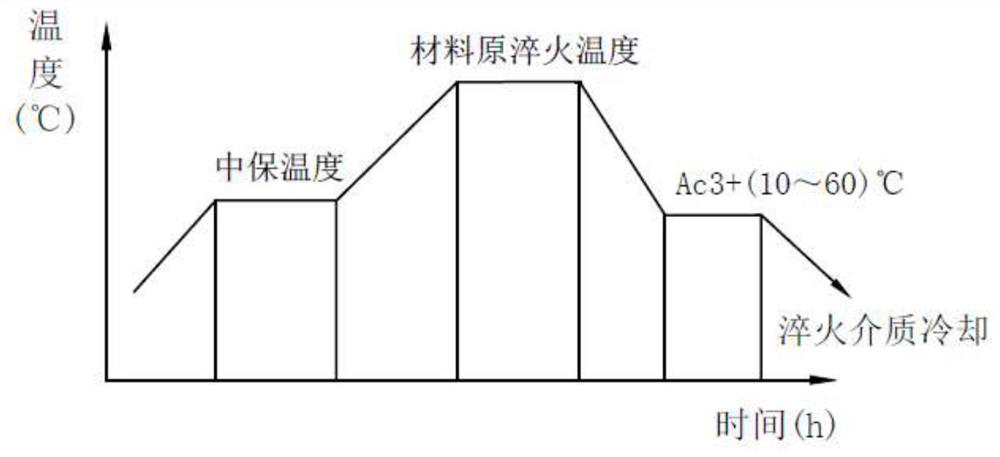
[0037]Taking the forging of φ2200mm×400mm as an example, heat the forging to the medium holding temperature at a heating rate of 40-80°C / h and keep it warm for 200min; then heat the forging to AC3+(50-70 )°C, keep warm for 300min; then cool the forging to AC3+(10-30)°C at a cooling rate of 30-50°C / h, keep warm for 120min; then use water as the quenching medium for quenching and cooling. Temper after cooling.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Taking the forging of φ2200mm×400mm as an example, heat the forging to the medium holding temperature at a heating rate of 40-80°C / h and keep it warm for 200min; then heat the forging to AC3+(50-70 )°C, keep warm for 300min; then cool the forging to AC3+(10-30)°C at a cooling rate of 30-50°C / h, keep warm for 120min; then use oil as the quenching medium for quenching and cooling. Temper after cooling.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Taking the forging of φ2200mm×400mm as an example, heat the forging to the medium holding temperature at a heating rate of 40-80°C / h and keep it warm for 250min; then heat the forging to AC3+(40-50 )°C, keep warm for 350min; then cool the forging to AC3+(10-30)°C at a cooling rate of 30-50°C / h, keep warm for 150min; then use water as the quenching medium for quenching and cooling. Temper after cooling.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com