Methods for recovering and reusing selective homogeneous hydrogenation catalyst
A hydrogenation catalyst and selective technology, which is applied in the direction of carbon compound catalyst, physical/chemical process catalyst, organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalyst, etc. period, the effect of reducing harmful effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
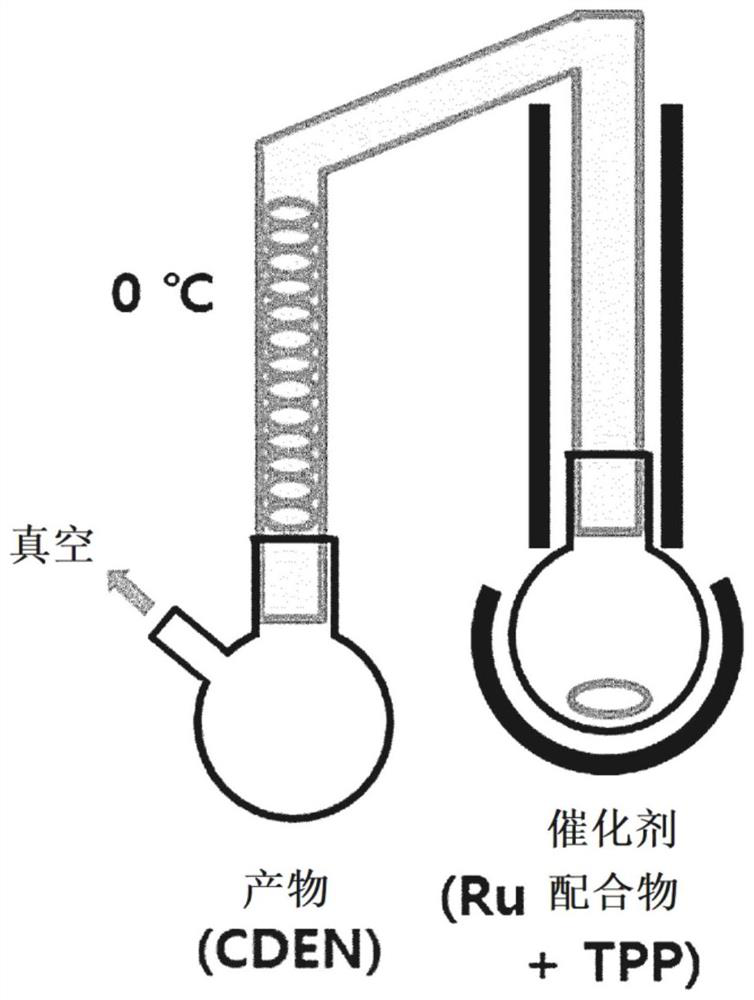
[0090] Cyclododecatriene (CDT), ruthenium chloride (RuCl 3 ), triphenylphosphine (TPP) and formaldehyde, the reaction solution was stirred under the condition of 6 bar hydrogen, and the selective hydrogenation was carried out at 160° C. and 20 bar for 2 hours. In this case, the reaction was carried out in a stirred tank reactor equipped with a gas induction hollow stirrer.
[0091] Selective hydrogenation was performed for 2 hours, the temperature was cooled to 30°C or lower under nitrogen to recover the reaction solution, and the reaction solution was distilled in a distillation apparatus at 0.1 bar or less and 110°C.
[0092] After the distillation is complete, the temperature is cooled to 30° C. or lower under nitrogen to recover the selective homogeneous hydrogenation catalyst.
Embodiment 2
[0094] Selective hydrogenation was performed by newly adding the recovered selective homogeneous hydrogenation catalyst to the reaction solution in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0095] More specifically, cyclododecatriene (CDT) and the recovered selective homogeneous hydrogenation catalyst were added in a molar ratio of 7500:1, the reaction solution was stirred under 6 bar hydrogen and kept at 160 °C and 20 bar Selective hydrogenation was carried out under the condition of 2 hours. In this case, the reaction was carried out in a stirred tank reactor equipped with a gas induction hollow stirrer.
[0096] Selective hydrogenation was performed for 2 hours, the temperature was cooled to 30°C or lower under nitrogen to recover the reaction solution, and the reaction solution was distilled in a distillation apparatus at 0.1 bar or less and 110°C.
[0097] After the distillation is complete, the temperature is cooled to 30° C. or lower under nitrogen to recover the selective ho...
experiment example 1
[0099]
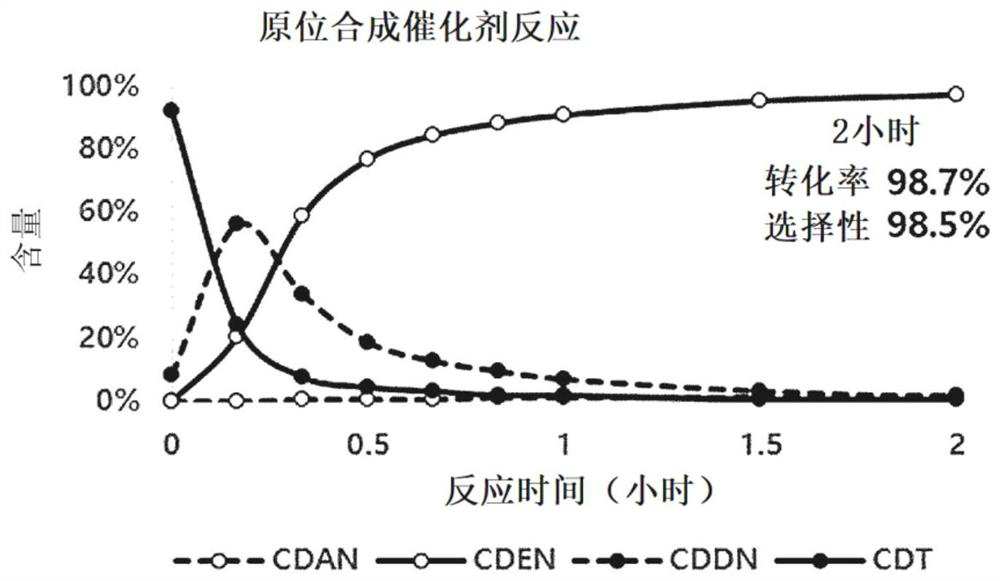
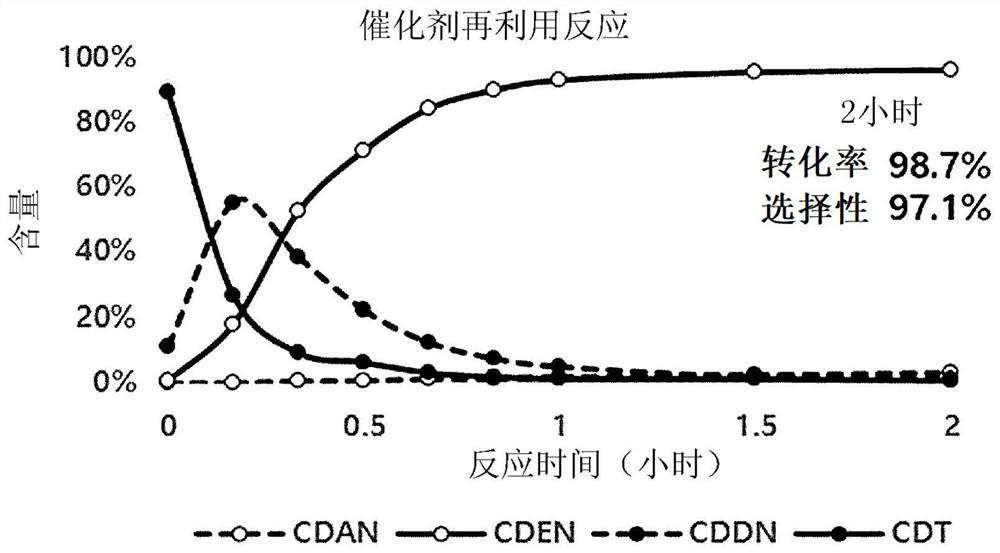
[0100] The conversion and selectivity of the recovered selective homogeneous hydrogenation catalyst for each of Example 1 and Example 2 were calculated. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0101] [Table 1]
[0102] Conversion rate(%) Selectivity (%) Example 1 98.7 98.5 Example 2 98.7 97.1
[0103] As a result, as shown in Table 1, it could be confirmed that the conversion and selectivity in the initial selective hydrogenation were almost the same as those in the second selective hydrogenation using the recovered selective homogeneous hydrogenation catalyst. Specifically, it can be determined that C 2 / C 1 × 100 is 100, which indicates that the conversions in the two reactions are the same as each other, and S 2 / S 1 ×100 was 98.6, which indicated that the selectivities in the two reactions were almost the same as each other.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com