Preparation method of solid waste-based cementing material early strength auxiliary agent
A technology of strong auxiliary agent and base glue, which is applied in the field of preparing early strength auxiliary agent for solid waste-based cementitious materials, can solve the problems of poor activity of steel slag and low early strength of cementitious materials, etc., so as to improve the early strength and the later stage. the effect of strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] 1) Calcining desulfurized gypsum at 700°C for 1 hour to obtain anhydrous desulfurized gypsum;
[0025] 2) Anhydrous desulfurized gypsum accounts for 30% of the weight of mixed desulfurized gypsum;
[0026] 3) Mix 85% slag, 5% waste incineration fly ash, 7% mixed desulfurized gypsum, 5% calcium aluminate cement, 3% refining slag and 35% water, place at room temperature for 48 hours, and then react at 70-80°C for 24 hours, Dried and ground to make early strength additives;
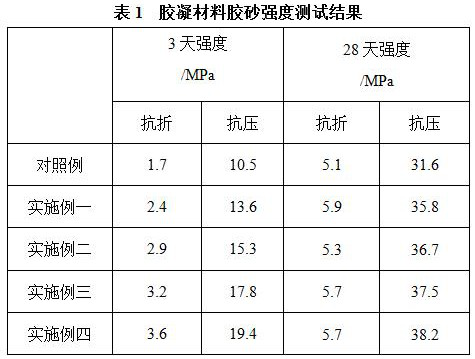
[0027] 4) Replace 1% of the steel slag in the control example with 1% of the early-strength additive to make a cement mortar test piece, and carry out the strength test after curing to the age.
Embodiment 2
[0029] 1) Calcining desulfurized gypsum at 600°C for 1 hour to obtain anhydrous desulfurized gypsum;
[0030] 2) Anhydrous desulfurized gypsum accounts for 45% of the weight of mixed desulfurized gypsum;
[0031] 3) Mix 90% slag, 2% waste incineration fly ash, 6% mixed desulfurized gypsum, 2% calcium aluminate cement, 2% refining slag and 35% water, place it at room temperature for 48 hours, and then react at 70-80°C for 24 hours, Dried and ground to make early strength additives;
[0032] 4) Replace 2% steel slag in the control example with 2% early strength additives to make cement mortar specimens, and perform strength tests after curing to age.
Embodiment 3
[0034] 1) Calcining desulfurized gypsum at 650°C for 1 hour to obtain anhydrous desulfurized gypsum;
[0035] 2) Anhydrous desulfurized gypsum accounts for 30% to 70% of the weight of mixed desulfurized gypsum;
[0036] 3) Mix 82% slag, 4% waste incineration fly ash, 10% mixed desulfurized gypsum, 3% calcium aluminate cement, 5% refining slag and 35% water, place it at room temperature for 48 hours, and then react at 70-80°C for 24 hours, Dried and ground to make early strength additives;
[0037] 4) Replace 3% of the steel slag in the control example with 3% early-strength additives to make cement mortar specimens, and perform strength tests after curing to age.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com