Tissue clearing kits and methods
A kit and reagent technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of shaping and inability to realize biological tissue, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] In this embodiment, the small intestine tissues of C57 mice (fixed by 4% paraformaldehyde and 2 cm in length) were used, and three experimental groups (numbered as I, II, III) and three control groups (numbered as IV, V) were set up. , VI). Please refer to Table 1 for the composition and concentration of reagent 1 and reagent 2 in the experimental group, and the composition and concentration of the replacement reagent in the control group. In the three control groups, the glucose was replaced by mannose, fructose and sorbitol, respectively. In this embodiment, the tissue clearing method of the present invention is adopted. For the incubation temperature and time of the tissue, please refer to Table 2. See Table 3 for the experimental results.
[0044] Table 1 Reagent composition and concentration of experimental group and control group
[0045]
[0046] Table 2 The incubation temperature and time of the experimental group and the control group
[0047]
[0048...
Embodiment 2
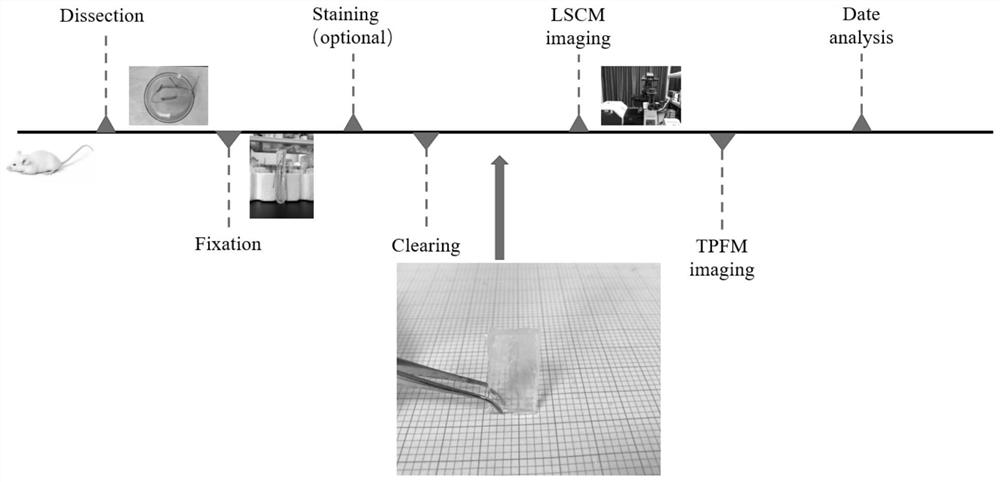
[0053] The cleared tissue can be sequentially imaged and observed under confocal, two-photon and light-sheet microscopes. figure 1 Observation process of mouse small intestine tissue imaging, including dissection (Dissection), fixation (Fixation), staining (Staining), clearing (Clearing), LSCM imaging (Imaging), TPFM imaging (Imaging) and data analysis (Date Analysis) . The specific process is: after the mouse is anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium, 0.01M sodium citrate-phosphate buffer solution is perfused through the apex of the heart, until the blood in the mouse body is completely replaced, the required After the tissue was fixed overnight with 4% paraformaldehyde, it was sequentially soaked in the reagent 1 and the reagent 2 for clearing treatment, and finally imaged under a microscope.
[0054] In this embodiment, the reagent one includes: 30% m-xylylenediamine, 5% urea, and 10% glucose; the second reagent includes: 40% m-xylylenediamine, and 40% glucose. In the rea...
Embodiment 3
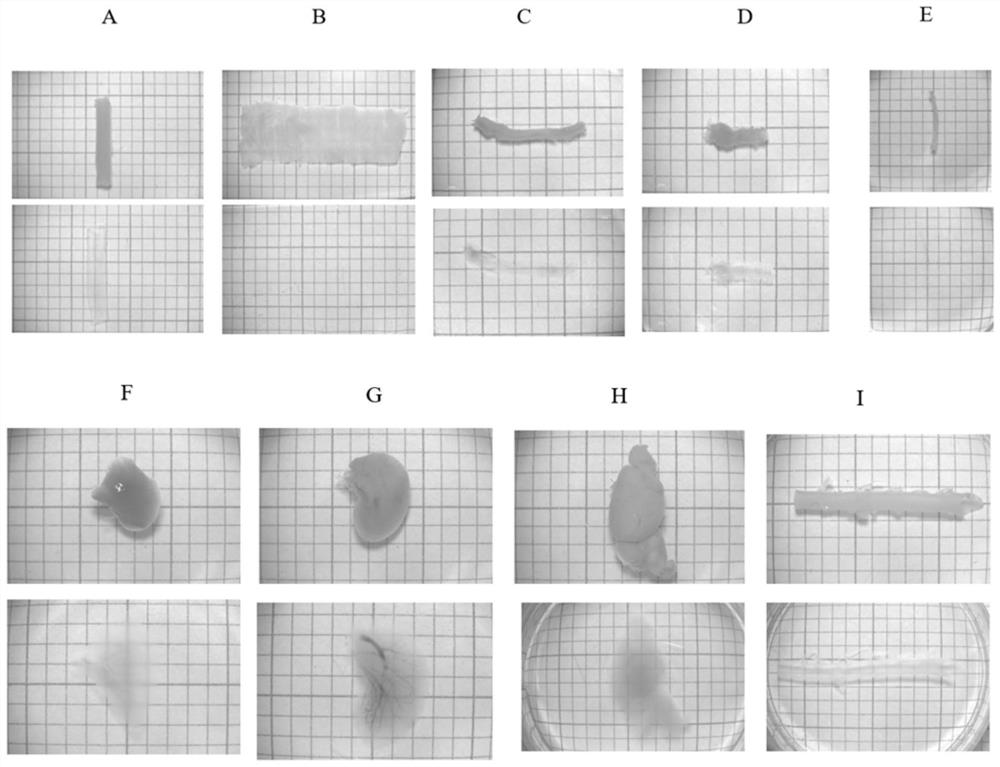
[0057] This embodiment compares the clearing effect of the method of the present invention and the existing clearing method on the tissue. The sample adopts the small intestine tissue of C57 mice, including the experimental group (the method of the present invention, PHCS) and three control groups (CUBIC, MACS, FOCM ). Three samples were selected for each group, and their light transmittances in the wavelength range of 400nm to 800nm were measured respectively, and the average value was calculated.
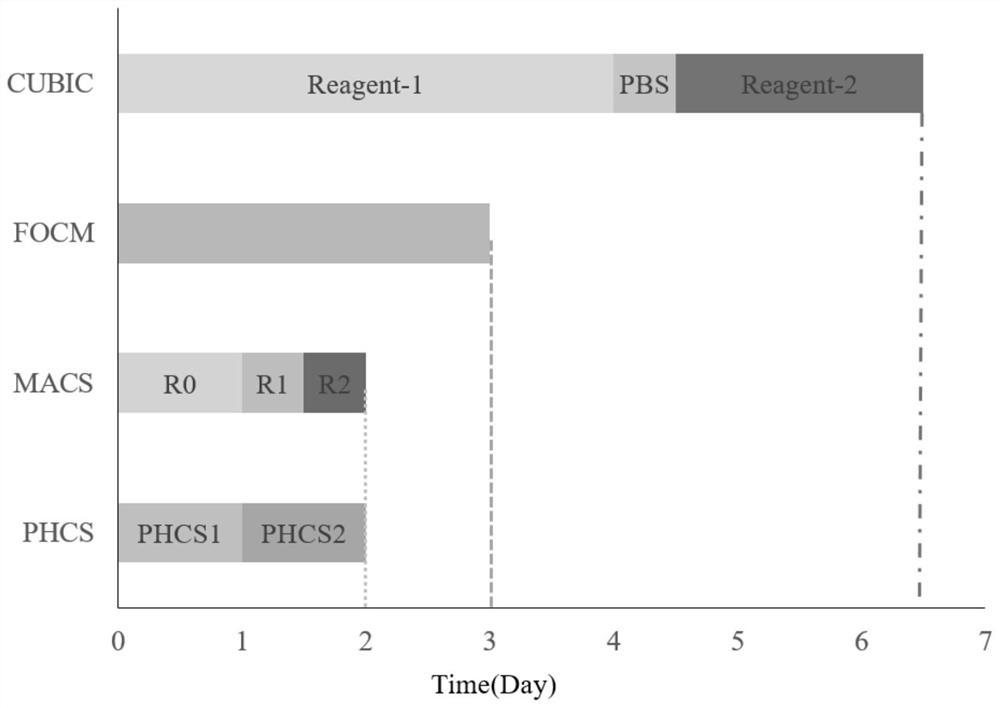
[0058] image 3 Procedure and timing for processing small intestinal tissue for four clearing methods. Specifically, the experimental group (PHCS): soak the tissue in the reagent one (PHCS1, containing 30% m-xylylenediamine, 5% urea, and 10% glucose), incubate at 25°C for 12h to 24h, and then The tissue was soaked in the reagent 2 (PHCS2, containing 40% m-xylylenediamine and 40% glucose), and incubated at 4°C for 12h-24h. Control group (CUBIC): soak the tissue in Reagent-1 (c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| transmittivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transmittivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com