First-order reliability analysis method based on kkt condition and differential evolution algorithm
A technology of differential evolution and analysis method, which applies in-effective reliability analysis model, reliability analysis of differential evolution group intelligent optimization algorithm, and first-order second-order moment method to analyze structural reliability, which can solve slow convergence and reliability analysis Problems such as poor result accuracy and loss of limit state function constraints have achieved the effects of ensuring accuracy, extending validity and versatility, and ensuring convergence and stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
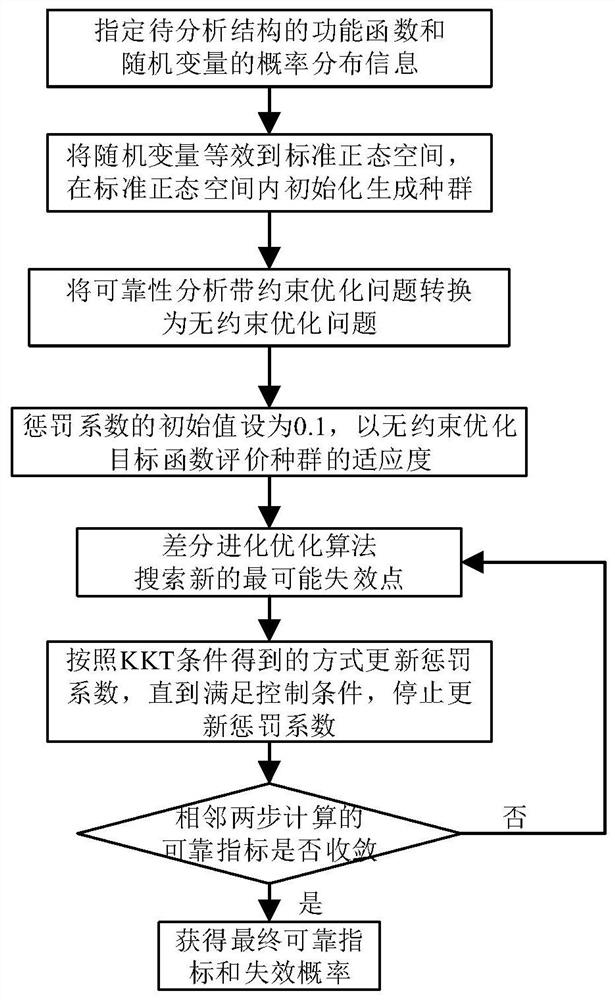
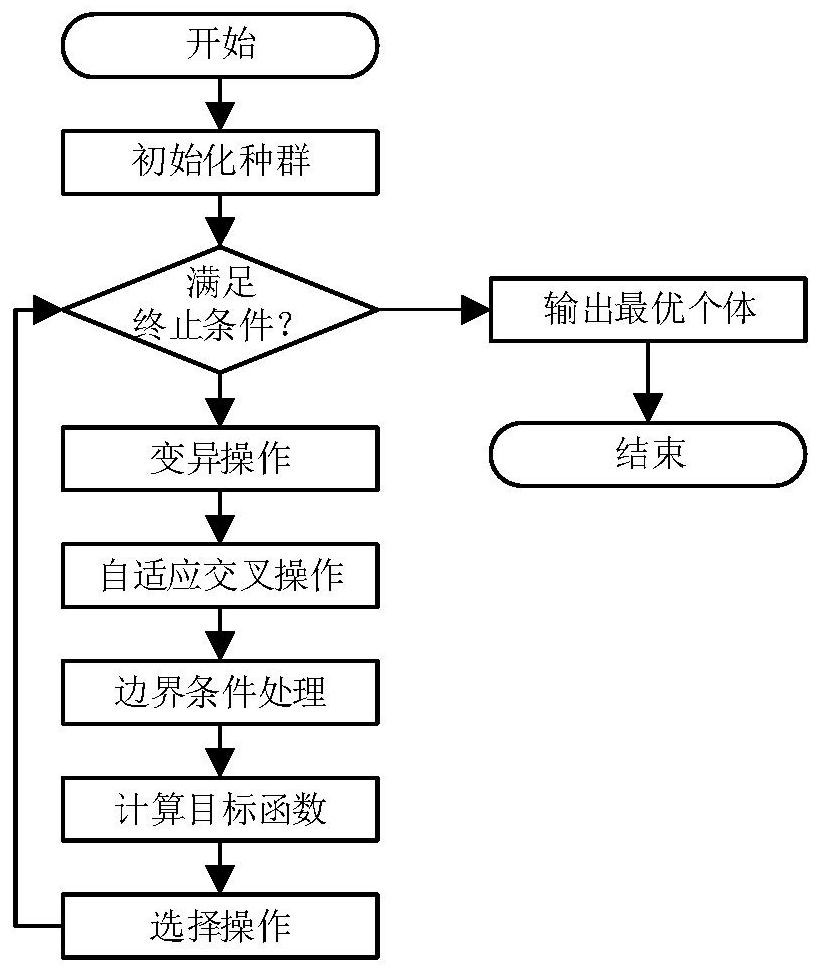
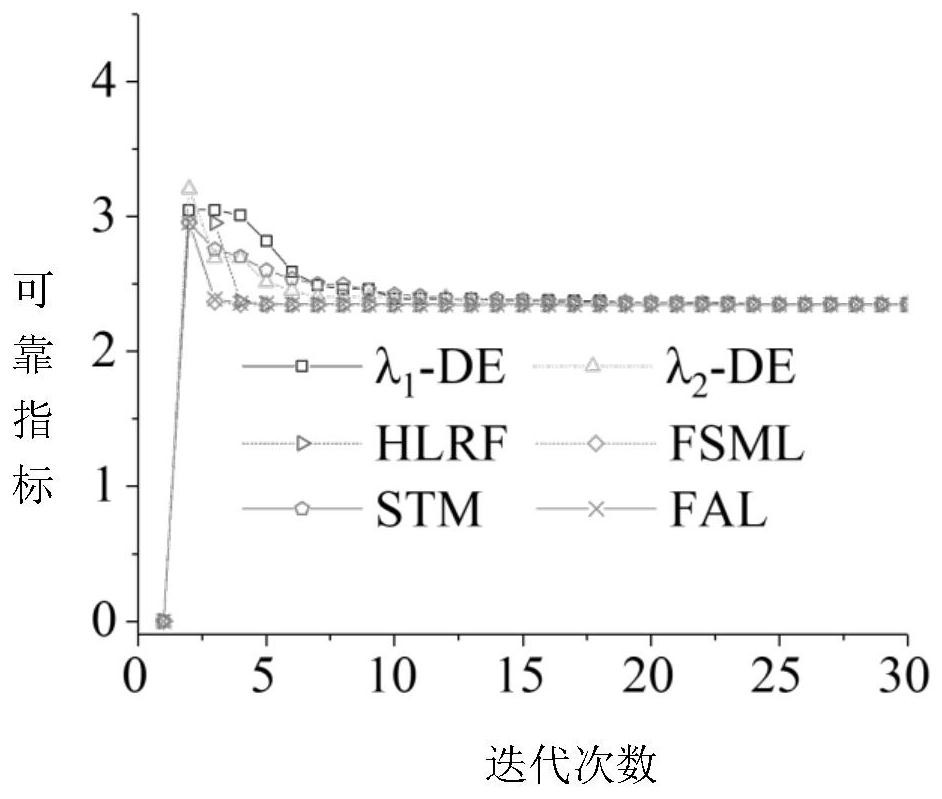
[0045] figure 1 This is a flow chart of a reliability analysis method based on the KKT conditional equivalent reliability analysis model and the differential evolution group intelligent optimization algorithm provided by this embodiment, and includes 7 steps in total. figure 2 This is the flow chart of the intelligent optimization algorithm of differential evolution swarms. The operators in the adaptive mutation operation mechanism are in the form of triangular distribution in the iterative process, and the number of consecutive successes of individuals reaches 15 dynamic adaptive adjustments. The present embodiment 1 further illustrates the present invention with a 6-dimensional application example.
[0046] Step S1, specify the function function g(x) of the structure to be analyzed, as follows:
[0047]
[0048] Random variable of function function x = [x 1 ,…,x i ,…] and its probability distribution information as follows:
[0049] Table 1. Random variable characte...
Embodiment 2
[0058] This embodiment continues to disclose a reliability analysis method based on the KKT conditional equivalent reliability analysis model and the differential evolution swarm intelligent optimization algorithm. The operators in the adaptive mutation operation mechanism are in the form of triangular distribution. The number of successful dynamic adaptive adjustments reaches 15 times, and the reliability analysis method includes the following steps:
[0059] Step S1, specify a master-slave two-degree-of-freedom dynamic system structure to be analyzed (such as Figure 4 The functional function g(x) of the schematic diagram shown) is as follows:
[0060]
[0061] g=F s -k s p[E(x s 2 )] 1 / 2
[0062] Among them, ω p =(k p / m p ) 0.5 , ω s =(k s / m s ) 0.5 , ω a =(ω p +ω s ) / 2, ξ a =(ξ p +ζ s ) / 2, v=m s / m p , η=(ω p -ω s ) / ω a , p=3. Random variable x=[m for function function p , m s , …] and its probability distribution information as follows:
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com