Method for QTL framework of tree quantitative traits based on Richards equation
A quantitative trait, positioning framework technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics analysis, can solve problems such as incompleteness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
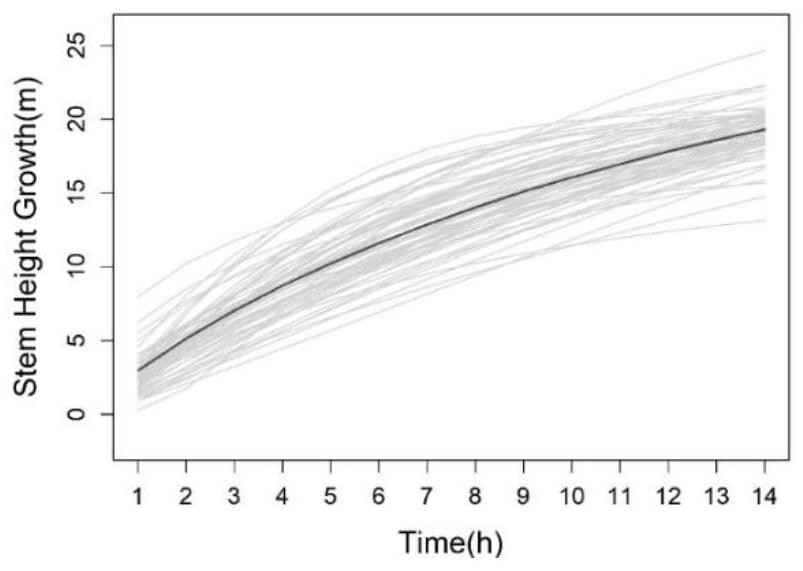
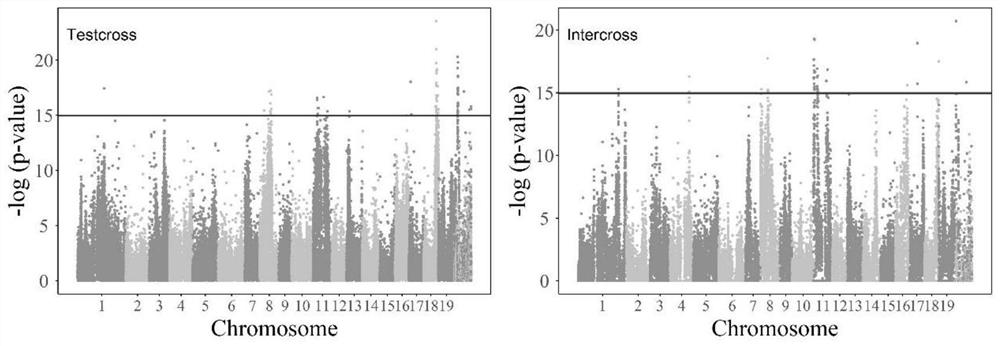
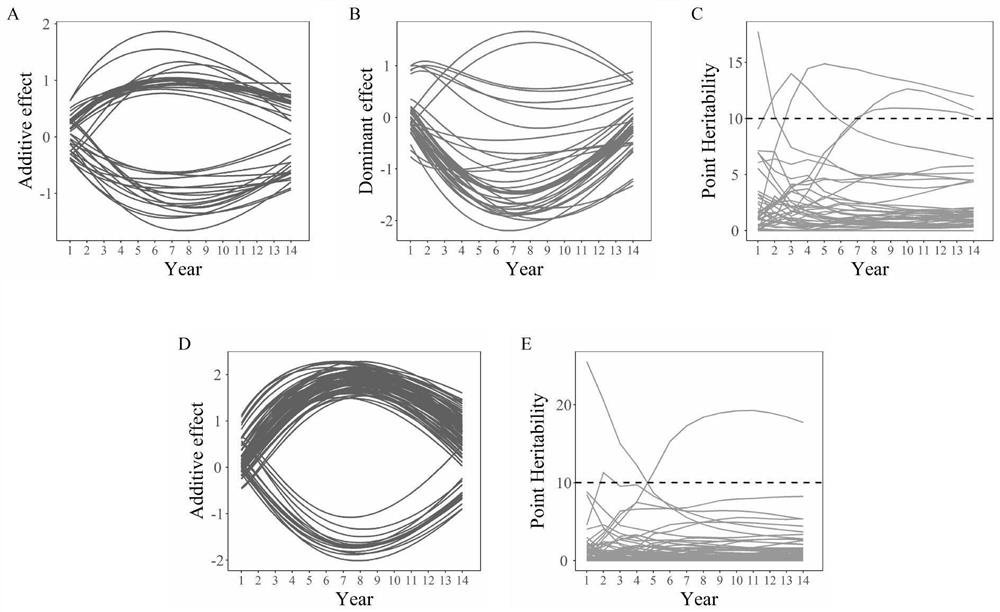
[0136]The stem height growth data disclosed in A computational framework for mapping the timing of vegetative phase change (New Phytologist; 211:750-60, 2016) published by Meng Xu et al. is used as an example to further describe the present invention in detail. The sample data comes from 450 progenies obtained by artificial crossing with the American black poplar clone (I-69) as the female parent and the European and American poplar clone (I-45) as the male parent, and they were uniformly planted in Zhangji Forest Farm (34.14° N, 117.38°W). The applied phenotypic data include the growth of stem height and diameter growth of 64 randomly selected offspring and female parent I-69, male parent I-45, a total of 66 forest poplar samples in the first 14 years of growth (1987-2010). Data, gene data is 156362 SNP information distributed on 19 chromosomes. In the genetic data, 94591 SNPs are test cross markers, and 61771 SNPs are hybrid markers. Tester markers are those in which one p...
Embodiment 2
[0194] 1. Use the quasi-Newton method to fit the growth data of the poplar sample diameter.
[0195] The above-mentioned phenotypic data of poplar quantitative traits were used to fit the Richard equation, and the estimated parameters of the equation were obtained by searching. The Richard equation is shown in equation (3):
[0196]
[0197] Among them, b 1 Represents growth limit; b 2 represents the shape parameter; b 3 is a parameter related to growth rate, and y represents the fitted value of diameter growth.
[0198] The fitting Richard equation is fitted by the least square method; the search method of the estimated parameter is the BFGS quasi-Newton method, and the Richard estimated parameter that makes the sum of the squares of the diameter phenotype value and the fitted value minimum is found, specifically through the R language General optimization method optim function implementation.
[0199] Figure 5 is the Richard growth curve of poplar diameter, wherein...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com