Hazard management method based on database model
A management method and database technology, applied in the field of safety-critical systems, can solve problems such as the inability to reflect hazards and sub-hazards, the relationship between hazards and mitigation measures, insufficient risk control, and increased workload, so as to avoid duplication of work or mistakes. Citing, improving efficiency and quality, reducing the effect of ambiguous errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
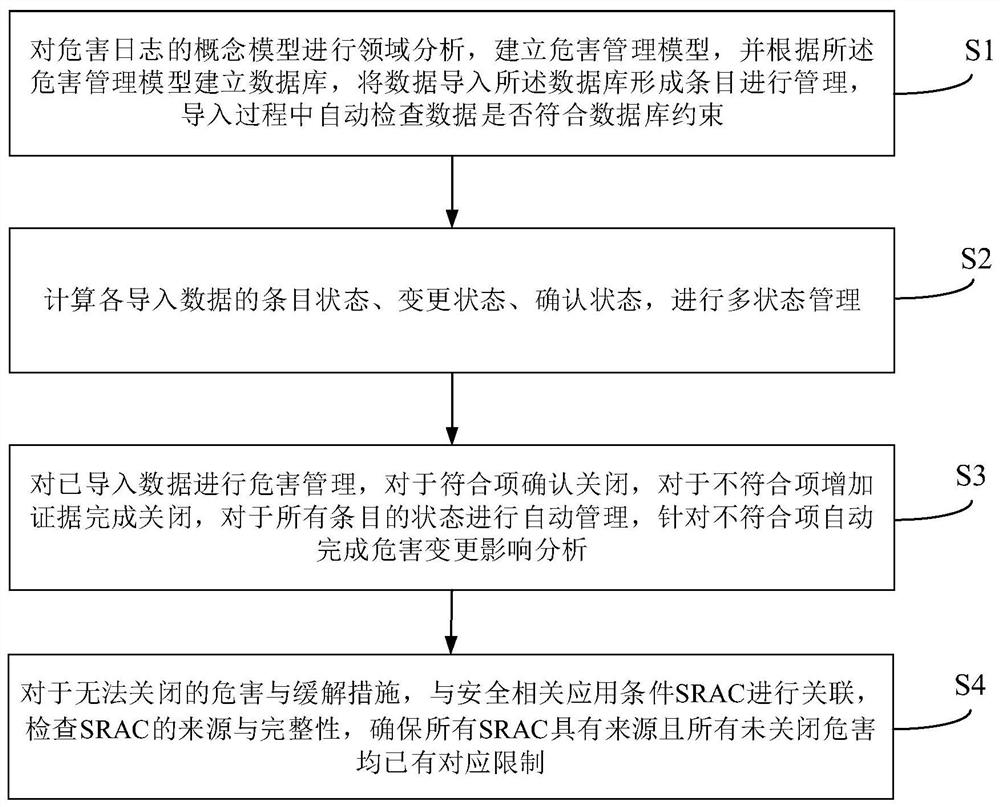
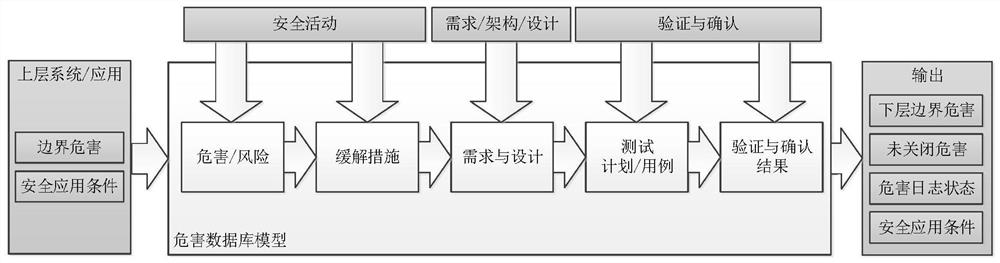
[0056] The solution proposed by the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. The advantages and features of the present invention will become clearer from the following description. It should be noted that the drawings are in a very simplified form and all use imprecise scales, which are only used to facilitate and clearly assist the purpose of illustrating the embodiments of the present invention. In order to make the objects, features and advantages of the present invention more comprehensible, please refer to the accompanying drawings. It should be noted that the structures, proportions, sizes, etc. shown in the drawings attached to this specification are only used to match the content disclosed in the specification, for those who are familiar with this technology to understand and read, and are not used to limit the implementation of the present invention. condition, so it has no te...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com