Method for detecting beta-carotene, astaxanthin and starch in haematococcus pluvialis under nitrogen stress
A technology of Haematococcus pluvialis and carotene, applied in the field of far-infrared spectroscopy, can solve problems such as the difficulty in realizing simultaneous and real-time monitoring of multiple metabolites, and achieve the effect of simplifying procedures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
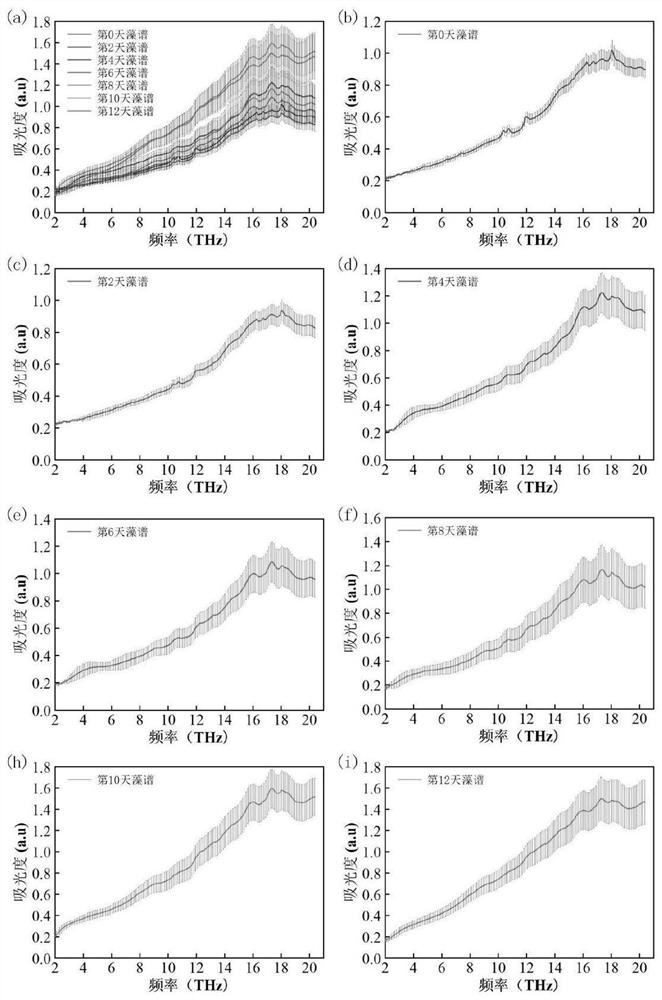
[0037] (1) Terahertz sample preparation
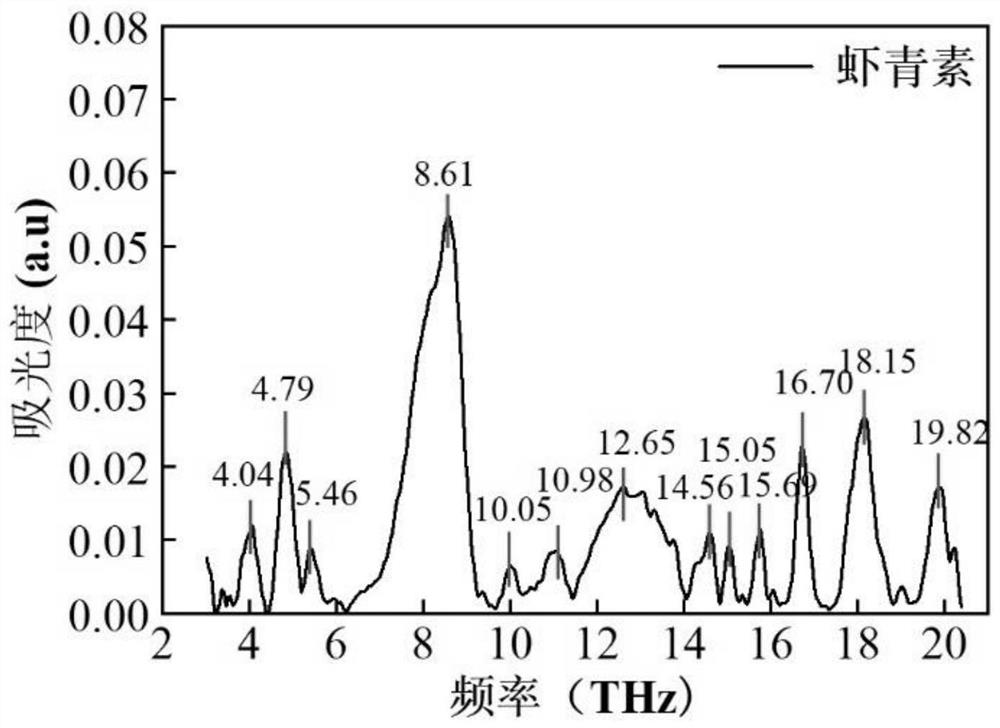
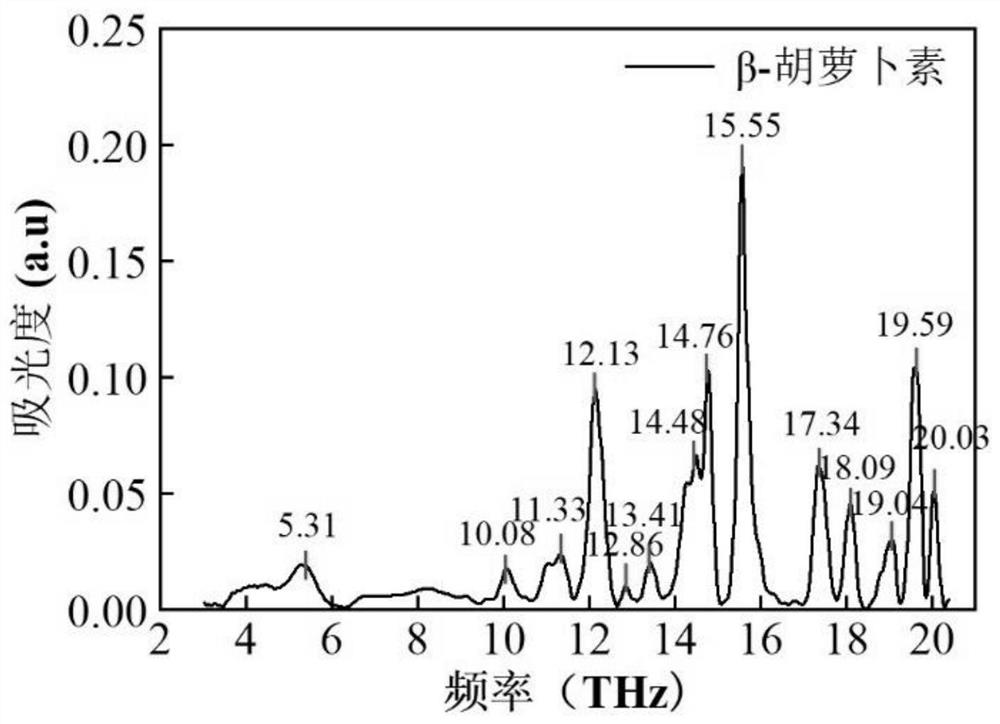
[0038] Pure product sample preparation: Weigh 15 mg of standard astaxanthin, 20 mg of starch, and 15 mg of β-carotene, and place them in a mold with a diameter of 13 mm for pressing. Two circular samples were prepared for each standard for terahertz standard spectrum testing. The spectrum acquisition of terahertz samples is easily affected by moisture, so it is necessary to dry the microalgae samples at a certain concentration into thin film samples to eliminate the influence of moisture.
[0039] Microalgae sample preparation: add distilled water to 1ml of 100mg of algae sludge obtained after repeated centrifugation of the algae liquid and washing with ultrapure water. Put each 1ml algae liquid sample into a smooth polystyrene mold with a diameter of 20mm for drying, set a drying oven at 30-40°C for 3 hours, and finally make a uniform and semi-permeable algae film, and measure each The thickness of a sample of algae film. The thick...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com