Interleaved Memory Pseudo-Random Mapping Method for Parallel Computing
A mapping method and parallel computing technology, applied in the field of memory, can solve the problems that different address lengths cannot be flexibly expanded, and the realization circuit is complicated, and achieve the effect of improving parallel access and parallel computing performance, easy design, and improving parallel storage performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] Suppose the interleaved memory contains 8 memory blocks, namely M=3, B=2 M =8; the block address of each storage block is K=29 bits. So the full address of the entire interleaved memory is M+K=32 bits.
[0111] S1: Since B-1≤M+K, there is no need to divide M;
[0112] S2: Use M=3 as the order to check the table of commonly used primitive polynomials to obtain the primitive polynomial F(x)=x 3 +x+1;
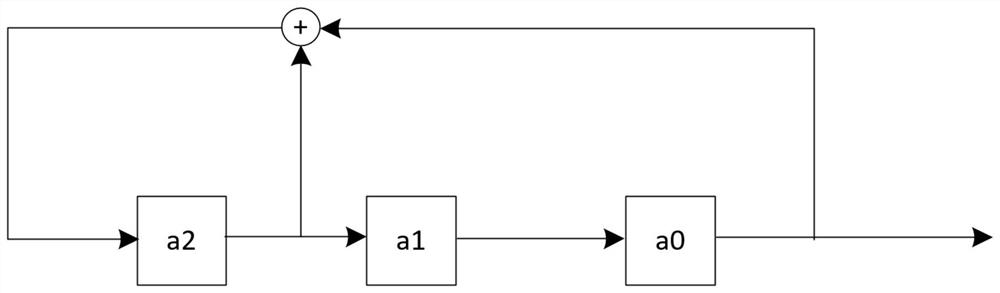
[0113] S3: The linear feedback shift register circuit corresponding to F(x) is as follows figure 1 .
[0114] Set the initial states of the three shift registers {a2,a1,a0}={0,0,1}, by shifting 6 times and adding the initial state, 7 groups of shift register states that do not repeat can be obtained, respectively {0,0,1}, {1,0,0}, {1,1,0}, {1,1,1}, {0,1,1}, {1,0,1}, {0 ,1,0}; Thus, each state as a column can form an H matrix with 3 rows and 7 columns, namely:
[0115] column 6 column 5 column 4 column 3 column 2 column 1 column 0 0 1 0 1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0126] Assume that the interleaved memory includes 128 memory blocks, ie M=7, B=2M=128; the address within the block of each memory block is K=25 bits. So the full address of the entire interleaved memory is M+K=32 bits.
[0127] S1: Since B-1>M+K, it is necessary to divide M, here M is divided into two parts, let M 1 = 4, M 2 = 3, then B 1 =16,B 2 = 8;
[0128] S2: Use M 1 and M 2 As the order, look up the primitive polynomial table to get the primitive polynomial F 1 (x)=x 4 +x+1 and F 2 (x)=x 3 +x+1.
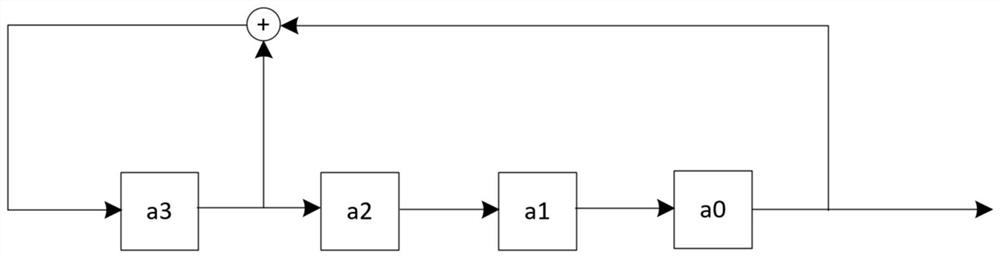
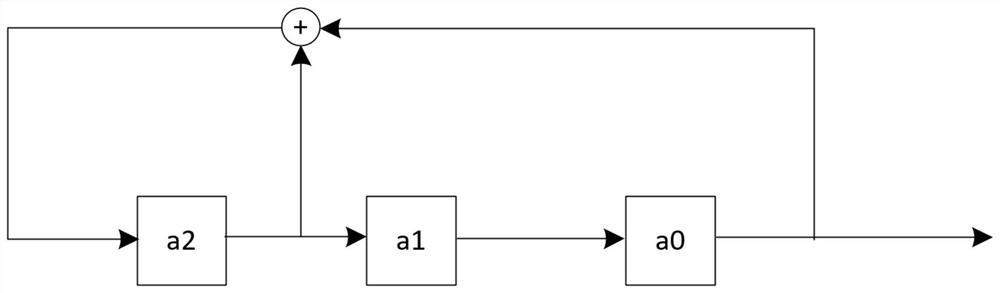
[0129] S3: According to F 1 (x) and F 2 (x) corresponds to the linear feedback shift register circuit (respectively as figure 2 with image 3 shown), get H 1 and H 2 matrix.
[0130] h 1 matrix:
[0131] column 14 column 13 column 12 column 11 column 10 column 9 column 8 column 7 column 6 column 5 column 4 column 3 column 2 column 1 column 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com