Magnesium phosphate cement containing C7A5M minerals and preparation method thereof
A magnesium phosphate cement, C7A5M15 technology, applied in the field of building materials, can solve problems such as poor water resistance, achieve the effects of improving mechanical properties, reducing preparation costs, and solving water resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
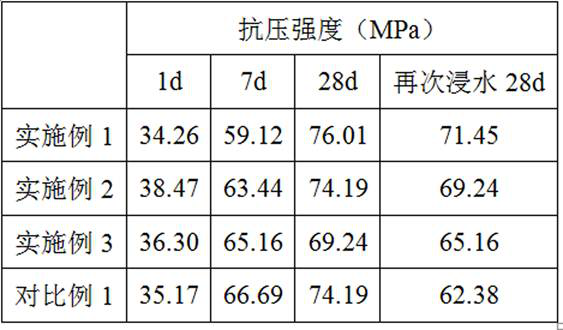
Embodiment 1
[0032] a C 7 A 5 Magnesium phosphate cement of M minerals, the principal components of which are by weight: C 7 A 5 35 parts of M, 40 parts of dead burnt MgO, NH 4 h 2 PO 4 18 parts, 7 parts of borax; Its preparation process mainly comprises the following steps:
[0033] (1) C7 A 5 M raw meal preparation according to C 7 A 5 The stoichiometry of M weighs the calcareous component, the magnesium component and the aluminum-containing component and mixes and homogenizes;
[0034] (2) Calcinate the above-mentioned raw meal at 1300°C for 20min~3h, take it out and cool it naturally, and then carry out grinding treatment, and the upper limit of the fineness is controlled at 75 μm.
[0035] (3) The ground C 7 A 5 M was prepared with commercially available dead-burned MgO, phosphate, and borax according to the component ratio of 35:40:18:7 to obtain the final magnesium phosphate cement.
Embodiment 2
[0037] a C 7 A 5 Magnesium phosphate cement of M minerals, the principal components of which are by weight: C 7 A 5 20 parts of M, 48 parts of MgO, 22 parts of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, and 7 parts of borax; including 3 parts of boron oxide for the synergistic preparation of C 7 A 5 Introduced when M -MgO;
[0038] The preparation of magnesium phosphate cement mainly includes the following steps:
[0039] (1) C 7 A 5 Preparation of M-MgO raw meal according to C 7 A 5 The ratio of M to MgO and C 7 A 5 The stoichiometry of M weighs dolomite, magnesite, bauxite and boron oxide, grinds and homogenizes, and controls the fineness below 75 μm.
[0040] (2) Calcinate the homogenized raw meal at 1400°C for 20min~3h, take it out and cool it naturally to obtain C 7 A 5 Mixture of M-MgO.
[0041] (3) Take the sintered product after rapid cooling in step (2), and perform grinding treatment, and the fineness is controlled below 75 μm.
[0042] (4) put C 7 A 5 The M-MgO...
Embodiment 3
[0044] a C 7 A 5 Magnesium phosphate cement of M, the main components of which are by weight: 42 parts C 7 A 5 M, 30 parts of MgO, 20 parts of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 8 parts of borax mainly include the following steps:
[0045] (1) C 7 A 5 Preparation of M-MgO raw meal according to C 7 A 5 M:MgO:B 2 o 3 The ratio is 58:42, and according to the oxide composition of dolomite, magnesite and aluminum ash, the above raw materials are accurately weighed.
[0046] (2) Take the homogenized precursor in step (1), calcinate it at 1350°C for 20min~3h, take it out and cool it naturally to get C 7 A 5 Mixture of M-MgO.
[0047] (3) Take the sintered product after rapid cooling in step (2), and perform grinding treatment, and the fineness is controlled below 75 μm.
[0048] (4) put C 7 A 5 The M-MgO mixture is prepared with phosphate and borax in a ratio of 72:20:8 to obtain the final magnesium phosphate cement.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com