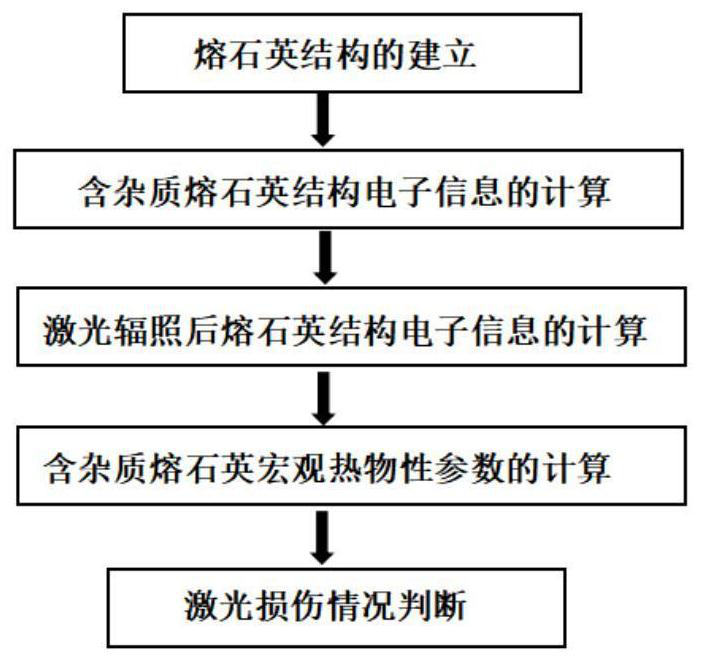
Fused quartz laser damage detection method based on first principle
A technology of laser damage and detection methods, applied in material defect testing, special data processing applications, design optimization/simulation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0088] For example: the pure fused silica structure model contains 96 atoms (Si: 32, O: 64). The fused silica model is generated based on a 2×1×2 quartz crystal supercell using the BSMC (Bond Switch of Monte Carlo) program.
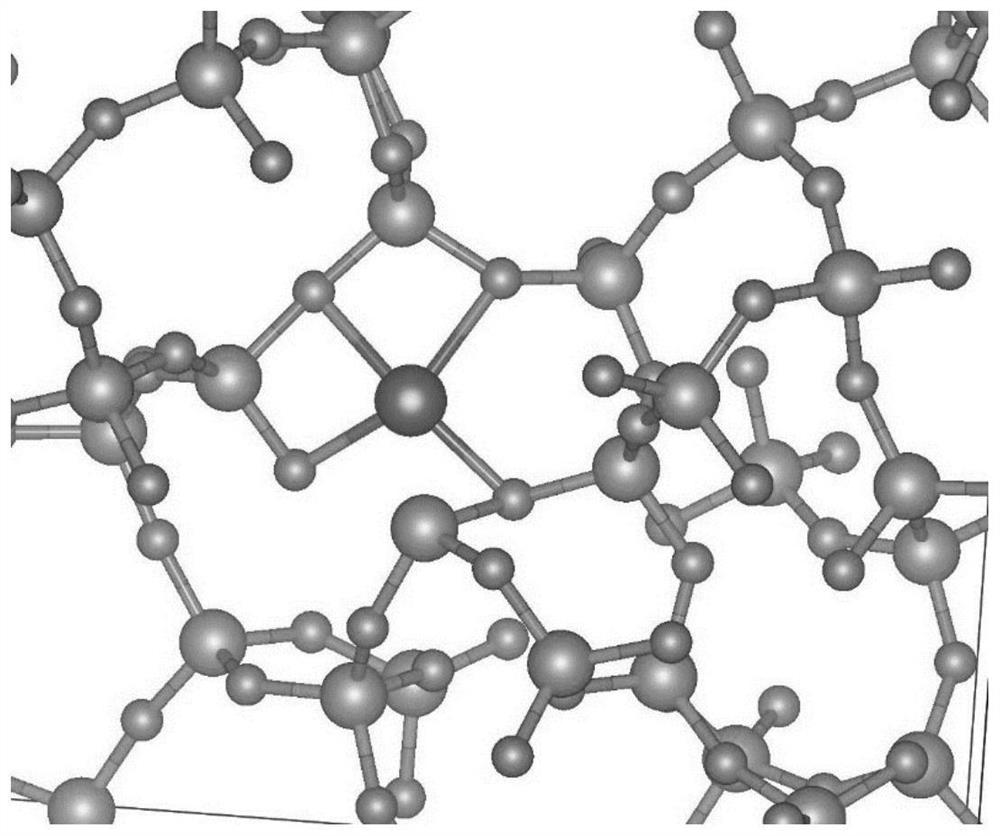
[0089] The fused silica structure model containing iron impurities has 97 atoms (Si: 32, O: 64, Fe: 1), such as figure 2 structure shown.
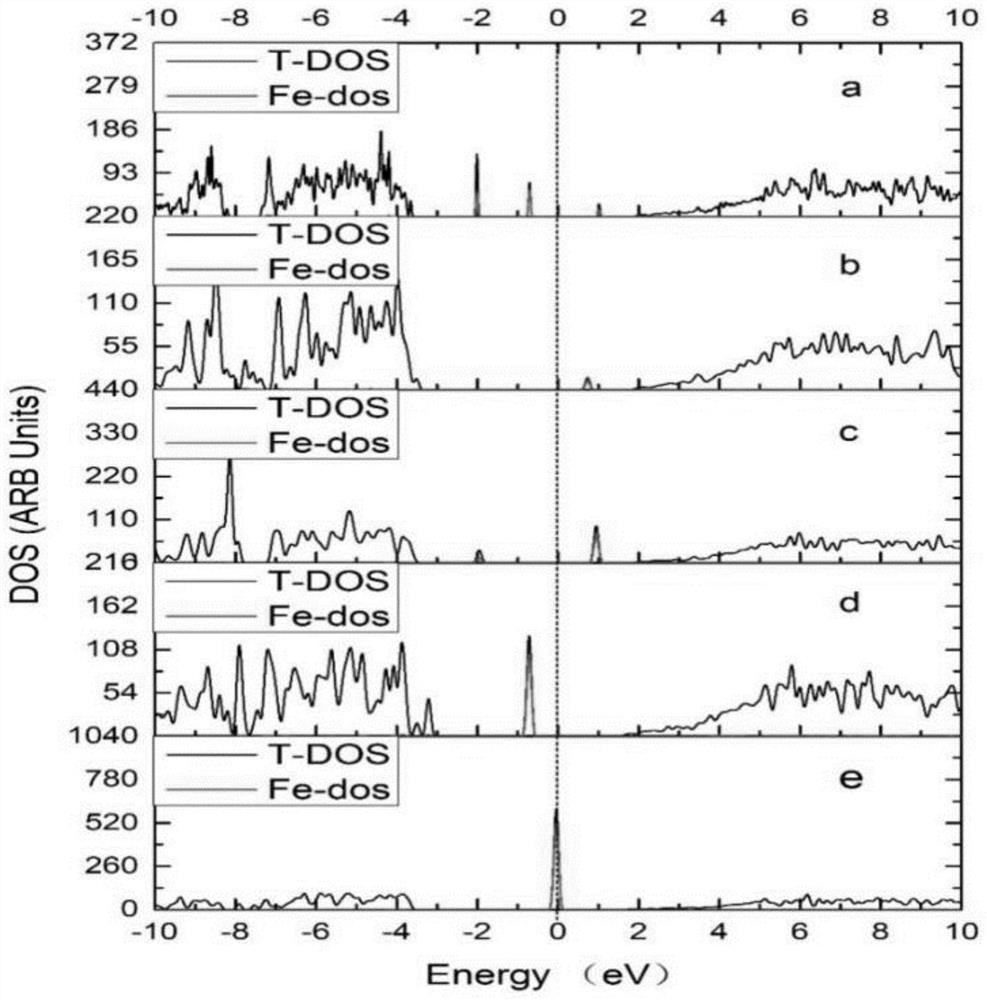
[0090] After the molecular dynamics calculation of the fused silica structure model containing iron impurities to simulate the irradiation process, the different DOS diagrams of energy absorbed by different numbers of oxygen atoms are given by image 3 shown. When only three oxygen atoms absorb energy, the impurity level formed by iron atoms below the Fermi level disappears, and the absorption peak of the defect level above the Fermi level begins to rise slightly. When the 5 oxygen atoms absorb energy, the impurity level below the Fermi level, which is mainly contributed by iron atoms and located near 0.71eV, disa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com