Method for exploring key regulatory factors for regulating plant development and application of key regulatory factors
A technology for plant development and regulatory factors, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of little value, regulatory factors or genes that cannot truly reflect the process of plant development, high probability of false positives for miRNA and target genes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
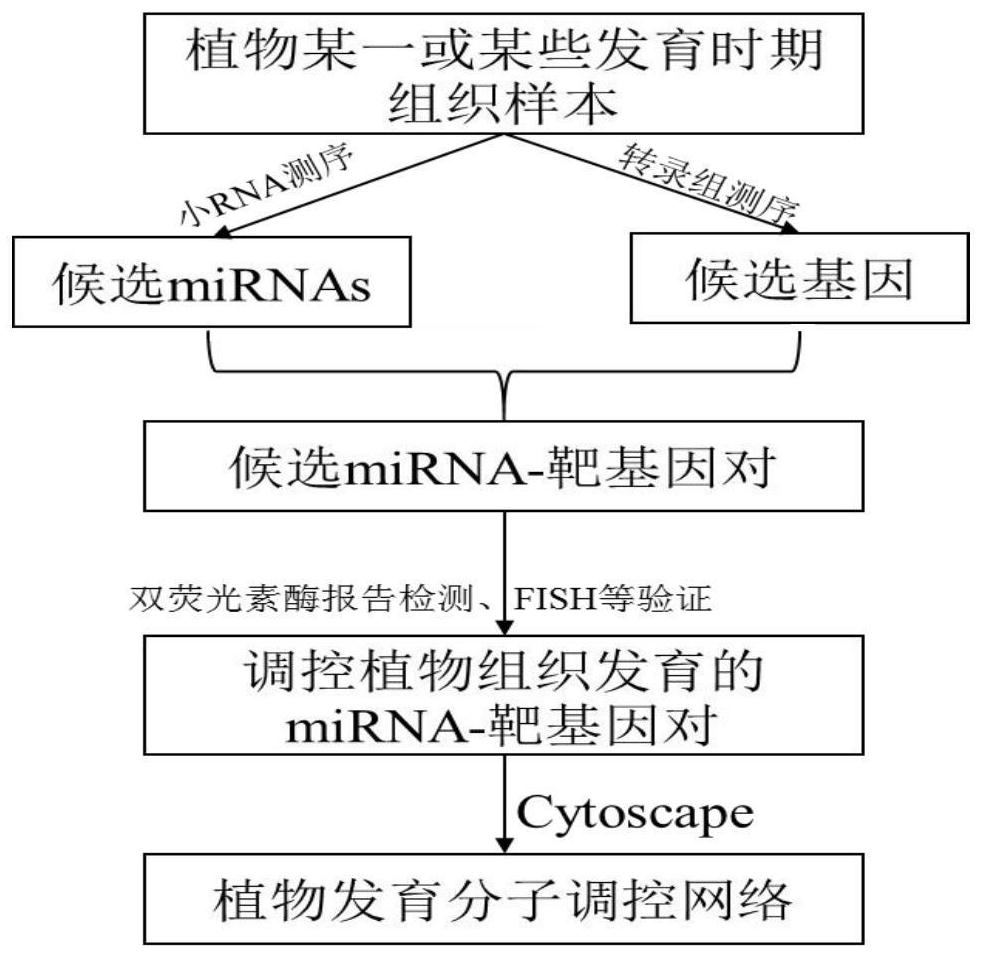
[0048] In this embodiment, the regulatory factors of plant tissues have been excavated, including the following steps:
[0049] (1) Plant tissues or organs are collected, and three replicates are set for each sample.
[0050] (2) cDNA library construction
[0051] 1. Use the kit purchased by Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd. to extract the RNA of the plant tissue in step (1), and perform the specific operation according to the kit instructions.
[0052] 2. Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 system (Agilent Technologies, CA, USA) was used to detect the purity, concentration and integrity of RNA samples.
[0053] 3. After the sample is qualified, construct the library according to the following process:
[0054] a. Enrichment of eukaryotic mRNA with magnetic beads containing Oligo(dT);
[0055] b. Add FragmentationBuffer to randomly interrupt the mRNA;
[0056] c. Using mRNA as a template, use six base random primers (random hexamers) to synthesize the first cDNA stra...
Embodiment 2
[0242] Utilize the method described in embodiment 1 to excavate the regulatory factor of the shoot shoot procambium in the middle stage of Phyllostachys pubescens development, the results are as follows:
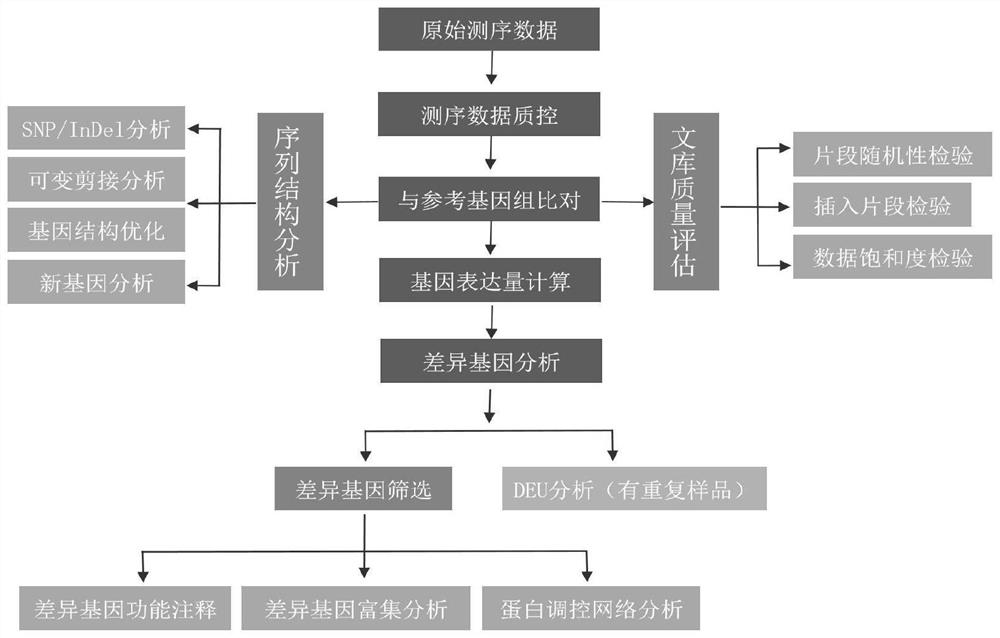
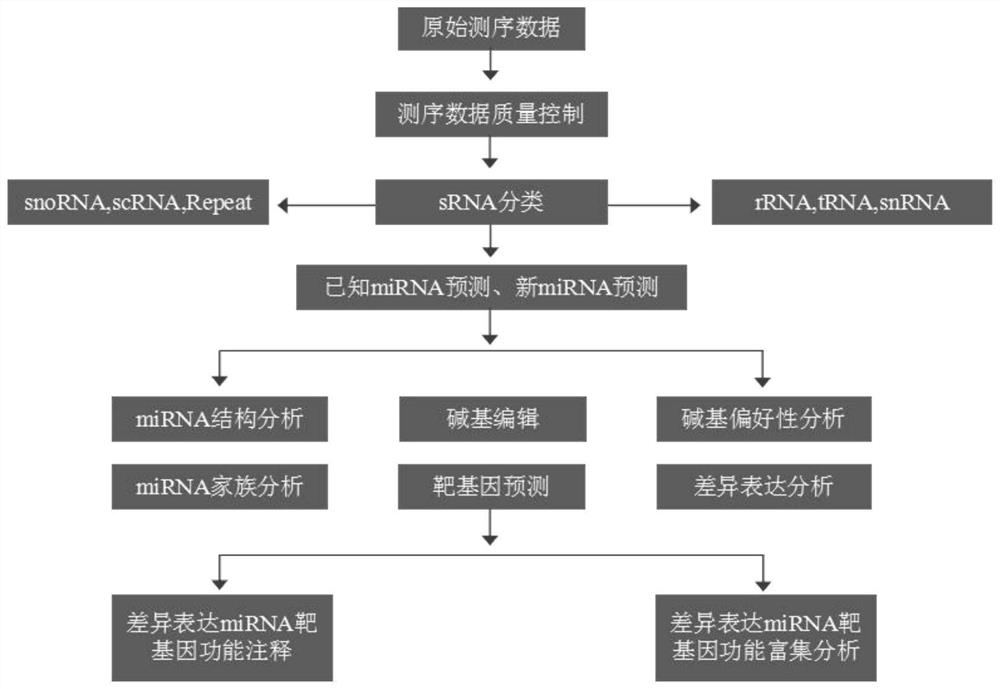
[0243] After testing, 137 miRNAs were identified in the early shoots of Phyllostachys pubescens, including 120 known and 17 new miRNAs; 38652 genes were identified. However, 130 miRNAs were identified in mid-developmental shoots, including 115 known and 15 new miRNAs; 39584 genes were identified. Expression analysis identified 30 differentially expressed miRNAs and 61 differentially expressed genes in the two groups of samples; degradome sequencing analysis identified 101 sets of miRNA-target gene pairs. The dual-luciferase reporter assay verified that 65 groups of miRNA-target gene pairs could interact in cells. Fluorescence in situ hybridization Fish experiments identified ped-miR160a-5p, etc., which can play a role in the procambium in the middle stage of shoot shoot dev...
Embodiment 3
[0245] Utilize the method described in embodiment 1 to excavate the regulatory factors of the shoot shoot top meristem in the early stage of Phyllostachys pubescens development, the results are as follows:
[0246] After detection, 129 miRNAs, including 117 known and 12 new miRNAs; 38462 genes were identified in the bud samples of Phyllostachys pubescens. However, 137 miRNAs were identified in early shoot shoot samples, including 120 known and 17 new miRNAs; 38652 genes were identified. Expression analysis identified 26 differentially expressed miRNAs and 75 differentially expressed genes in the two groups of samples; degradome sequencing analysis identified 98 sets of miRNA-target gene pairs. The dual-luciferase reporter assay verified that 56 groups of miRNA-target gene pairs could interact in cells. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assay identified ped-miR166a-3p that can play a role in the apical meristem in the early shoot development ( Figure 7 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com