Compound for organic luminescence and application thereof
A compound and organic technology, applied in the field of organic light-emitting compounds, can solve problems such as insufficient development, and achieve the effects of high charge transfer ability, high glass transition temperature, and high stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
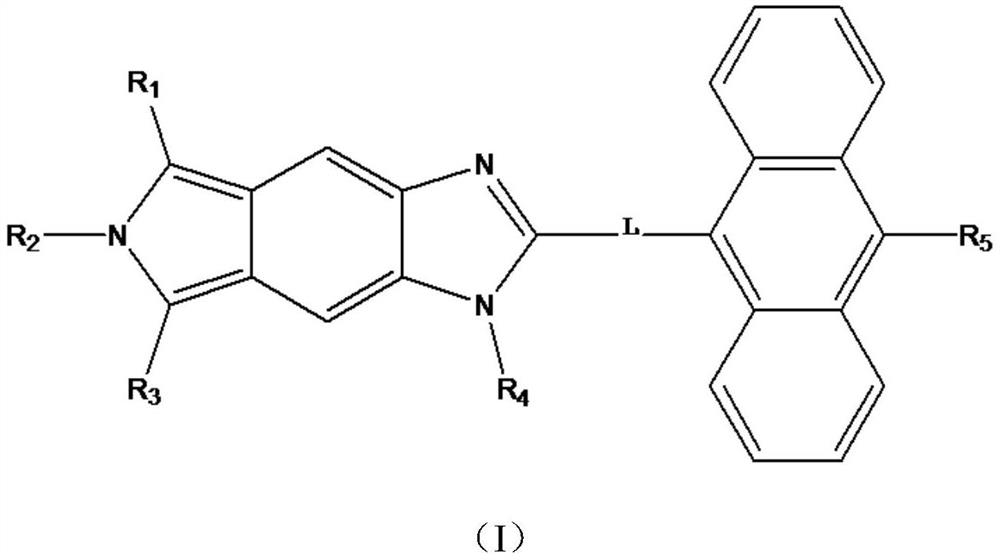
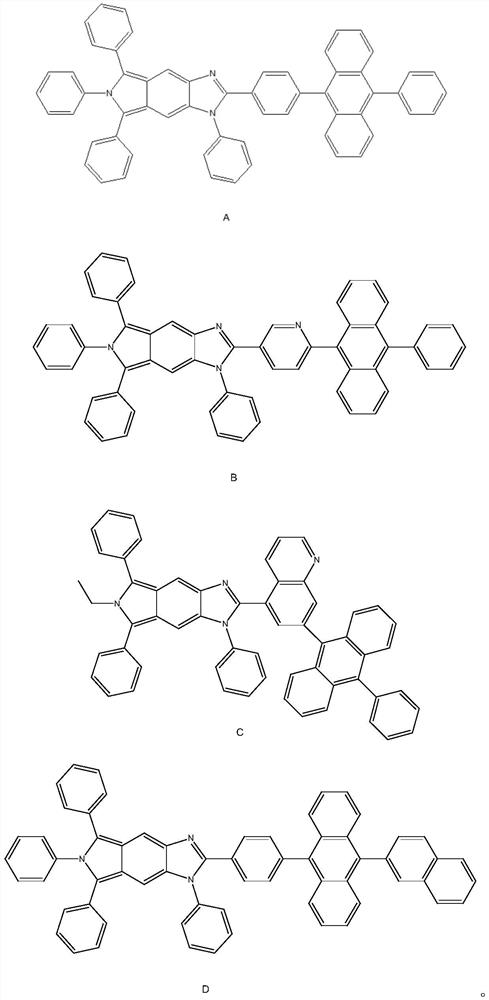
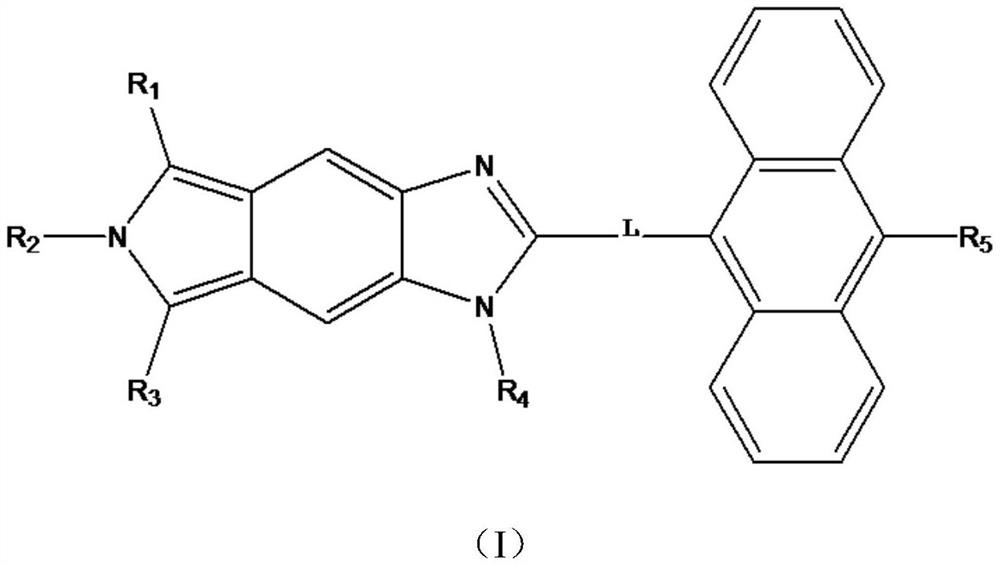
[0025] The first aspect of this embodiment is to provide a compound for organic luminescence, the structure of which is shown in Formula A:
[0026]
[0027] The second aspect of this embodiment is to provide a kind of synthetic method of above-mentioned compound:
[0028]
[0029]
[0030] Step (a): 40mmol compound 1, 47mmol diboronic acid pinacol ester and 118mmol potassium acetate were dissolved in 150mL dioxane, the mixture was heated to 50°C, and 0.4mmol Pd(DBA) 2 and 0.8mmol P(Cy) 3 This was added and the resulting mixture was heated with stirring for 12 hours. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, 100 mL of distilled water was added thereto, and the mixture was extracted with dichloromethane, and the organic layer was concentrated and recrystallized with ethanol to obtain compound 2.
[0031] Step (b): Suspend 99.95 mmol of compound 3 and 99.98 mmol of compound 4 in 200 mL of 1,4-dioxane and 20 mL of acetic acid. The resulting mixture was sti...
Embodiment 2
[0035] This embodiment provides a compound for organic luminescence, the structure of which is shown in formula B:
[0036]
[0037] The synthesis method of this compound is the same as that of Example 1, except that the substituents in the raw materials are replaced accordingly.
[0038] The yield of compound B was 84%. Characterization data: melting point (DSC) 284°C, purity 99.9%; 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ(ppm): 9.20(s,1H),8.11-7.91(m,5H),7.78-7.48(m,7H), 7.39-7.30(m,15H),7.22-7.00(m,6H),6.62 -6.46(m,4H).
Embodiment 3
[0040] This embodiment provides a compound for organic luminescence, the structure of which is shown in formula C:
[0041]
[0042] The synthesis method of this compound is the same as that of Example 1, except that the substituents in the raw materials are replaced accordingly.
[0043] The yield of compound C was 79%. Characterization data: melting point (DSC) 284°C, purity 99.9%; 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ(ppm): 8.81-8.51(m,2H),8.29(s,1H),8.00-7.91(m,5H), 7.48-7.39(m,10H),7.32-7.22(m,10H),7.01 -6.46(m,7H),3.89-1.51(m,5H).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com