Surface modification method of MXene material
A technology of surface modification and molten salt, which is applied in the field of surface modification of MXene materials, can solve problems such as limiting the diversity of MXene surface end groups, and achieve the effect of promoting functional applications and large-scale preparation, and the method is simple and efficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] (1) Precursor MAX phase Ta 2 AlC powder, ZnCl 2 Lewis acid molten salt, Sb powder, inorganic salt (such as NaCl, KCl) are ground and mixed in a molar ratio of 1:2:1:5 to obtain a mixture.
[0038] (2) Put the mixture into an alumina crucible, then put it into a high-temperature vacuum tube furnace to react at 600° C. under the protection of an inert atmosphere, and after the sintering temperature drops to room temperature, take out the reaction product in the alumina crucible.
[0039] (3) Product post-treatment: put the reaction product into a beaker, add deionized water, stir and ultrasonically clean the remaining salt in the reaction product, then perform suction filtration, and finally dry to obtain a powder product.
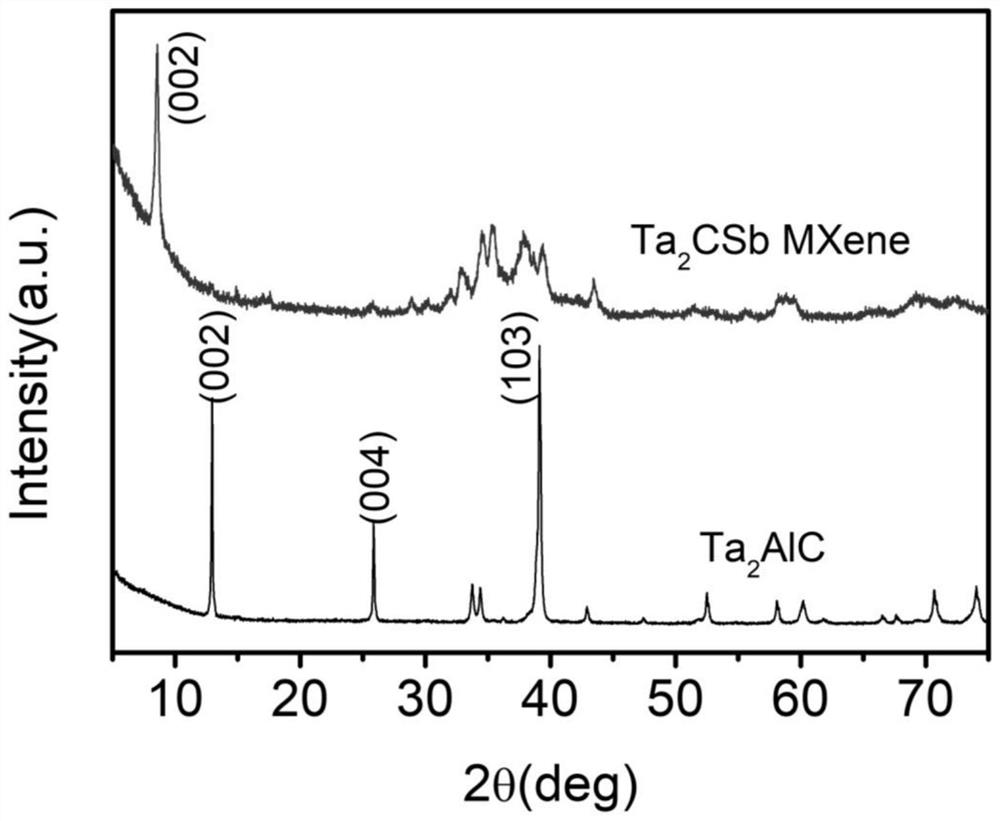
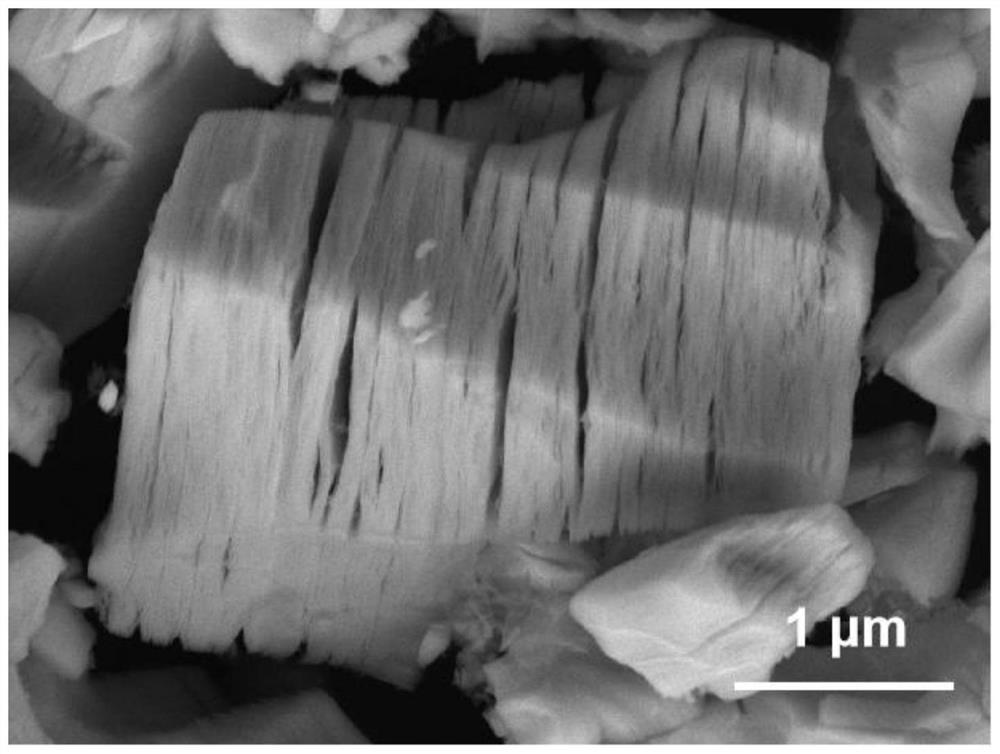
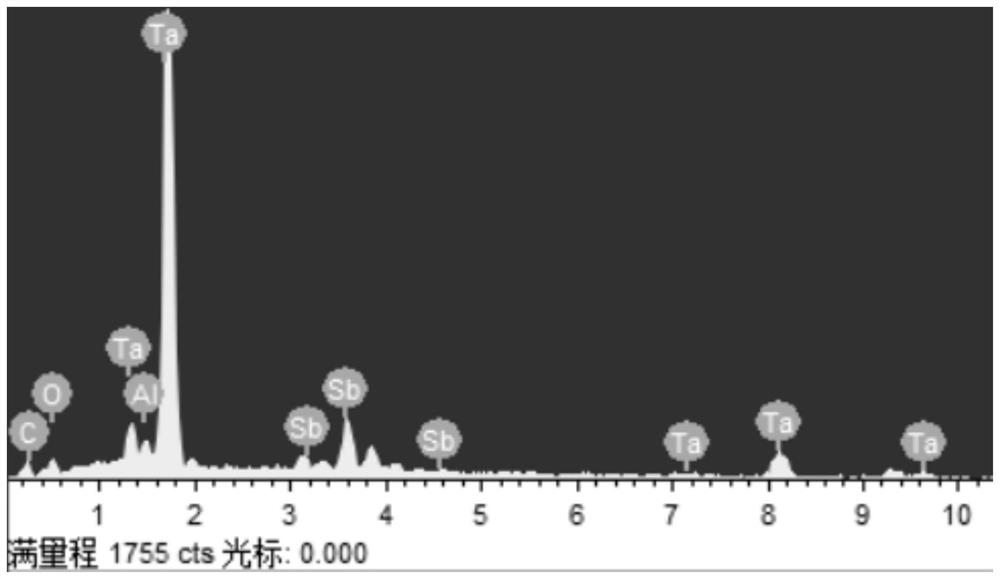
[0040] Use X-ray diffraction (XRD) to detect the powder and precursor MAX phase treated in step (3), such as figure 1 shown. Compared with the precursor MAX phase, Ta 2 The diffraction peak of CSb broadens or even disappears, while the characteris...
Embodiment 2
[0042] (1) Precursor MAX phase Ti 2 AlC powder, FeCl 2 Lewis acid molten salt, As 2 Cd 3 Powder, inorganic salts (such as NaCl, KCl) are ground and mixed in a molar ratio of 1:1.5:1:8 to obtain a mixture.
[0043] (2) Put the mixture into an alumina crucible, then put it into a high-temperature vacuum tube furnace to react at 700° C. under the protection of an inert atmosphere, and after the sintering temperature drops to room temperature, take out the reaction product in the alumina crucible.
[0044] (3) Product post-treatment: put the reaction product into a beaker, add deionized water, stir and ultrasonically clean the remaining salt in the reaction product, then perform suction filtration, and finally dry to obtain a powder product.
[0045] Image 6 is the As-containing MXene Ti at the end group in this example 2 XRD patterns of CAs. Compared with the precursor MAX phase, the characteristic peaks are weakened, indicating that the crystal structure has changed, but ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] (1) The precursor MAX phase Ti 3 AlC 2 Powder, CuBr 2 Lewis acid molten salt, P powder, inorganic salts (such as NaCl, KCl) are ground and mixed in a molar ratio of 1:2.5:1:10 to obtain a mixture.
[0048] (2) Put the mixture into an alumina crucible, then put it into a high-temperature vacuum tube furnace to react at 800° C. under the protection of an inert atmosphere, and after the sintering temperature drops to room temperature, take out the reaction product in the alumina crucible.
[0049] (3) Product post-treatment: put the reaction product into a beaker, add deionized water, stir and ultrasonically clean the remaining salt in the reaction product, then perform suction filtration, and finally dry to obtain a powder product containing end groups containing MXene material Ti of P and Br 3 C 2 (Br 0.66 P 0.33 ). Figure 9 Ti is the MXene material in this example 3 C 2 (Br 0.66 P 0.33 ), from which the layered structure due to the etching can be observed, i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com