Method for extracting and preparing lithium ion battery negative electrode carbon material from printing and dyeing wastewater
A lithium-ion battery, printing and dyeing wastewater technology, applied in the direction of battery electrodes, secondary batteries, textile industry wastewater treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high price, high price of power battery, hindering the application and development of carbon negative electrode materials, etc., to achieve cost Low cost, significant energy and environmental protection significance, good batch stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
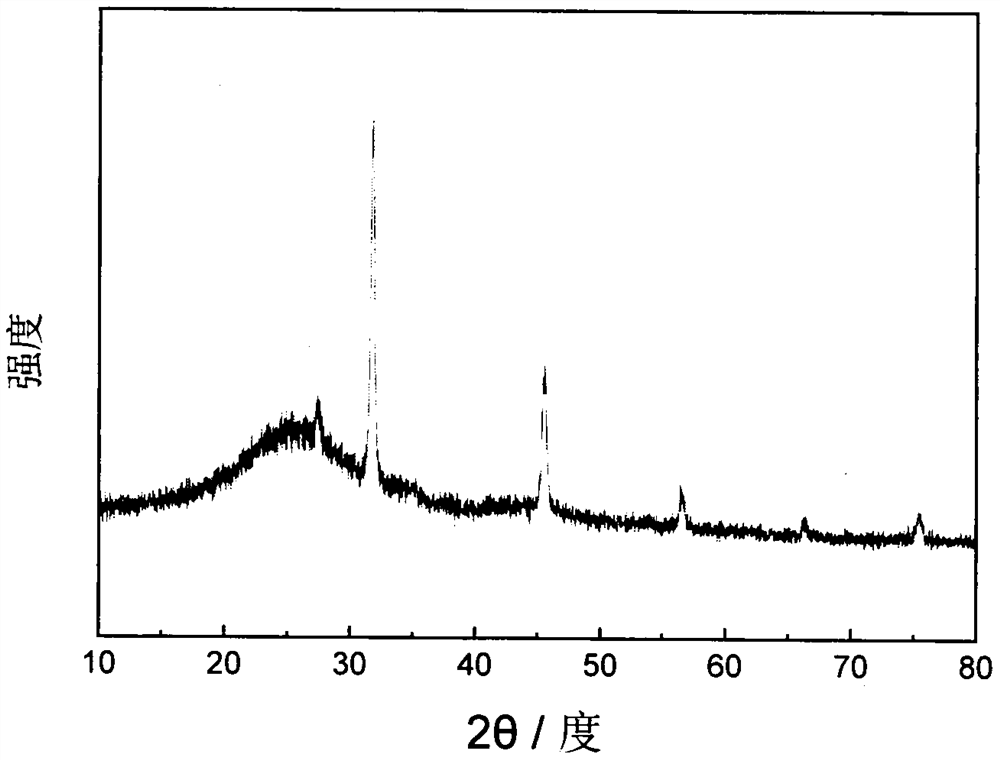
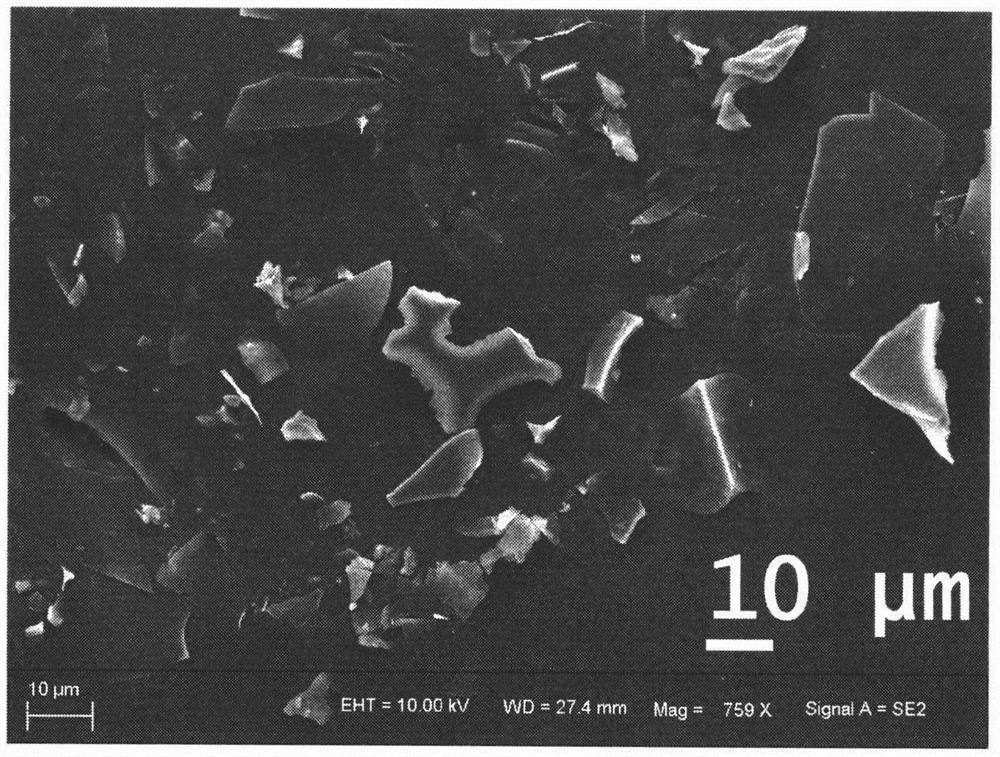
[0018] Add 0.1M hydrochloric acid solution into the printing and dyeing wastewater, adjust the pH of the solution to 6, add a flocculant, the volume ratio of the flocculant to the printing and dyeing wastewater is 1:100, after sufficient flocculation, carry out suction filtration, and put the obtained solid at 100°C Dry for 12 hours, take out and grind to obtain a carbon material precursor. The prepared precursor was put into a tube furnace, and calcined at 450° C. for 1 h in nitrogen gas. After the material was cooled, it was ground to obtain a carbon negative electrode material. Its XRD figure ( figure 2 ) shows that the material is a carbon material, containing sodium salt, and no other heterogeneous phases are found. SEM image ( image 3 ) shows that its morphology is an irregular sheet structure. The first charge and discharge diagram at room temperature ( Figure 4 ) shows that the first discharge specific capacity of the material at 0.1C in the 0-3V range is 904mAh...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Add 0.1M hydrochloric acid solution to the printing and dyeing wastewater, adjust the pH of the solution to 6, add a flocculant, the ratio of the flocculant to the printing and dyeing wastewater is 1:100, after sufficient flocculation, perform suction filtration, and put the obtained solid into an oven at 100 °C for 12 hours, taken out and ground to obtain a carbon material precursor. The prepared precursor was calcined in nitrogen at 400° C. for 1 h, and after the material was cooled, it was ground to obtain a carbon negative electrode material. Its XRD pattern shows that the material is a carbon material containing sodium salt, and no other impurity phases are found. The charge-discharge diagram shows that the carbon material has an initial discharge specific capacity of 542mAh / g at 0.1C in the 0-3V range. At room temperature, the initial cycle is the activation stage, and after 50 cycles, the capacity retention rate is 83.1%.
Embodiment 3
[0022] Add 0.1M hydrochloric acid solution to the printing and dyeing wastewater, adjust the pH of the solution to 6, add flocculant, the ratio of flocculant to printing and dyeing wastewater is 1:100, after sufficient flocculation, use vacuum pump to filter, and put the obtained solid into an oven at 100 °C for 12 hours, taken out and ground to obtain a carbon material precursor. 4.08 g of the prepared precursor was put into a tube furnace, and calcined at 350° C. for 1 h in nitrogen gas. After the material was cooled, it was ground to obtain a carbon negative electrode material. The XRD of the material shows that the material is a carbon material containing sodium salt, and no other impurity phases are found. The first charge specific capacity of the material at 0.1C under 0-3V is 306mAh / g, and the first discharge specific capacity is 622mAh / g. At room temperature, the initial cycle is the activation stage, and after 50 cycles, the capacity retention rate is 99.2%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com