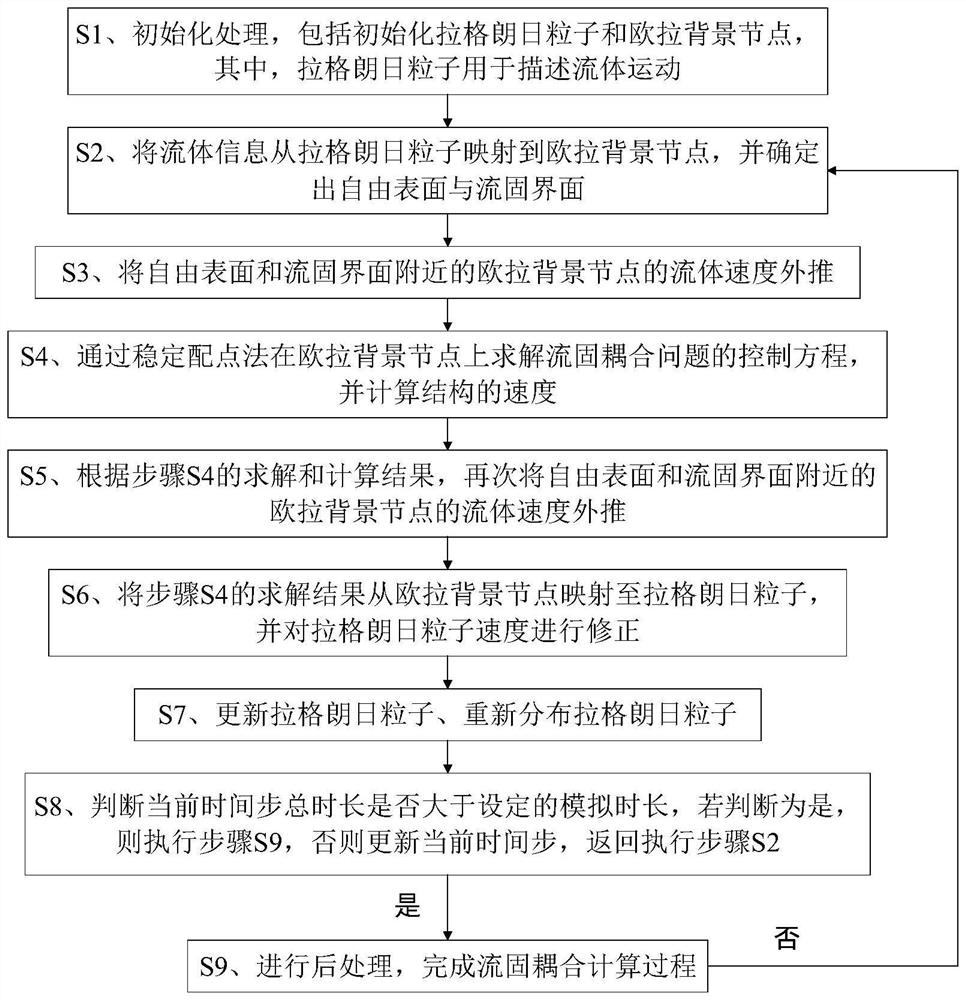
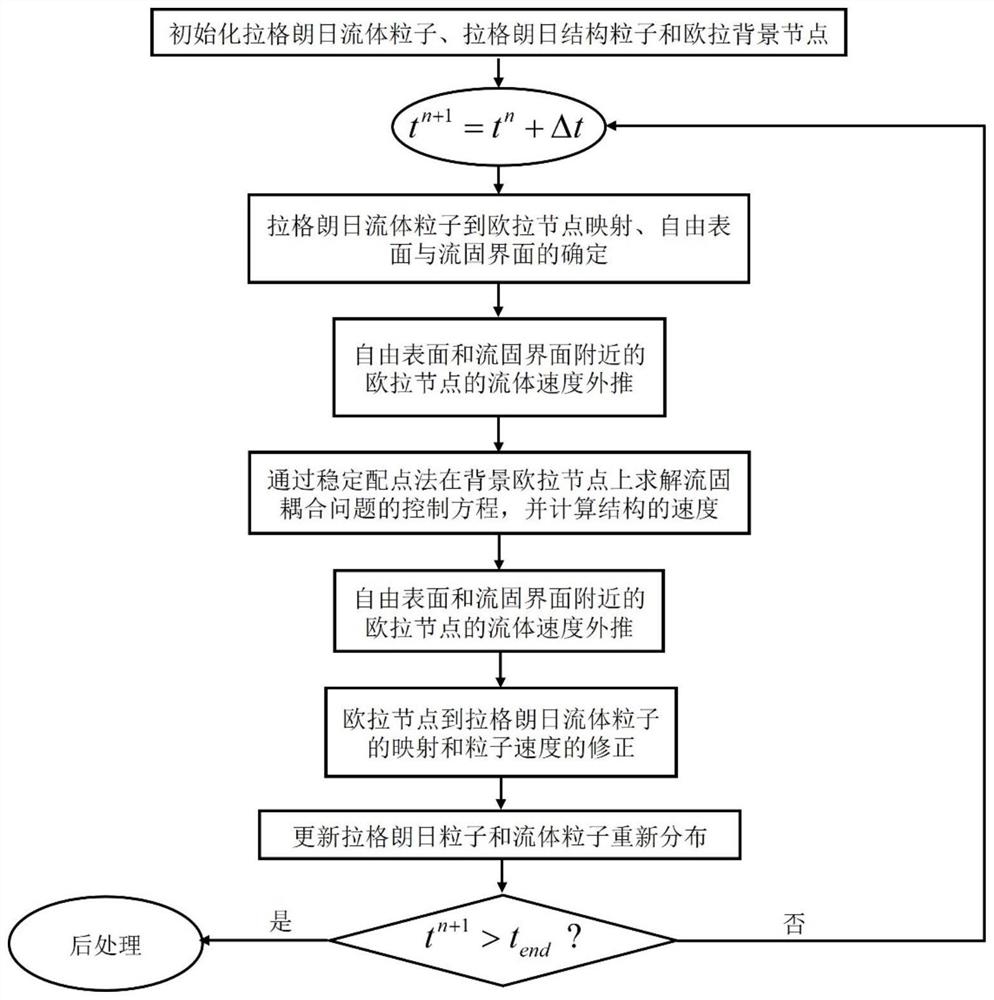
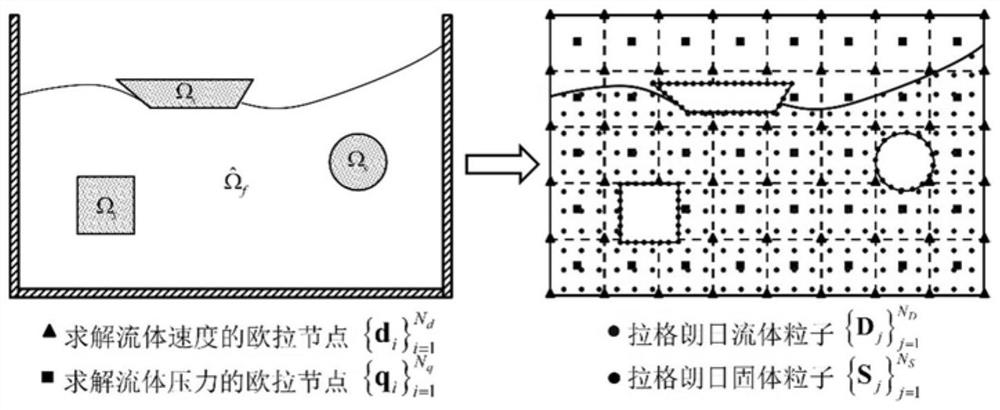
Fluid-solid coupling calculation method based on Lagrange-Euler stable collocation
A technology of fluid-solid coupling and calculation methods, applied in calculation, computer-aided design, complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve problems such as instability, achieve accurate capture, achieve strong coupling calculations, and improve accuracy and efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0145] This embodiment solves and calculates for the two-dimensional cylindrical water entry problem, such as Image 6 shown, a radius r 0 =0.055m two-dimensional semi-buoyant cylinder from H c = 0.5m in initially calm water. "Semi-buoyant" means that the weight of a cylinder is equal to half of the buoyancy of the cylinder when it is fully submerged in water. The densities of the cylinder and water are ρ c =0.5×10 3 kg / m 3 and ρ w =1.0×10 3 kg / m 3 , the kinematic viscosity of water is υ=1.01×10 -6 m 2 / s. Since the cylinder falls freely before it touches the water surface, the instantaneous velocity of the cylinder when it touches the water surface can be calculated from Newton's law, namely v 0 =-2.955m / s. The entire pool is discretized into 302 × 364 Euler background nodes as an Euler domain, and the water in the pool is discretized using 235,332 Lagrangians. According to the stability condition, the time step of the solution is set to Δt = 5.0 × 10 -4 s.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com