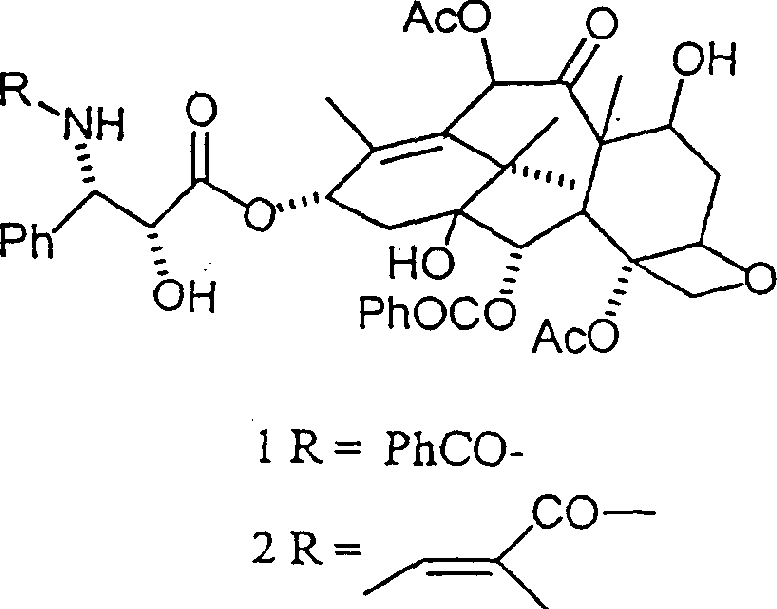
Chromatographic separation method of paclitaxel and cephalomannin
A technology of cephalomannine and paclitaxel, which is applied in the fields of pharmaceutical formulations, organic active ingredients, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, and can solve problems such as difficult synthesis methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Isolation of paclitaxel from the extract of Taxus japonica containing cephalomannine
[0036] By HPLC analysis, it was found that 290 g of extract prepared from 620 kg of Taxus densely grown (whole plant) according to the method described by V. Senilh et al. (J. Nat. Prod. 47, 131, 1984) contained 183 g of paclitaxel and 81 g of cephalomannine . This extract was dissolved in 3.5 liters of tert-butyl acetate and loaded onto a column containing 60 kg of silica gel. A total of 1200 liters of tert-butyl were eluted. After elution with 350 liters of solvent, 400 liters of a fraction containing paclitaxel and less than 3% cephalomannine and 200 liters of another fraction containing cephalomannine and less than 3% paclitaxel were obtained. The two fractions are separately concentrated to dryness in vacuo and the residue is crystallized from hexane-acetone. Then, obtained 154g paclitaxel and 70g cephalomannine, their HPLC purity is greater than 99%, and their physic...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Separation of paclitaxel and cephalomanine from their mixture
[0038] A mixture containing 70 g of paclitaxel and 30 g of cephalomannine was dissolved in 1.5 liters of tert-butyl formate and loaded onto silica gel containing 10 kg suspended in the same solvent. The column was eluted with tert-butyl formate and the fractions were combined after HPLC / TLC analysis. Fractions containing paclitaxel and cephalomannine were concentrated to dryness, respectively, and these residues were crystallized with appropriate proportions of acetone and heptane to obtain paclitaxel and cephalomannine with HPLC purity over 99%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com