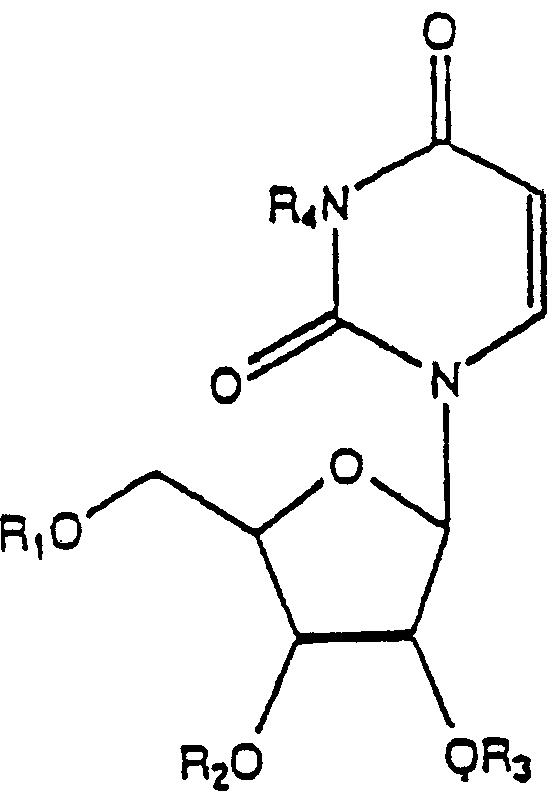
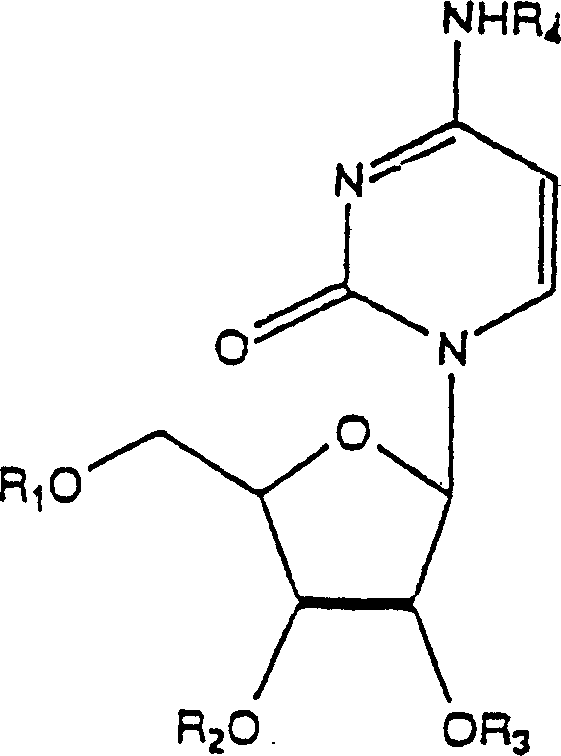
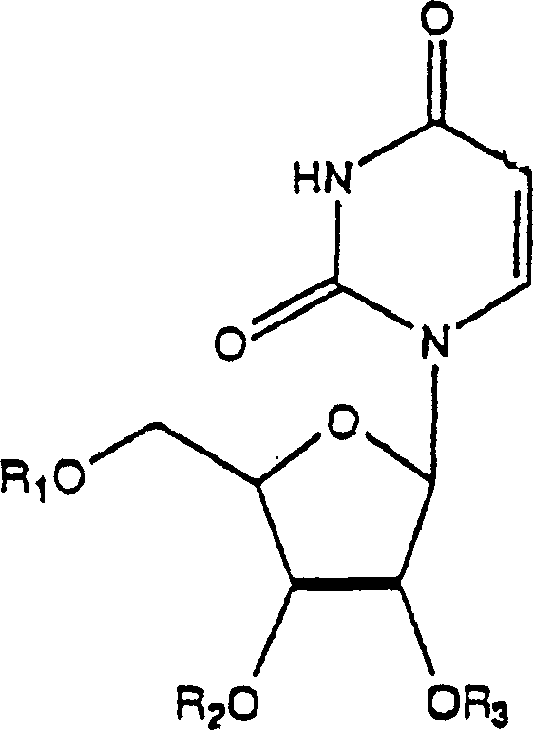
Application of uridine phosphorylase inhibitor and composition containing the same
A technology of uridine phosphorylase and inhibitors, which can be used in drug combinations, carbohydrate active ingredients, anti-toxins, etc., and can solve problems such as discomfort and infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0200] Triacetyluridine and uridine increase the survival of mice treated with dead E. coli
[0201] Purpose:
[0202] Sepsis can be caused by G - Bacteria trigger, even in G - In near nonviable cases, because the main trigger is endotoxin (a component of the bacterial cell wall). The purpose of the study in this Example was to examine the effect of oral administration of triacetyluridine and parenteral administration of uridine on the survival of mice treated with lethal doses of dead E. coli.
[0203] method:
[0204] Eighteen female Balb / c mice (8 weeks old) were divided into groups of 6 animals. All mice were given 500 ug of sonicated E. Coli (serotype 0111:B4) in acetone powder suspended in 0.2 ml saline. One group of mice was injected intraperitoneally with uridine (2000 mg / kg in 0.2 ml saline) 2 hours before administration of E. coli. Another group of mice was given triacetyluridine (6000 mg / kg in a 1:1 corn oil / water vehicle containing 2.5% Tween 80) via laryngea...
Embodiment 2
[0211] A Dose-Response Study of Uridine in Protecting Tissues from Endotoxin Damage
[0212] Purpose:
[0213] The purpose of this study was to determine the dose-response profile of uridine in preventing inflammatory tissue damage caused by endotoxin (LPS).
[0214] method:
[0215] Female Balb / c mice (8 weeks old) were divided into 6 groups of 6 animals each. One group of animals was left untreated to provide baseline serum chemistry values indicative of tissue damage. The remaining five groups of mice were given 100 μg of S. typhimurium endotoxin in 0.2 ml saline by intraperitoneal injection. Two hours before endotoxin administration, the five groups of mice were given uridine at 0.500, 1000, 2000 and 4000 mg / kg (in 0.2 ml saline) by intraperitoneal injection, respectively. Eighteen hours after endotoxin administration, blood samples were collected for determination of serum chemical indicators of tissue damage.
[0216] result:
Embodiment 3
[0233] Oral administration of triacetyluridine increases survival in mice treated with lethal doses of Salmonella typhimurium endotoxin
[0234] Purpose:
[0235] by G - The sepsis syndrome caused by bacteria is mediated by endotoxin, a lipopolysaccharide component of the bacterial wall. The aim of this experiment was to determine the effect of oral administration of technical uridine (triacetyluridine; TAU) on the survival of mice treated with lethal doses of purified Salmonella typhimurium endotoxin (LPS).
[0236] method:
[0237] Twenty female Balb / c mice (8 weeks old) were divided into two groups, 10 in each group. All mice were injected intraperitoneally with 100 ug of S. typhimurium endotoxin dissolved in 0.2 ml of saline. One group of mice was intragastrically administered triacetyluridine (6000 mg / kg in a 1:1 corn oil / water vehicle containing 2.5% Tween 80). Survival was monitored for one week.
[0238] result:
[0239] All 10 animals given endotoxin only died ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com