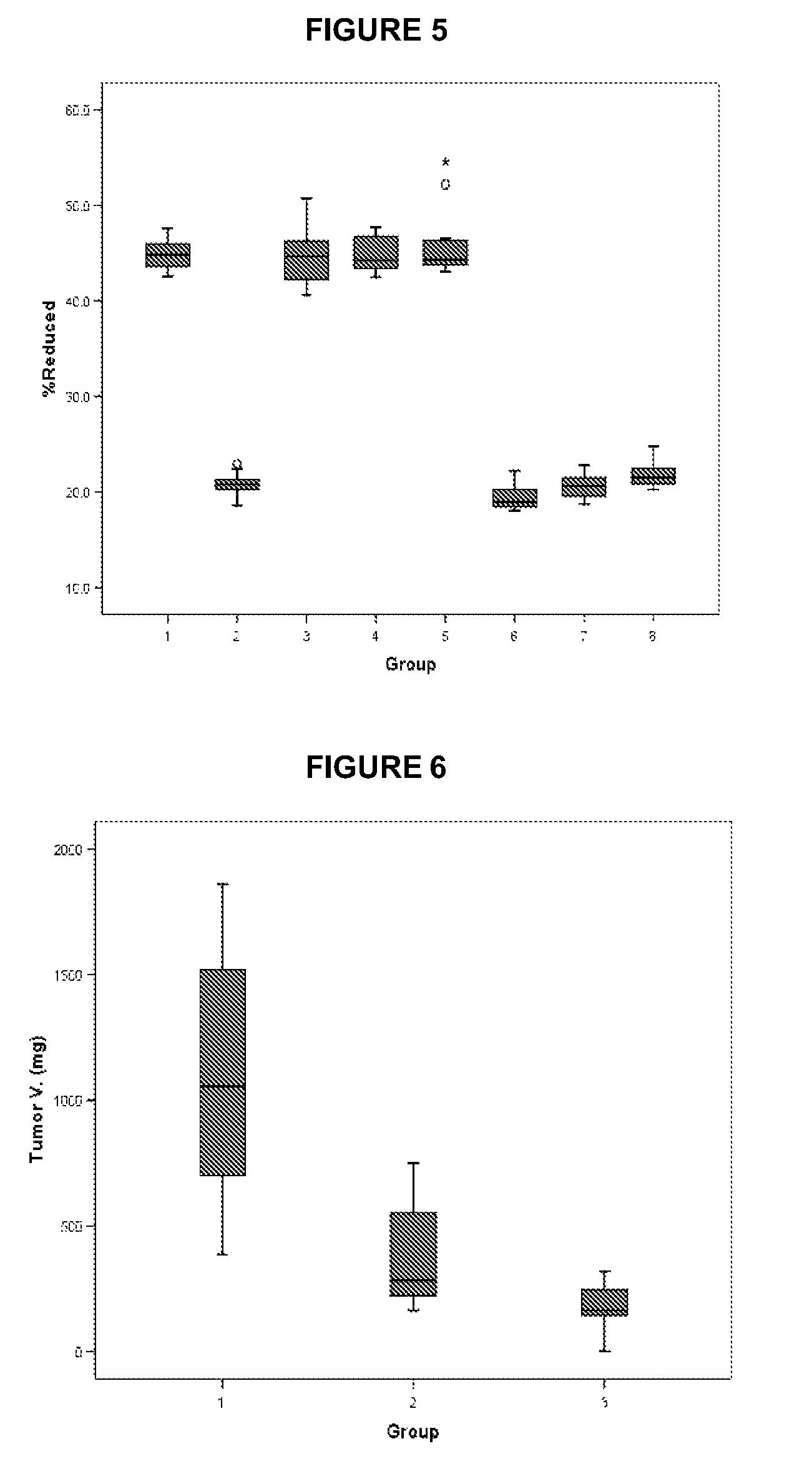
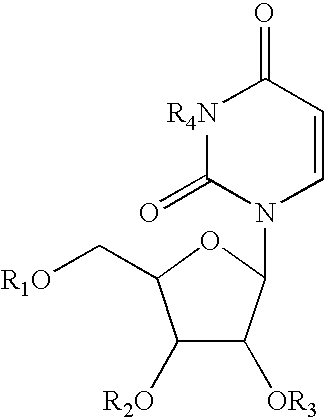
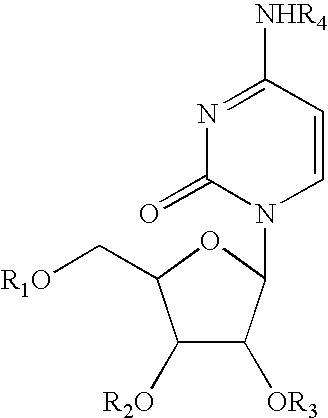
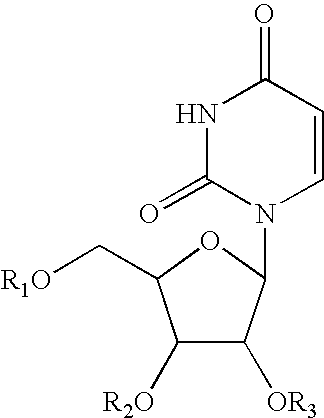
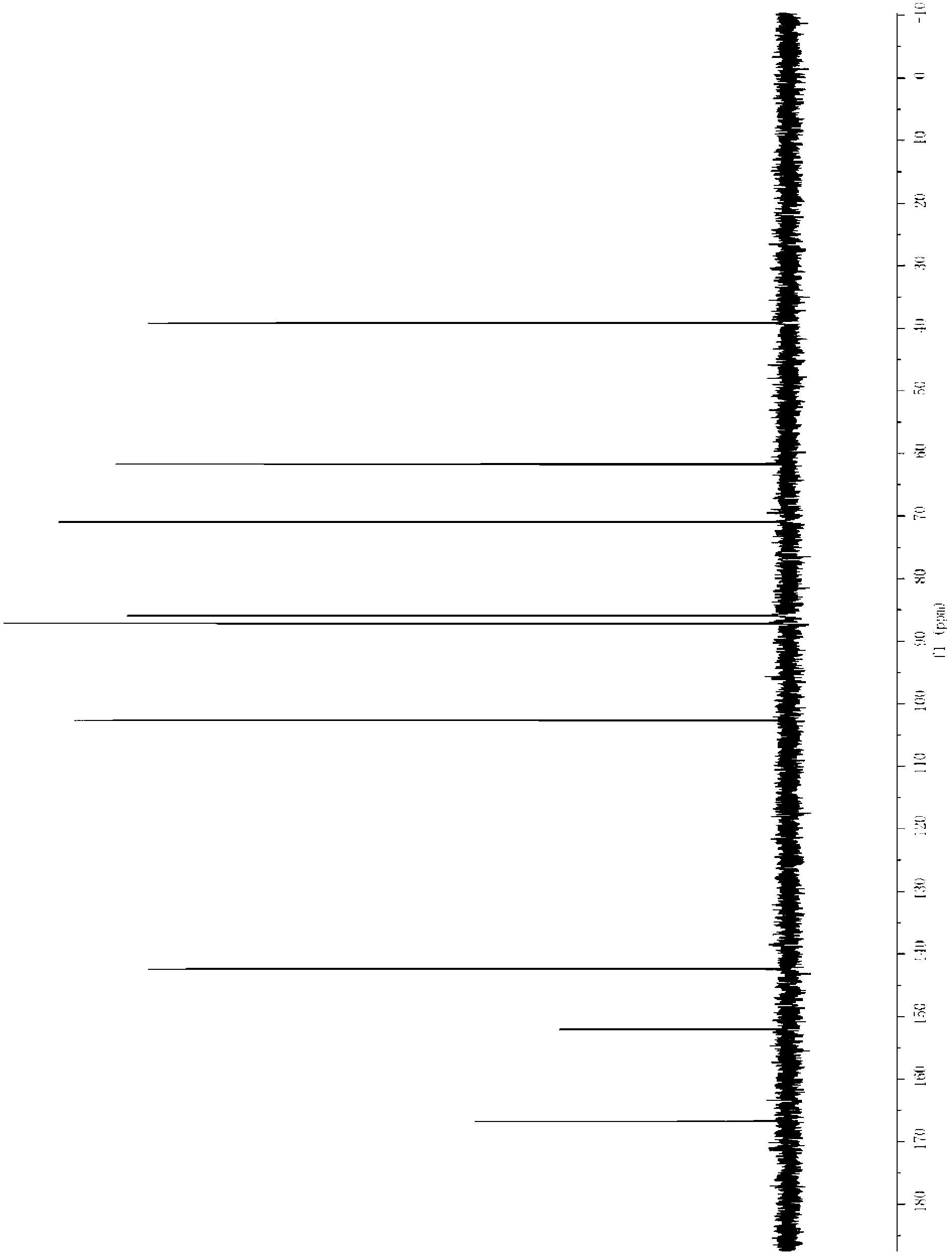
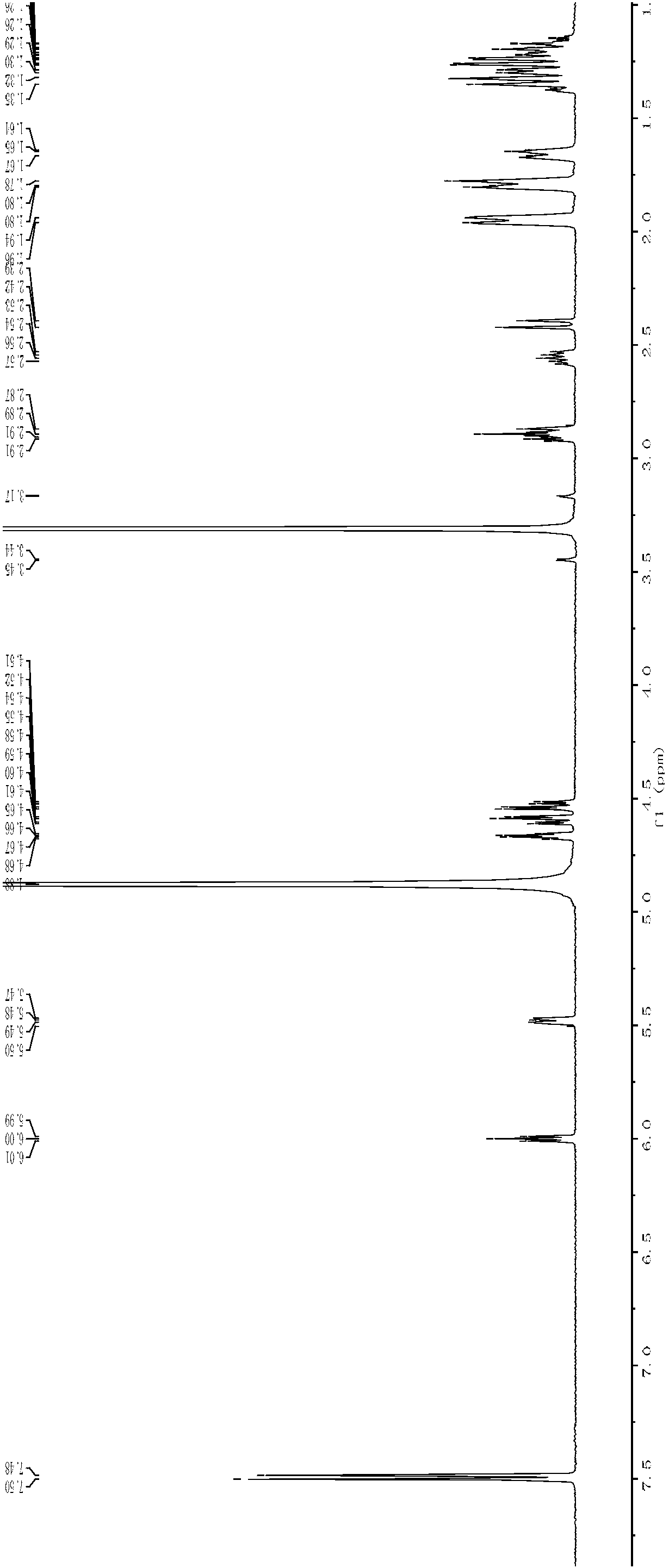
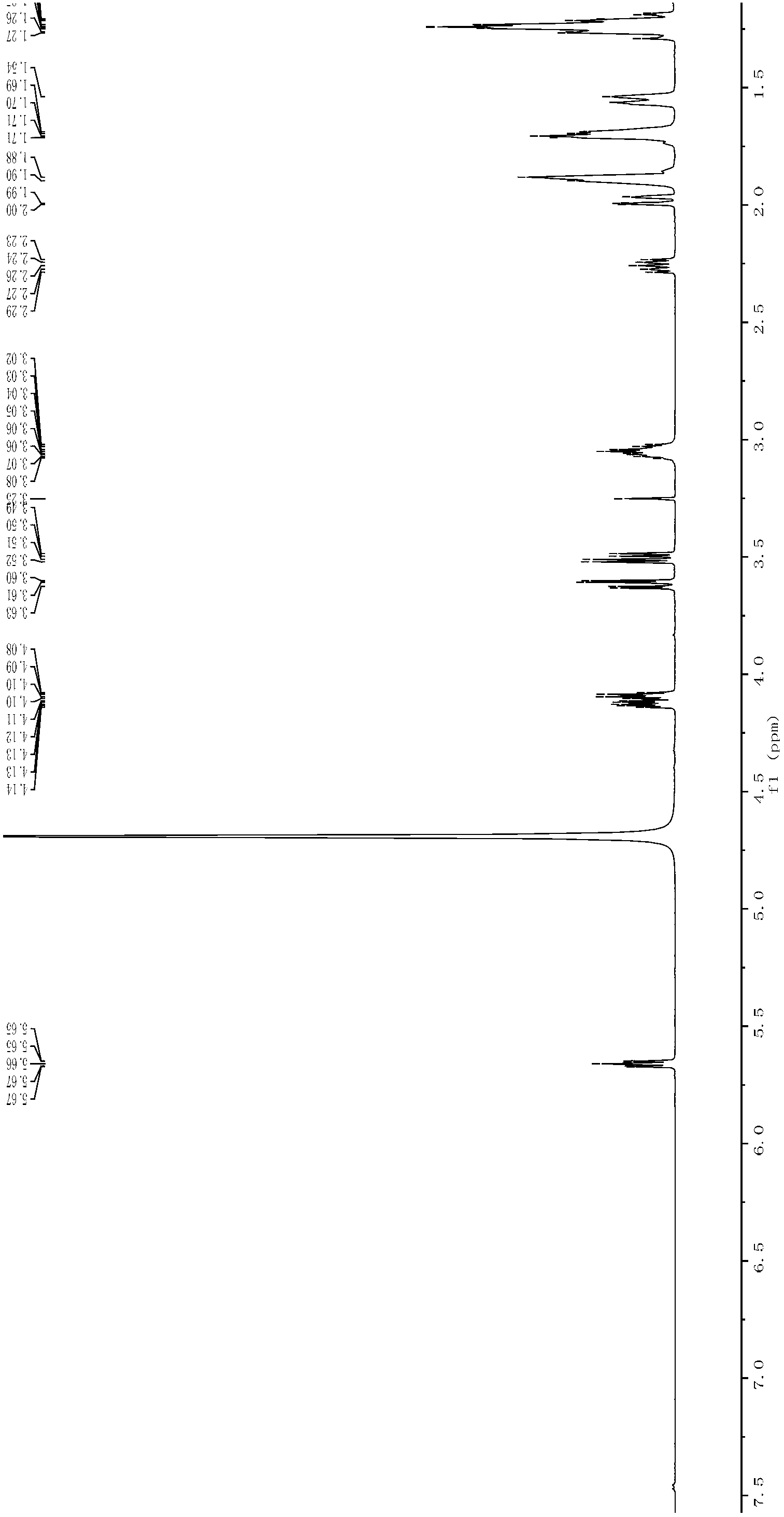
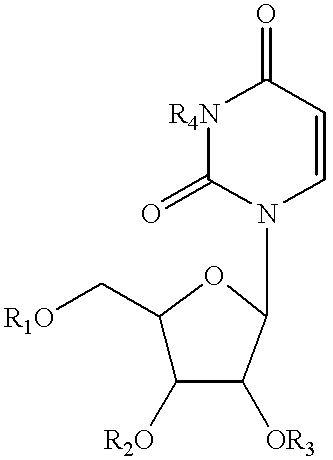
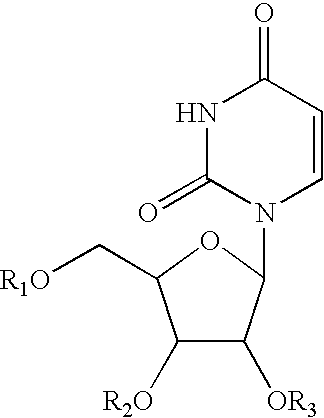
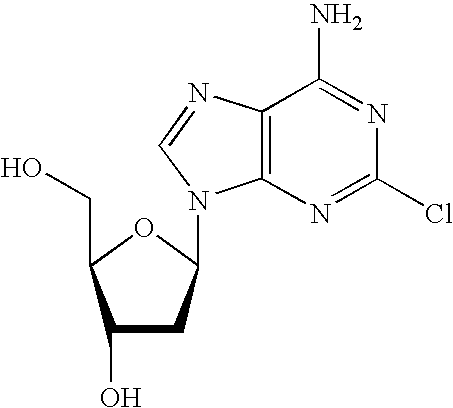
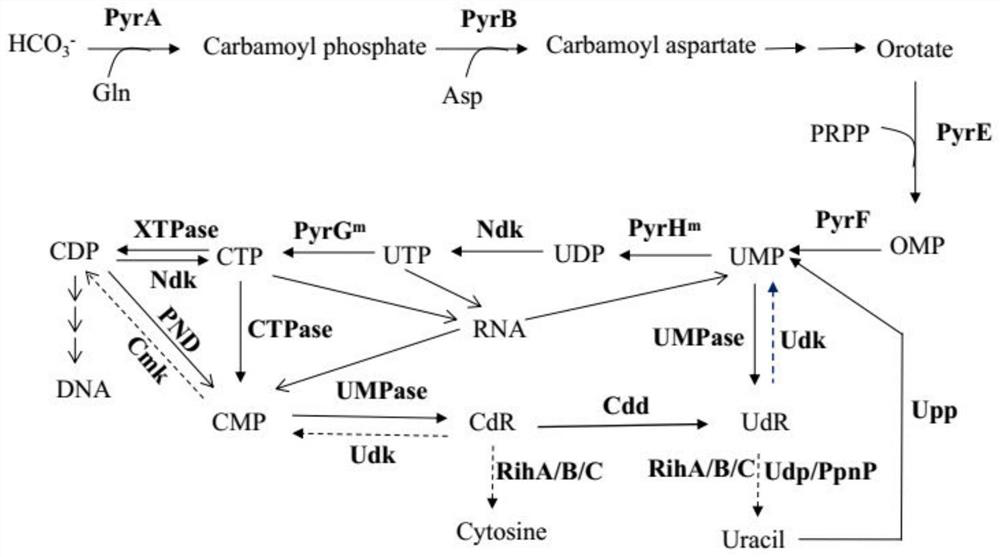
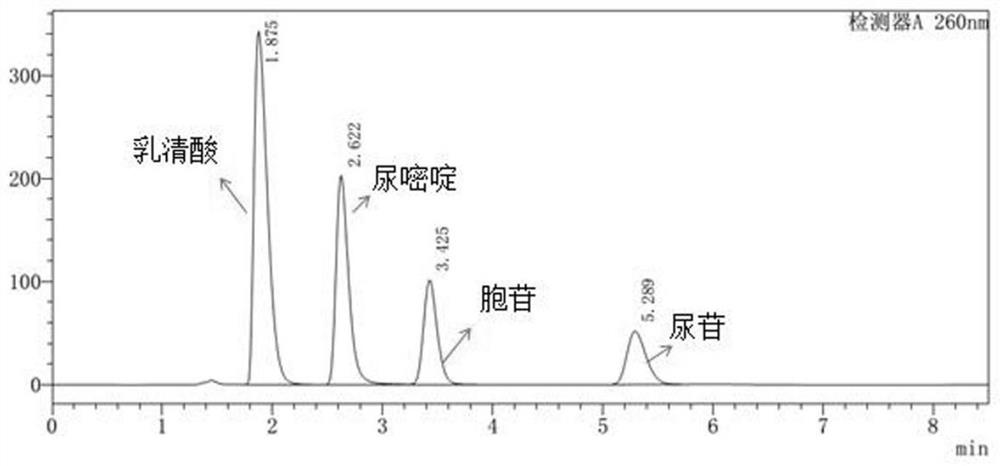
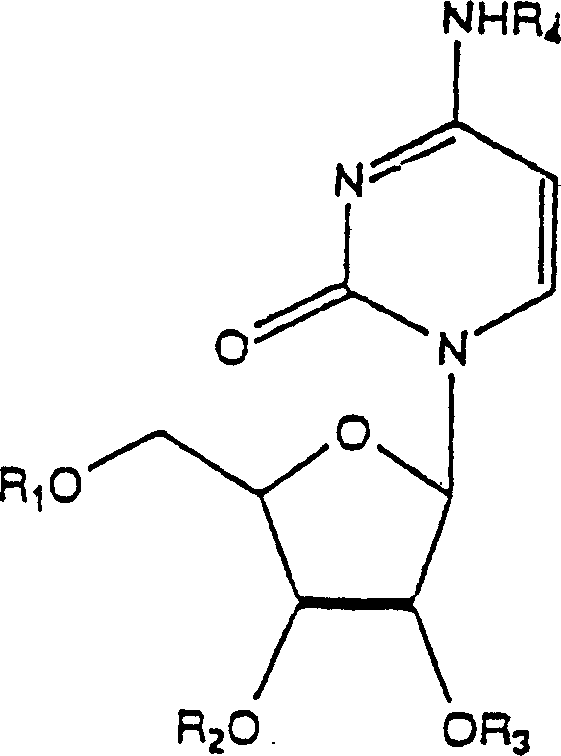
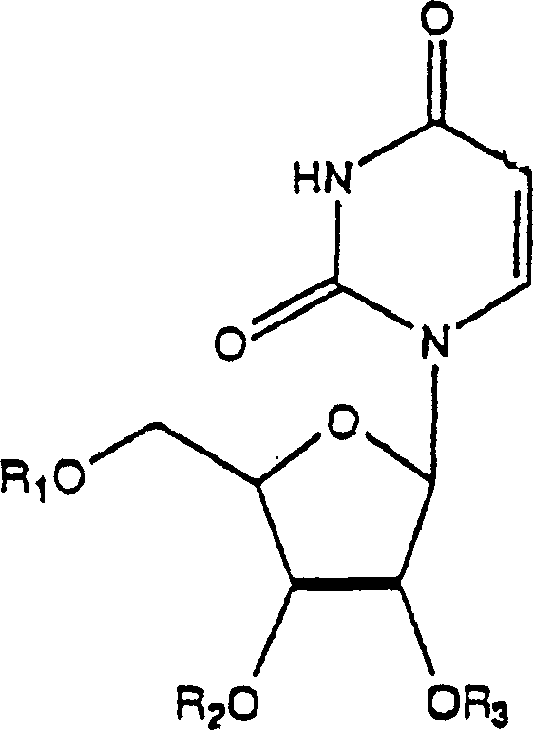
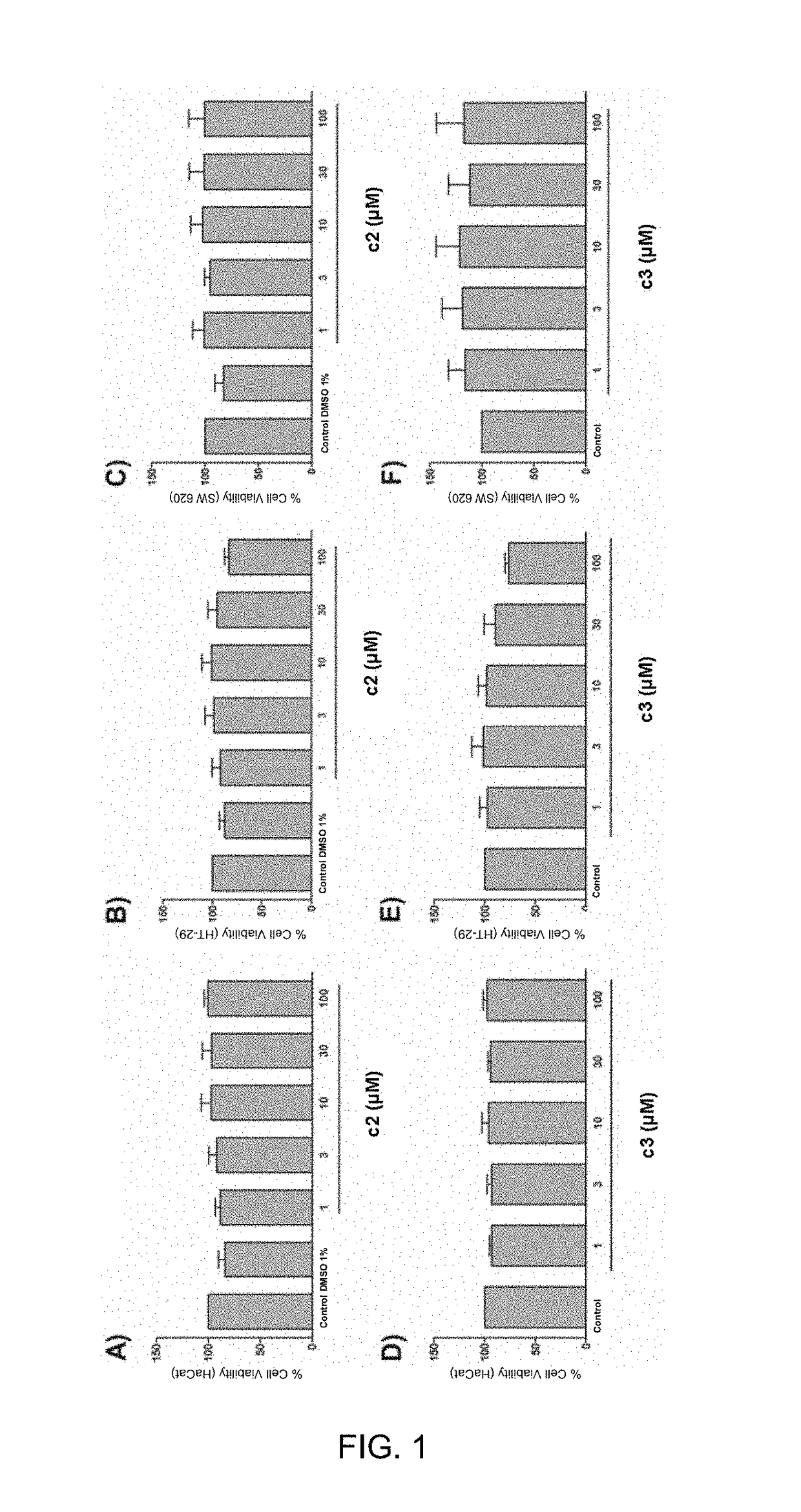
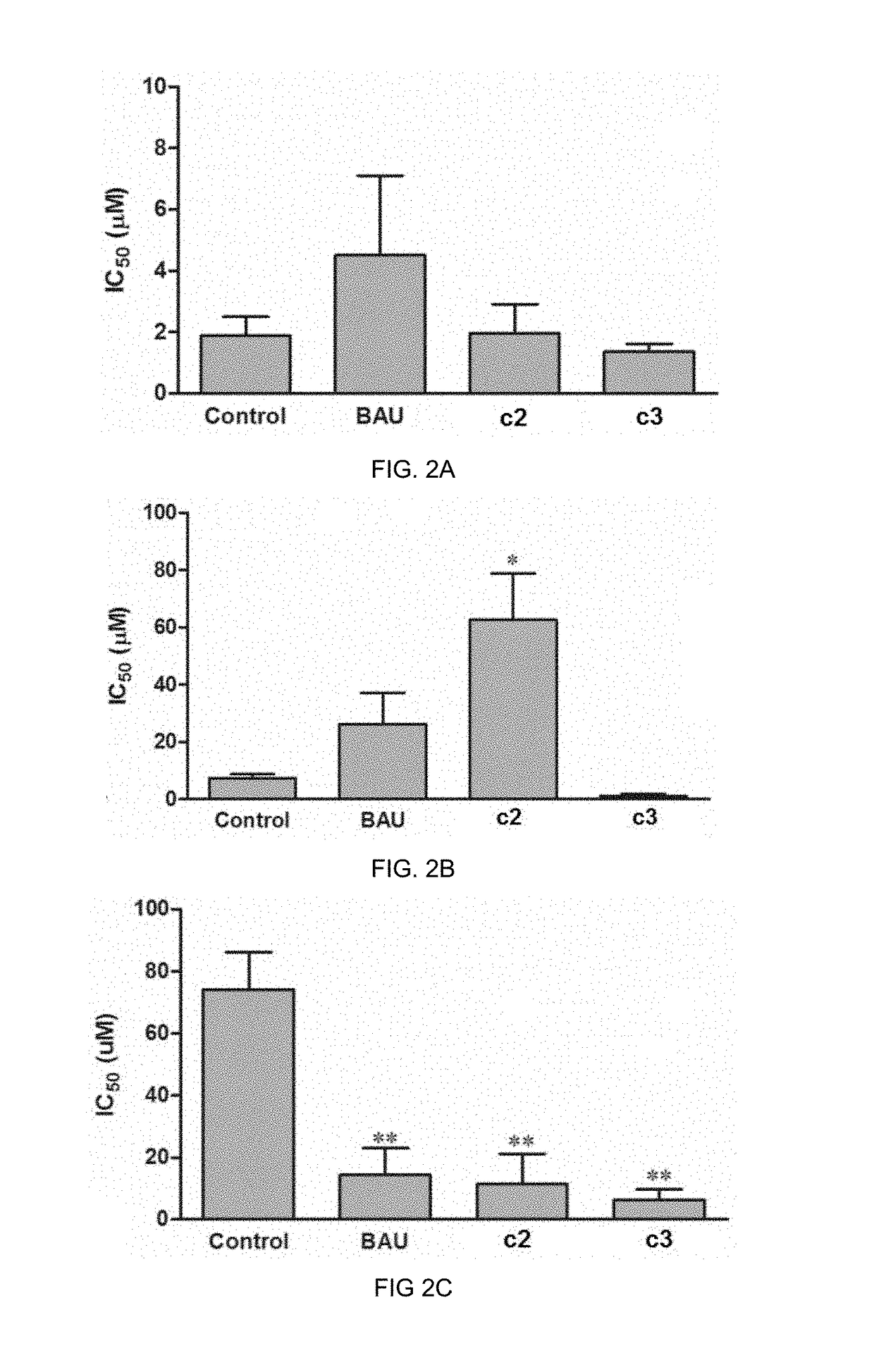
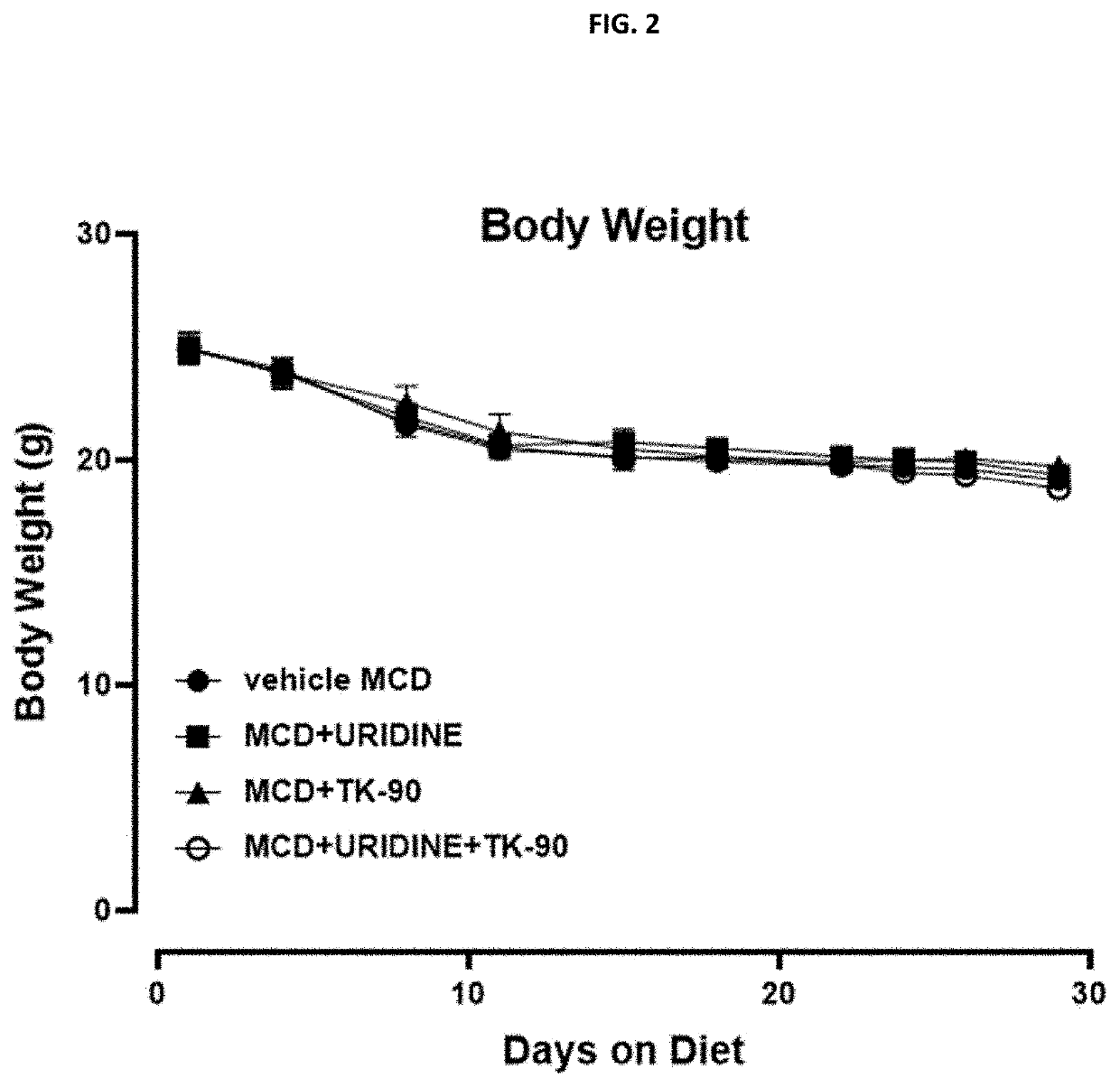
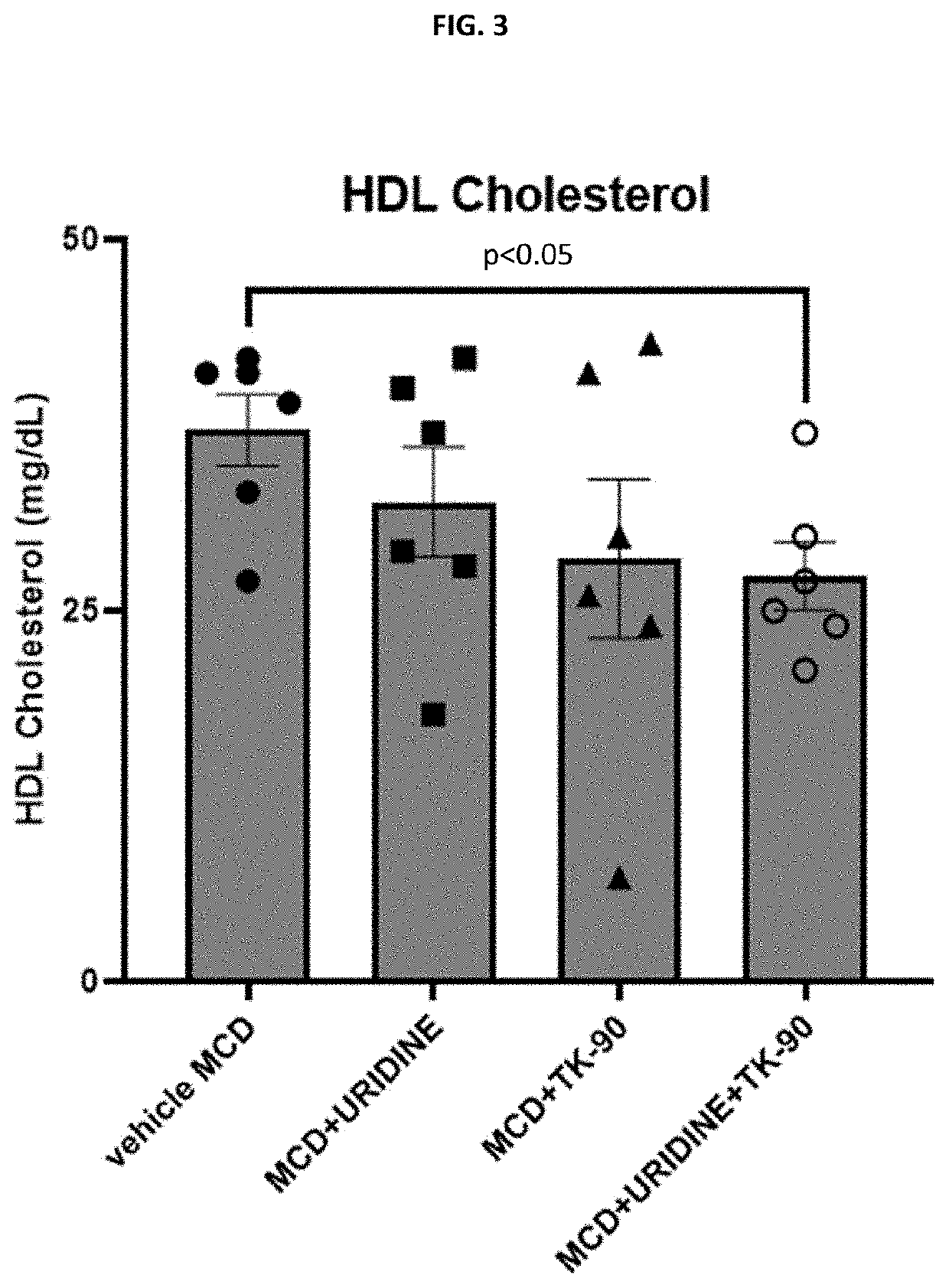
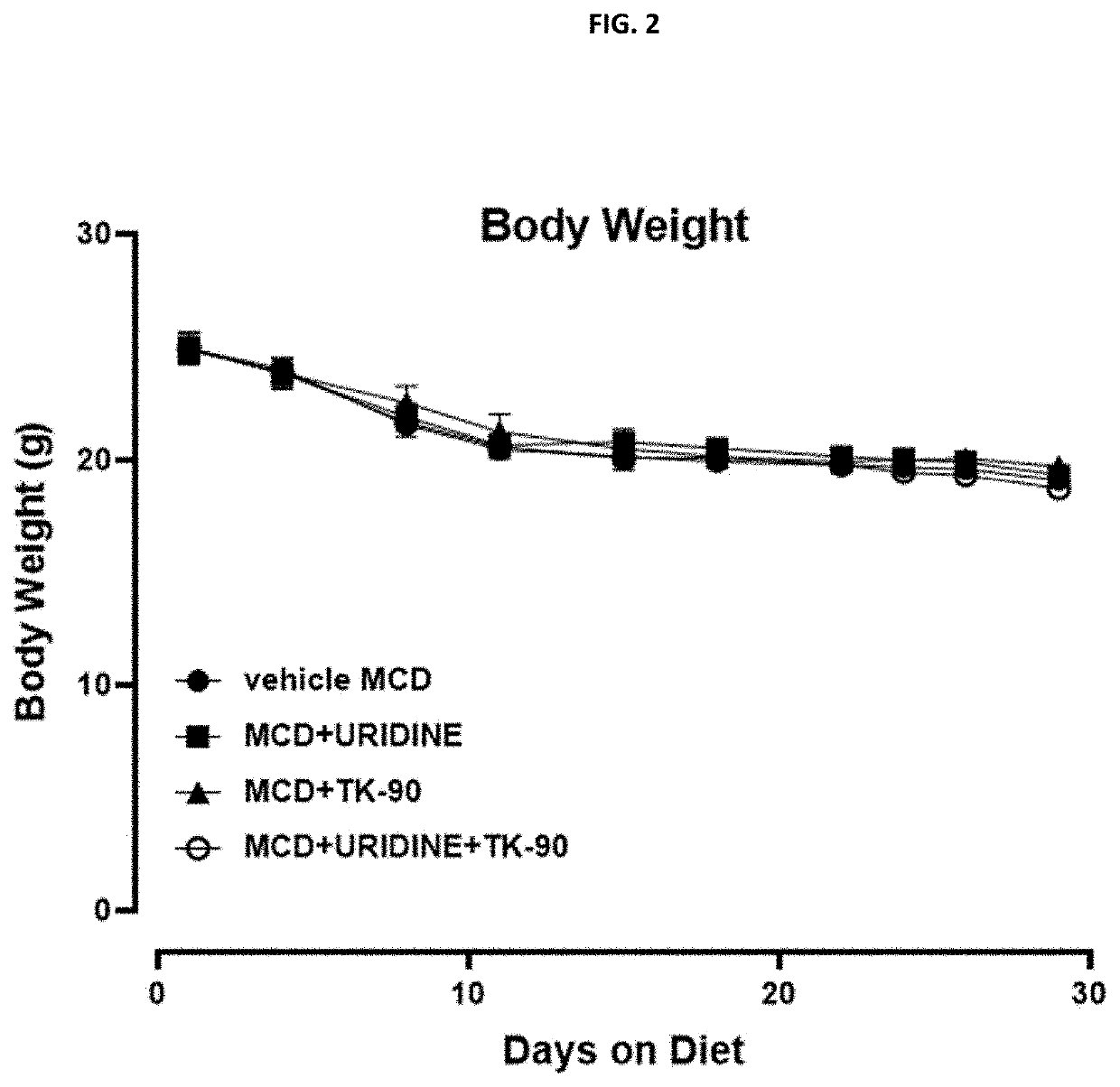
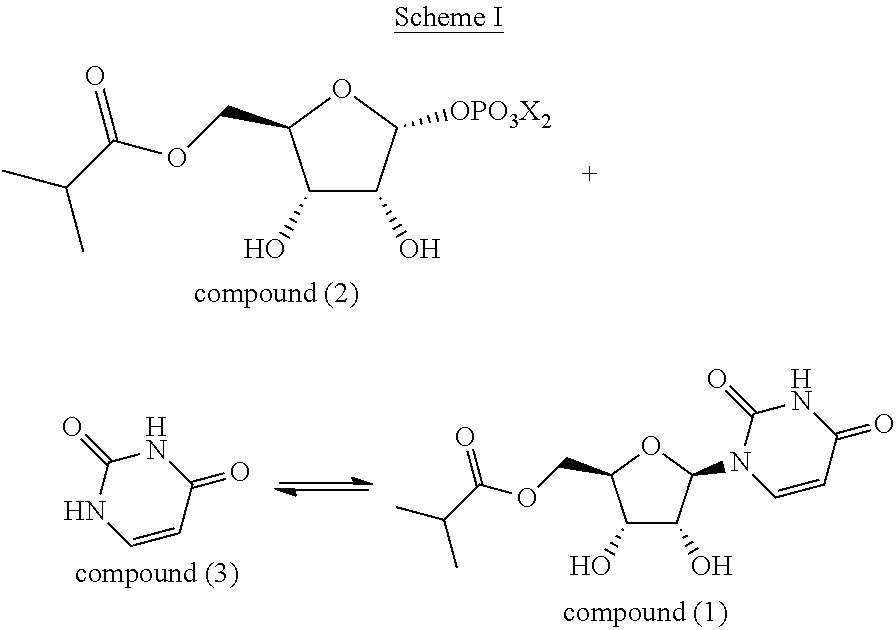
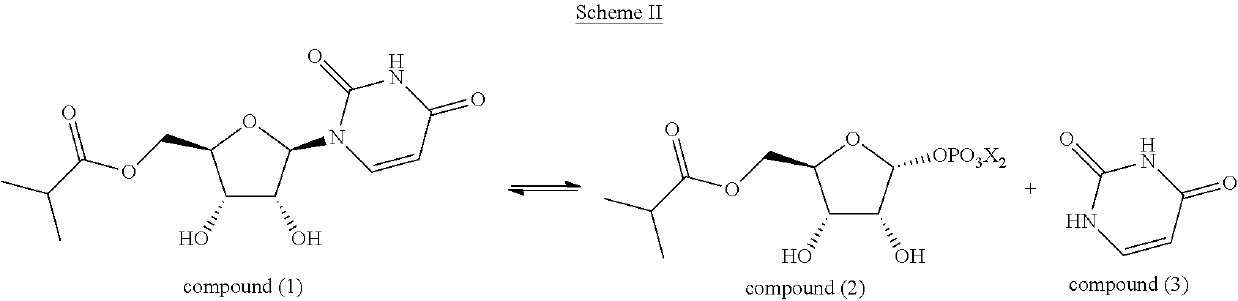
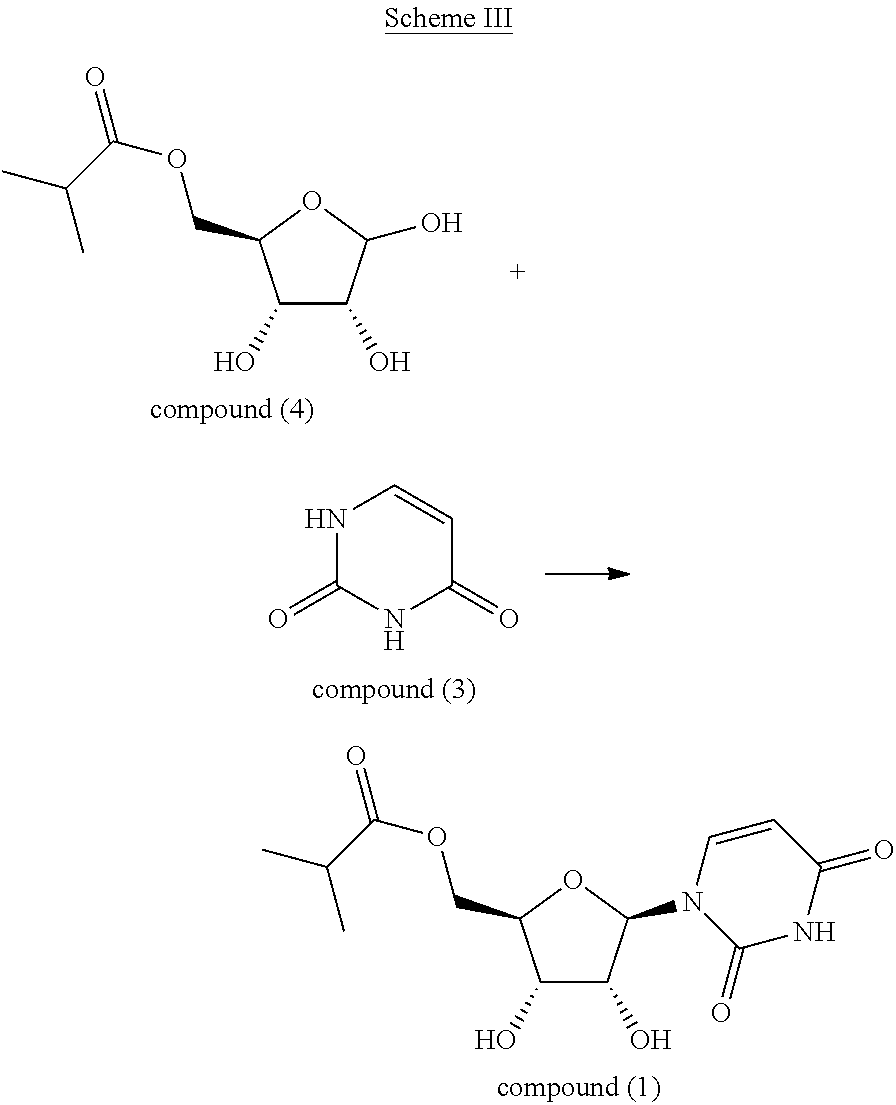
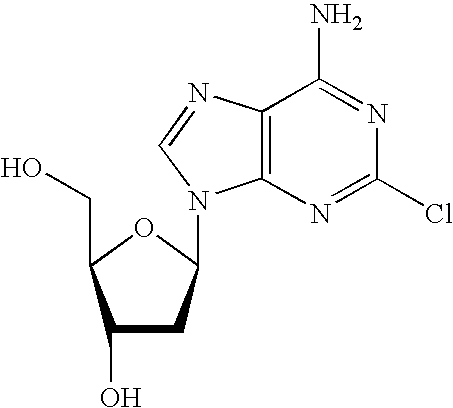
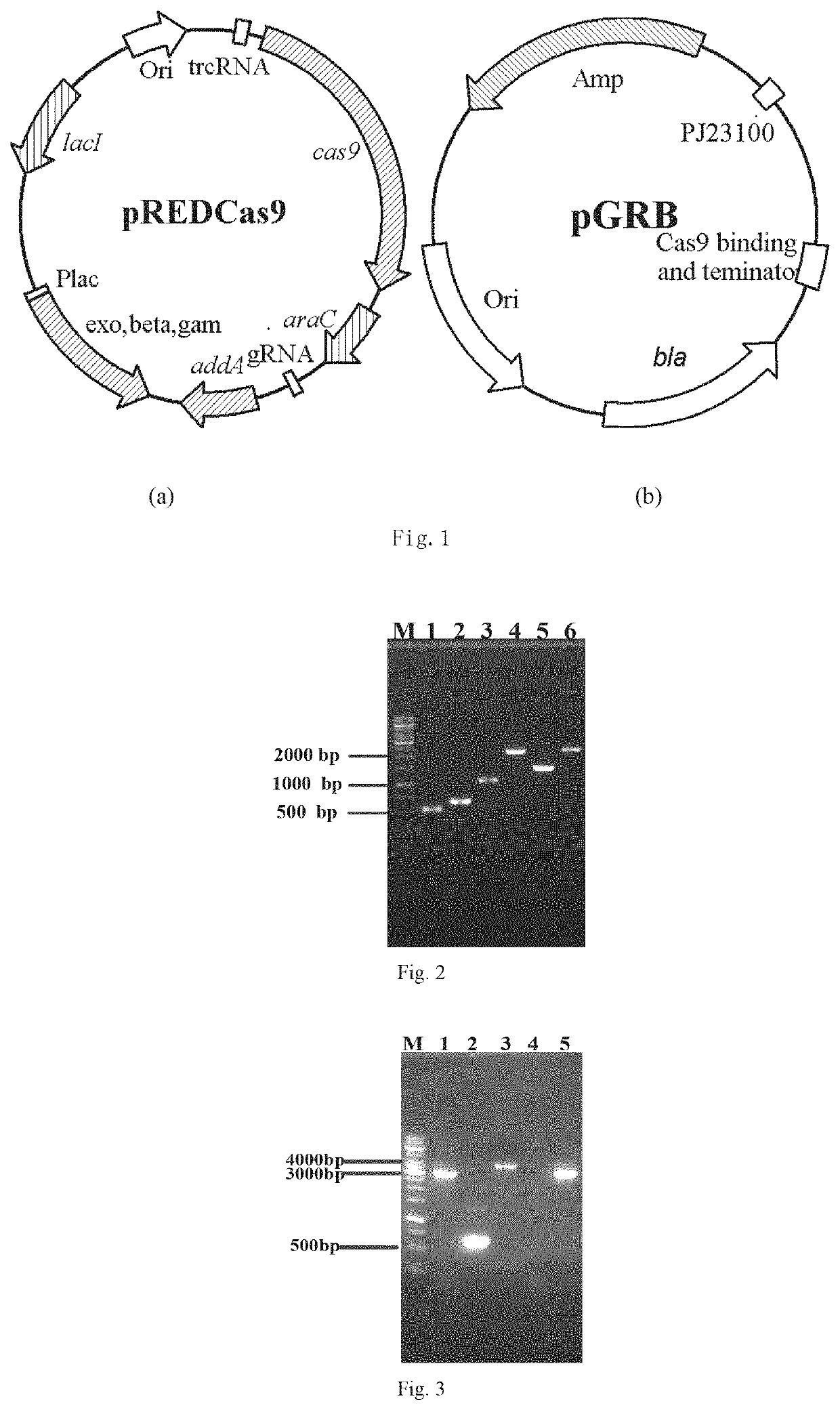
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Uridine phosphorylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
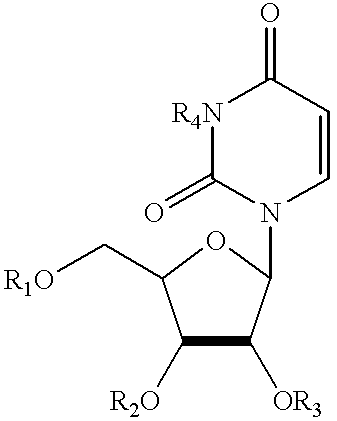
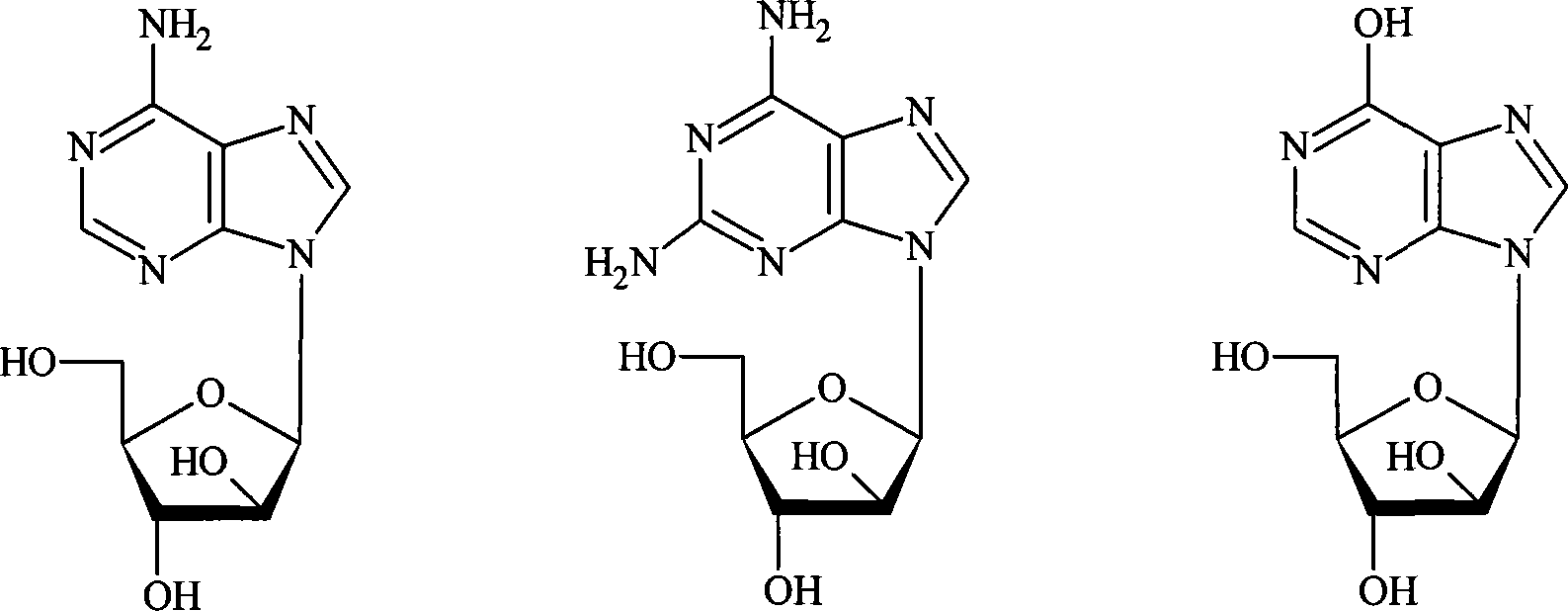
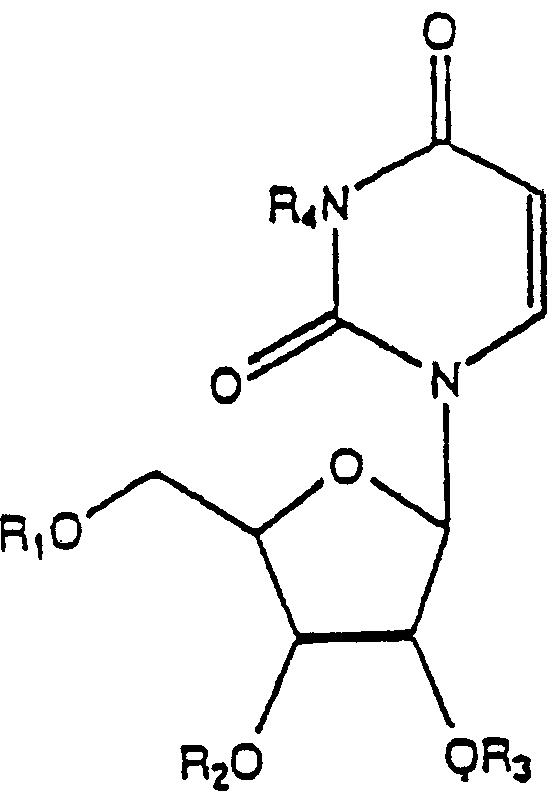
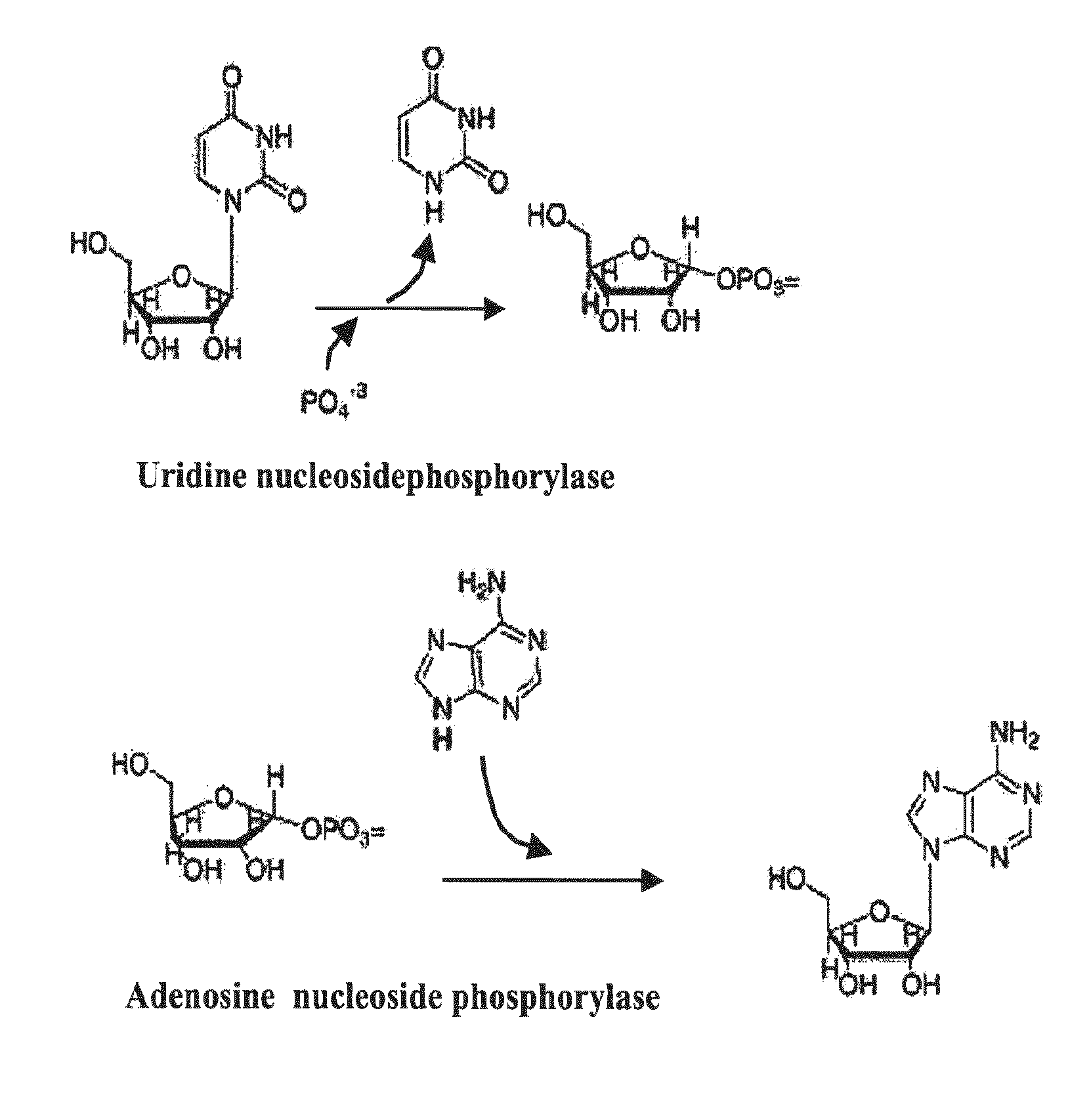
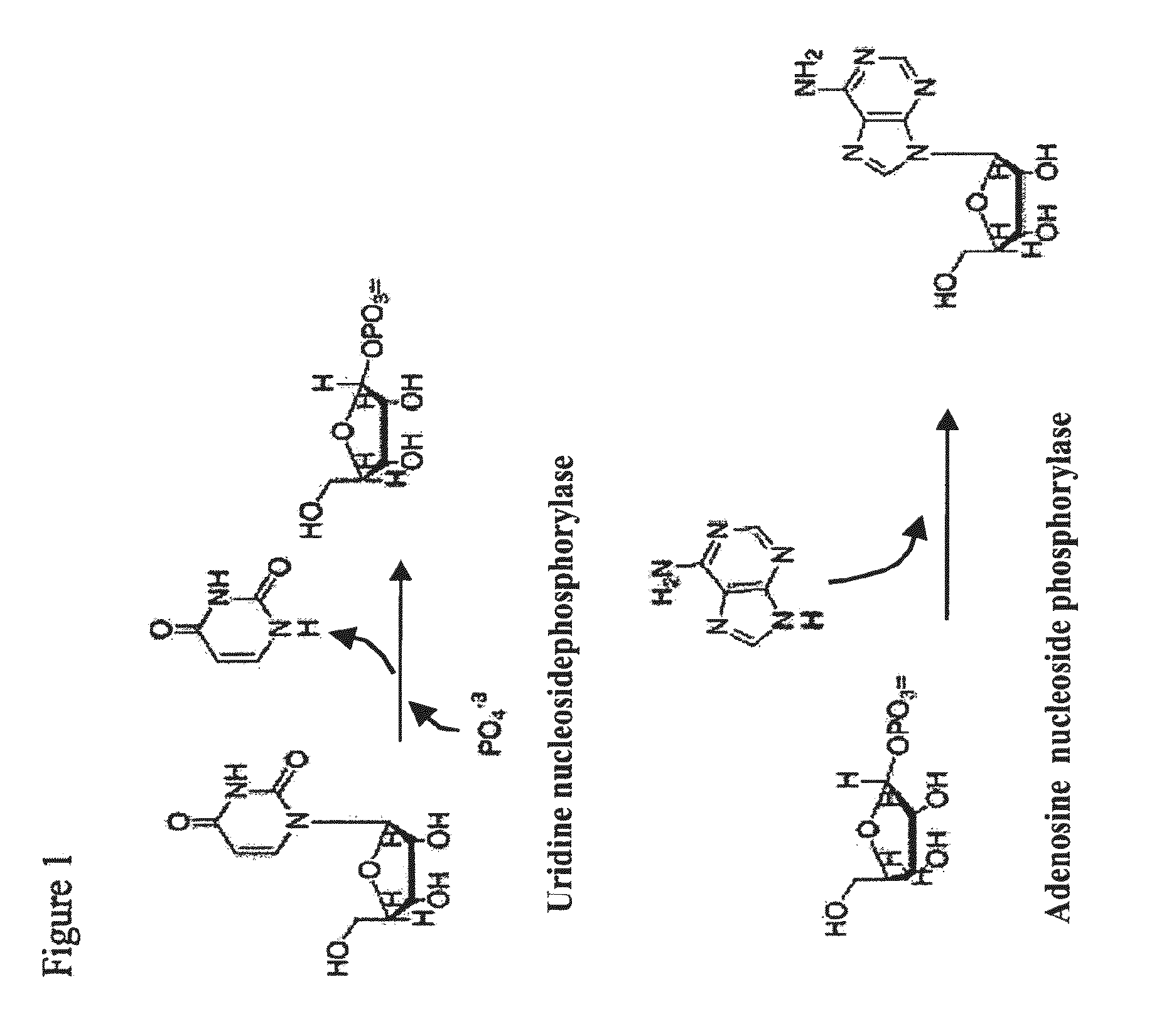
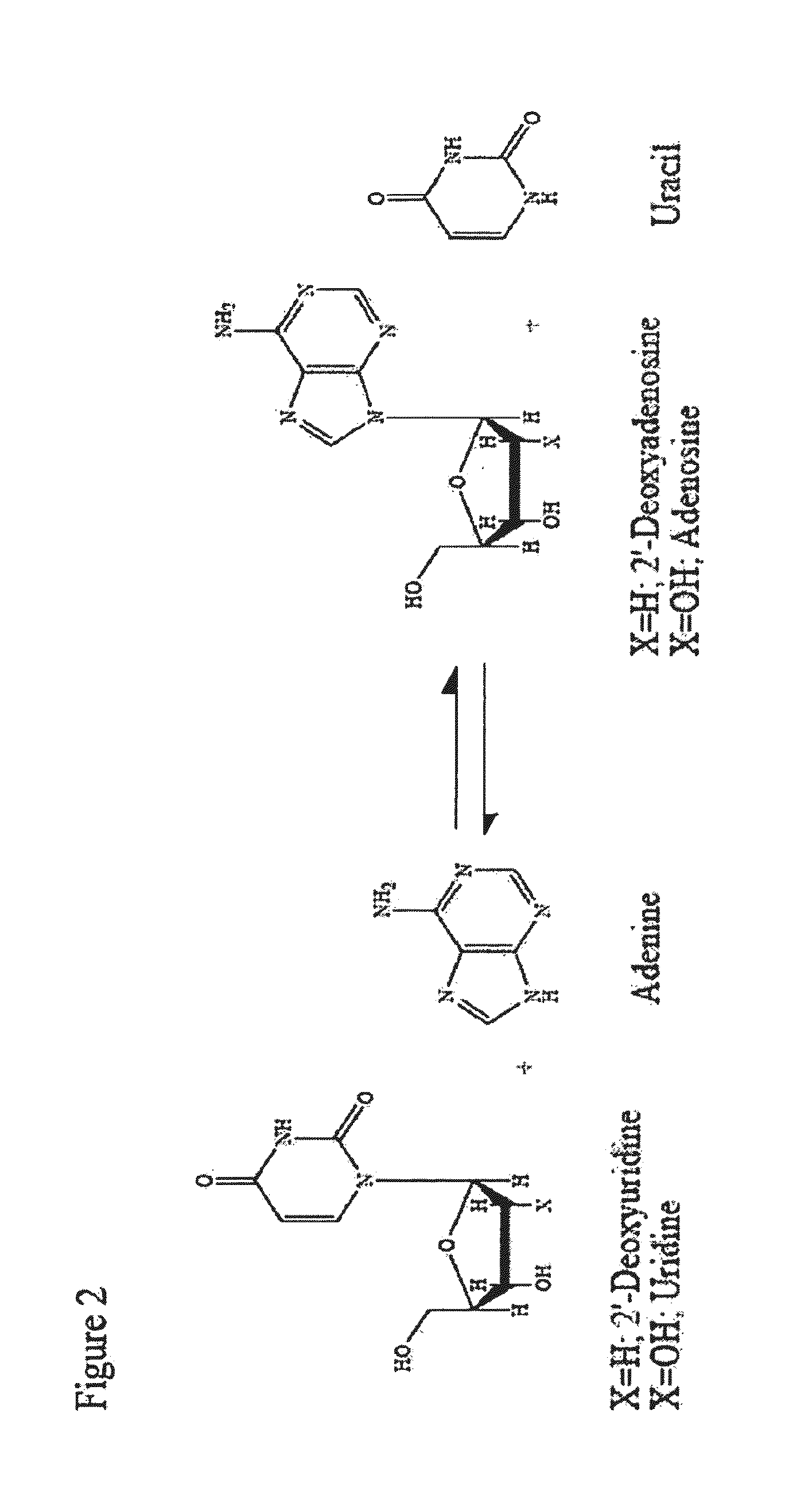
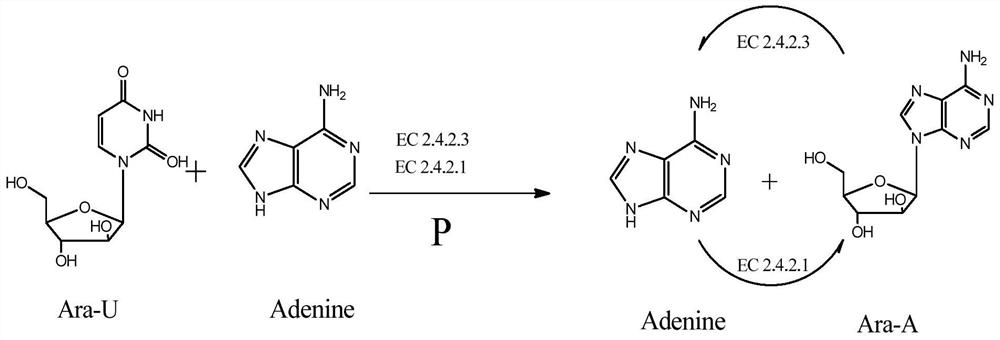
In enzymology, an uridine phosphorylase (EC 2.4.2.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction uridine + phosphate ⇌ uracil + alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are uridine and phosphate, whereas its two products are uracil and alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate. This enzyme belongs to the family of glycosyltransferases, specifically the pentosyltransferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is uridine:phosphate alpha-D-ribosyltransferase.
Genetic engineering bacterium capable of producing uridine at high yield as well as building method and application thereof
ActiveCN108130306AImprove growth traitsIncrease productivityBacteriaEnzymesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention provides a genetic engineering bacterium capable of producing uridine at high yield as well as a building method and application thereof. The genetic engineering bacterium is characterized in that pyrimidine nucleoside operons pyrBCAKDFE with the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1 is integrated on a genome of colon bacillus; the starting is realized by a strong promoter P[trc];a uridine synthesis path is reconstituted; the self PRPP synthetase coding gene prsA on the genome is subjected to dual copying, and the starting is realized by the strong promoter P[trc]; meanwhile,the activity of udk, udp, and rihA, rihB and rihC is lacked; the thrA activity is lacked; the argF activity is lacked. The genetic engineering bacterium is applied to fermentation production of uridine; 40 to 67g / L of uridine can be produced after the fermentation is performed for 40 to 70h in a 5L fermentation tank; the maximum production intensity can reach 1.5g / (L*h); the glucoside conversionrate is 15 to 25 percent; the genetic engineering bacterium belongs to the highest level for producing the uridine by the fermentation method reported in the prior art.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
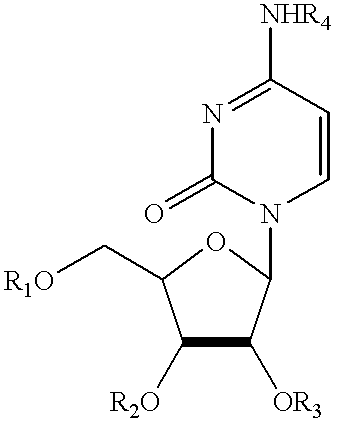
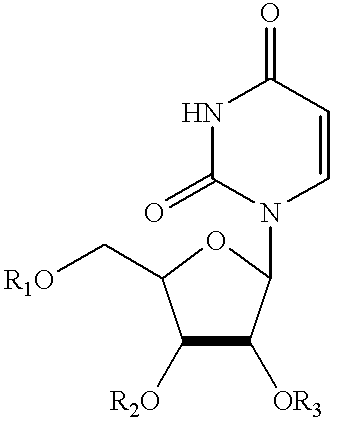
Pyrimidine nucleotide precursors for treatment of systemic inflammation and inflammatory hepatitis
InactiveUS6232298B1Avoid tissue damageImprove survivalBiocideSugar derivativesIncreased orotic acidHepatitis
Pyrimidine nucleotide precursors including acyl derivatives of cytidine, uridine, and orotate, and uridine phosphorylase inhibitors, and their use in enhancing resistance to sepsis or systemic inflammation are disclosed.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
Methotrexate adjuvants to reduce toxicity and methods for using the same
Methods are provided for using methotrexate (MTX) in which reduced host toxicity is observed. Aspects of the methods include administering to a subject an effective amount of MTX in conjunction with a MTX toxicity-reducing adjuvant, such as a 2,2′-anhydropyrimidine, a derivative thereof or a uridine phosphorylase inhibitor. Also provided are compositions that find use in practicing embodiments of the invention. The methods and compositions find use in a variety of applications, including the treatment of a variety of different disease conditions.
Owner:TOSK INC +1
Pyrimidine nucleotide precursors for treatment of systemic inflammation and inflammatory hepatitis
Pyrimidine nucleotide precursors including acyl derivatives of cytidine, uridine, and orotate, and uridine phosphorylase inhibitors, and their use in enhancing resistance to sepsis or systemic inflammation are disclosed.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
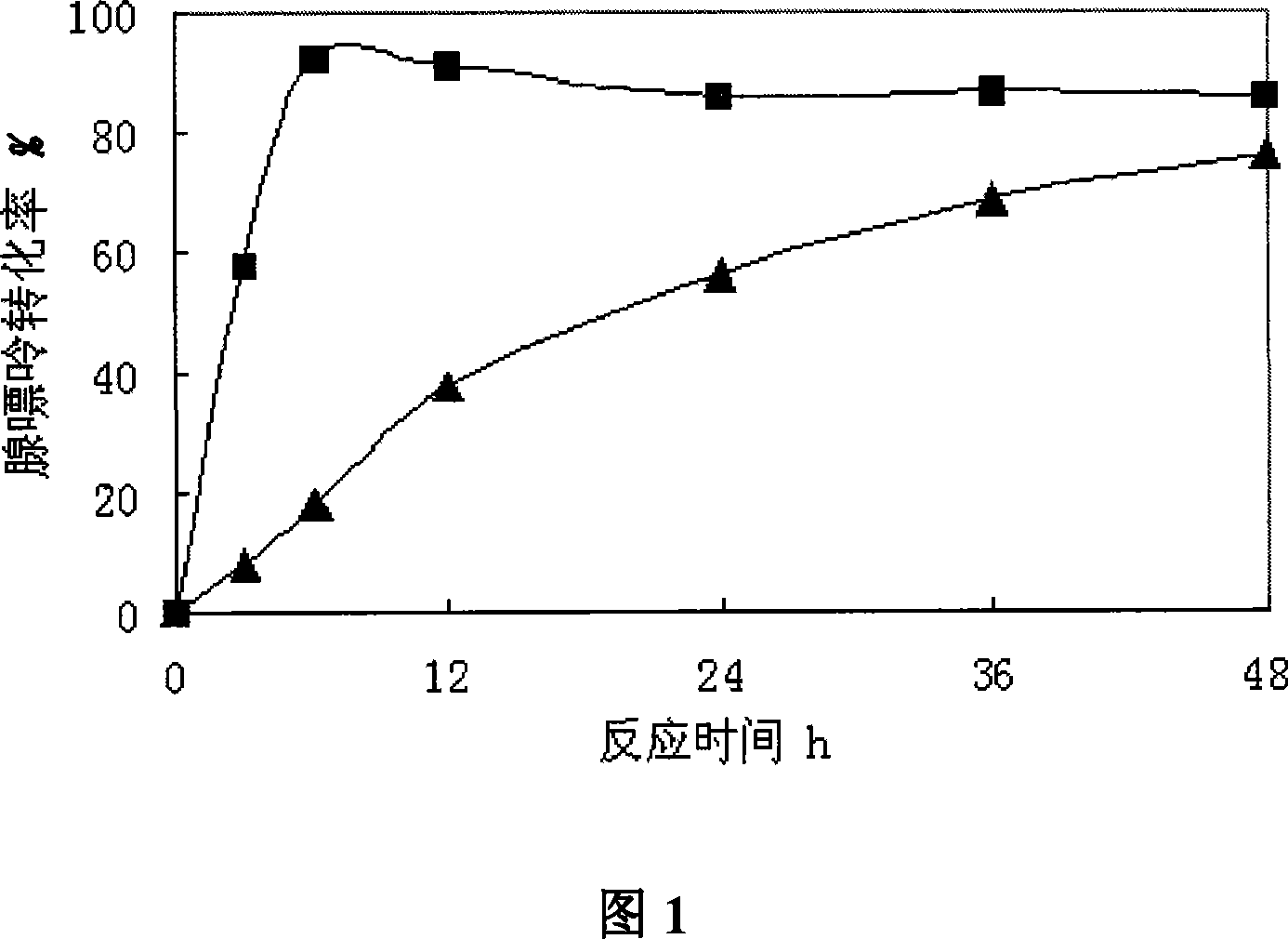
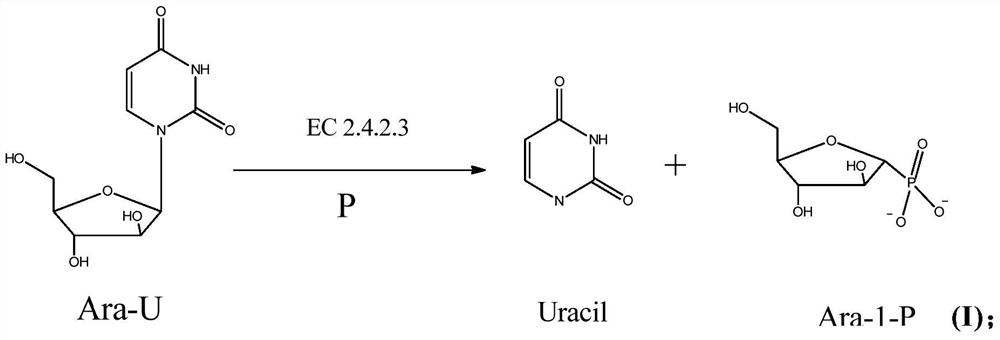
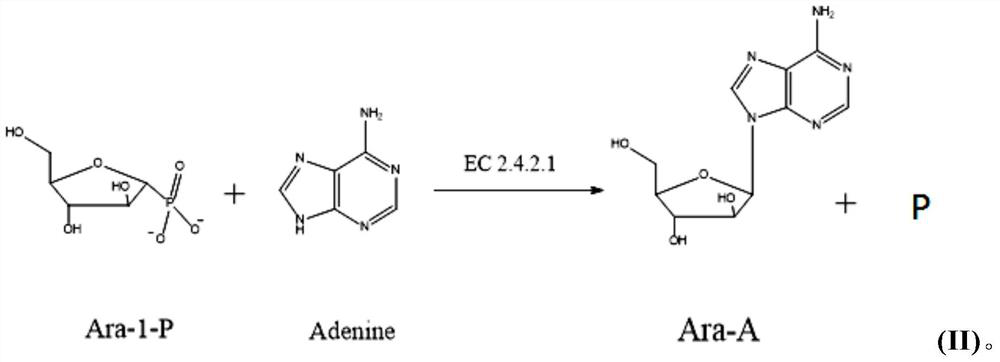
Method for preparing 2'-deoxyuridine by chemical-biological enzyme method in combination
ActiveCN102827902AHigh yieldImprove conversion rateChemical recyclingFermentationUracil2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
The invention provides a method for preparing 2'-deoxyuridine by a chemical-biological enzyme method in combination. A 'crystallization induction asymmetric transformation' technology is adopted to synthetize and obtain single alpha-configuration nucleoside analogues medicine intermediate 2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose-1-phosphate; the intermediate is utilized as a substrate; uracil is added, and 2'-deoxyuridine is synthetized and obtained by biotransformation under the action of uridine phosphorylase. By applying the chemical-biological combination technology disclosed by the invention, the advantages of a chemical method and a biological method are combined; the defects of the chemical method and the biological method are avoided; the yield is high; the method is suitable for industrial production; enough supply can be obtained by the 'crystallization induction asymmetric transformation' technology; 2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose-1-phosphate intermediate with single configuration does not need to be separated and purified; the biotransformation process is finished by catalysis with efficient and specific uridine phosphorylase in one step; the specificity is strong; the conversion rate is high; the condition is mild and the environment is friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Pyrimidine nucleotide precursors for treatment of systemic inflammation and inflammatory hepatitis
InactiveUS6329350B1Avoid tissue damageImprove survivalBiocideSugar derivativesIncreased orotic acidHepatitis
Pyrimidine nucleotide precursors including acyl derivatives of cytidine, uridine, and orotate, and uridine phosphorylase inhibitors, and their use in enhancing resistance to sepsis or systemic inflammation are disclosed.
Owner:PRO NEURON INC
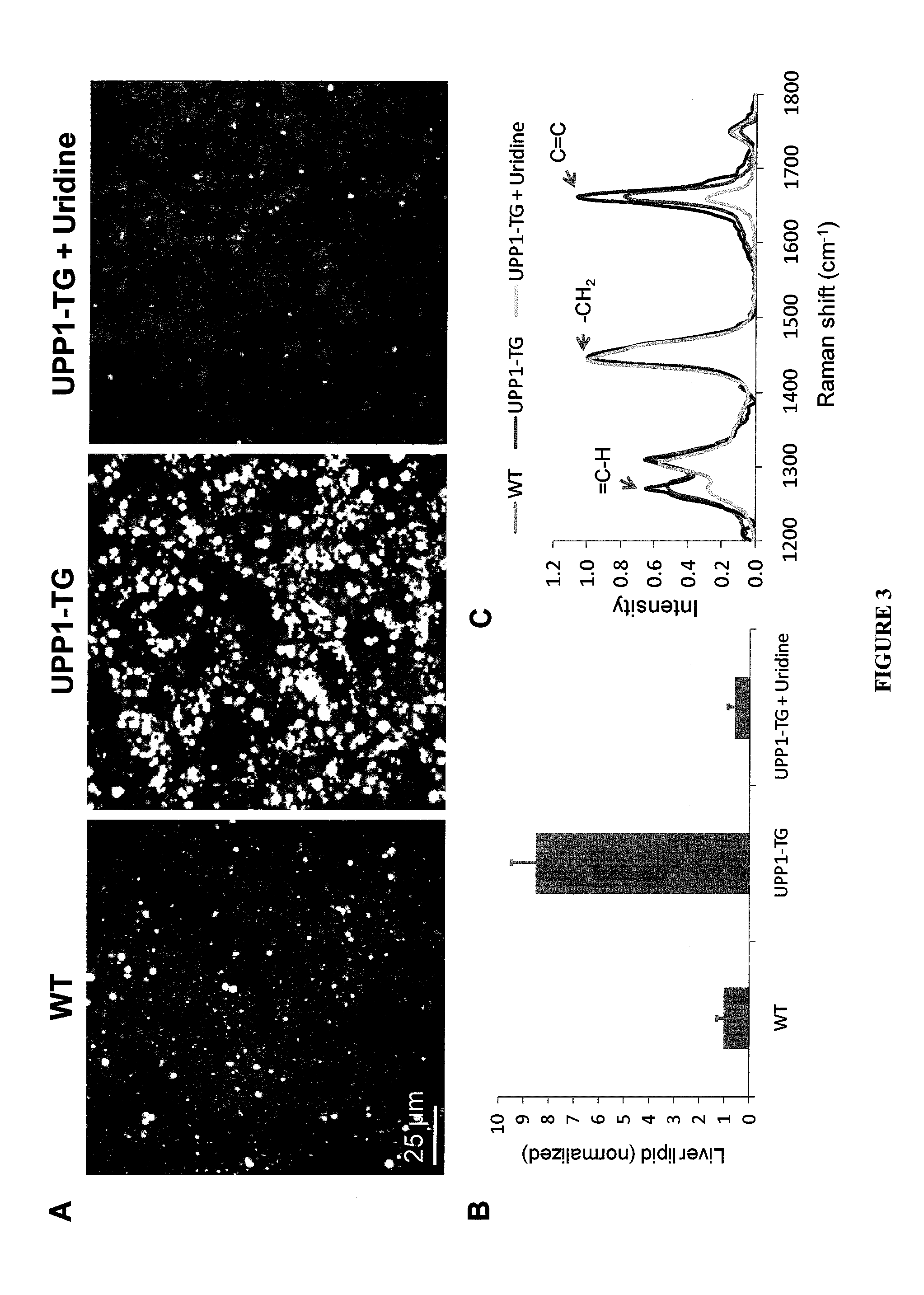
Methods for Treating Fatty Liver Disease
InactiveUS20120294869A1Increased serum half-lifePromote absorptionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsLiver diseaseNon alcoholic
The present invention relates to the compositions, formulations and methods of treating fatty liver disorders, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and their sequelae by administration of uridine or a compound that modulates one or more uridine phosphorylases in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:NEVADA CANCER INST FOUND
Bacterial with high-yield of nucleoside phosphorylase and method for synthesizing arabinose nucleoside
InactiveCN101113420AIncrease vitalityImprove conversion rateBacteriaFermentationFlucytosineNucleoside phosphorylase
A compound method of high-yield nucleoside phosphorylase strains and arabinose nucleoside pertains to biochemical engineering field, in particular to the high-yield nucleoside phosphorylase strains and a method for compounding arabinose purine nucleoside with the strains by an enzyme method. The invention aims at solving a technical problem for providing the strains of the high-yield nucleoside phosphorylase and strains of uridine phosphorylase and the method for producing the arabinose purine nucleoside with the strains. The invention discloses enterobacter aerogenes with a preservation number of CGMCC No.2035 and the method for producing the arabinose purine nucleoside with the strains, and the invention comprises steps that (1) the enterobacter aerogenes DWOQ-58 of the invention is cultured and collected, and (2) the enterobacter aerogenes DWOQ-58 is contacted with arabinose donor and receptors of purine base. The strains of the invention are rich in vigor and resists 5-flucytosine with an average conversion rate of more than 80 percent in general and the reaction time of the invention is shortened to less than 12 hours.
Owner:SHANGHAI WEIPING BIOLOGICAL TECH
Preparation method of vidarabine monophosphate
InactiveCN104372050ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleoside phosphorylaseGenetically engineered
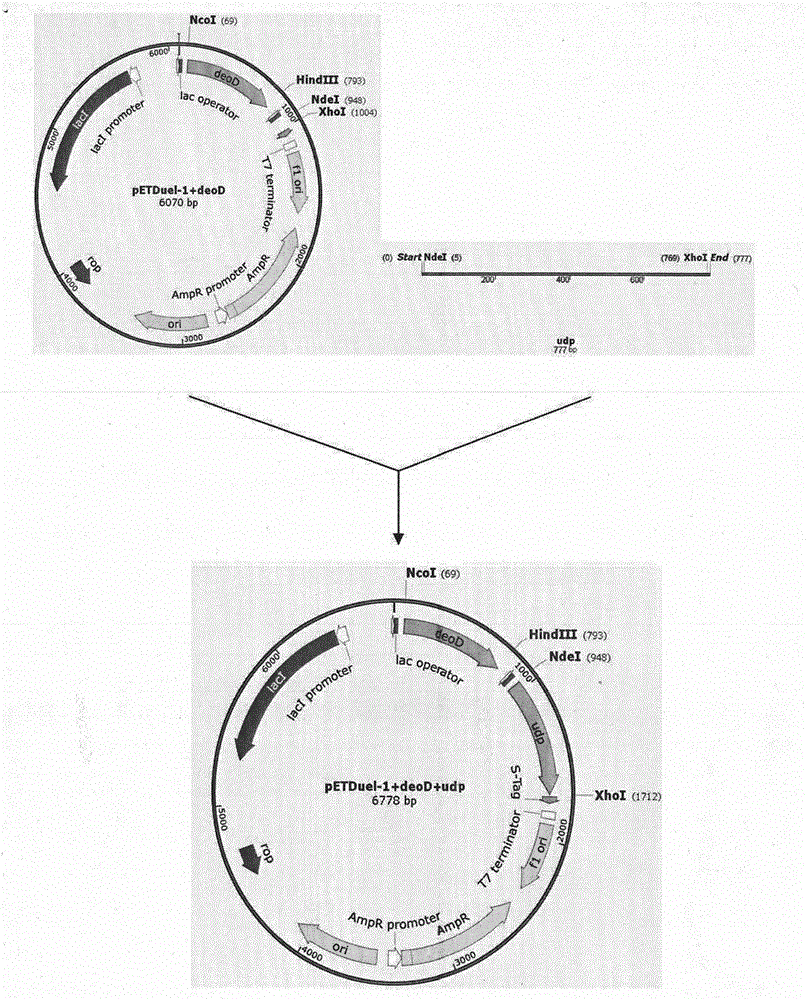
The invention discloses a preparation method of vidarabine monophosphate. The method first prepares genetically engineered bacterium with co-expression of purine nucleoside phosphorylase and uridine phosphorylase, and then uses the genetically engineered bacterium to prepare vidarabine monophosphate. The method is characterized in that coexpression of purine nucleoside phosphorylase and uridine phosphorylase is realized in genetically engineered bacterium by using a molecular cloning method, so as to obtain vidarabine biotransformation bacteria with high enzyme specific activity; the thalli obtained by the invention is used to produce vidarabine; and the reaction substrate concentration can be increased to more than 100 mM, the reaction conversion rate is more than 90%, the dosage of reaction thalli is less than 0.3% (thalli wet weight / reaction volume ml), and reaction time is shortened to 6 h.
Owner:GUANGDONG XIANQIANG PHARMA
Pyrimidine nucleotide precursors for treatment of systemic inflammation and inflammatory hepatitis
InactiveUS20040033981A1Avoid tissue damageImprove survivalBiocideSugar derivativesHepatitisPyrimidine Nucleotides
Pyrimidine nucleotide precursors including acyl derivatives of cytidine, uridine, and orotate, and uridine phosphorylase inhibitors, and their use in enhancing resistance to sepsis or systemic inflammation are disclosed.
Owner:PRO NEURON INC
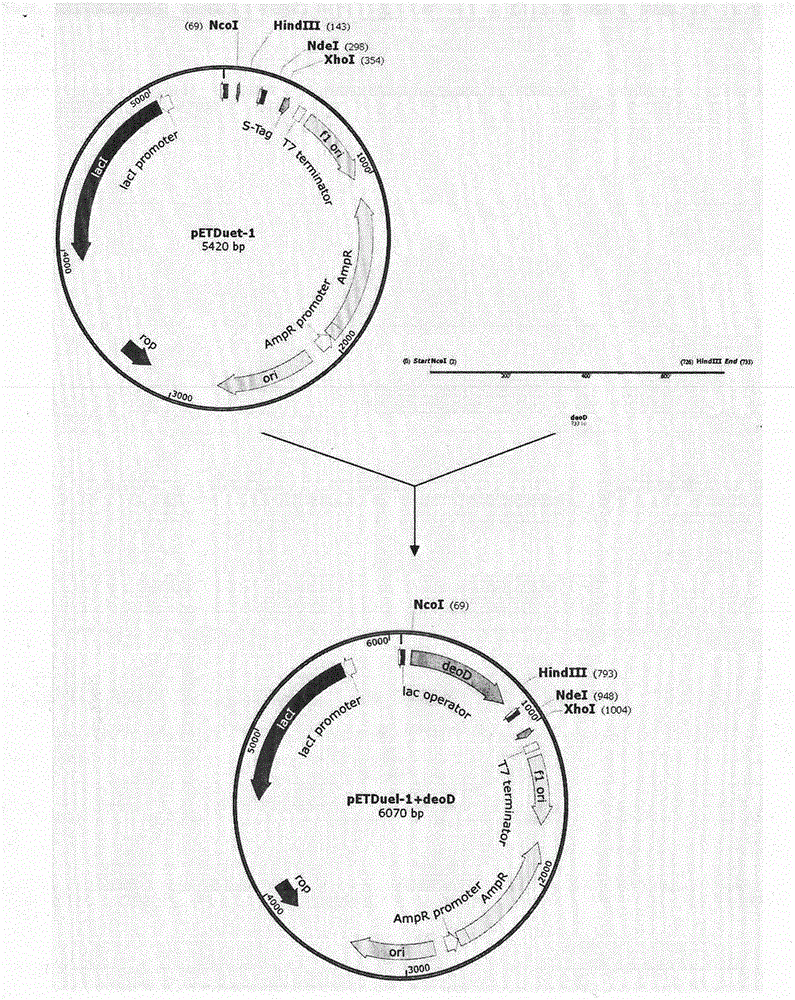
Fermentation medium and method for fermentation production of uridine phosphorylase using the same
A fermentation medium comprises: NaCl (3-12 g / L), glucose (10-25 g / L), extract yeast (5-15 g / L), peptone (2-15 g / L), K2HPO4-H2O (1 / 3) (2-5 g / L), uridine (7-25 mmol / L), inosine (15-30 mmol / L) and double distilled water. A fermentation method based on the fermentation medium comprises: streaking, inoculating and culturing lactobacillus brevis for 12-48 h, preserving at 4 DEG C for a standby application; taking and dissolving a certain amount of extract yeast in double distilled water, adjusting pH at 6.0-8.0, disinfecting at 121 DEG C for 15-20 min, and obtaining an activating solution containing 1-10% by mass of extract yeast; picking lactobacillus brevis, inoculating to the activating solution, activating at 30-40 DEG C for 4-12 h, and obtaining activated lactobacillus brevis thalluses; inoculating the lactobacillus brevis thalluses to the fermentation medium with an inoculation volume of 1-10% by volume; fermenting for 4-12 h with a medium temperature of 30-40 DEG C and a shaking-table rotating speed of 90-180 r / min, and obtaining a fermentation liquor; centrifuging the fermentation liquor for 10-30 min with a speed of 3000-5000 r / min, in a centrifuge tube obtaining a deposition which is the fermented whole-cell lactobacillus brevis wet thallus, and taking the fermented whole-cell lactobacillus brevis wet thallus as a uridine phosphorylase source to carry out nucleosides fermentation.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method for the production of cladribine
InactiveUS20100291632A1Improve isolationHigh yieldOrganic chemistryFermentationPurine nucleoside phosphorylaseSolvent
A method for producing cladribine (2-chloro-2′-deoxyadenosine) comprising the steps of:a) reaction of 2-deoxyuridine with 2-chloroadenine, in the presence of uridine phosphorylase (UPase) and purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNPase) in an aqueous reaction medium possibly containing up to 40% v / v of an aprotic dipolar solvent, to obtain cladribine dissolved in said reaction medium;b) isolation of the cladribine by precipitation by means of concentration and alkalinisation of the reaction medium up to pH 11.5-12.5.
Owner:EXPLORA LAB
Recombinant microorganism for producing uridine and method for producing uridine
PendingCN113755414ARealize large-scale industrial productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRibonucleosidePhosphorylation
The invention provides a recombinant microorganism for producing uridine and a method for producing uridine by using the recombinant microorganism. Wherein the uridine is degraded and knocked out by using genes, and the genes encode ribonucleoside hydrolase, uridine phosphorylase, nucleoside phosphorylase, cytidine / uridine kinase and nucleoside transporter protein. Meanwhile, overexpression is carried out on key enzymes in a uridine biosynthetic pathway, including cytidine triphosphate pyrophosphorylase for degrading cytidine triphosphate to cytidine monophosphate and uridine monophosphate phosphorylase for catalyzing uridine monophosphate to uridine. In addition, a pyrimidine nucleoside pathway is subjected to genetic engineering modification, and feedback inhibition of a synthetic pathway is relieved. The recombinant strain can reach the uridine yield of 20 g / L or above in a 5-liter fermentation tank through a biological fermentation method, industrial mass production can be achieved, meanwhile, the uridine production cost is low, pollution is reduced, the method is green and environmentally friendly, and the method has high application and popularization value.
Owner:SUZHOU BIOSYNTHETICA CO LTD
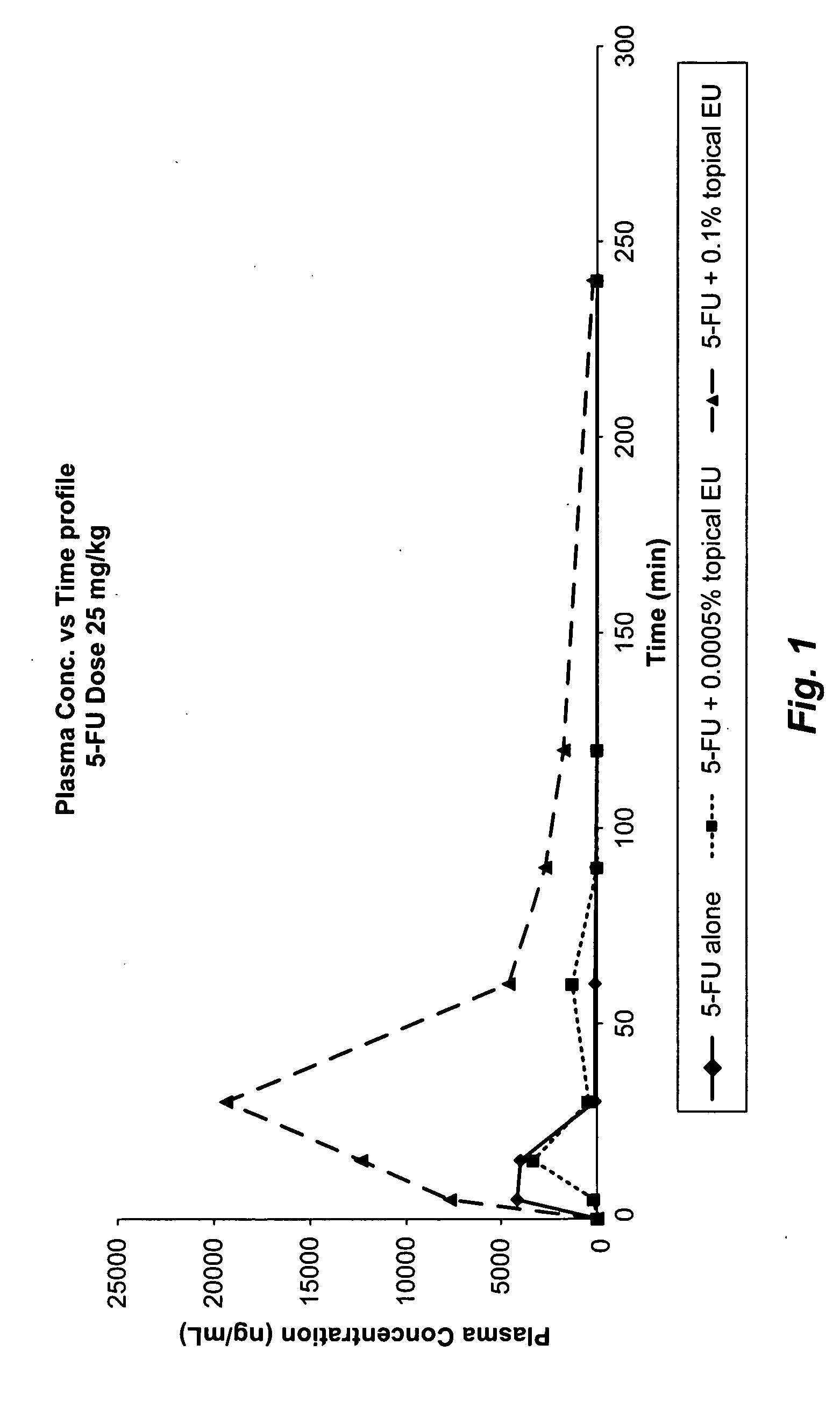
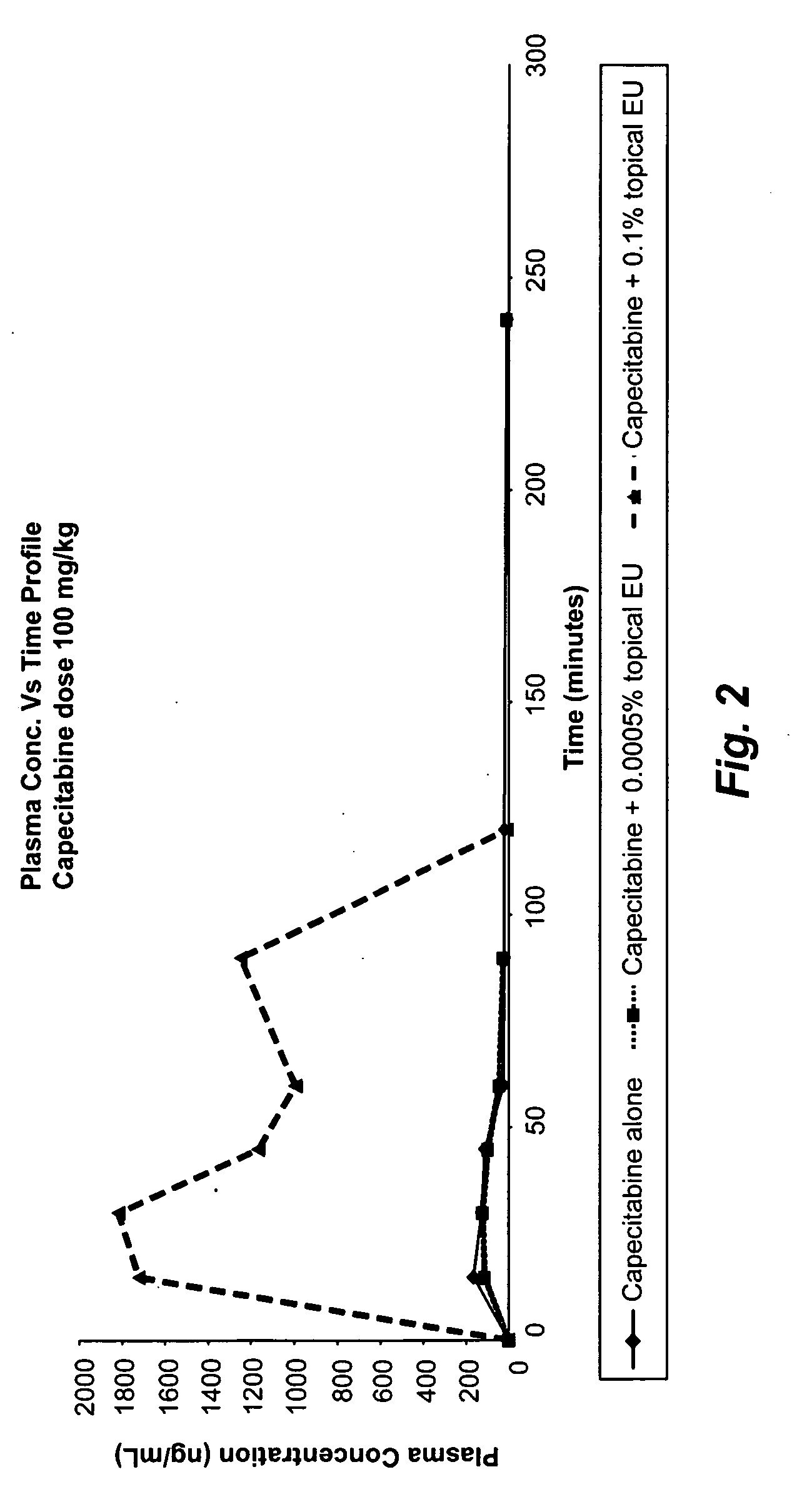
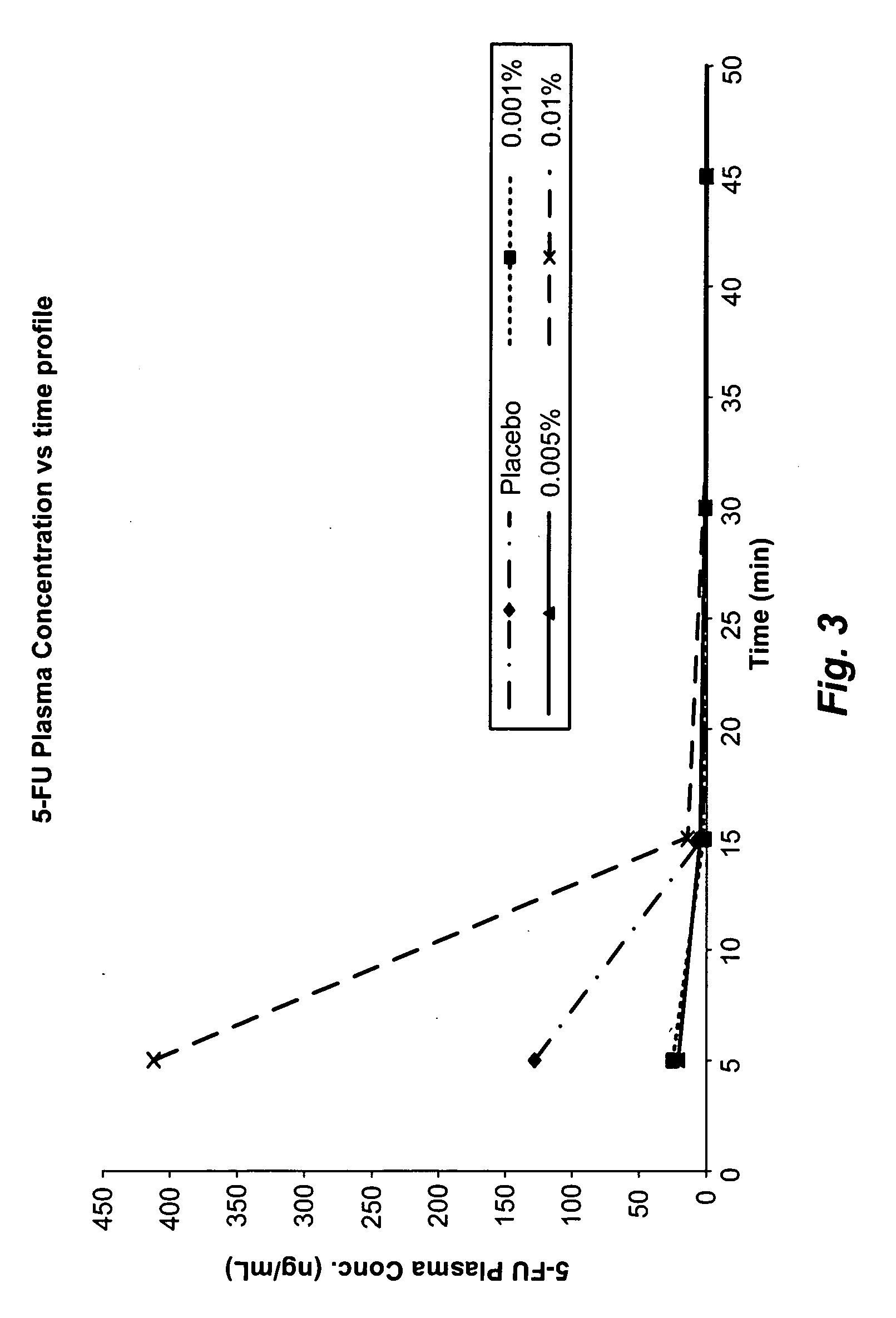
Compositions comprising topical dpd inhibitors and methods of using same in the treatment of hand-foot syndrome
InactiveUS20090196833A1Reduce frequencyReduce severityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideThymidine Phosphorylase DeficiencyMedicine
Topical formulations comprising inhibitors of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), thymidine phosphorylase (TP) and / or uridine phosphorylase (UP) enzyme inhibitors are provided for the treatment of hand-foot syndrome (HFS) in cancer patients undergoing treatment with 5-FU and 5-FU prodrugs.
Owner:ADHEREX TECH
Application of uridine phosphorylase inhibitor and composition containing the same
InactiveCN1211089CAvoid toxicityAvoid damageAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsParenteral nutritionDepressant
Pyrimidine nucleotide precursors including acyl derivatives of cytidine, uridine, and orotate, and uridine phosphorylase inhibitors, and their use in enhancing resistance to sepsis or systemic inflammation are disclosed.
Owner:PRO NEURON INC
Use of 6-hydroxy-2-pyridones and derivatives thereof for preparing a pharmaceutical composition that acts by inhibiting the human uridine phosphorylase enzyme
Owner:UNIAO BRASILEIRA DE EDUCACAO E ASSISTENCIA MANTENEDORA DA PUC RS
Thermostable biocatalyst combination for nucleoside synthesis
The present invention relates to a recombinant expression vector comprising: a) the sequence encoding a purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNPase, E. C. 2.4.2.1), b) the sequence encoding a uridine phosphorylase (UPase, E. C. 2.4.2.3), c) or both; each of the sequences operably linked to one or more control sequences that direct the production of said phosphorylases in a suitable expression host; said sequences originating from the Archaea Thermoprotei class, characterized in that the PNPase is from Sulfolobus solfataricus (SEQ ID NO. 7) and the UPase is from Aeropyrum pernix (SEQ ID NO. 8). In addition, the present invention relates to A transglycosylation method between a sugar-donating nucleoside and an acceptor base in the presence of phosphate ions, characterised in that said method comprises the use of a uridine phosphorylase (UPase) of Aeropyrum pernix (NC_000854.2), a purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PN-Pase) of Sulfolobus solfataricus (NC_002754.1), or a combination thereof.
Owner:PLASMIA BIOTECH
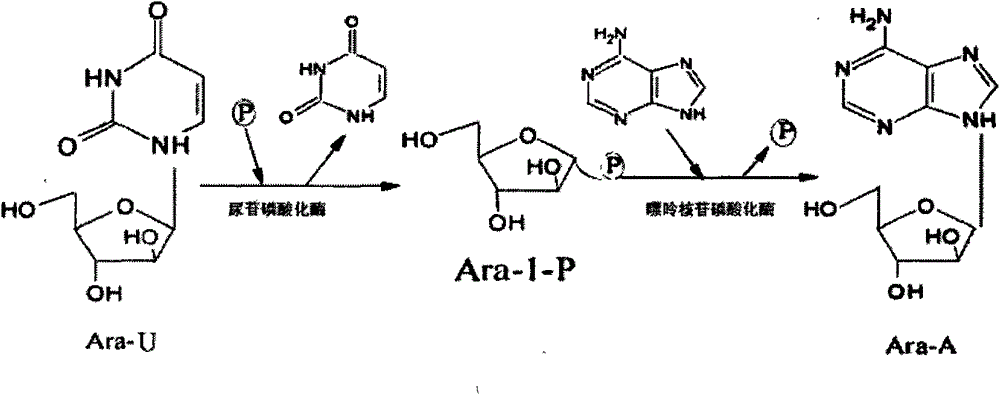
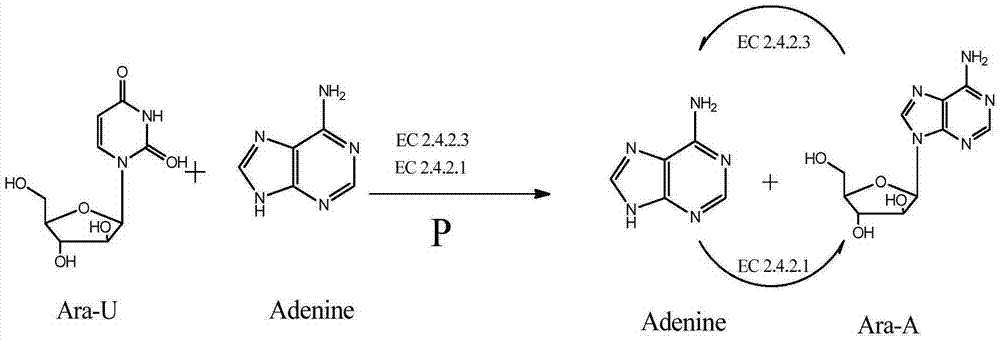
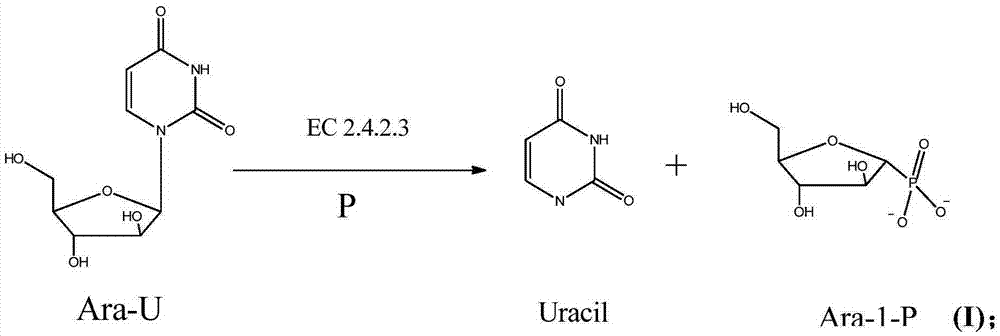
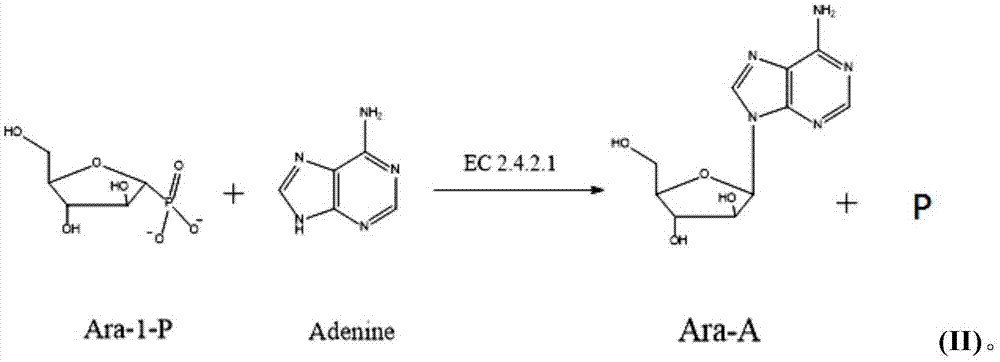
Method for synthesizing vidarabine by enzymic method
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing vidarabine by an enzymic method, and provides a method for preparing vidarabine by a two-step method. According to the method, different functions of uridine phosphorylase and purine nucleoside phosphorylase are utilized fully, so that reaction is carried in one direction; reverse reaction is eliminated; and conversion rate of the vidarabine is increased remarkably.
Owner:上海鑫欣生物科技有限公司
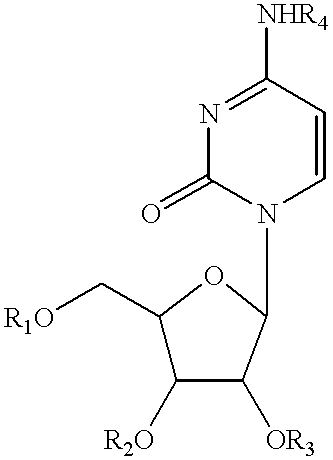
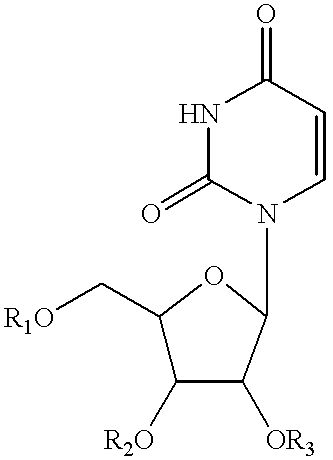
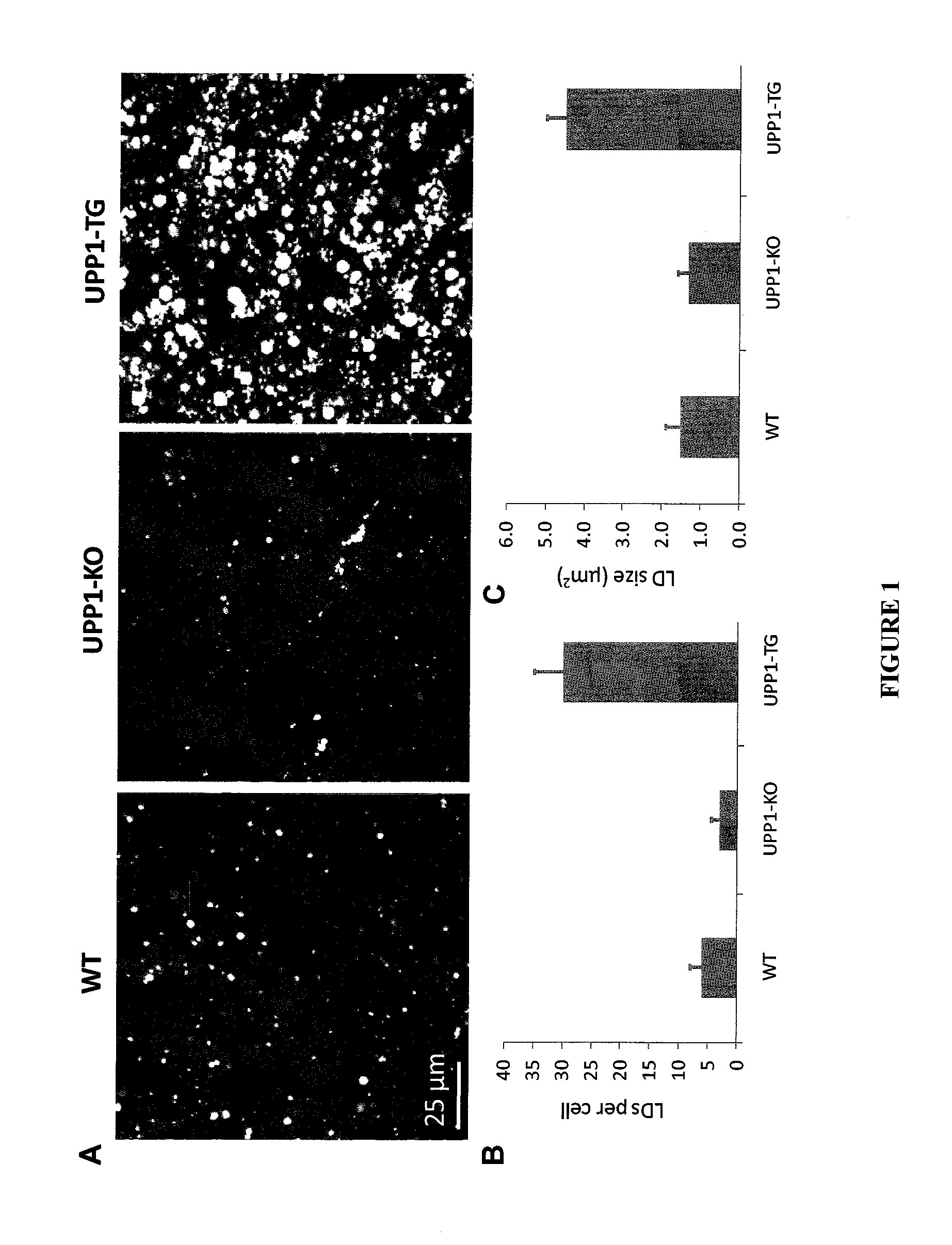
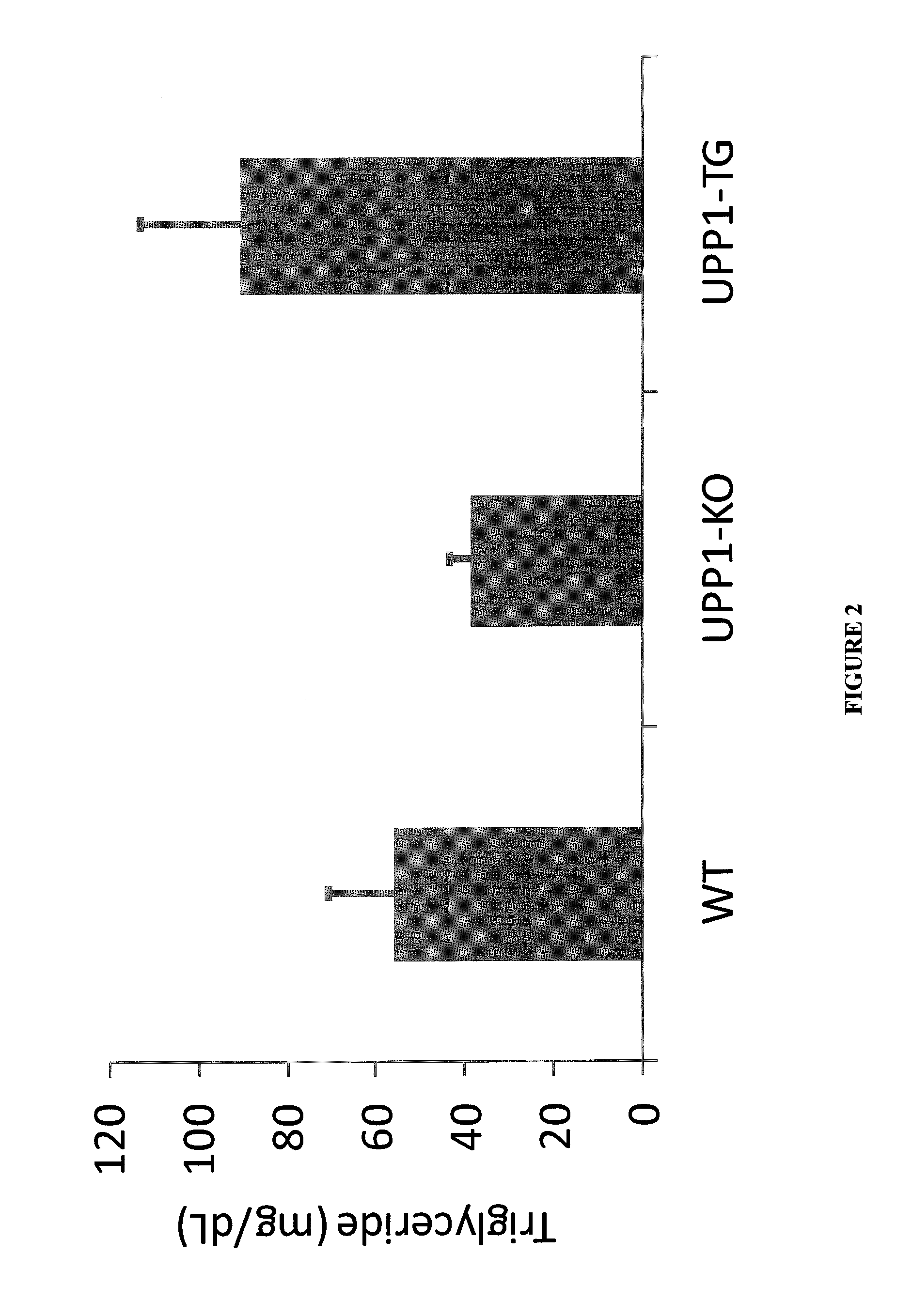
Uridine Phosphorylase (UPase) Inhibitors for Treatment of Liver Conditions
Methods of treating a subject for a liver condition, e.g., NAFLD, NASH, and / or DILI, are provided. Aspects of the methods include administering to the subject an effective amount of a UPase inhibitor, optionally in combination with a uridine active agent (e.g., uridine (UR), a UR pro-drug or a UR mimetic), such as supplemental uridine, to treat the subject for the liver condition. Also provided are compositions for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:TOSK INC
Uridine phosphorylase (UPase) inhibitors for treatment of liver conditions
Methods of treating a subject for a liver condition, e.g., NAFLD, NASH, and / or DILI, are provided. Aspects of the methods include administering to the subject an effective amount of a UPase inhibitor, optionally in combination with a uridine active agent (e.g., uridine (UR), a UR pro-drug or a UR mimetic), such as supplemental uridine, to treat the subject for the liver condition. Also provided are compositions for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:TOSK INC
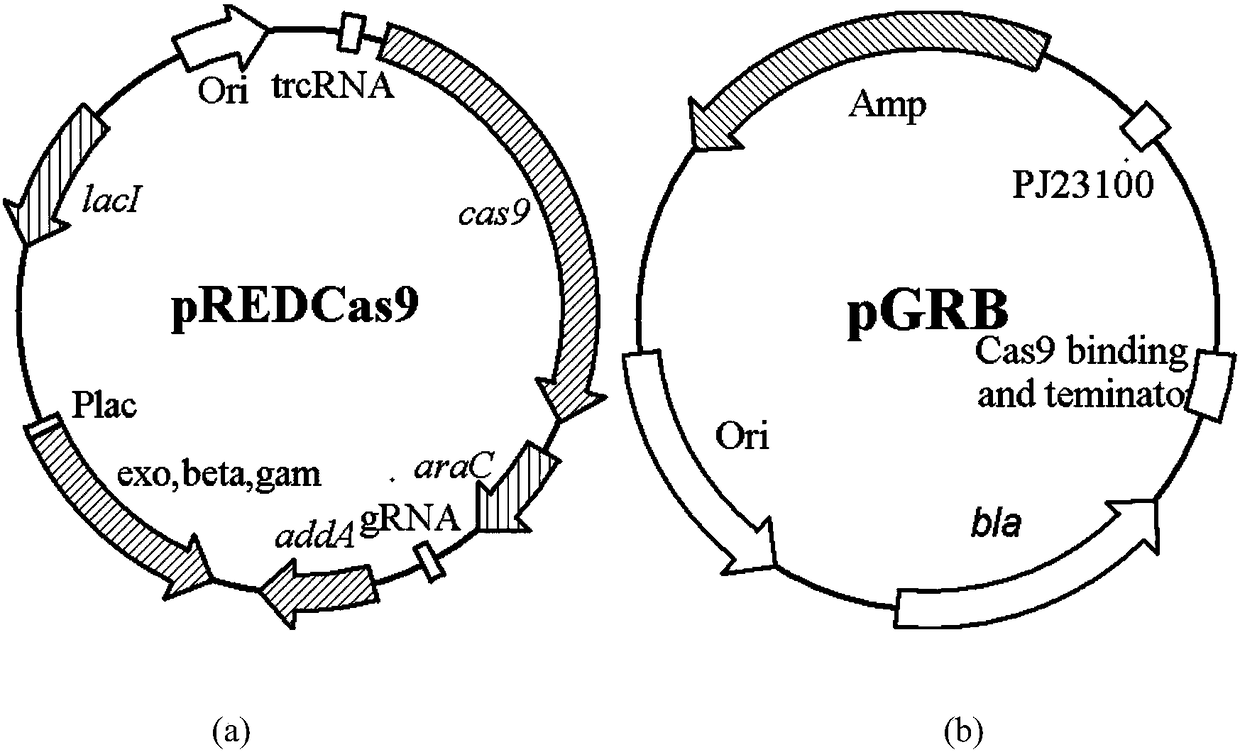
Genetically engineered bacteria with high uridine production and its construction method and application
ActiveCN108130306BImprove growth traitsIncrease productivityBacteriaEnzymesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention provides a genetic engineering bacterium capable of producing uridine at high yield as well as a building method and application thereof. The genetic engineering bacterium is characterized in that pyrimidine nucleoside operons pyrBCAKDFE with the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1 is integrated on a genome of colon bacillus; the starting is realized by a strong promoter P[trc];a uridine synthesis path is reconstituted; the self PRPP synthetase coding gene prsA on the genome is subjected to dual copying, and the starting is realized by the strong promoter P[trc]; meanwhile,the activity of udk, udp, and rihA, rihB and rihC is lacked; the thrA activity is lacked; the argF activity is lacked. The genetic engineering bacterium is applied to fermentation production of uridine; 40 to 67g / L of uridine can be produced after the fermentation is performed for 40 to 70h in a 5L fermentation tank; the maximum production intensity can reach 1.5g / (L*h); the glucoside conversionrate is 15 to 25 percent; the genetic engineering bacterium belongs to the highest level for producing the uridine by the fermentation method reported in the prior art.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method for enzymatically synthesizing vidarabine
The invention relates to a method for enzymatically synthesizing vidarabine. The invention provides a two-step method for preparing vidarabine adenosine. The method makes full use of the different effects of uridine phosphorylase and purine nucleoside phosphorylase to make the reaction proceed in one direction, eliminate the occurrence of reverse reaction, and significantly improve The conversion rate of vidarabine.
Owner:上海鑫欣生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing 2'-deoxyuridine by chemical-biological enzyme method in combination
ActiveCN102827902BHigh yieldImprove conversion rateChemical recyclingFermentationUracil2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
The invention provides a method for preparing 2'-deoxyuridine by a chemical-biological enzyme method in combination. A 'crystallization induction asymmetric transformation' technology is adopted to synthetize and obtain single alpha-configuration nucleoside analogues medicine intermediate 2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose-1-phosphate; the intermediate is utilized as a substrate; uracil is added, and 2'-deoxyuridine is synthetized and obtained by biotransformation under the action of uridine phosphorylase. By applying the chemical-biological combination technology disclosed by the invention, the advantages of a chemical method and a biological method are combined; the defects of the chemical method and the biological method are avoided; the yield is high; the method is suitable for industrial production; enough supply can be obtained by the 'crystallization induction asymmetric transformation' technology; 2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose-1-phosphate intermediate with single configuration does not need to be separated and purified; the biotransformation process is finished by catalysis with efficient and specific uridine phosphorylase in one step; the specificity is strong; the conversion rate is high; the condition is mild and the environment is friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Determination of 5'-nucleotidase activity and its diagnostic reagent kit of 5'-nucleotidase
InactiveCN1778948AStrong specificityLess susceptible to interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidaseAbsorbance
The invention is about a method of measuring the activation of 5í»-phosphonuclease, and it also concerns the reagent box of 5í»-phosphonucleasediagnosis. This invention belongs to the field of medical testing and measuring technology. The reagent box is consisted of buffer solution, uridine monophosphate, reduced coenzyme, uridine phosphorylase, dihydrothymine dehyddrogenase and stabilizer. Firstly, we cause an enzyme-coupled reaction through mixing the sample and the reagent according to a certain proportion of volume; secondly, put the final reactant under the biochemical analyzer and test the absorbance variational situation (speed) of dominant wavelength; then we can get theactivation of 5í»-phosphonuclease. By using this invention, we can get the necessary measuring result with high sensitiveness and fine precision through biochemical analyzer, and the result would not be contaminated by material of internal and exogenous sources. Thus, this method can be conveniently promoted and applied.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Genetic engineering strain for producing thymidine as well as construction method and application of genetic engineering strain
ActiveCN114410561AClear genetic backgroundIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and relates to breeding of industrial microorganisms, in particular to a genetic engineering strain for producing thymidine as well as a construction method and application of the genetic engineering strain. According to the genetic engineering strain, a pyrimidine nucleoside operon gene pyrBCAKDFE of bacillus subtilis, a uridine monophosphate kinase mutant gene pyrHD90A, a thymidylate synthase gene thyX of streptomyces coelicolor and a 5 '-nucleotidase gene TMPase of bacteriophage PBS1 are subjected to heterologous overexpression; the ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase operon gene nrdABC of the escherichia coli is over-expressed; in addition, a pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase gene deoA, a thymidine kinase gene tdk, a uridine phosphorylase gene udp and nucleoside hydrolase genes rihA, rihB and rihC are not expressed. From the escherichia coli genome level, modules of a uridylic acid synthesis pathway, a thymidine decomposition pathway and a thymidine branch synthesis pathway are systematically and comprehensively combined and optimized mainly through a metabolic engineering technical means, and the thymidine fermentation performance of the strain is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Pyrimidine nucleotide precursors for treatment of systemic inflammation and inflammatory heptitis
InactiveUS20030212036A1Improve survivalAvoid tissue damageAntibacterial agentsBiocidePyrimidine NucleotidesSystemic inflammation
Pyrimidine nucleotide precursors including acyl derivatives of cytidine, uridine, and orotate, and uridine phosphorylase inhibitors, and their use in enhancing resistance to sepsis or systemic inflammation are disclosed.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
Engineered uridine phosphorylase variant enzymes
The present invention provides engineered uridine phosphorylase (UP) enzymes, polypeptides having UP activity, and polynucleotides encoding these enzymes, as well as vectors and host cells comprising these polynucleotides and polypeptides. Methods for producing UP enzymes are also provided. The present invention further provides compositions comprising the UP enzymes and methods of using the engineered UP enzymes. The present invention finds particular use in the production of pharmaceutical compounds.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Fermentation medium and method for fermentation production of uridine phosphorylase using the same
A fermentation medium comprises: NaCl (3-12 g / L), glucose (10-25 g / L), extract yeast (5-15 g / L), peptone (2-15 g / L), K2HPO4-H2O (1 / 3) (2-5 g / L), uridine (7-25 mmol / L), inosine (15-30 mmol / L) and double distilled water. A fermentation method based on the fermentation medium comprises: streaking, inoculating and culturing lactobacillus brevis for 12-48 h, preserving at 4 DEG C for a standby application; taking and dissolving a certain amount of extract yeast in double distilled water, adjusting pH at 6.0-8.0, disinfecting at 121 DEG C for 15-20 min, and obtaining an activating solution containing 1-10% by mass of extract yeast; picking lactobacillus brevis, inoculating to the activating solution, activating at 30-40 DEG C for 4-12 h, and obtaining activated lactobacillus brevis thalluses; inoculating the lactobacillus brevis thalluses to the fermentation medium with an inoculation volume of 1-10% by volume; fermenting for 4-12 h with a medium temperature of 30-40 DEG C and a shaking-table rotating speed of 90-180 r / min, and obtaining a fermentation liquor; centrifuging the fermentation liquor for 10-30 min with a speed of 3000-5000 r / min, in a centrifuge tube obtaining a deposition which is the fermented whole-cell lactobacillus brevis wet thallus, and taking the fermented whole-cell lactobacillus brevis wet thallus as a uridine phosphorylase source to carry out nucleosides fermentation.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method for the production of cladribine
InactiveUS8012717B2High yieldSimple and effective and economical mannerOrganic chemistryFermentationPurine nucleoside phosphorylaseSolvent
A method for producing cladribine (2-chloro-2′ deoxyadenosine) comprising the steps of: a) reaction of 2-deoxyuridine with 2-chloroadenine, in the presence of uridine phosphorylase (UPase) and purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNPase) in an aqueous reaction medium possibly containing up to 40% v / v of an aprotic dipolar solvent, to obtain cladribine dissolved in said reaction medium; b) isolation of the cladribine by precipitation by means of concentration and alkalinisation of the reaction medium up to pH 11.5-12.5.
Owner:EXPLORA LAB
Genetically engineered bacterium used for producing uridine with high-yield
The present disclosure relates to a genetically engineered strain with high production of uridine and its construction method and application. The strain was constructed as follows: heterologously expressing pyrimidine nucleoside operon sequence pyrBCAKDFE (SEQ ID NO:1) on the genome of E coli prompted by strong promoter Ptrc to reconstruct the pathway of uridine synthesis; overexpressing the autologous prsA gene coding PRPP synthase by integration of another copy of prsA gene promoted by strong promoter Ptrc on the genome; deficiency of uridine kinase, uridine phosphorylase, ribonucleoside hydrolase, homoserine dehydrogenase I and ornithine carbamoyltransferase. When the bacteria was used for producing uridine, 40-67 g / L uridine could be obtained in a 5 L fermentor after fermentation for 40-70 h using the technical scheme provided by the disclosure with the maximum productivity of 0.15-0.25 g uridine / g glucose and 1.5 g / L / h respectively which is the highest level of fermentative producing uridine reported at present.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com