Method for widening the cell hereditable basic of cultivated soybeans using wild soybeans
A technology for cultivating soybeans and wild soybeans, applied in the fields of botany equipment and methods, application, plant genetic improvement, etc., to achieve the effect of stabilizing beneficial traits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] (1) Obtain F1 generation true hybrids with wild soybean as female parent
[0045] In 1984, high-protein Guxin wild soybeans were planted, and the flowering period was observed. The Guxin wild soybeans from southern Hebei were late-maturing in Chengde, northern Hebei, and flowering began on August 20. At this time, all spring soybeans All the varieties have finished blooming, and the work of pollination and hybridization has not been completed. It was sown again in 1985. After the seedlings emerged, they were treated with short-day light for 20 days. They were shaded from 5:00 pm to 8:00 the next day, so that they bloomed on June 23, 57 days earlier than under natural conditions, creating a good environment for hybridization. condition. In order to reduce the plant height and increase the high yield of interspecific hybrid offspring, a limited plant height of 60 cm and good high yield Chengdou No. 1 was selected as the male parent for hybridization, and one F0 generatio...
Embodiment 2
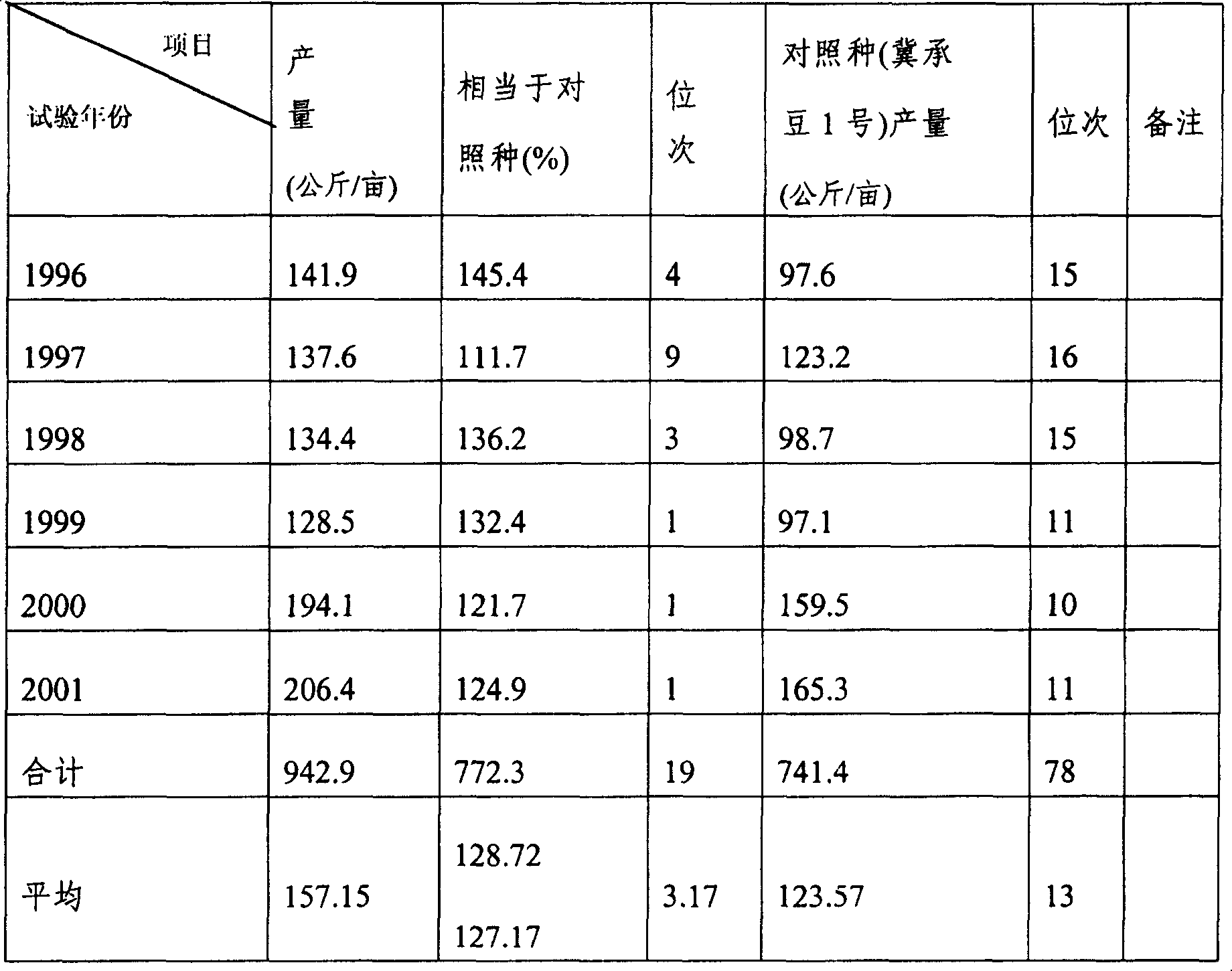
[0051] In order to prove the reproducibility of successful hybridization between wild soybeans and cultivated soybeans, Kongqiao wild soybeans were used as female parents in 1994. After 18 days of short-day treatment, after flowering, Henan soybeans with limited grain size were used as male parents. The hybridization was successful again, and the combination number was 9441. Both F1 and F2 were crossed in a broad sense, and the F3 substitute Zhongpin 661 was crossed in a broad sense, and 5 F0 seeds were obtained, and the combination number was 9718. In the future, use 9718F4 and 9441-7 as the female parent, and use multiple cultivated soybeans such as Yudou 18, Chengdou 5, Zhongpin 5016, Yudou 12, Wuyi Yanzhongying soybean, Jiqing No. 1, 9039-1-8= 1 et al. conducted generalized hybridization and now obtained a batch (204 of 10 combinations) of interspecific hybrid progeny materials with thick stems, large grains, and wild soybean cytoplasm. This batch of materials is being sele...
Embodiment 3
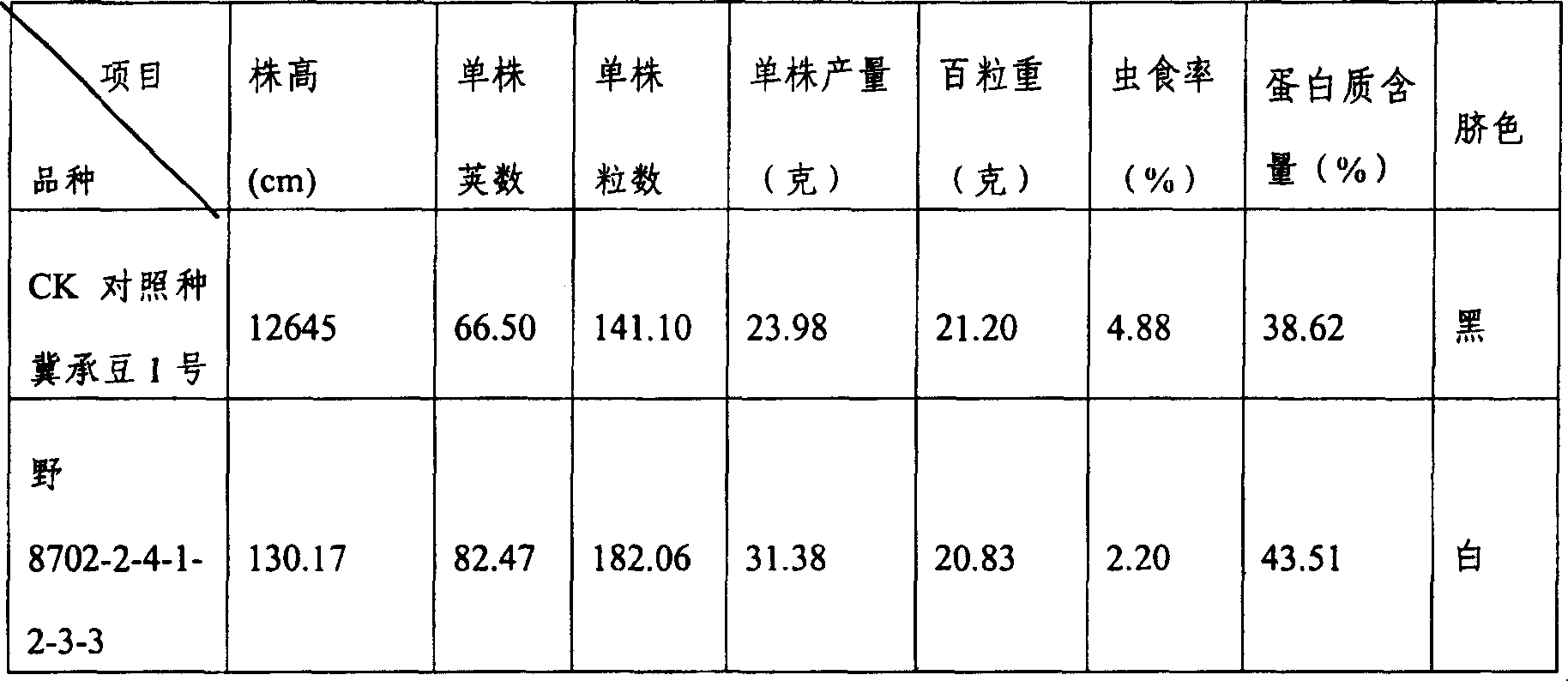
[0053] In order to broaden the cytoplasmic genetic basis of cultivated soybean and to reveal the reason and mechanism of the narrow and single cytoplasmic genetic basis of cultivated soybean in my country, in 1995, wild soybean Xinmin No. 6 was used as the parent, and four cultivated soybeans Hefeng No. 8412, Kai 81 57 Soybean conducted 4 pairs of reciprocal crossing experiments. From 1996 to 1998, the main agronomic traits segregation and maternal effect of F1, F2, F3 generation reciprocal crossing experiments were observed and analyzed in detail.
[0054] The test results showed that plant height had a very significant maternal effect (reached 0.01% significant). The number of main stem nodes and the number of pods per plant also had maternal effects. The number of grains per plant has a significant maternal effect, reaching 0.05% significant. The last pair of combinations of 100-kernel weight showed maternal effect. The first three combinations showed the dominant effect o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com