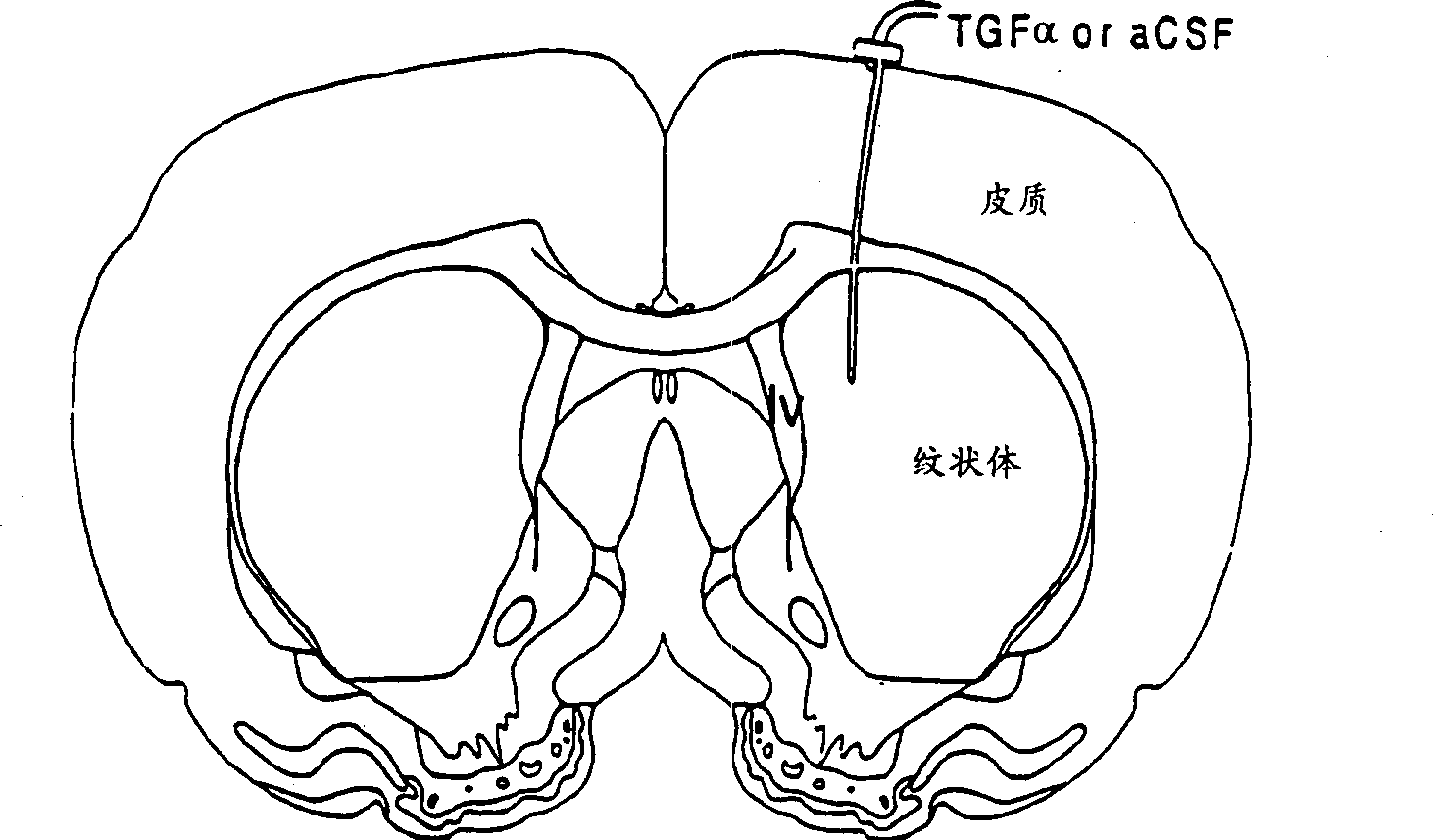
Method for treating neurological deficits
A nerve and central nervous system technology, applied in nervous system diseases, pharmaceutical formulations, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc., can solve problems such as undetermined nutritional effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0124] Example 1: Expression of TGFα and EGF receptor mRNAS in the normal developing and adult nigrostriatal system
[0125] As described in the Detailed Description of the Invention, mRNAs encoding EGF-family neurotrophic factors are developmentally regulated in the nigrostriatal system. In the studies described below, the expression of TGF[alpha] and EGF receptor mRNAs were examined in normal developing and adult rodent systems.
[0126] A. Animal and Tissue Preparation
[0127] Adult male and female Sprague-Dawley pregnant mice (250-350 g) were purchased from Simonsen (Gilroy, CA). In these experiments, and in all other experiments described here, animals were maintained in room temperature and humidity controlled zoos. The use of animals in all experimental procedures was approved by the Animal Research Institute at the University of California, Irvine, in accordance with the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health.
[0128] Neonatal (P0), postnatal day 1 (P1) a...
Embodiment 2
[0140] Example 2: Modulation of TGFα and TGF receptor mRNA expression by 6-hydroxydopamine injury and striatal TGFα infusion.
[0141] In situ hybridization was used to determine whether nigrostriatal TGFα or EGF receptor mRNA was affected by intrastriatal infusion of TGFα. In addition, the effect of unilateral 6-OHDA injury on receptor expression in infused and non-infused animals was also examined.
[0142] A. Treatment group
[0143] Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 250-300 g were purchased from Simonsen (Gilroy, CA) and assigned to each of the five treatment groups:
[0144] (1) Striatal TGFα infusion, substantia nigra 6-OHDA injury (hereinafter referred to as “injury”); (2) TGFα infusion, no injury; (3) artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) infusion, injury; (4) aCSF infusion, no injury; (5) no infusion, no injury. Each experimental group used 4 to 8 animals. Animals were monitored after each surgery until full recovery, at all other times animals were housed in ...
Embodiment 3
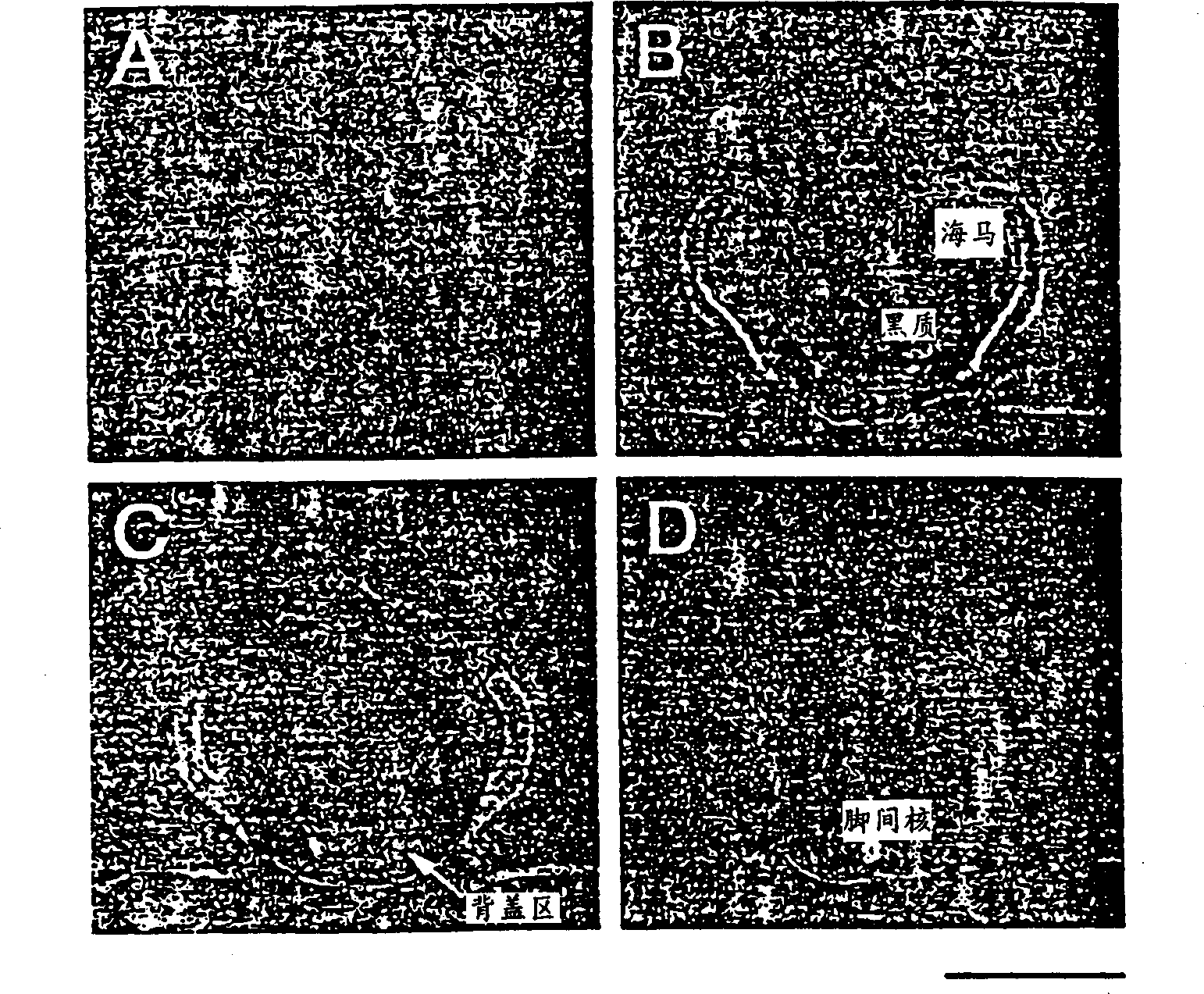
[0189] Example 3: Properties of striatal cristae
[0190] As noted above, striatal infusion of TGFα in combination with substantia nigra 6-OHDA induced the formation of striatal body cell crests expressing EGF receptor mRNA in abundance, but not TGFα more than surrounding tissue. The cristae consisted of a large number of dense cells, making it clearly detectable using a simple sulfur stain. The identity of the abnormal striatal cristae is unclear, but three possibilities are considered.
[0191] Gliosis in response to injury is a hallmark of brain tissue damaged by injury and neurotoxicity. In general, both types of brain injury promote astrogliosis and infiltration of injured tissue by astrocytes and microglia (Fernaud-Espinoza et al., Glia 8:277-291, 1993 ). Astrocytes have been shown to express EGF receptor immunoreactivity, particularly in response to brain injury (Gomez-Pinilla et al., Neurosci. Lett. 91:276-282, 1988). Furthermore, TGF itself stimulates astrogliosis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com