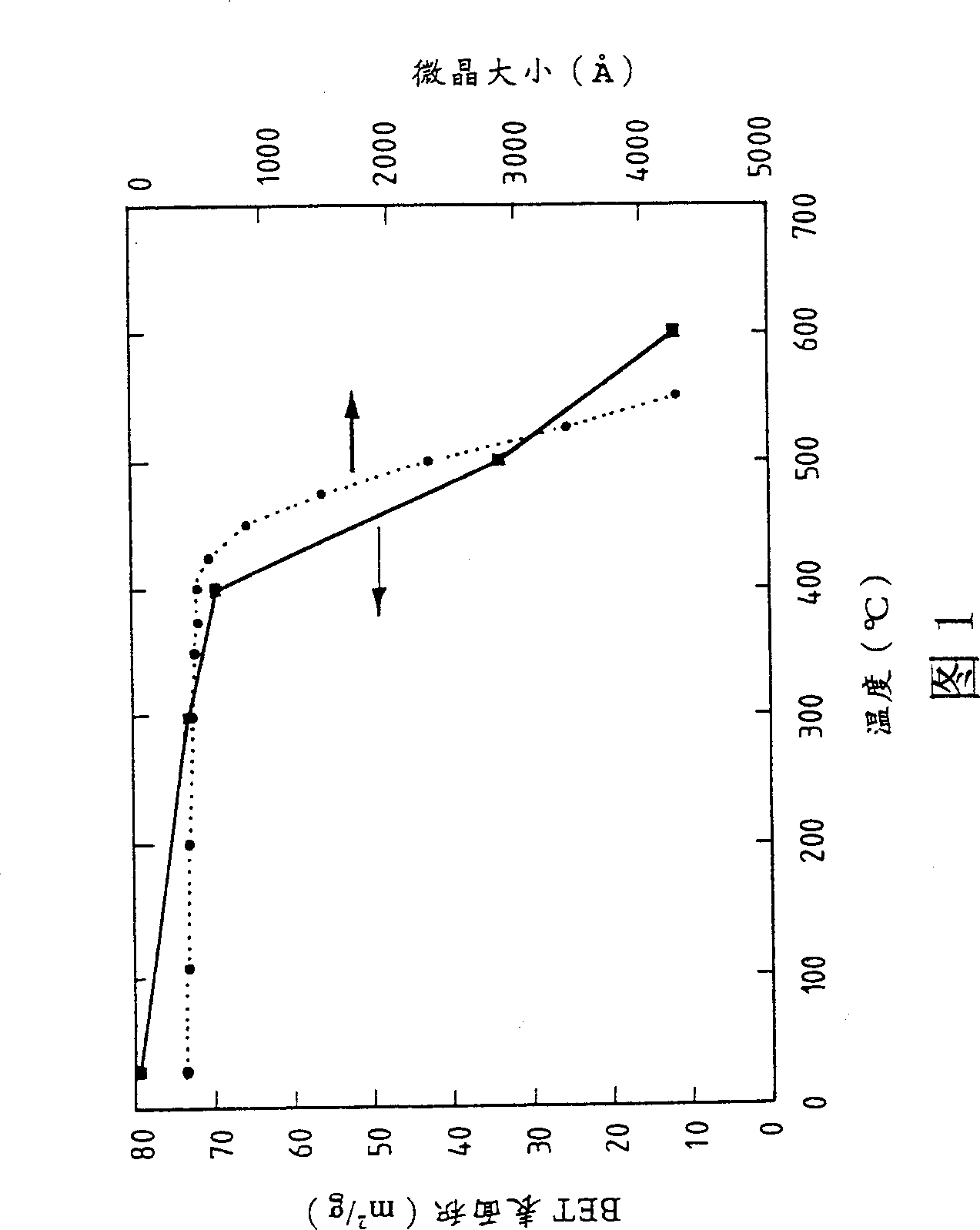
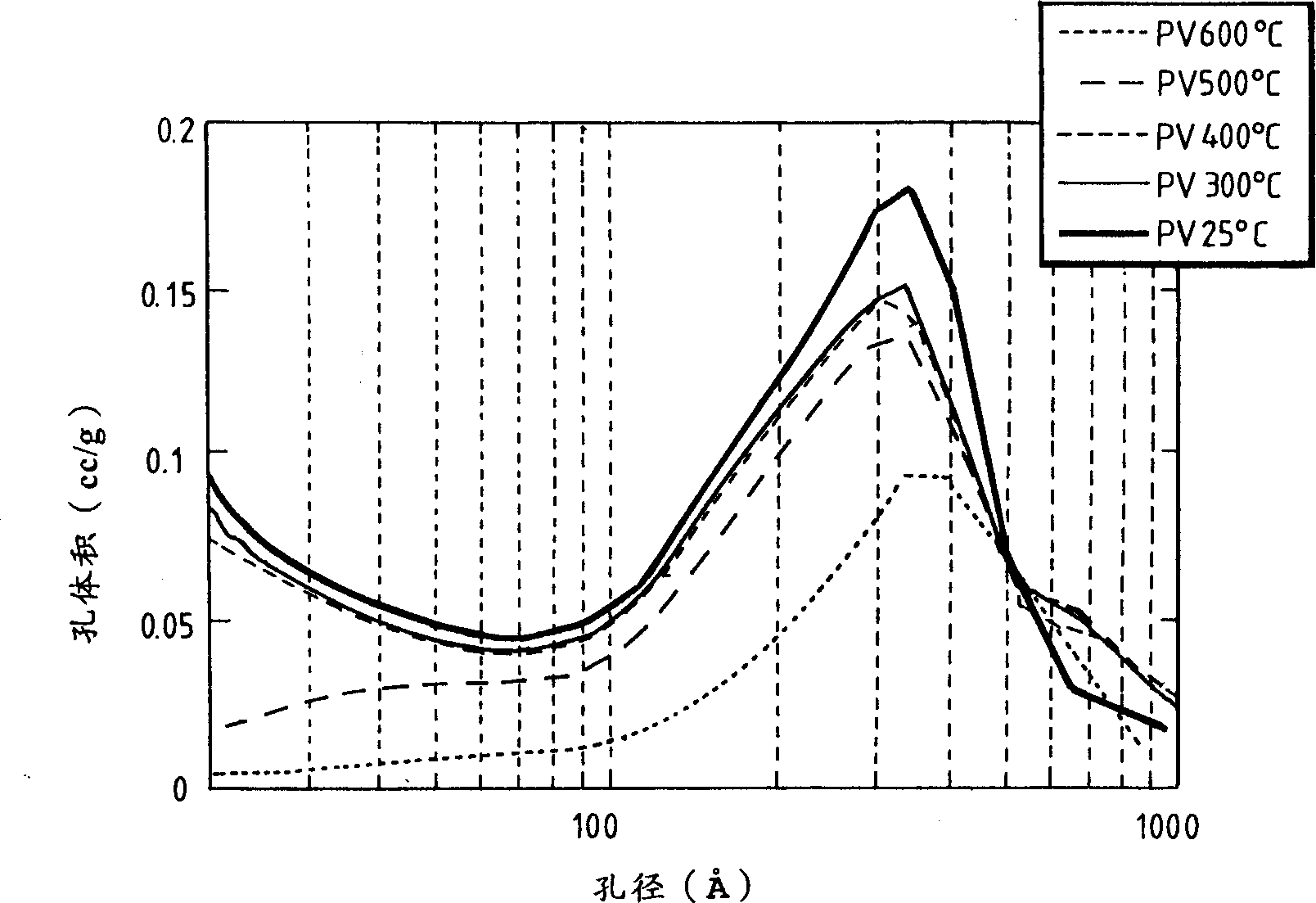
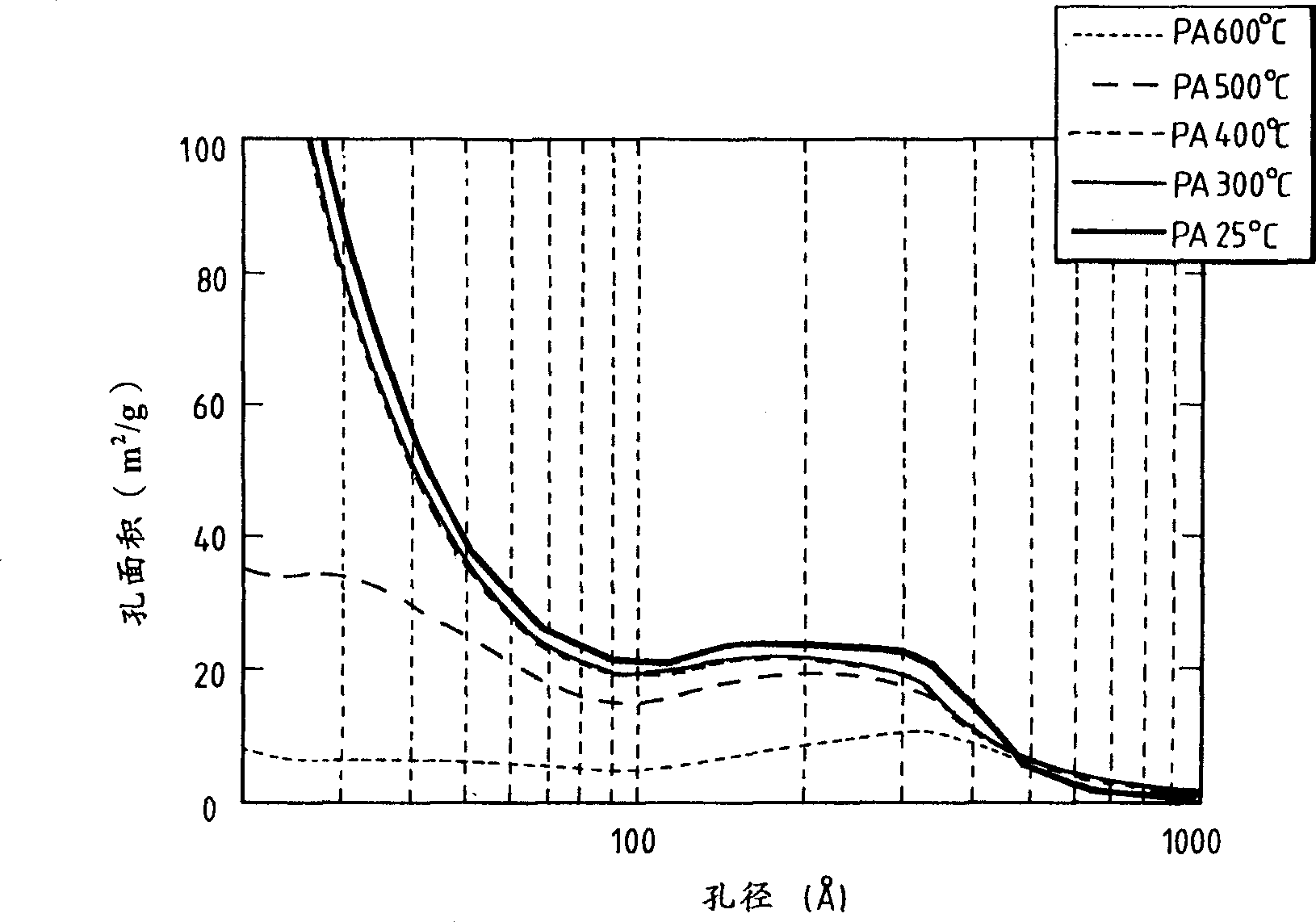
Heteropoly acid/multimetal oxacid salt catalyst
A technology of polyoxometalates and heteropolyacids, applied in metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, physical/chemical process catalysts, catalyst activation/preparation, etc. The method of salt carrier pore size and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] The heteropolyacid catalyst and polyoxometallate support were prepared according to the following general procedures.
[0111] Heteropolyacids
[0112] Phosphotungstic acid and phosphomolybdic acid used in the following examples, H 3 PW 12 o 40 and H 3 PMo 12 o 40 purchased for the market.
[0113] H used in the following examples 3+x (PM 12-x V x o 40 )-type catalysts are prepared by the following general procedure, with H 5 PV 2 Mo 10 o 40 for example. h 5 PV 2 Mo 10 o 40 Prepared by the following method: 48.8g NaVO in 200g deionized water 3 and 14.2g Na in 200g deionized water 2 HPO 4 Mix at 95°C. After the mixture had cooled, 18.4 g of concentrated sulfuric acid was added, at which point the solution turned red and an exotherm was observed. With the addition of acid, the pH dropped from 9.1 to 3.7. Then Na 2 MoO 4 400 g of deionized water was added, followed by 312 g of concentrated sulfuric acid, keeping the temperature below 50°C during t...
Embodiment 2
[0132] The polyoxometalate-supported heteropolyacid catalysts used in the following examples were prepared in the following general steps to prepare H 3 PMo 12 o 40 / Cs 3 PMo 12 o 40 for example.
[0133] h 3 PMo 12 o 40 / Cs 3 PMo 12 o 40 (0.02 / 1.0 molar ratio - about 10% surface coverage) was prepared by the following method: 0.7196g H 3 PMo 12 o 40 20H 2 O, 34.02g Cs 3 PMo 12 o 40 Mix with 315g deionized water. After stirring at room temperature for 80 minutes, the water was removed by evaporation and the resulting solid was dried. The sample was heat treated in air at 150°C for 1 hour to yield 32.69 g of the desired catalyst. The catalyst is then pelletized to be filled in the oxidation reactor.
[0134] Examples of catalysts prepared according to this procedure are reported in Table 3, along with the approximate surface areas of the coated supports.
[0135] sample
[0136] Prepared four kinds of loaded Cs 3 PMo 12 o 40 (VO) on 1.5 PMo 1...
Embodiment 4
[0141] prepared two loaded Cs 3 PMo 12 o 40 (VO) on 1.5 PMo 12 o 40 catalyst samples. Each sample contains enough (VO) 1.5 PMo 12 o 40, so that 100% of the POM surface area is covered. As described in Example 3, one sample was heat treated at 300°C as a control. Another sample was heat treated in situ at 420°C in a catalytic reactor. The heat-treated samples were placed in a catalytic reactor under air at room temperature, propane was added to the reactor, and the temperature was raised to 420°C. The reactor was held at this temperature for less than 10 minutes and then cooled to 380°C to continue the reaction. The yield of acrylic acid at 30% propane conversion was determined. As described in Example 3, a control sample was also used to catalyze the conversion of propane to acrylic acid. The data for the control samples and the samples heat treated in situ are reported in Table 5.
[0142] temperature(℃)
[0143] The above data clearly show that in sit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com