Novel NEUROPILIN/growth factor binding and use thereof
A NP-1, molecular technology, applied in the direction of growth factors/inducing factors, growth factors/growth regulators, receptors/cell surface antigens/cell surface determinants, etc., can solve problems such as unresearched effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
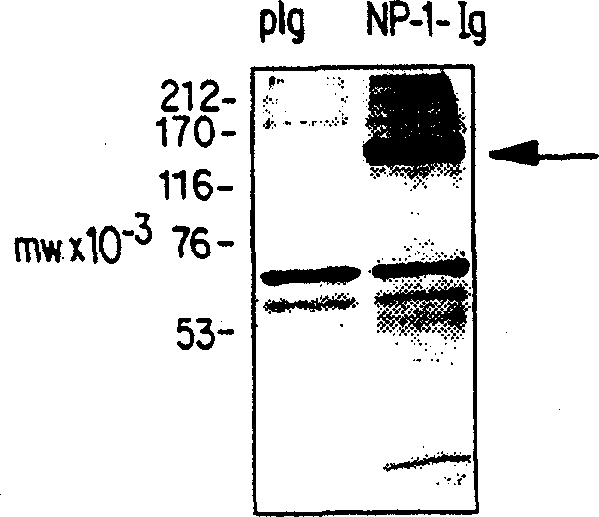
[0087] Example 1: Cloning of soluble Neuropilin-1-Ig fusion constructs
[0088] The extracellular domain of murine NP-1 (248-2914 bp of murine Neuropilin cDNA, accession number D50086) was cloned into pIgplus (Ingenius). The 3' part (2738-2914bp) of this extracellular domain was first ligated into pIgplus as an EcoRV-BamHI fragment, and the 5' part (248-2738bp) was then ligated into the pIgplus as an EcoRV fragment (the 5' EcoRV site was derived from the pBluescript KSII vector). carrier. The sequence of the extracellular domain was thus cloned in frame with the pIgplus vector sequence encoding the Fc part of human IgG to generate a fusion protein that could be precipitated from the medium of transfected 293T cells by protein A sepharose, Then SDS-PAGE and silver staining were performed. The results are shown in figure 1 . NP-pIgplus or pIgplus were transfected into cells, and serum-free conditioned medium was collected between 24-32 hours after transfection. Proteins wer...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Example 2: Transfection, immunoprecipitation and soluble receptor binding
[0090] By calcium phosphate precipitation with the encoding soluble receptor Ig-fusion protein VEGFR-1-Ig (Olofsson et al., Proc. The 1-Ig plasmid was transfected into 293-T cells. VEGFR-3 was constructed by amplifying the seven Ig loops of R3, plus placing the Fc portion of human Ig in the vector pREP7.
[0091] 293-T cells were cultured for 24 hours after transfection, washed with Dulbecco's minimal essential medium (DMEM) containing 0.2% bovine serum albumin (BSA), and starved for 24-32 hours. The medium was collected and clarified by centrifugation, and the fusion protein was precipitated with protein A sepharose.
[0092] encoded with hVEGF 165 ,mVEGF-B 167 ,mVEGF-B 186 , hVEGF-C, hVEGF-D, PlGF-1 or PlGF-2 plasmid similarly transfected 293-T or 293EBNA cells, and 24 hours after transfection with 100μCi / ml Pro-mix TML- 35 S (Amersham) metabolically labeled transfected cells for 6-7 hou...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3: Binding of VEGF family members to specific antibodies, NP-1, Flt-1 and Flt-4
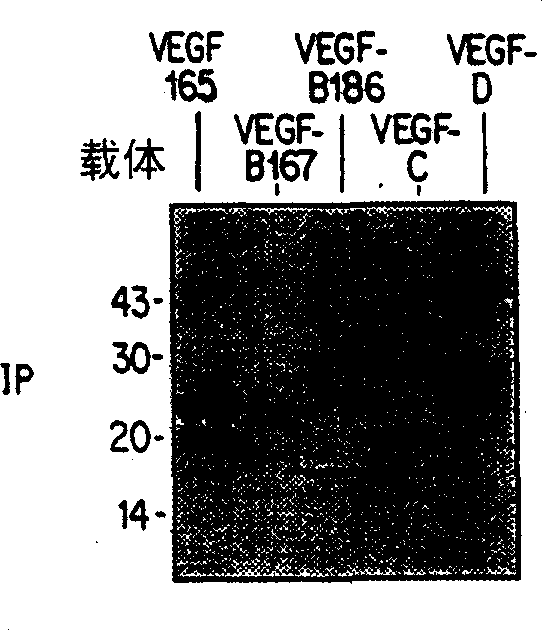
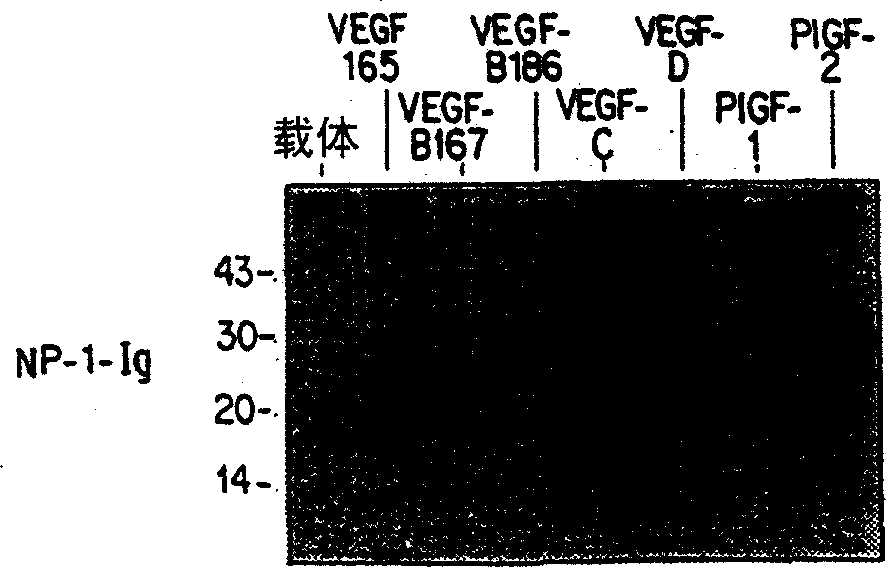
[0096] express VEGF-B with 167 ,VEGF-B 186 ,mVEGF-B kEx1-5 (produced by expressing a construct containing exons 1-5 of murine VEGF-B), VEGF 165 , VEGF-C, VEGF-C△N△C (a construct consisting of amino acids 102-225 of VEGF-C constructed as described in Joukov et al., EMBO Journal, 16:3898-911 (1997), VEGF- D, and VEGF-D ΔN ΔC (construct composed of amino acids 93-201 of VEGF-D constructed as described in Achen et al., Proceedings of the American Academy of Sciences 95:548-53 (1998)) cell conditions Medium The general procedure of Example 2 was repeated. The results are shown in Figure 5-8 .
[0097] Figure 5 Ligand VEGF-B 167 and VEGF-B 186 Binding analysis with NP-1-Ig, Flt-1-Ig and Flt-4-Ig, Figure 6 shows ligand mVEGF-B kEx1-5 and VEGF 165 Binding assays to NP-1-Ig, Flt-1-Ig and Flt-4-Ig. In the figure, IP refers to immunoprecipitation of ligand with antibody precipit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com