Inhibitor of stem cell proliferation and uses thereof
A stem cell and sequence technology, applied in the directions of cytokines/lymphokines/interferons, applications, growth factors/inducing factors, etc., can solve the problems of increased infection rate, low frequency of stem cells, and high susceptibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
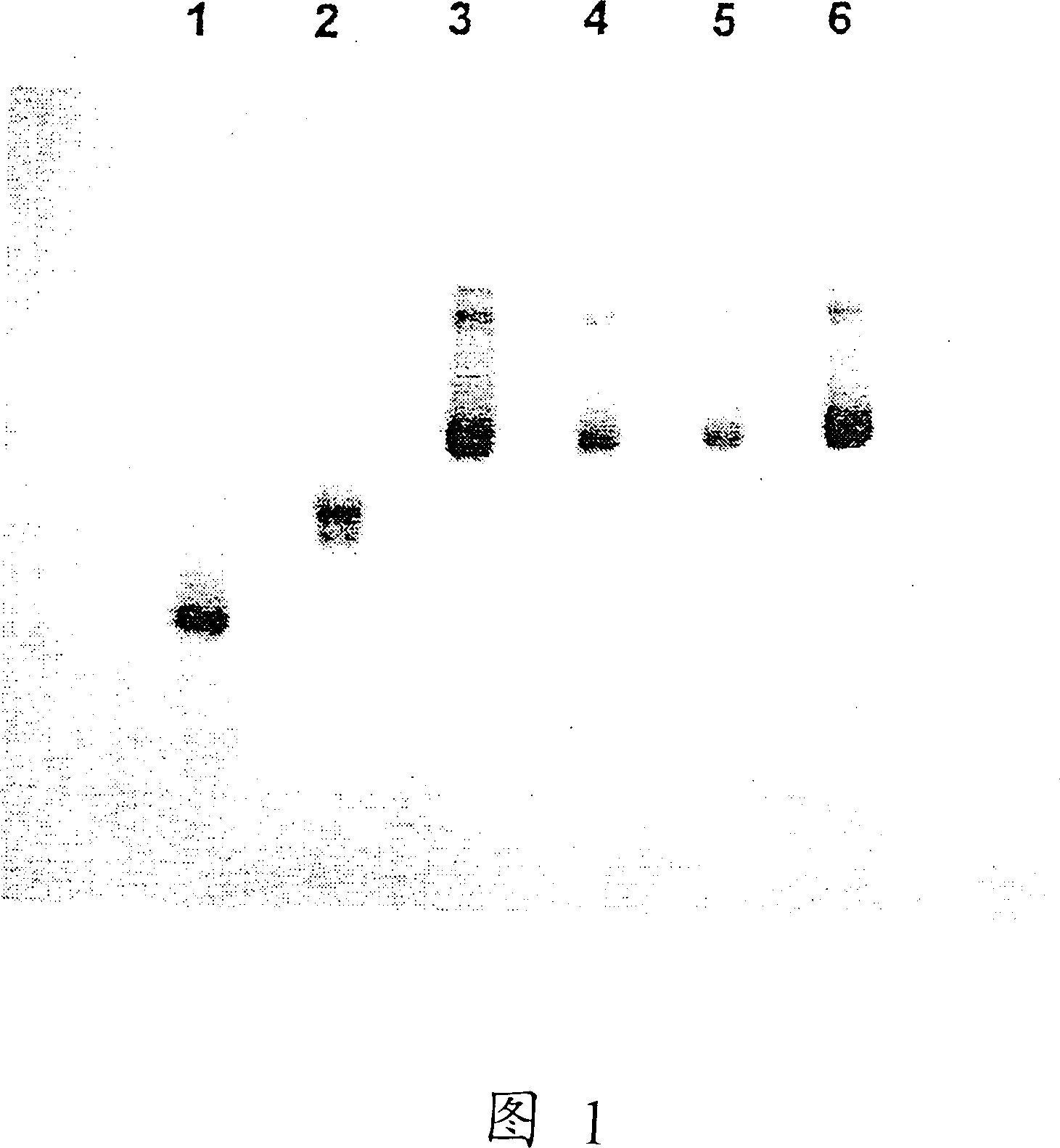
[0154] Example 1: In vivo stem cell proliferation inhibition analysis
[0155] To measure the proliferation of stem cells, the 3 The H-TdR "suicide method" measures the number of CFU-S in the S phase of the cell cycle (Becker et al., Blood 26:296-308, 1965).
[0156] Immature hematopoietic progenitors-spleen colony-forming units (CFU-S) can be detected in vivo by macroscopic colonies formed in the spleens of lethally irradiated mice 8–12 days after intravenous injection of hematopoietic cells (Till & McCulloch 1961).
[0157] For standard CFU-S proliferation assays, usually using 3 H-TdR "suicide method" (Becker et al., 1965). The method is based on radiolabeled thymine ( 3 H-TdR) is incorporated into cells as a synthetic DNA precursor. CFU-S in the S phase of the cell cycle at the time of detection were killed by high radioactivity and thus failed to form colonies in the spleen. Then, by injecting with 3 Cell samples co-cultured with H-TdR and without 3 The differenc...
Embodiment 2
[0176] Example 2 In vitro stem cell proliferation inhibition analysis
[0177] The direct effect of INPROL was shown using the following assay system (Lord et al., The Inhibitors of Hematopoiesis, pp. 227-239, 1987). Multilineage factor (IL-3) dependent cell line FDCP mix A 4 (A 4 ), maintained in IMDM medium containing 20% horse serum and 10% WEHI-3 conditioned medium as a source of colony-stimulating IL-3.
[0178] use 3 Proliferation detected by H-TdR incorporation assay: A 4 cells (5×10 4 In 100 μl medium containing 20% horse serum and 50% WEHI-3 conditioned culture supernatant) at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Incubate for 16 hours.
[0179] Begin adding INPROL or crude BME (bone marrow extract) (component IV), then add to each group 3 H-TdR (3.7KBq in 50μl at 740GBq / mmol) was cultured for another 3 hours. Proliferation rates were determined by harvesting cells and calculating percent inhibition using the following formula.
[0180]
[0181] FDCPmix-A grown in the prese...
Embodiment 3
[0182] Example 3 In vivo injection of INPROL results in inhibition of CFU-S proliferation: dose and effect duration
[0183] In vivo injection of INPROL showed that INPROL can effectively block the recruitment of CFU-S into the cell cycle. Thus, these cells are protected from the cytotoxic effects of further treatment. Show its clinical potential application value.
[0184] The purpose of this experimental protocol was twofold: to examine the effect of INPROL on CFU-S when injected in vivo and to determine the effective duration of INPROL activity involved in cell cycle stem cells.
[0185] To stimulate CFU-S proliferation, according to the effects mentioned in Example 1, testosterone propionate (TSP) was injected.
[0186] BDF at day 0 1 The mice were injected with TSP (10mg / 100g), and 24 hours later, the mice in each experimental group (4 mice / group) were intraperitoneally injected with pINPROL 0μg, 5μg, 10μg and 15μg / mouse.
[0187] 24 hours after pINPROL injection,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com