Internal combustion engine for driving propeller shaft
A technology for internal combustion engines and crankshafts, applied in the direction of motor-driven engines, engine components, sliding contact bearings, etc., can solve the problems of no thrust bearing bush, difficulties, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
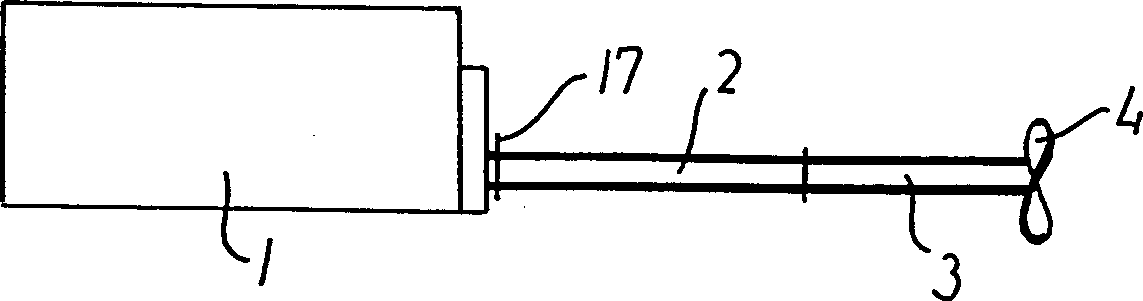
[0024] figure 1 There is illustrated an internal combustion engine 1 connected via an intermediate shaft 2 to a propeller shaft 3 with a propeller 4 . The internal combustion engine may be a four-stroke engine or a two-stroke engine, such as the applicant's ME or MC two-stroke crosshead engine, which are known to those skilled in the art. The engine may have a bore of 30 to 120 cm, the number of cylinders may be 5 to 20, and for a crosshead engine, the rotational speed may be 60 to 300 rpm. The output power of the engine can be, for example, 3000 to 130000 kW. The engine preferably has a relatively large output power, such as at least 30,000 kW, with at least 8 cylinders and a bore of at least 70 cm.
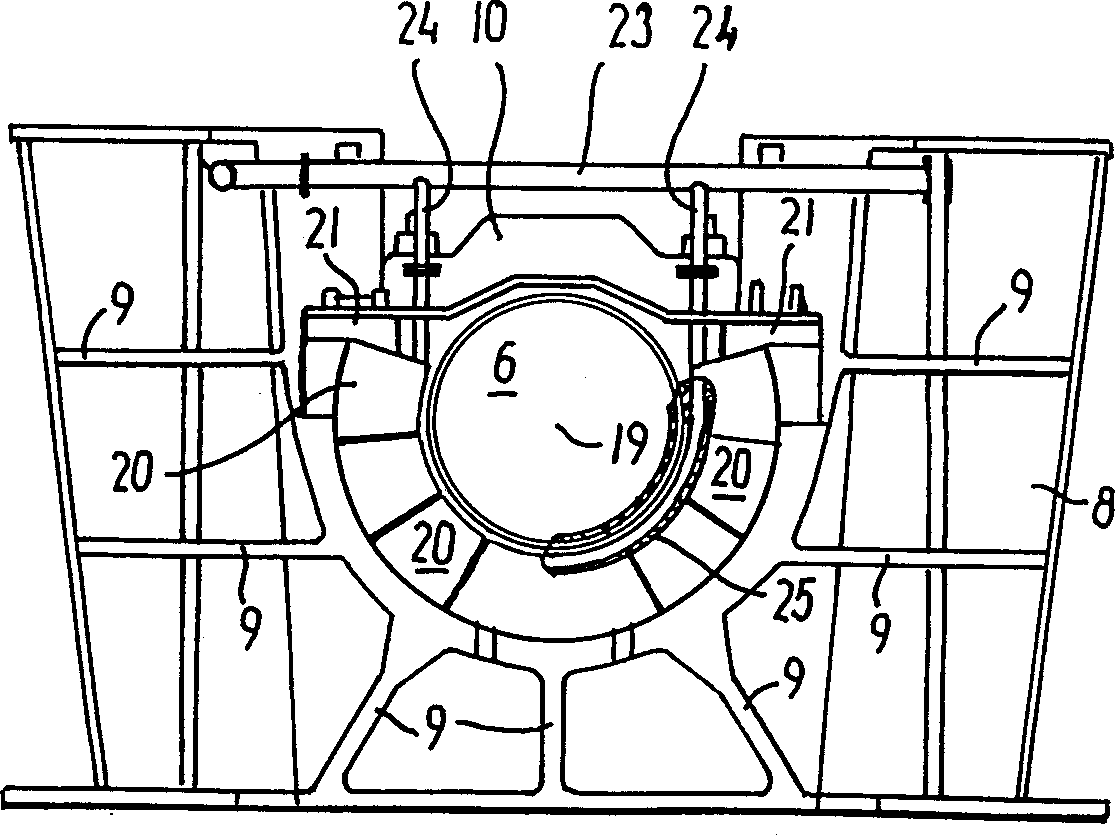
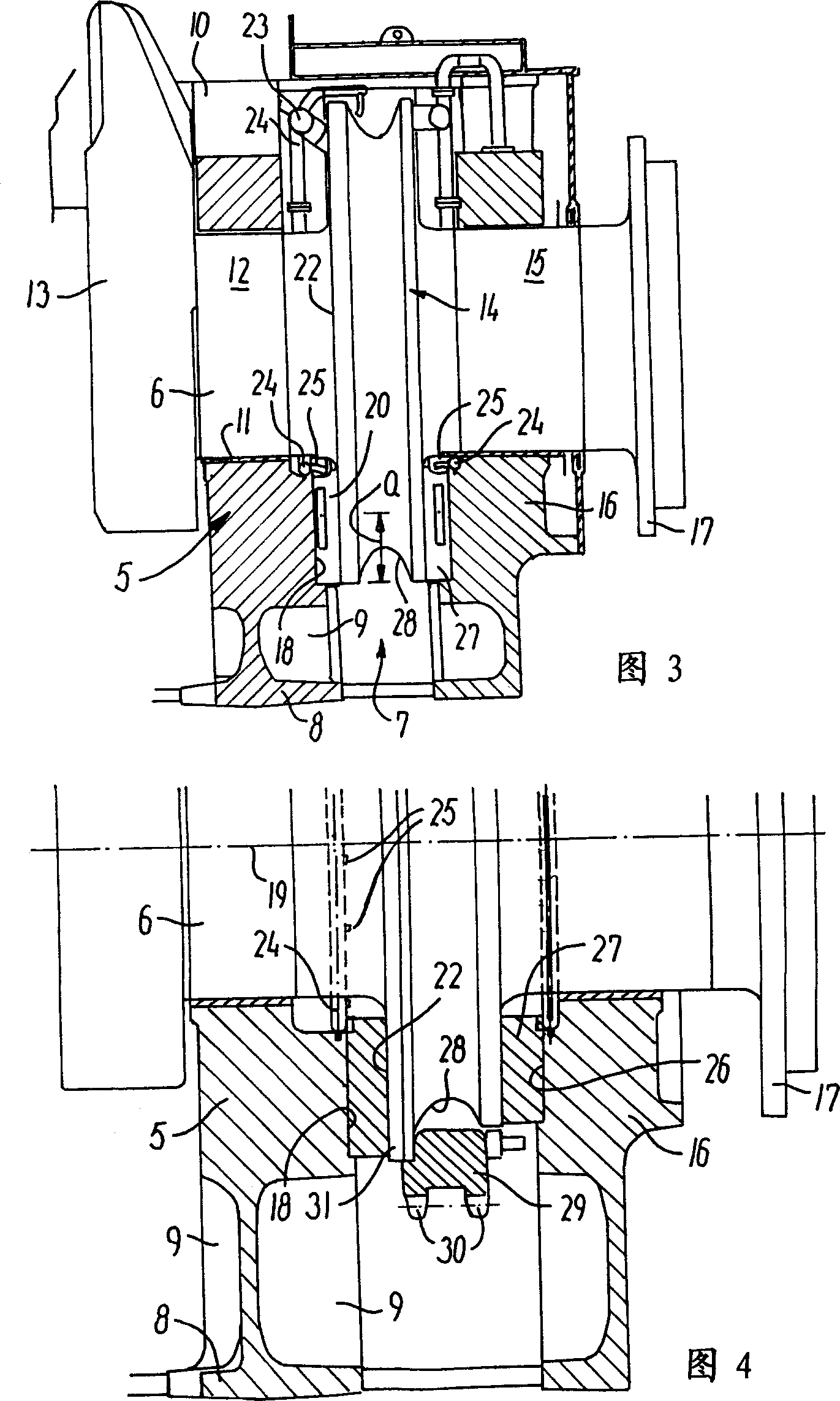
[0025] In the rearmost main bearing 5 of the crankshaft 6, the internal combustion engine 1 has a figure 2 The rear view of the thrust bearing 7, the longitudinal section of the thrust bearing is shown in Figure 3. The fixed bearing seat of the main bearing 5 is cast in one...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com