Motor control device
A control device and motor technology, applied in AC motor control, electronic commutation motor control, single motor speed/torque control, etc., can solve the complex calculation of reactive power command value, easy stop of motor rotation, unstable action, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of short feedback control cycle, large operating range and simple debugging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
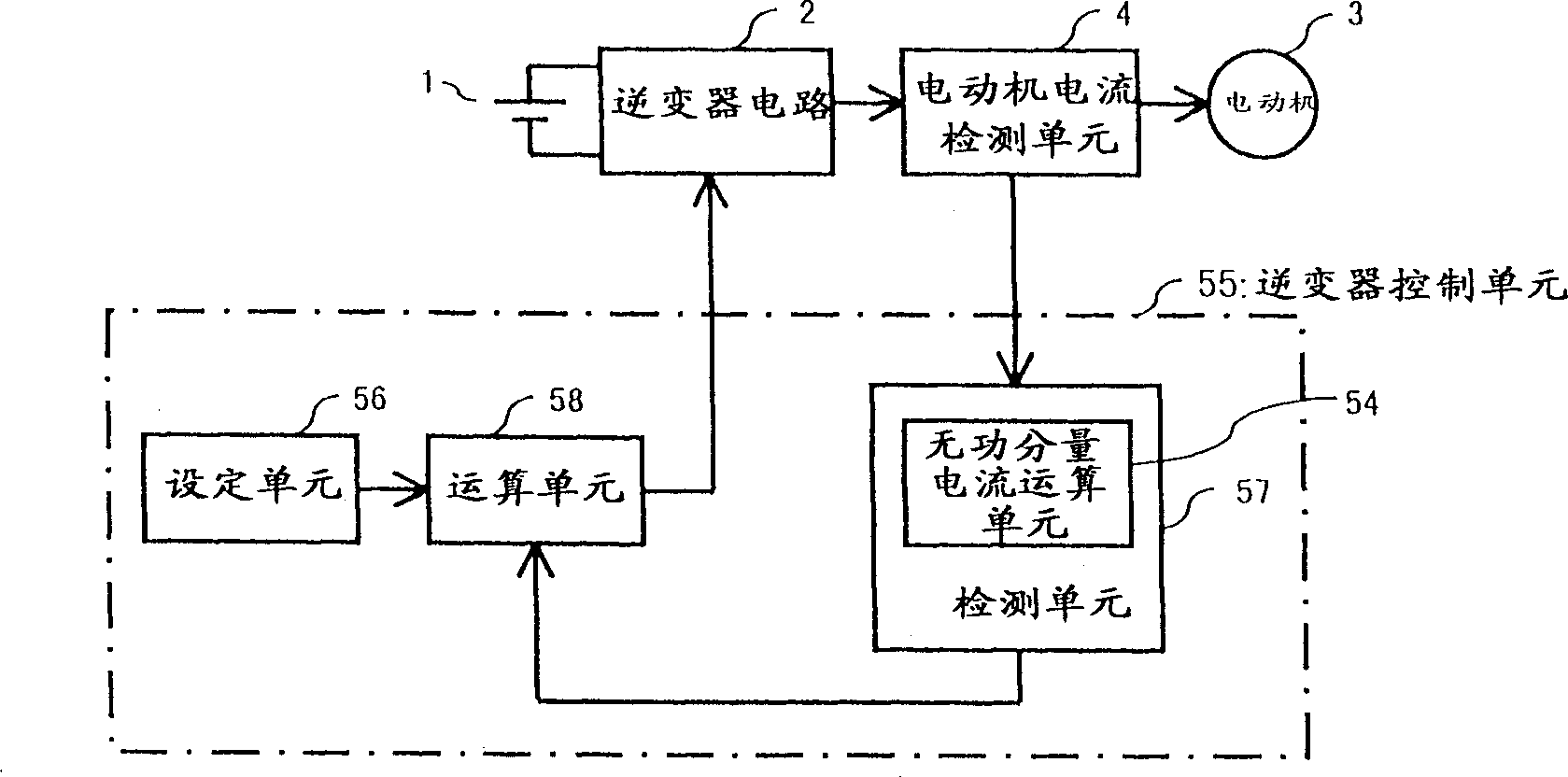
[0058] figure 1 Shown is a block diagram showing the basic configuration of the motor control device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. exist figure 1 Among them, the DC of the DC power supply 1 is added to the inverter circuit 2, converted into AC, and supplied to the motor 3 through the motor current detection unit 4. The motor 3 is, for example, a synchronous brushless motor and does not have a position sensor for detecting the rotor position. The output of the motor current detection unit 4 is used as the input of the detection unit 57 having the reactive component current calculation unit 54 of the inverter control unit 55 . In the detection unit 57, the reactive component current is calculated, and the detection value is output according to the value, and added to the calculation unit 58, and the setting unit 56 is used to set various settings for controlling the inverter circuit 2, which will be described in detail later. A fixed value, which...
no. 2 Embodiment
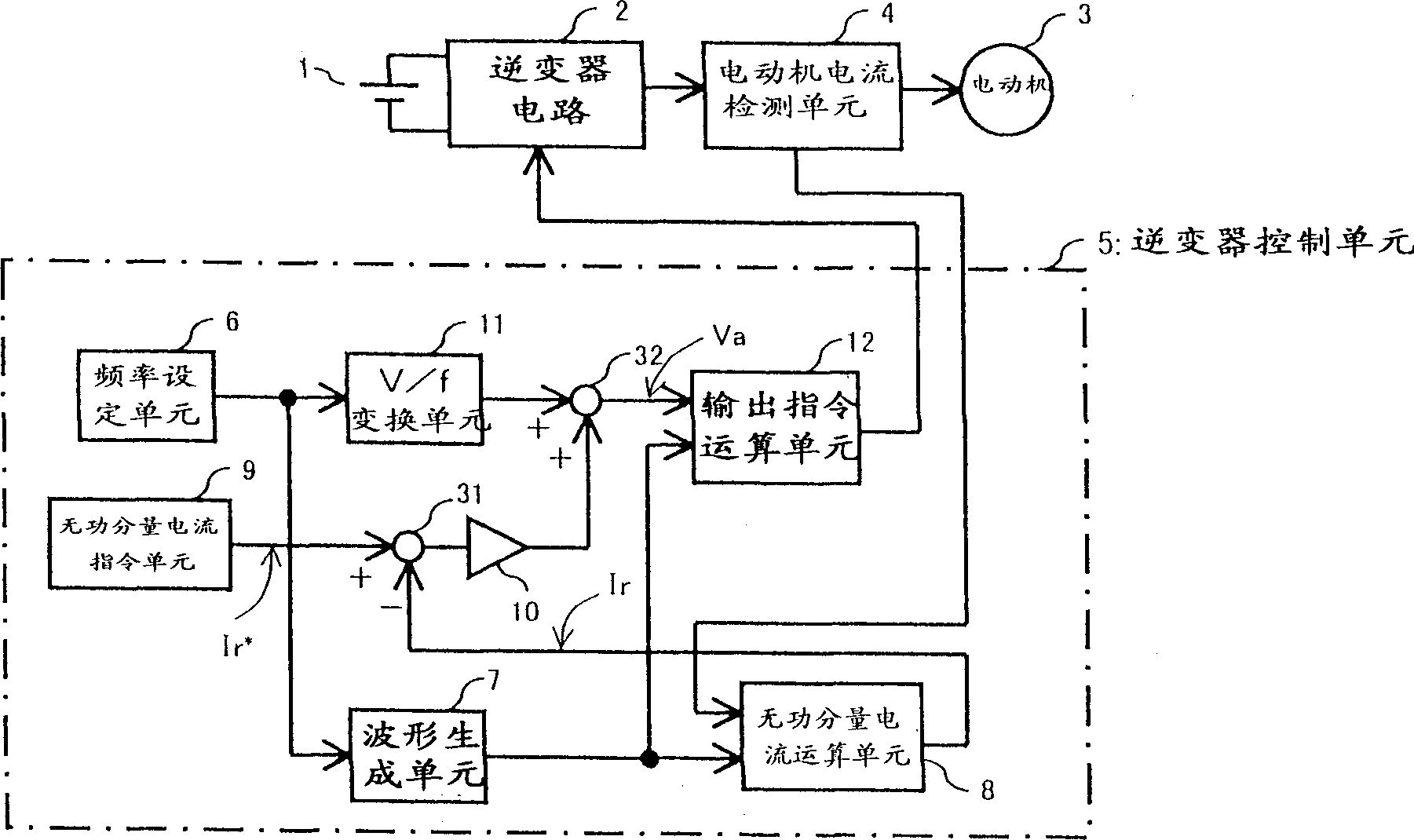
[0071] Figure 4 It is a block diagram of a motor control device according to a second embodiment of the present invention. In the figure, the inverter control unit 5A is the figure 2 In the inverter control unit 5, an active component current calculation unit 13 and a phase difference Φ calculation unit 14 are added, and the reactive component current command unit 9 is changed into a phase difference Φ command unit 15. Other configurations are the same as those of the aforementioned first embodiment. The phase difference Φ is the phase difference between the applied voltage command value Va and the motor current Is. The active component current calculation unit 13 obtains the active component current Ia by the calculation of the formula (4). Ia = 2 3 × [ Iu × sin θ + Iv × sin ( ...
no. 3 Embodiment
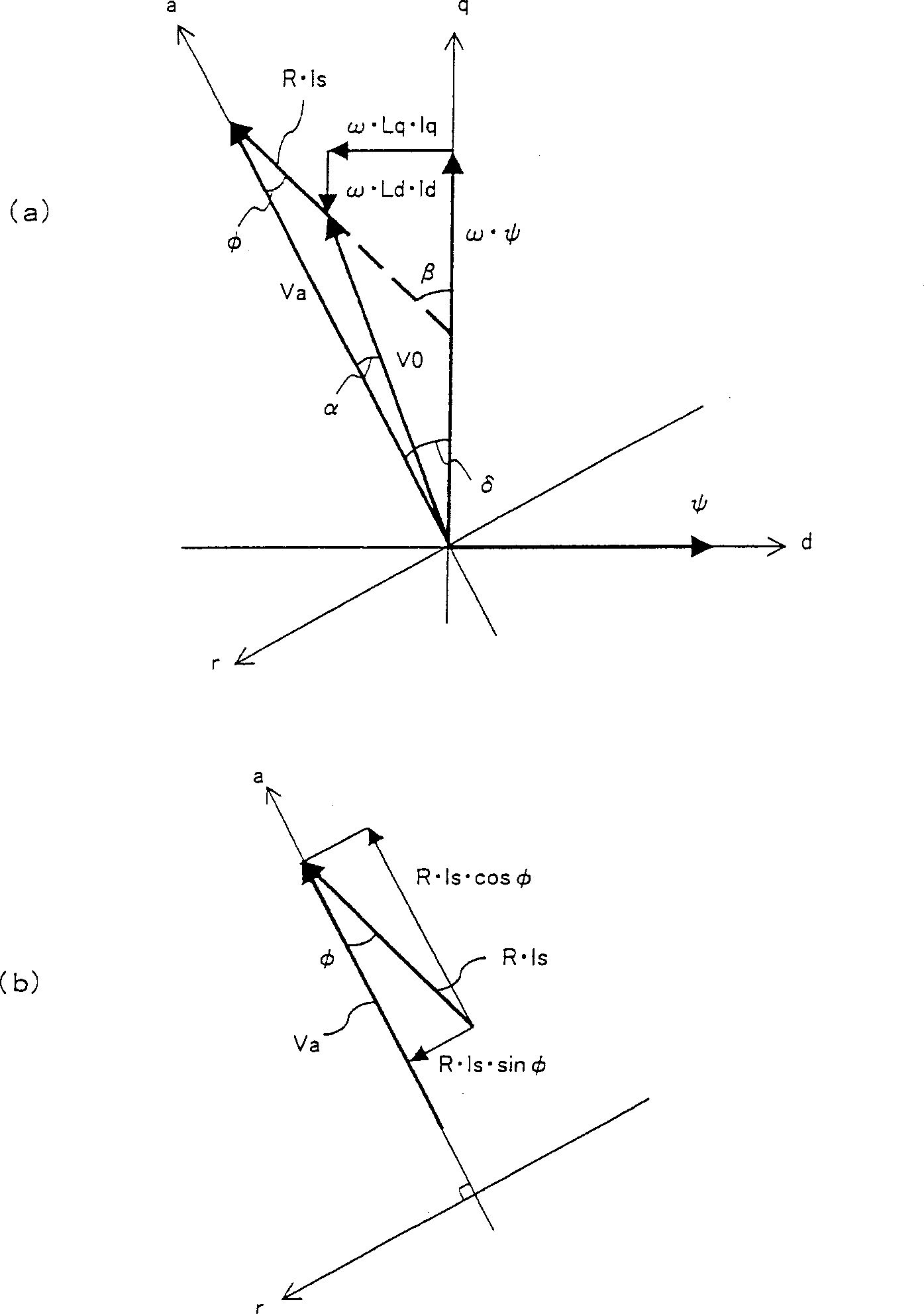
[0080] Figure 5 It is a block diagram of a motor control device according to a third embodiment of the present invention. In the figure, the inverter control unit 5B is the second embodiment Figure 4 The phase difference Φ calculation unit 14 in the inverter control unit 5A is replaced with a phase difference d calculation unit 16 , and the phase difference Φ command unit 15 is replaced with a phase difference d command unit 17 . The phase difference α computing unit 16 calculates the phase difference α from the output of the reactive component current computing unit 8, the output of the active component current computing unit 13, and the output of the adding unit 32, namely the voltage command value added by the motor, according to formula (7). α = Tan - 1 ( R × Ir Va ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com