Photographing lens
A fiber amplifier and long-wavelength technology, applied in lasers, laser components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as high noise figure, increased instantaneous gain change of long-wavelength fiber amplifiers, and low conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In the following description, when the subject of the present invention may be made more unclear, detailed descriptions of known functions and configurations included herein will be omitted.
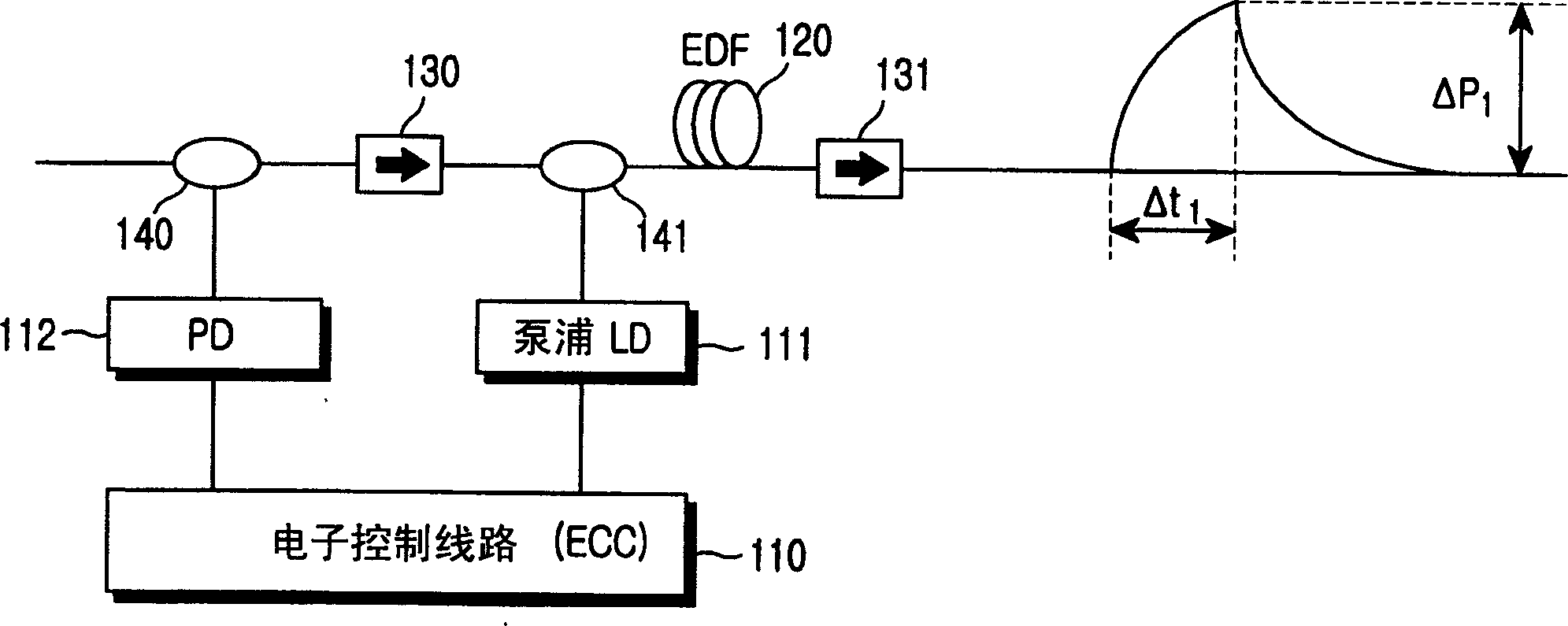
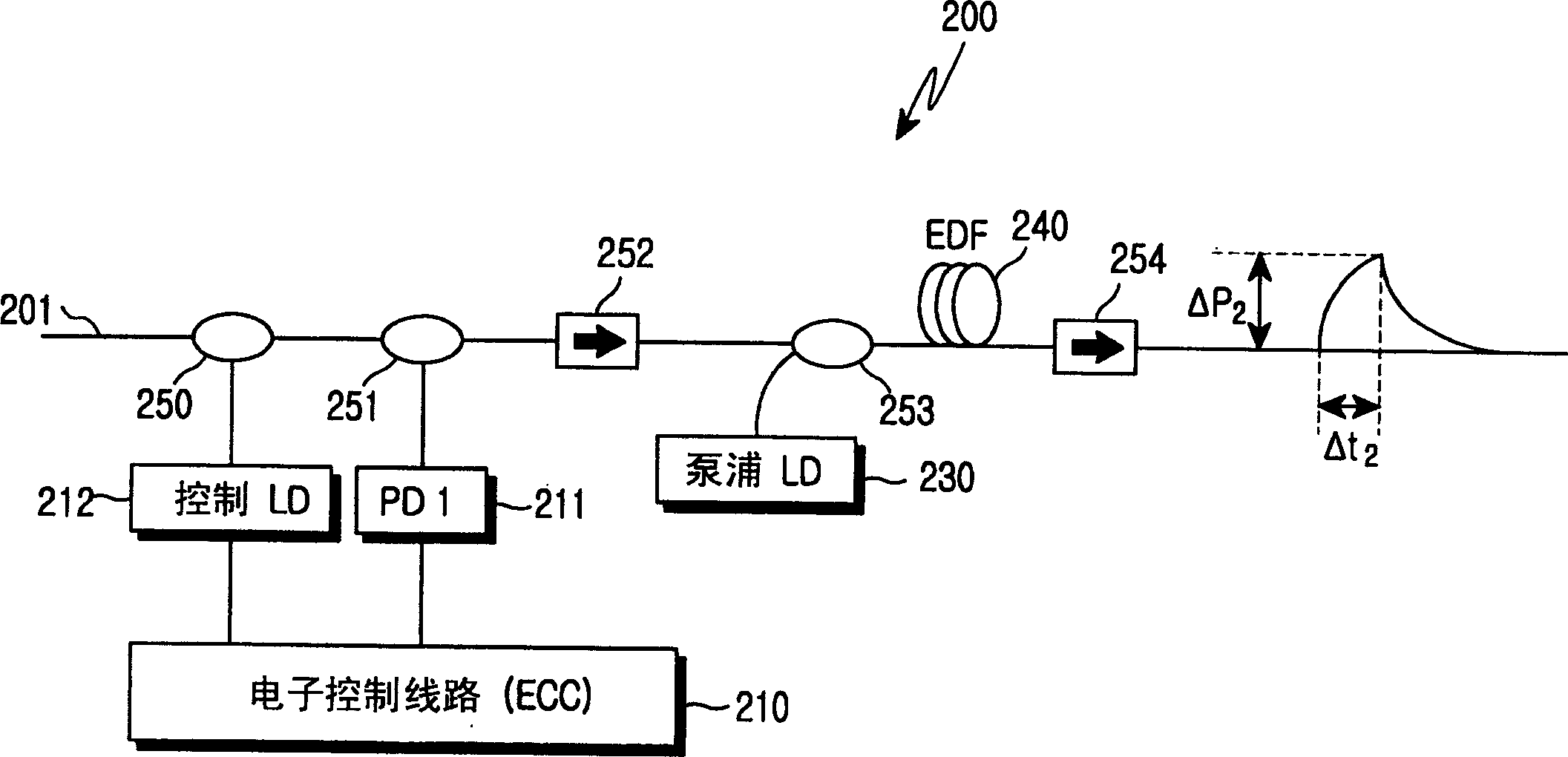
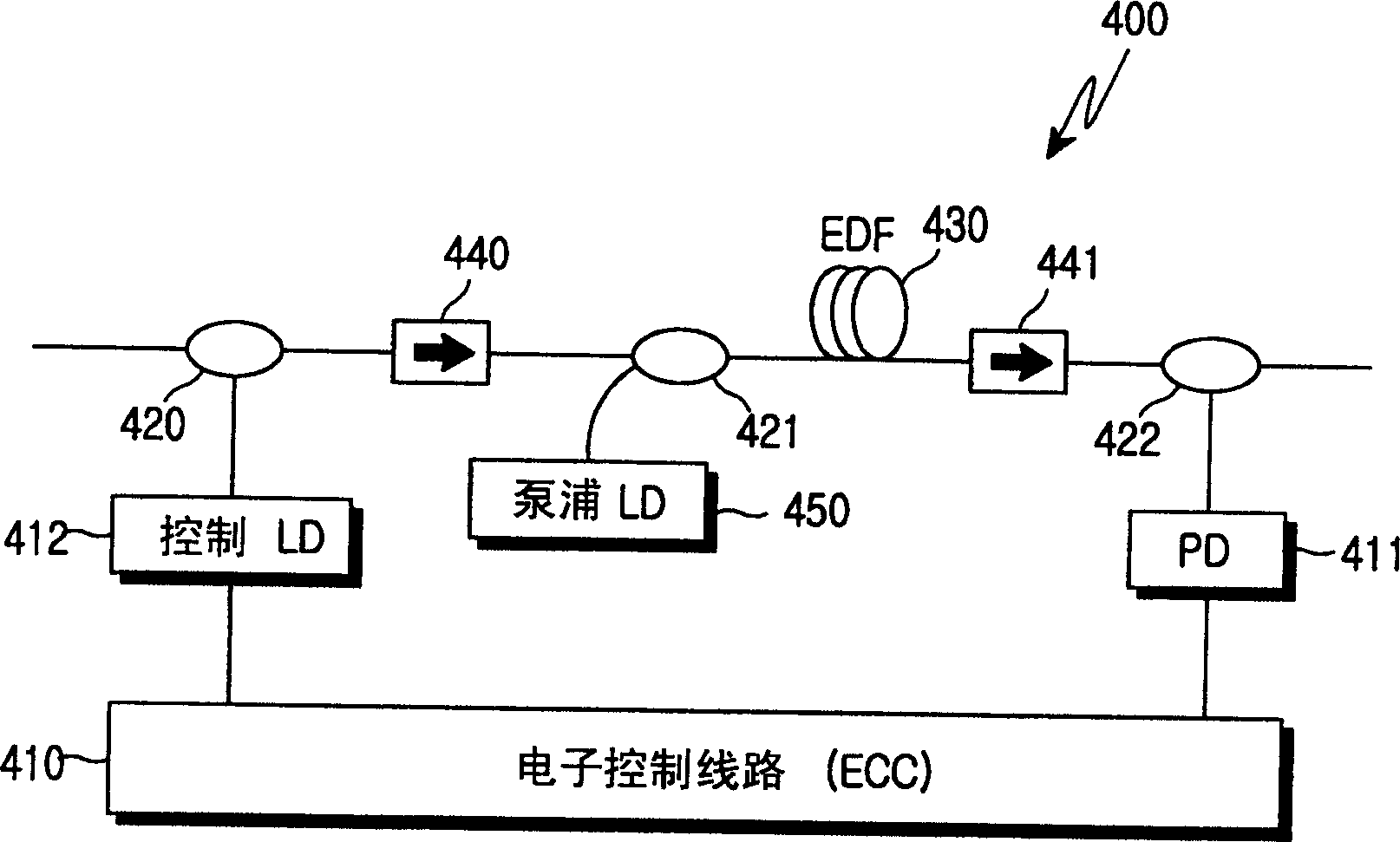
[0021] reference figure 2 According to the first embodiment, the long-wavelength fiber amplifier 200 for amplifying the long-wavelength input optical signal 201 includes: a first pump light source 230, a photodetector 210, first and second wavelength selective couplers 250 and 253, A beam splitter 251, and first and second isolators 252 and 254. The first pump light source 230 generates and outputs the first pump light of 980 nm. The photodetector 211 detects the light intensity of the input optical signal 201. The controller 210 calculates the amount of light intensity loss of the input optical signal 201 and the number of channels, and provides an output control signal acc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com