Genetic polymorphisms in the preprotachykinin gene
A polymorphism, gene technology, applied in the direction of tachykinin, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as difficult identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0178] Embodiment 1: polymorphism detection
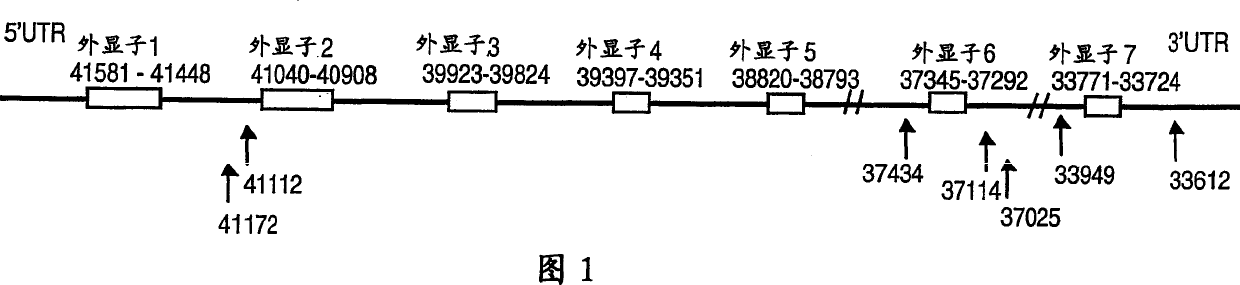
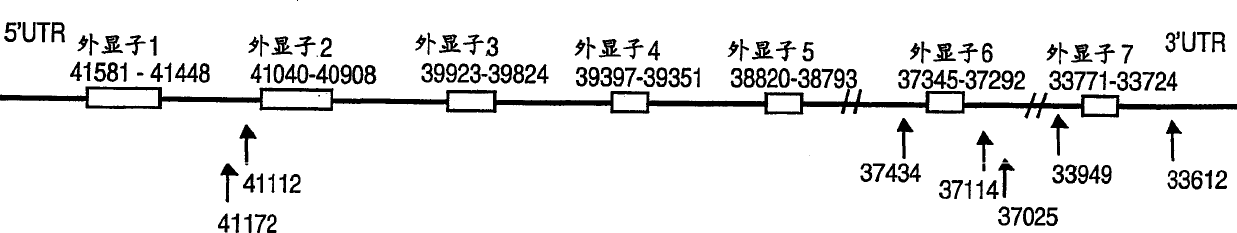
[0179] All SNPs were discovered by double-stranded DNA sequencing using ABI capillary sequencer and Big Dye chemistry (ABI). First, the genomic structure of the NKNA gene was obtained from a PAC clone with accession number EM-HUM1: AC004140.1 in the EMBL database, which was found by BLAST search with NKNA mRNA (accession number U37529.1 in the EMBL database). Exon-intron boundaries were obtained, as indicated in Figure 1, and primers were designed to amplify all coding and regulatory regions of the gene. Primers used to amplify all exons are shown below and were also used as sequencing primers. All polymorphisms were targeted using these primer pairs:
[0180] Primer type
Nucleotide sequence
SEO ID NO
Primer 1
CATGTTTACAATACATATTGGCAC
SEQ ID NO.2
Primer 2
GTATATGATGAATGATG
SEQ ID NO.3
Primer 3
CACCCTCATTCTTCCCTGC
SEQ ID NO.4
Primer 4
CTTCAGTCTCACCA...
Embodiment 2
[0184] Example 2: Genotype Detection
[0185] a) Selection of experimental subjects
[0186] The study protocol and informed consent form were submitted to the local ethics committee for approval. All subjects made a written commitment to have their blood samples used for genotyping. This promise is rescindable after no more than one month if the subject changes their mind.
[0187]All samples are assigned new independent codes, and the link between the new codes and the original codes will be deleted within six months after the closure of the clinical database. This was an additional measure to ensure subject confidentiality; however, it turned out that it was not possible to find genotype information by subject's name or original clinical trial number. After about 15 years, all blood and DNA samples will be destroyed.
[0188] b) Genotype detection experiment
[0189] Single blood samples (9 ml) were collected in EDTA tubes. The blood samples were frozen and stored bet...
Embodiment 3
[0203] Example 3: Vomiting Test
[0204] The emesis test described was performed in two studies, one single dose augmentation study (SAD) and the other multiple dose augmentation study (MAD). In SAD, the emesis test was tested after ingestion of 2-(3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-N-methyl-N-(6-morpholin-4-yl-4-O-tolyl -pyridin-3-yl)-isobutyramide 6 and / or 24 hours later. In MAD, emesis tests were performed 6 or 24 hours after the last dose following once-a-day dosing for 14 days.
[0205] SAD
[0206] 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160, 230 and 400 mg of 2-(3,5-di-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-N-methyl-N- (6-Morpholin-4-yl-4-O-tolyl-pyridin-3-yl)-isobutyramide was administered orally to subjects in a drinking emulsion. Six or 24 hours after oral administration of the drug, subjects were subcutaneously injected with 50 μg / kg of apomorphine in the lower abdomen. The time of apomorphine injection was recorded. Subjects were asked to sit upright immediately after injection. They remained in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com