Dibismuth trioxide enveloped ceramic phase reinforced aluminium base composite material
A technology of bismuth trioxide and reinforced aluminum base is applied in the field of composite materials and can solve the problems of reducing the mechanical properties of composite materials, uneven distribution of reinforcements, and increasing the cost of secondary processing of composite materials.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
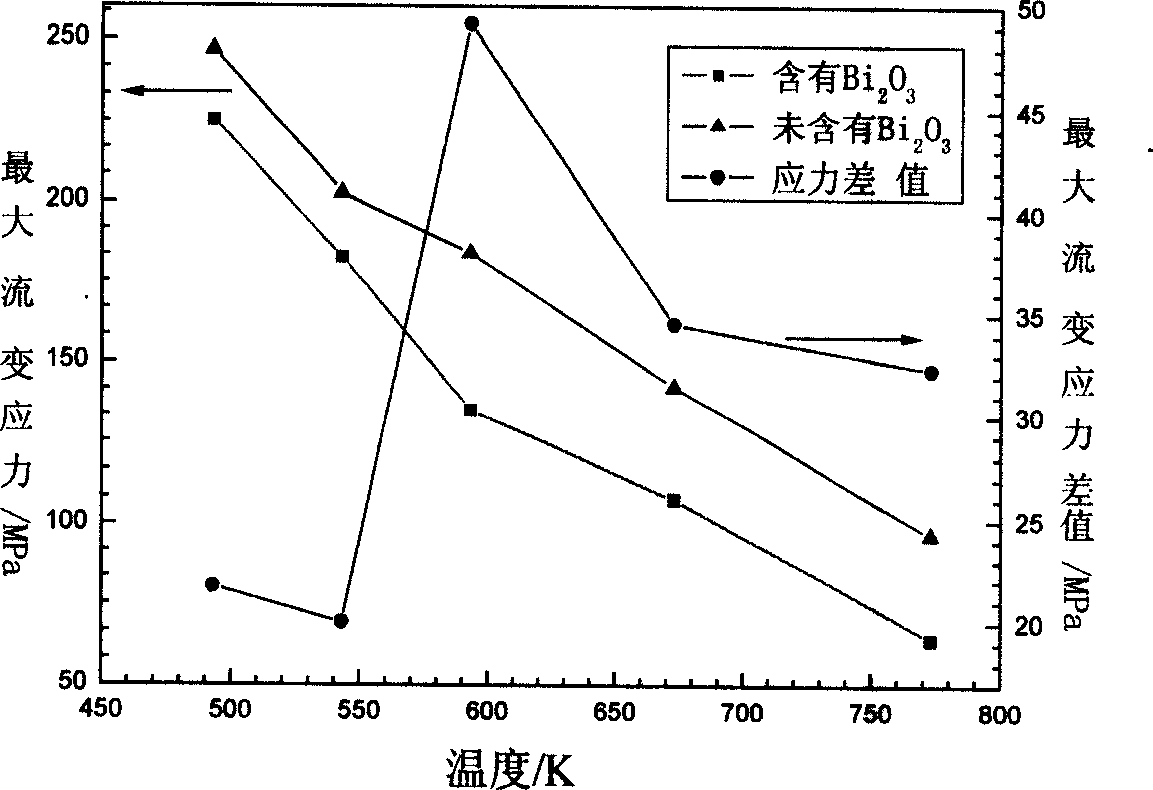
[0012] Specific embodiment one: the composite material of this embodiment is made of bismuth trioxide (Bi 2 o 3 ), ceramic phase reinforcement and aluminum matrix, wherein the volume fraction of ceramic phase reinforcement accounts for 5-50% of the total volume fraction, and the addition of bismuth trioxide accounts for 2-20% of the mass of ceramic phase reinforcement First, bismuth trioxide is coated on the surface of the ceramic phase reinforcement; then the composite material is prepared by coating the bismuth trioxide ceramic phase and aluminum or aluminum alloy on the surface. The surface-coated bismuth trioxide ceramic phase-reinforced aluminum matrix composite material undergoes thermoplastic deformation at 270°C higher than the melting point of metal bismuth, which can not only reduce the thermal deformation temperature and processing cost of the composite material, but also significantly reduce the ceramic phase reinforcement. The damage of the body, so that the mech...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0013] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 in that the volume fraction of the ceramic phase reinforcement accounts for 8% of the total volume fraction, and the addition of bismuth trioxide accounts for 5% of the mass of the ceramic phase reinforcement.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0014] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiments one and two is that the volume fraction of the ceramic phase reinforcement accounts for 15% of the total fraction, and the addition of bismuth trioxide accounts for 10% of the mass of the ceramic phase reinforcement .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com