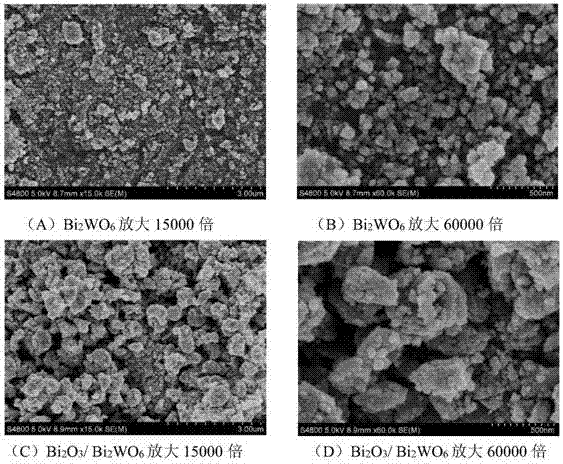
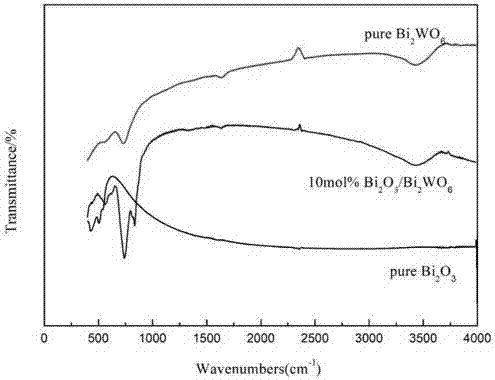
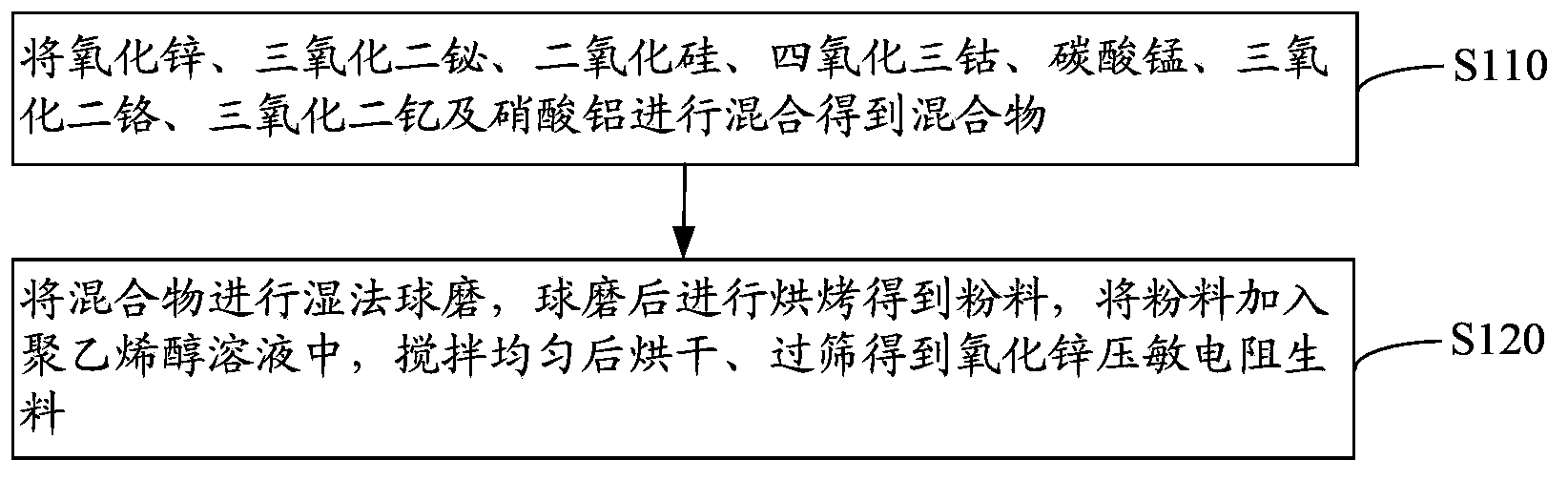
Patents
Literature
380 results about "Bismuth trioxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
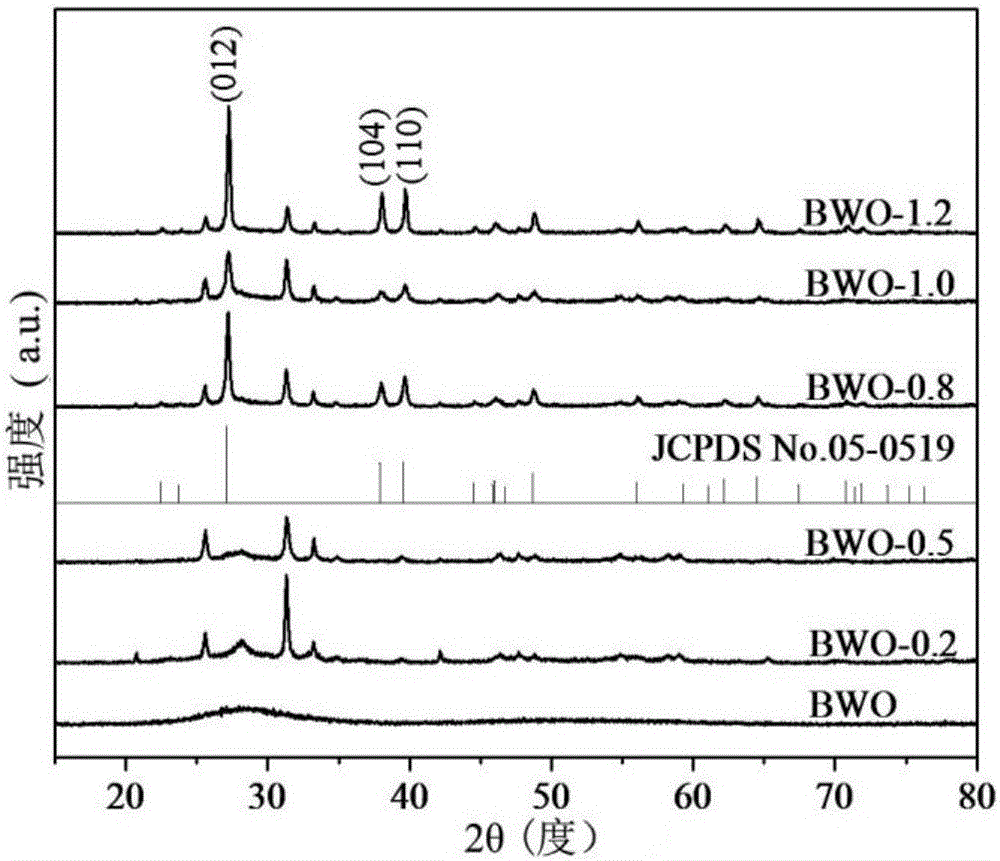
Bismuth(III) oxide is perhaps the most industrially important compound of bismuth.It is also a common starting point for bismuth chemistry. It is found naturally as the mineral bismite (monoclinic) and sphaerobismoite (tetragonal, much more rare), but it is usually obtained as a by-product of the smelting of copper and lead ores. Bismuth trioxide is commonly used to produce the "Dragon's eggs ...
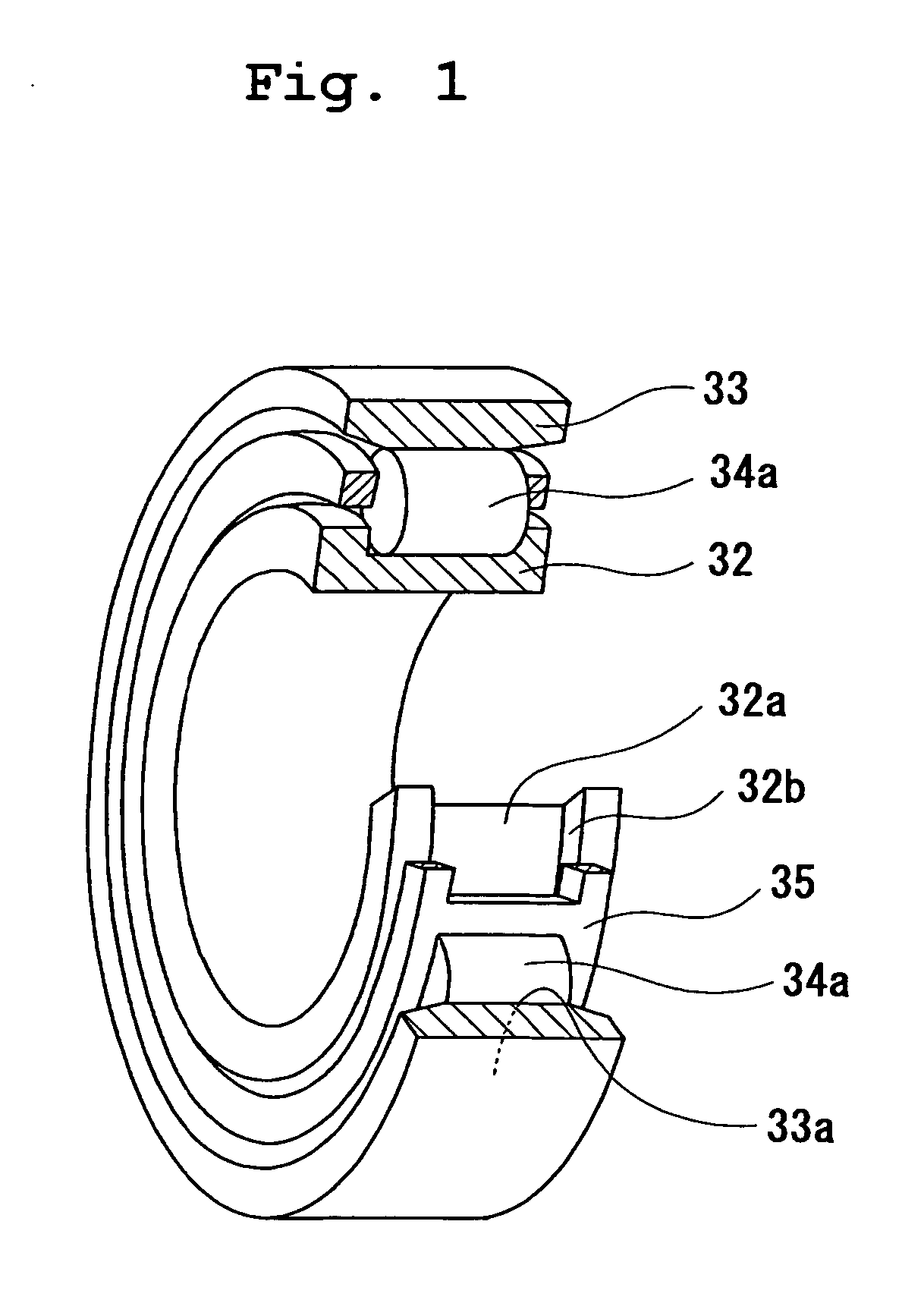
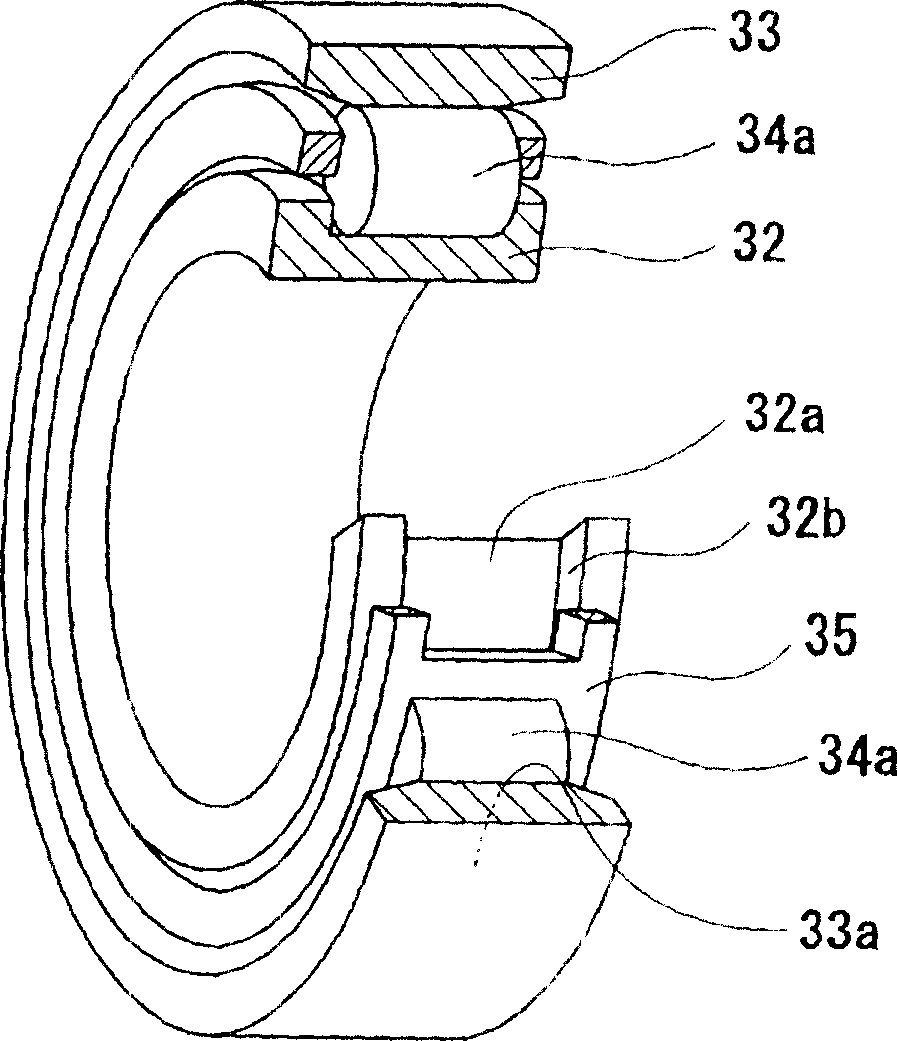
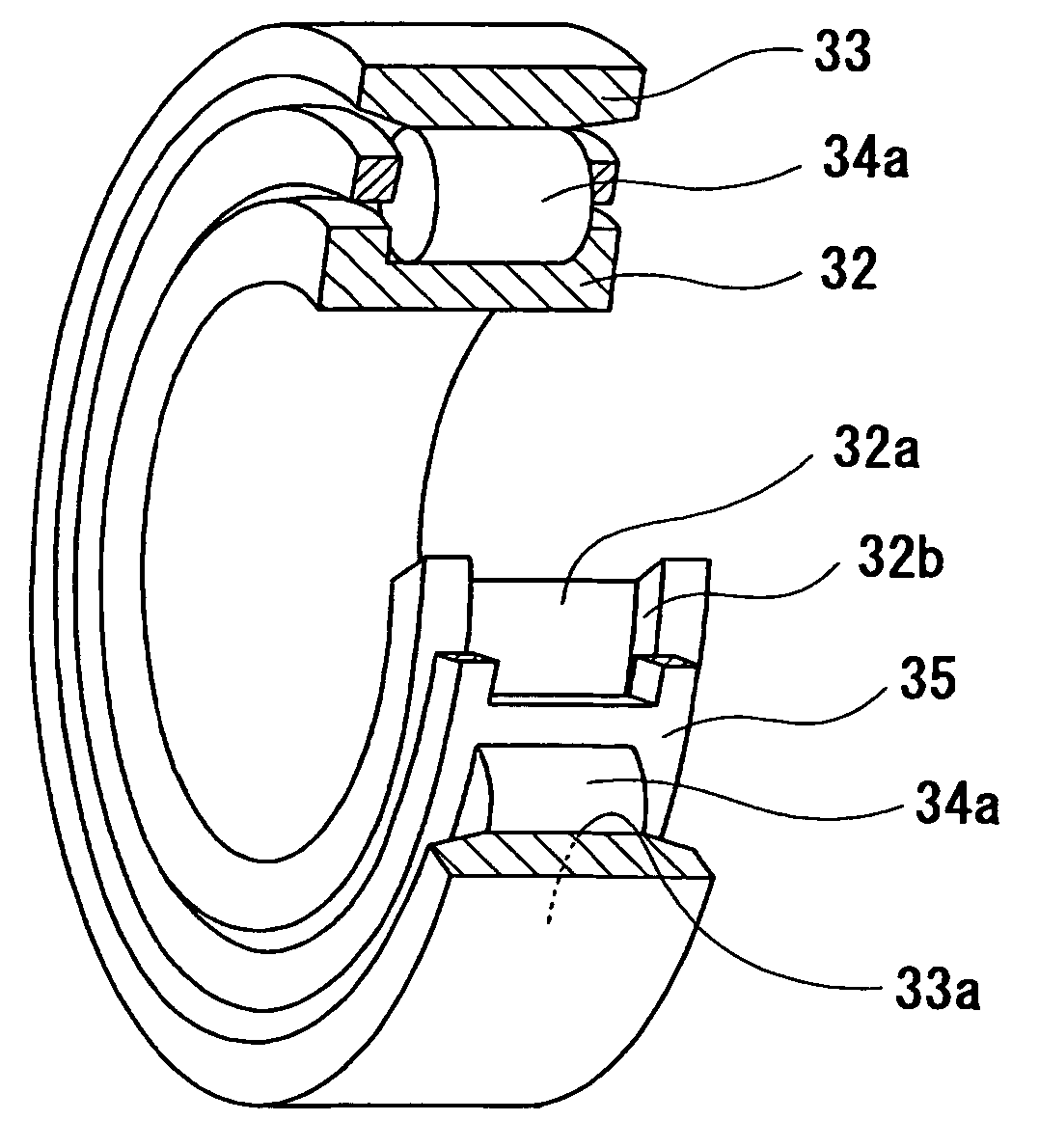
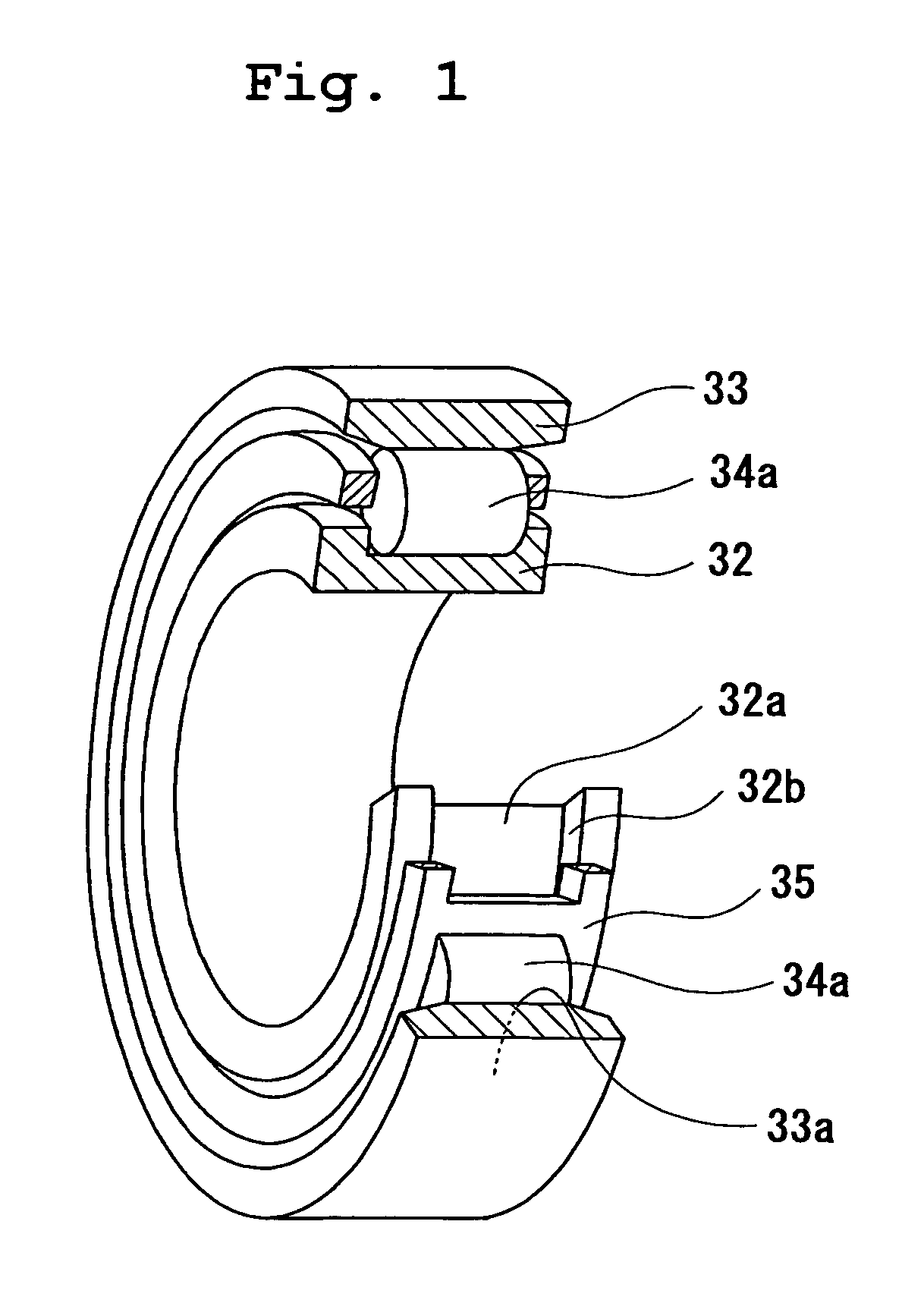
Grease, rolling bearing, constant velocity joint and rolling parts
InactiveUS20070154128A1Resistance to durabilityHeat resistantClutchesMachines/enginesBismuth compoundSulfate
The present invention provides grease which prevents frictional wear on a lubricating surface and excellent in performance of preventing occurrence of flaking, heat-resistant performance, and long-term durability, a grease-enclosed rolling bearing, a constant velocity joint, and rolling parts. Grease is composed of base grease, essentially containing a thickener, to which at least 0.01 to 15 wt % of one substance selected from among bismuth and inorganic bismuth compounds is added. The inorganic bismuth compounds are at least one inorganic bismuth selected from among bismuth sulfate, bismuth trioxide, bismuth carbonate, and sodium bismuthate. The above-described grease is used for the rolling bearing and the constant velocity joint. A coating film of at least one substance selected from among the bismuth and the inorganic bismuth is formed on surfaces of the rolling parts.
Owner:NTN CORP
High-capacity formation lead paste and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102931410AIncrease capacityExtended service lifeLead-acid accumulator electrodesFiberPolyester
The invention discloses a high-capacity formation lead paste. An anode lead paste comprises the raw materials of lead powder, deionized water, dilute sulphuric acid and anode auxiliary materials, and particularly comprises 100 parts by weight of lead powder, 6.6-7.4 parts by weight of dilute sulphuric acid, 10-11 parts by weight of deionized water, 3-5 parts by weight of red lead, 0.1-0.3 part by weight of aquadag, 0.08-025 part by weight of stannous mono-sulphate, 0.03-0.05 part by weight of bismuth trioxide, 0.03-0.05 part by weight of antimonous oxide and 0.06-0.1 part by weight of polyester staple fiber; and a cathode lead paste comprises the raw materials of lead powder, deionized water, dilute sulphuric acid and cathode auxiliary materials, and particularly comprises 100 parts by weight of lead powder, 6.5-8.5 parts by weight of dilute sulphuric acid, 9-10 parts by weight of deionized water, 0.5-0.8 part by weight of barium sulfate, 0.15-0.25 part by weight of acetylene carbon black, 0.30-0.40 part by weight of humic acid and 0.06-0.1 part by weight of polyester staple fiber. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the high-capacity formation lead paste.
Owner:CHAOWEI POWER CO LTD
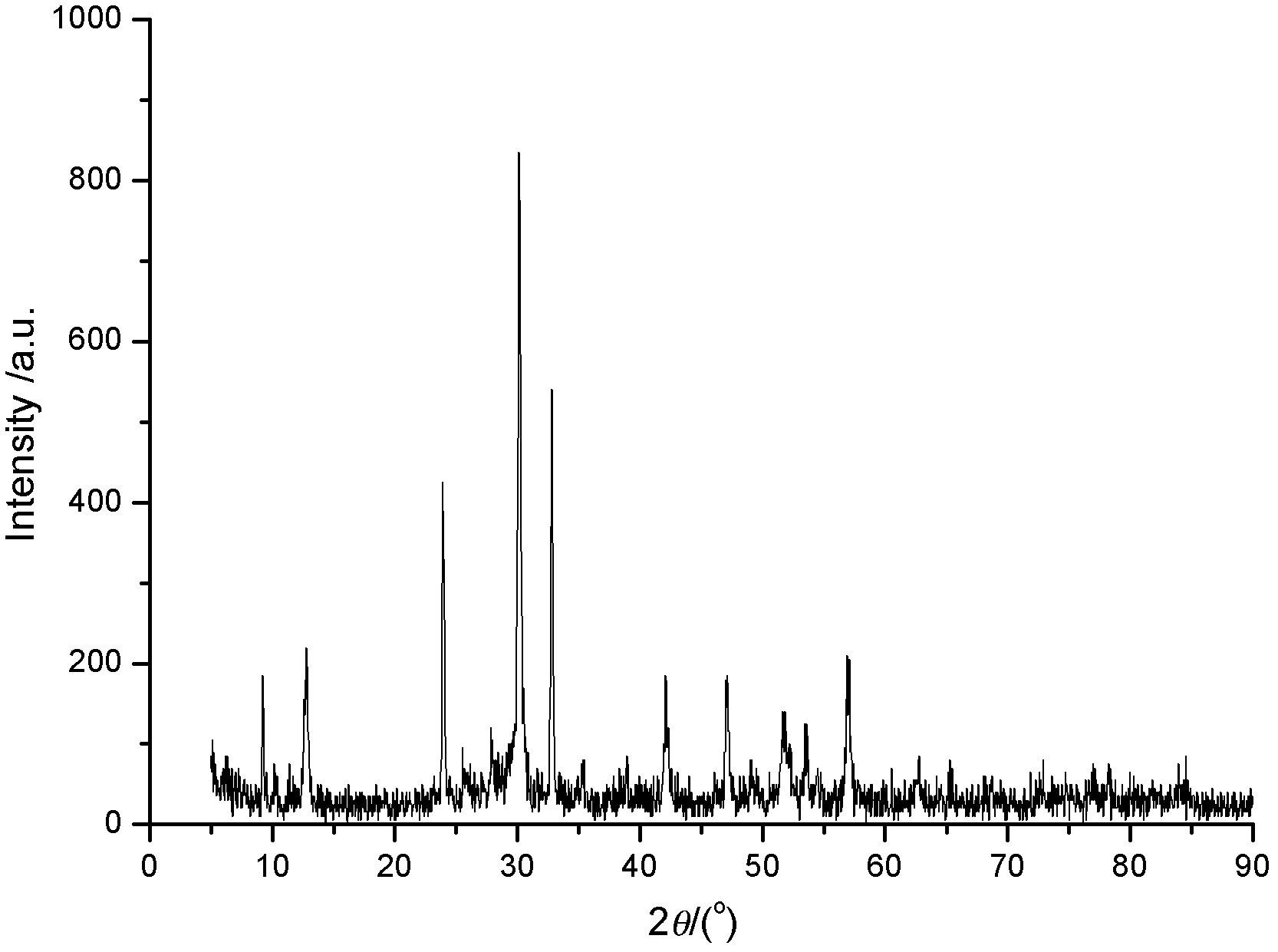
Method for preparing ball-flower-shaped gamma-bismuth trioxide powder
InactiveCN102491417ADiffraction peak is weakHigh purityNanotechnologyBismuth compoundsDispersityFiltration
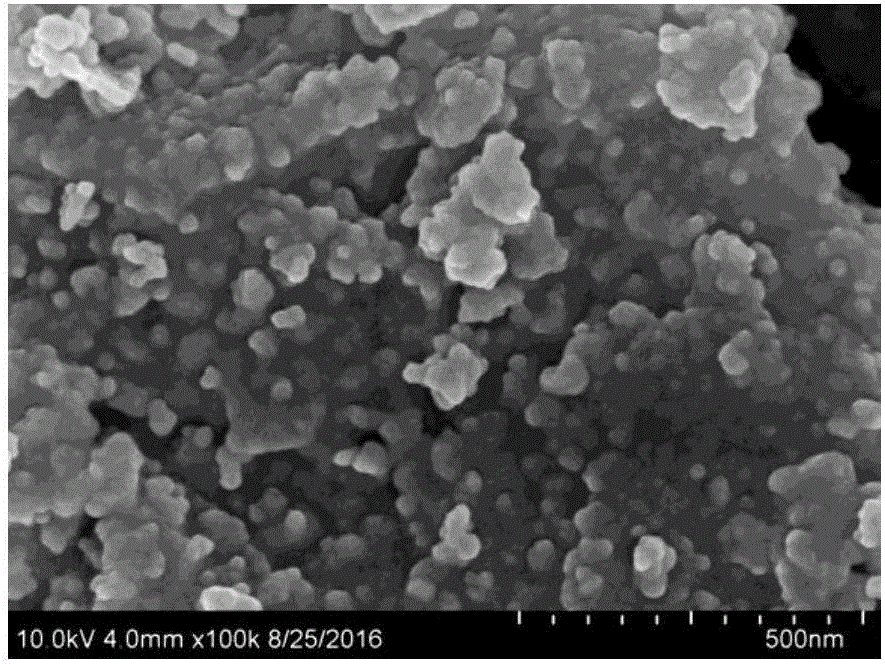
The invention discloses a method for preparing ball-flower-shaped gamma-bismuth trioxide powder, which comprises the following steps: 1 adding Bi(NO3)3 5H2O into glycol, and performing stirring to enable the Bi(NO3)3 5H2O to be dissolved, 2 sequentially adding NaOH solution, water and polyethylene glycol into prepared bismuth salt solution during the stirring to obtain reaction solution, adding the prepared reaction solution into a hydrothermal reaction kettle containing a polytetrafluoroethylene substrate, and performing hydrothermal reaction for producing Bi2O3 in an airtight state, and 3 cooling an obtained material to the room temperature and then performing air pump filtration, washing and drying to obtain a gamma-Bi2O3 powder product. The prepared gamma-Bi2O3 has uniform morphology and good dispersity. The microstructure is in a ball-like shape, and further, the ball-like shape is a ball-flower shape with diameter of 1-25 micrometers and large specific surface area. The thickness of nanometer sheets for forming micro-balls is smaller than 100 micrometers, visible light response is good, and photo-catalytic activity is high.
Owner:临沂润泰新型建材有限公司
Bismuth scandate-lead titanate high-temperature piezoelectric ceramic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102180665AStoichiometric ratio is accurateLower sintering temperatureCeramic sinteringCurie temperature
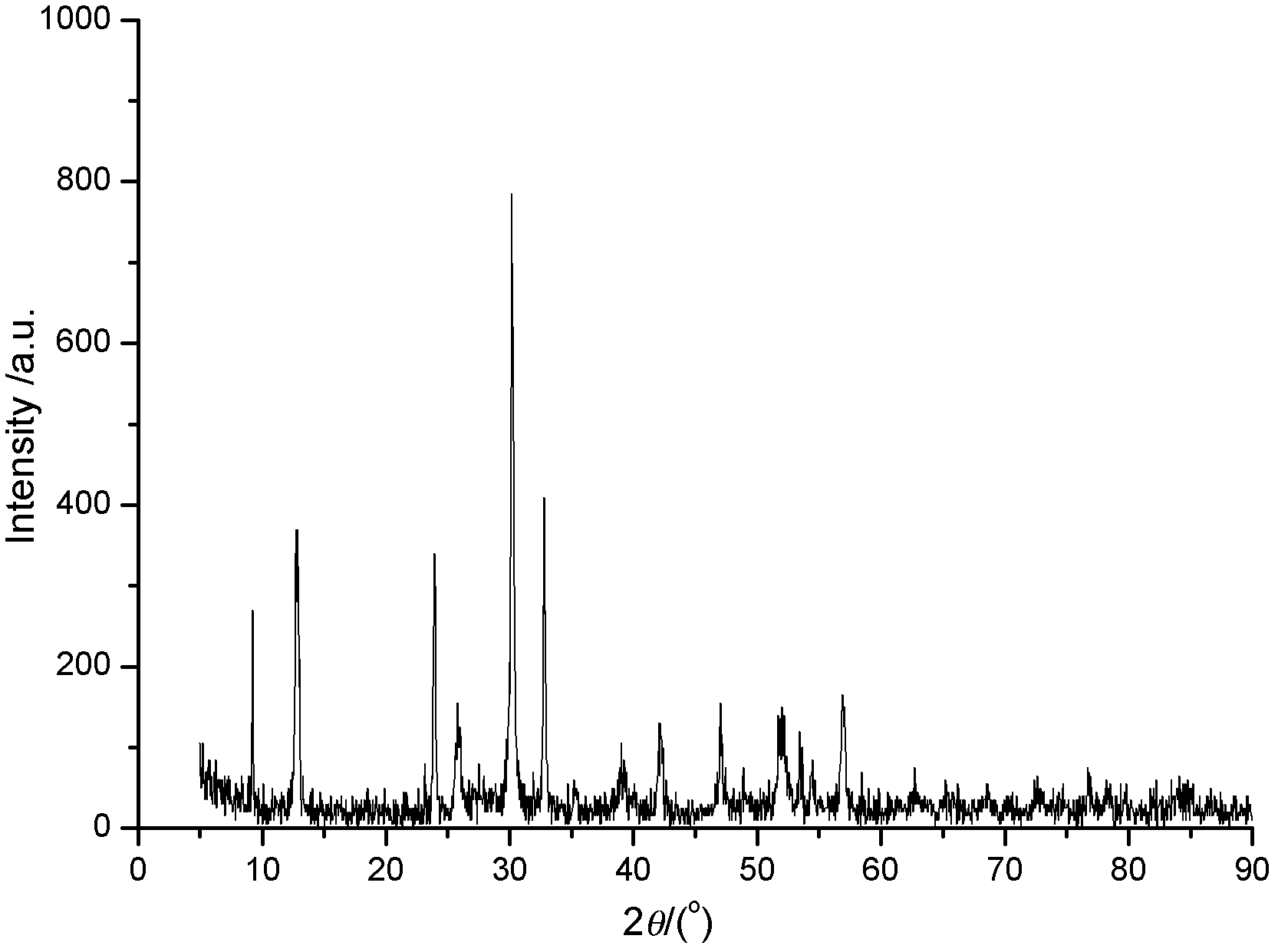
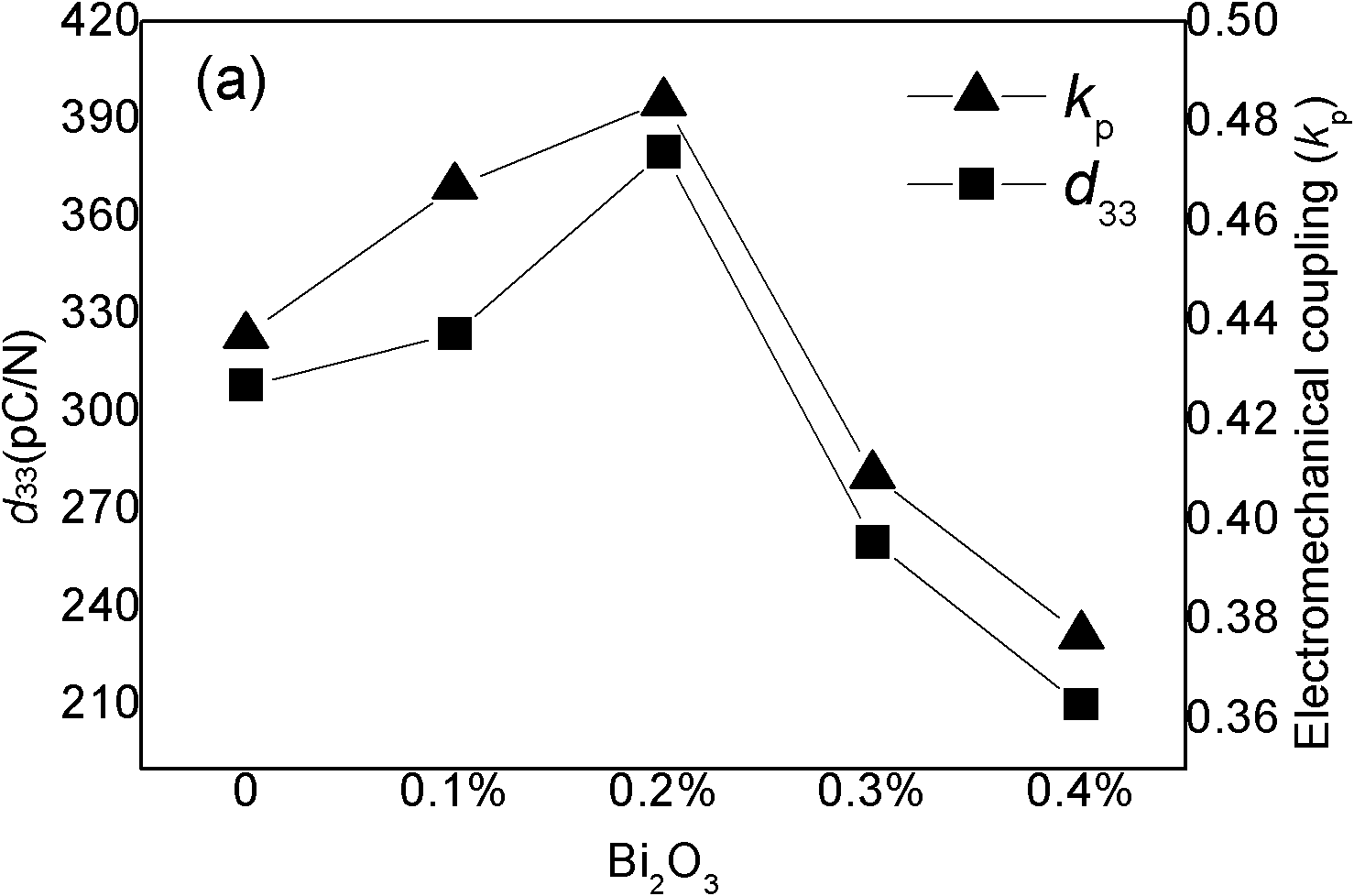
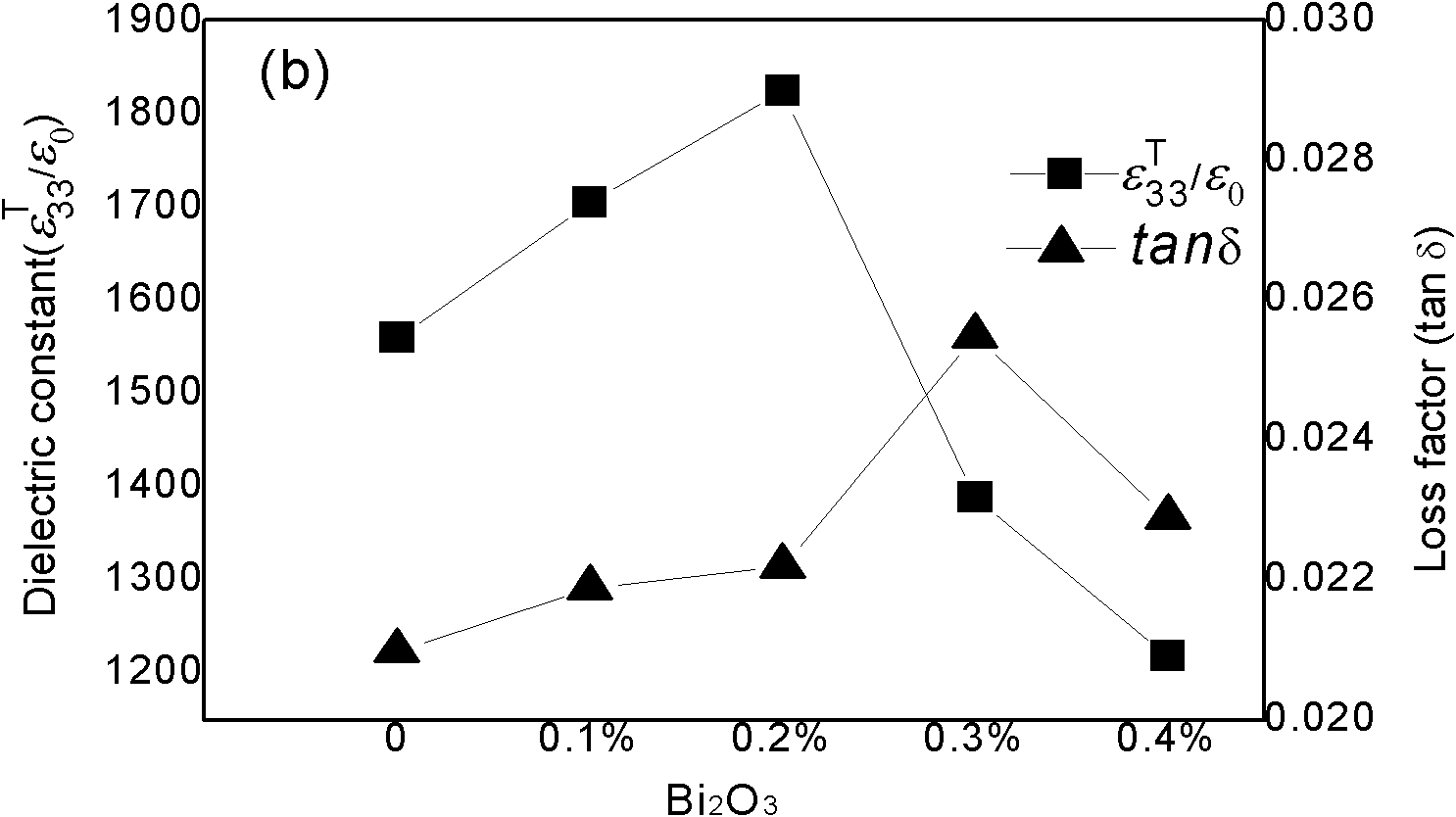
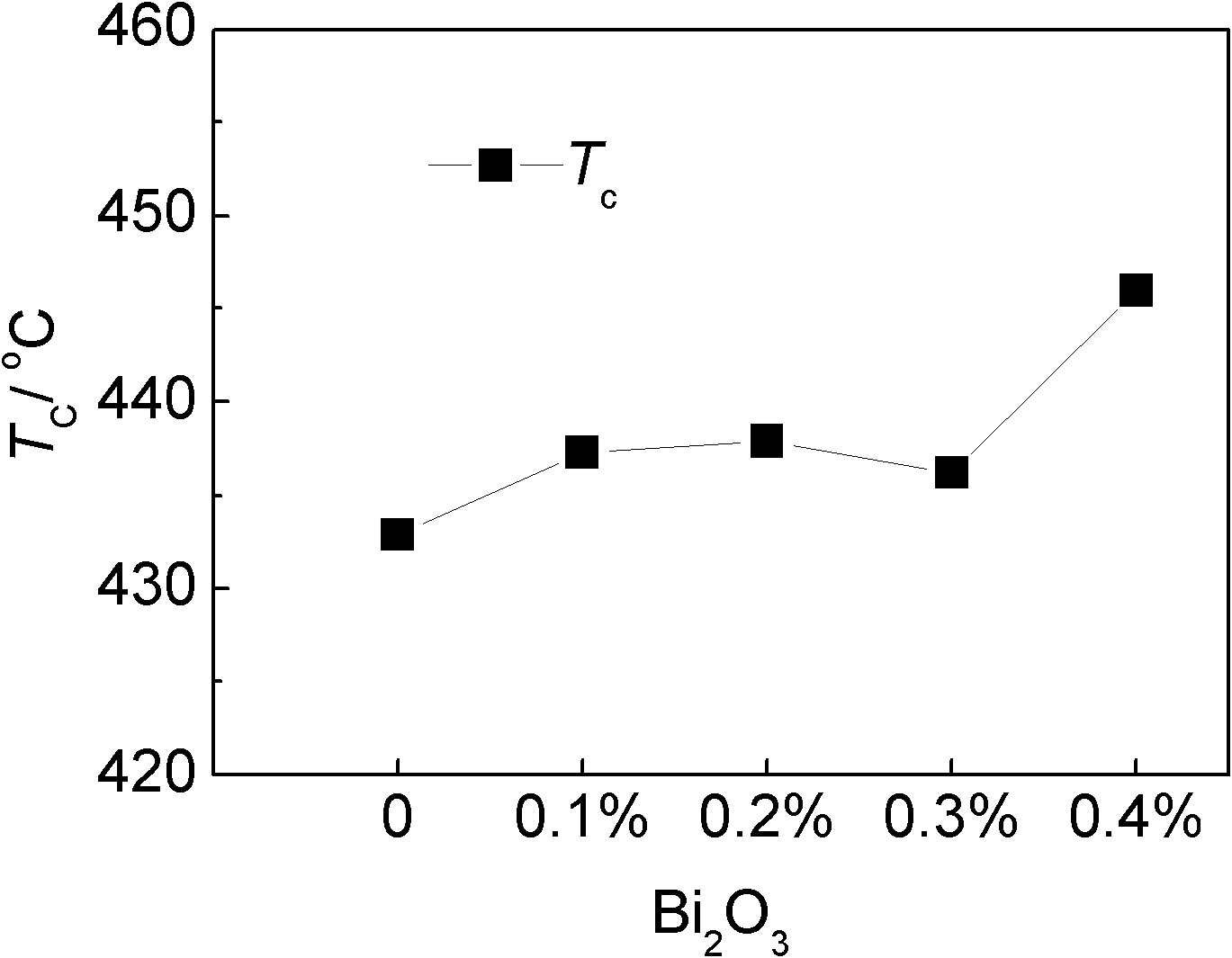
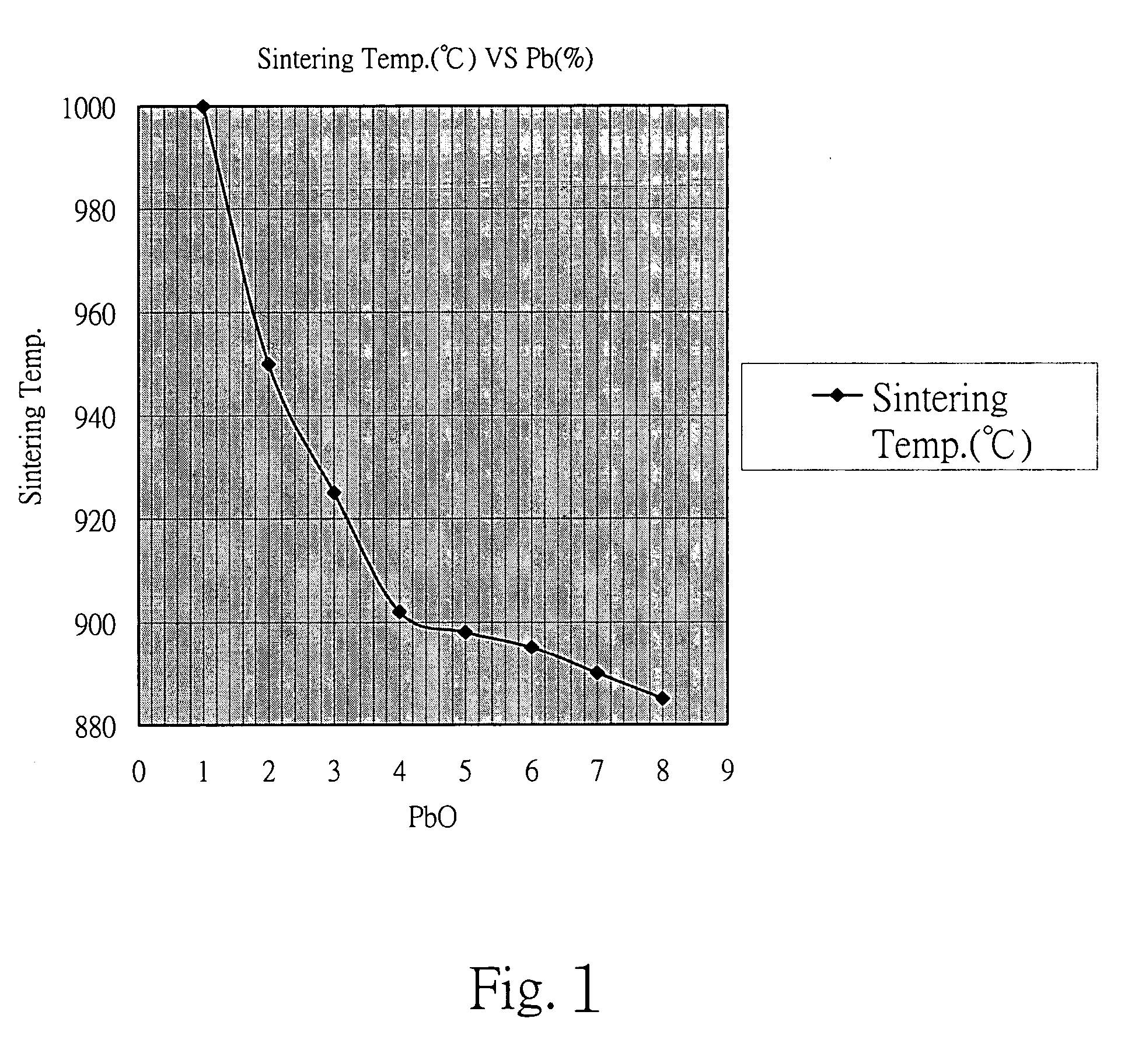
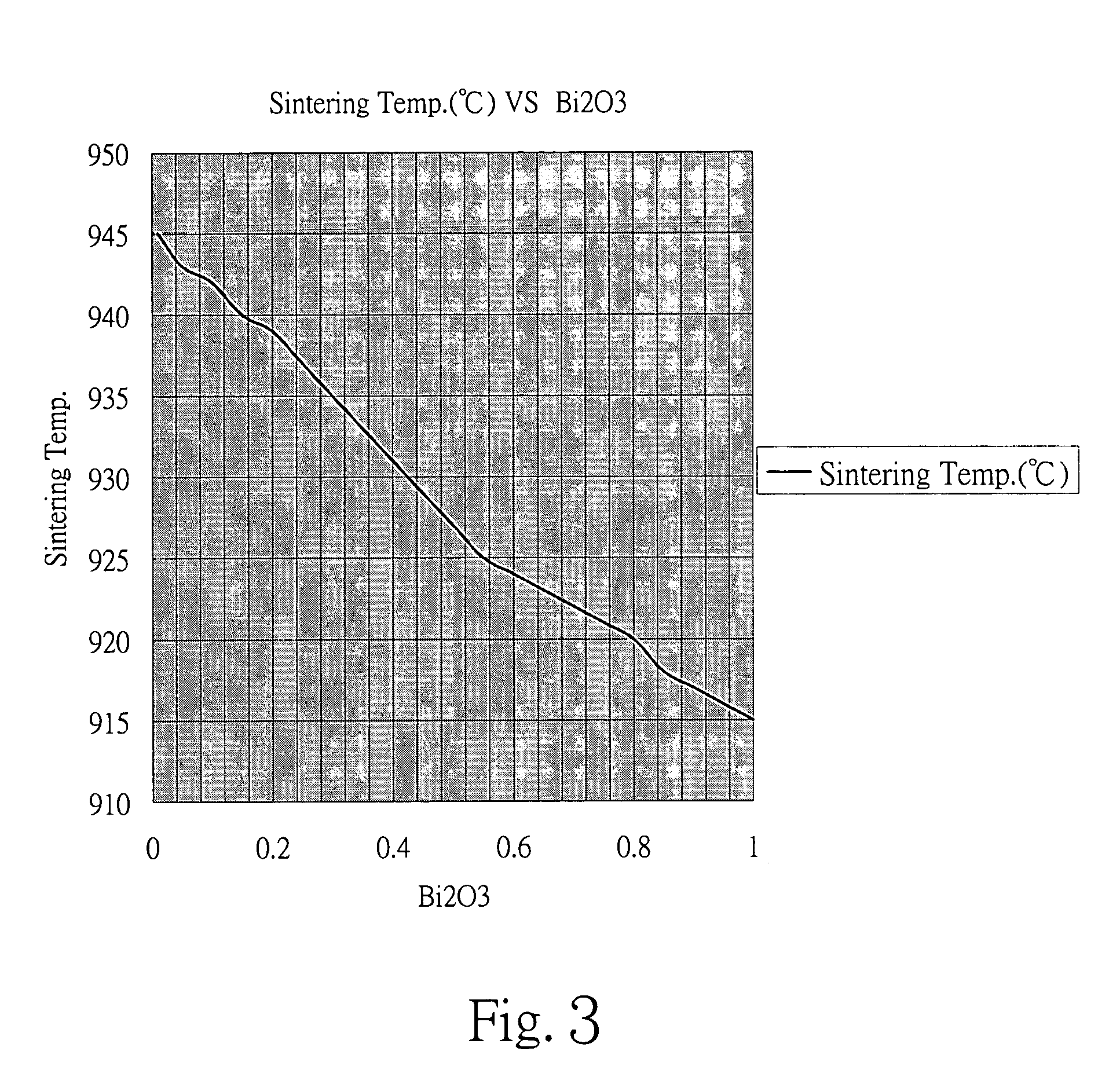
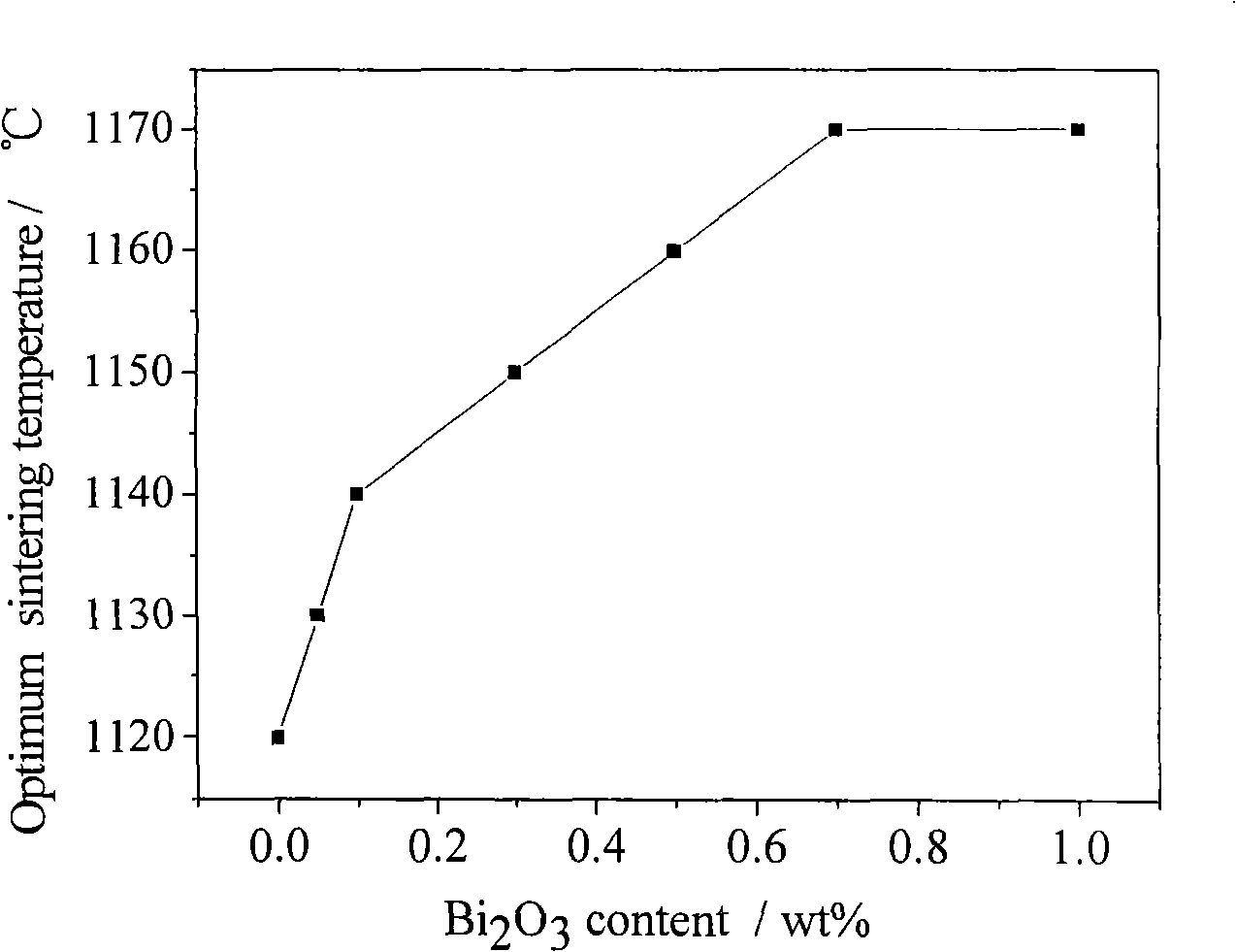
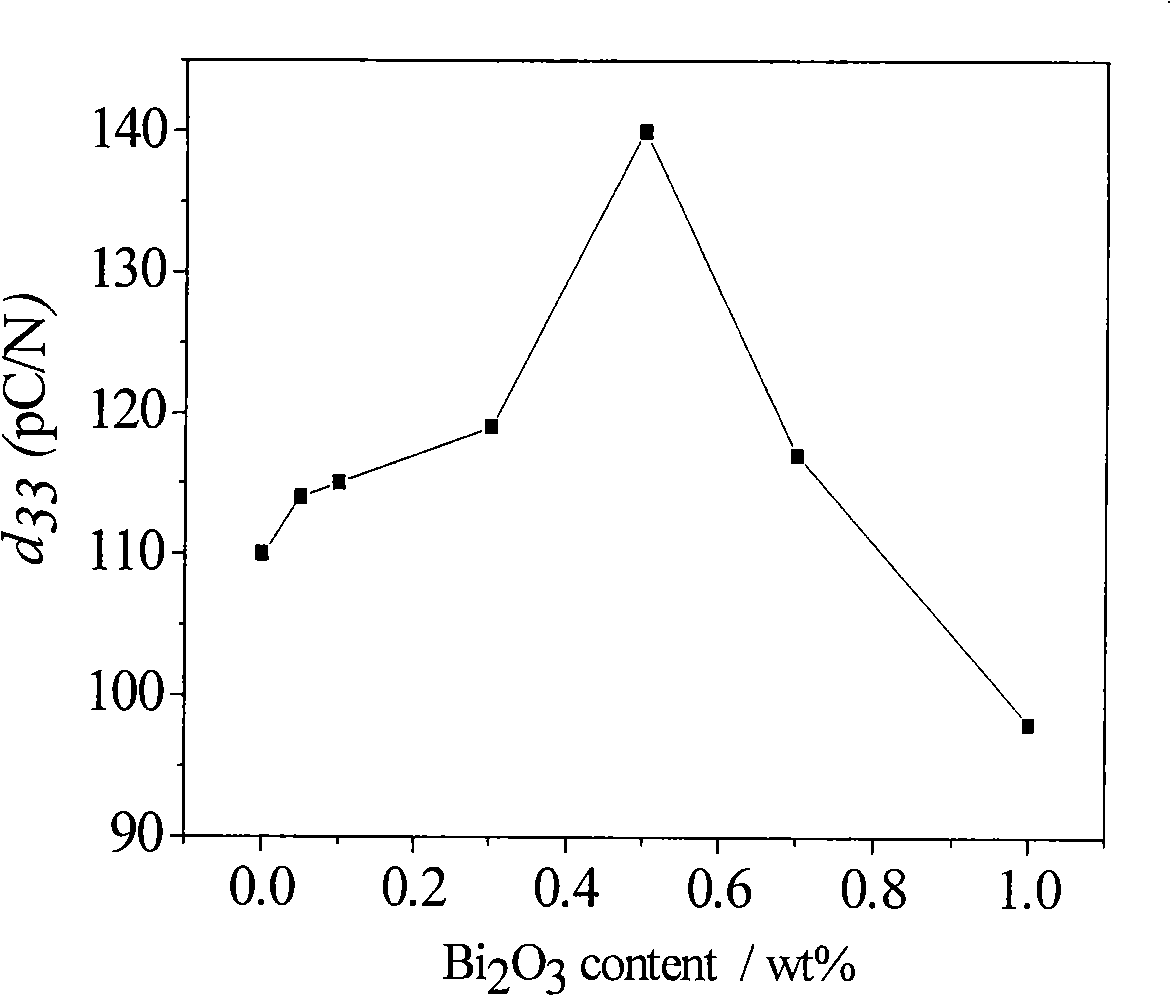
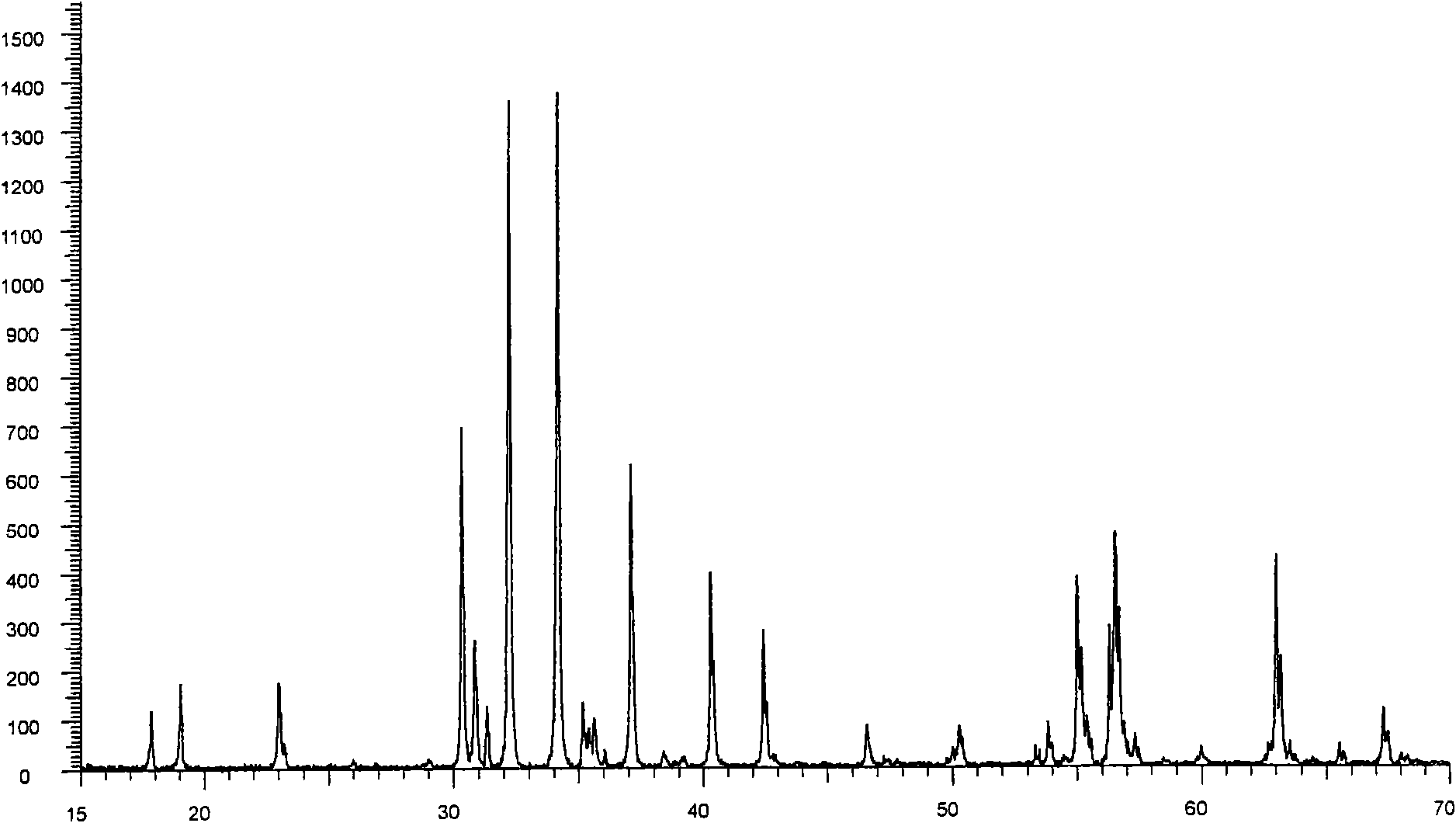
The invention discloses a bismuth scandate-lead titanate high-temperature piezoelectric ceramic material. The bismuth scandate-lead titanate high-temperature piezoelectric ceramic material comprises a matrix with the chemical formula of xBiScO3-(1-x)PbTiO3 and bismuth trioxide (Bi2O3) in an amount which is less than 0.4 percent of the total weight of the matrix. The bismuth scandate-lead titanate high-temperature piezoelectric ceramic material is prepared by adding excess Bi2O3 into raw materials of Sc2O3, Bi2O3, Pb3O4 and TiO2 in the metering ratio according to the chemical formula of xBiScO3-(1-x)PbTiO3, wherein x is 0.35 to 0.38; and the using amount of the excess Bi2O3 is 0.1 to 0.4 percent of the total weight of the raw materials of Sc2O3, Bi2O3, Pb3O4 and TiO2 in the metering ratio according to the chemical formula of xBiScO3-(1-x)PbTiO3. The bismuth scandate-lead titanate high-temperature piezoelectric ceramic material solves the problems that ceramic sintering temperature is increased and piezoelectric and dielectric properties are reduced due to deviation of a stoichiometric ratio caused by bismuth volatilization in the sintering process of BSPT ceramic, and has high Curie temperature, excellent piezoelectric property and an actual application value in high-temperature electronic equipment. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the bismuth scandate-lead titanate high-temperature piezoelectric ceramic material. In the preparation method, the piezoelectric ceramic material is prepared by synthesizing and sintering at lower temperature, so production cost is reduced, process steps are simplified, and the material has actual application value.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH +1
Low-temperature-resistant storage battery internally formed lead plaster
The invention discloses a low-temperature-resistant storage battery internally formed lead plaster. The low-temperature-resistant storage battery internally formed lead plaster consists of a positive electrode lead plaster and a negative electrode lead plaster, wherein based on the mass of lead powder of the positive electrode lead plaster, the positive electrode lead plaster comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 6.8 to 8 percent of dilute sulfuric acid, 10 to 11 percent of deionized water, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of colloidal graphite, 0.06 to 0.2 percent of tin oxide, 0.03 to 0.08 percent of bismuth trioxide and 0.07 to 0.11 percent of polyester staple fiber; and based on the mass of lead powder of the negative electrode lead plaster, the negative electrode lead plaster comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 6.8 to 8.7 percent of dilute sulfuric acid, 9 to 11 percent of deionized water, 1.0 to 1.3 percent of barium sulfate, 0.2 to 0.5 percent of acetylene carbon black, 0.2 to 0.6 percent of lignin sodium sulfonate, 0.20 to 0.50 percent of humic acid and 0.08 to 0.12 percent of polyester staple fiber. By the methods of improving the formula of the lead plaster, the proportion of electrolyte, the weight ratio of positive electrode active substances to negative electrode active substances and the like, the battery is more suitable for the northern environment, so that the life of the battery is prolonged.
Owner:CHAOWEI POWER CO LTD
Colloidal electrolyte formula for lead-acid storage battery
ActiveCN101908649AStrong water retentionEliminate passivationFinal product manufactureLead-acid accumulators constructionPolyethylene glycolPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a colloidal electrolyte formula for a lead-acid storage battery, comprising the following components in percentage by weight: 0.8-10 percent of fumed silica, 0.4-0.8 percent of polyethylene glycol, 0.03-0.6 percent of bismuth trioxide, 0.05-0.3 percent of antimonous oxide, 0.05-0.5 percent of stannous sulfate, 0.3-1 percent of phosphoric acid, 0.5-2 percent of anhydrous sodium sulfate, 25-40 percent of sulfuric acid and 50-60 percent of water. The invention has the advantages that: after using a colloidal electrolyte of the invention, with regard to the lead-calcium alloy storage battery, the phenomenon that a common colloidal electrolyte cannot adapt to a lead-calcium alloy storage battery can be effectively improved, the early-stage capacity attenuation effect of the lead-calcium alloy battery can be improved, the deep electrical discharge cycle life, the low-temperature heavy-current charging and discharging performances and the rechargeable performance after being discharged of the lead-calcium battery can be further enhanced, the use safety of the battery can be improved and the overall use cost of the battery can be reduced.
Owner:CHAOWEI POWER CO LTD
Positive lead paste of lead-acid storage battery pole plate for deep circulation
InactiveCN105140511APromote growthNot easy to fall offLead-acid accumulatorsCell electrodesFiberGas phase
The invention discloses a positive lead paste of a lead-acid storage battery pole plate for deep circulation. The positive lead paste comprises the following components based on a proportion by weight: 750-1,000 of lead powder, 0.5-2 of antimonous oxide, 0.5-2 of bismuth trioxide, 0.5-2 of stannous sulfate, 0-2 of magnesium sulfate, 0-2 of aluminum sulfate, 0.5-2 of zinc oxide, 0.5-3 of colloidal graphite, 0.5-2 of fiber, 50-250 of red lead, 80-98 of dilute sulphuric acid, 1-5 of carboxy methylated cellulose (CMC), 0.5-5 of silicon dioxide and 100-110 of pure water, wherein the dosages of the magnesium sulfate and the aluminum sulfate in the raw materials are not 0 simultaneously, and the length of the fiber is 4 to 10 millimeters. In the positive lead paste of the lead-acid storage battery pole plate for deep circulation, disclosed by the invention, the antimonous oxide and the bismuth trioxide which can be used for preventing a hydrated polymer chain from being decomposed, reducing a crystallization trend and preventing softening and shedding are added, the gas-phase silicon dioxide and the CMC which can be used for improving the adhesion strength of an active substance and the magnesium sulfate, the aluminum sulfate and the zinc oxide which can be used for facilitating the generation of a hydrated active substance chain and improving an interface of a grid and the active substance are added, the optimal effect of the positive lead paste is achieved by adjusting the proportion of the additives, thus, the capacity fading of a front stage is avoided, and the service lifetime for deep circulation of a battery is prolonged.
Owner:武汉非凡储能电源系统有限公司
Catalyst Bi2O3/Bi2MoO6 for photodegradation of organic matters and method for preparing the same
InactiveCN102658121AGood repeatabilityImprove thermal stabilityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationCatalyst activation/preparationHeterojunctionHeat stability
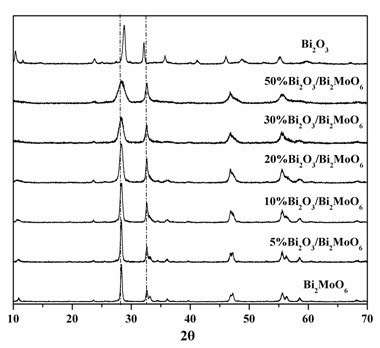
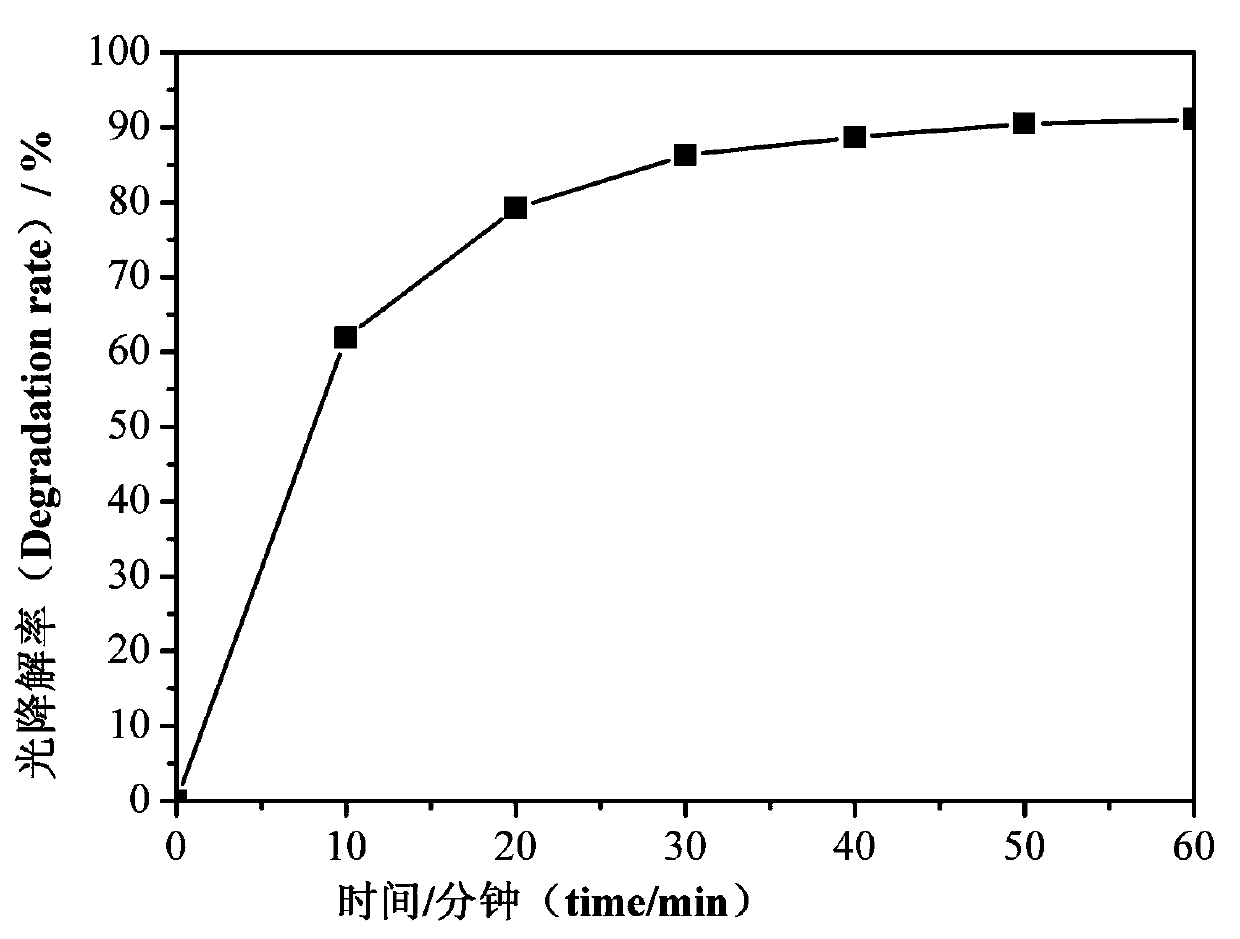
A catalyst Bi2O3 / Bi2MoO6 for photodegradation of organic matters is synthesized by a one-step hydrothermal method. The catalyst is composed of bismuth oxide (Bi2O3) and bismuth molybdenum oxide (Bi2MoO6), wherein the mole ratio of bismuth oxide and bismuth molybdenum oxide is 20%. With the visible light induction, 0.1 gram of the catalyst can completely degrade 100 milliliters of Rhodamine B of 10-5 mol / liter in 80 minutes. The advantages are that: 1. the catalyst is directly synthesized by the one-step hydrothermal method which is simple in operation, low in production cost, high in synthesis yield and purity, and good in repeatability, and suitable for magnified production; 2. the catalyst has a stable heat stability and a strong resistance to acids and alkalis; 3. the catalyst prepared has a better effect on photocatalytic degradation of organic matters than that of single bismuth molybdenum oxide (Bi2MoO6) or single bismuth oxide (Bi2O3) or Bi2O3 / Bi2MoO6 heterojunction with other load ratios.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
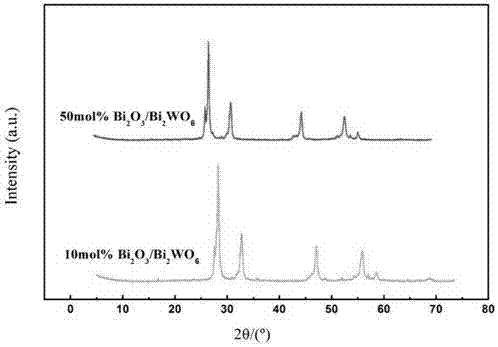
Bismuth trioxide-bismuth tungstate heterojunction photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107486199AAchieve separationHigh activityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsHeterojunctionSpectral response
The invention belongs to the field of semiconductor catalysis, and discloses a preparation method of a bismuth trioxide-bismuth tungstate heterojunction photocatalyst. The method comprises the steps of compounding bismuth trioxide and bismuth tungstate with the molar ratio being 0.1:1 to 0.5:1, so as to form a heterojunction structure, and ensuring that bismuth trioxide is loaded on the surface of bismuth tungstate. According to the method, bismuth nitrate and ammonium metatungsten are taken as raw materails, and the bismuth trioxide-bismuth tungstate heterojunction photocatalyst is formed by one step through a solvothermal method. The preparation method is simple, the synthesis period is short, and a formed sample is high in purity and has a typical p-n heterojunction structure, can effectively restrain the compounding of photo-induced electron and holes, promotes the separation of photon-generated carriers, has the characteristics of high activity and wide spectral response, and is of great importance.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Unleaded glass powder used for electronic paste and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an unleaded glass powder used for electronic paste and a preparation method thereof. The unleaded glass powder is composed of the following components by mass ratio: 10-60% of diboron trioxide, 2.5-30% of silicon dioxide, 30-75% of bismuth trioxide, 0.1-5% of sodium oxide, 0.1-3% of calcium oxide, 0.5-10% of strontium oxide, 1.5-20% of titanium dioxide, 0.5-8% of zirconium oxide, 0.1-5% of stannic oxide, 0.5-6% of aluminium oxide, 0.5-5% of antimonous oxide and 0.1-5% of calcium fluoride, the components are fully mixed to be uniform and then heated to 1050-1250 DEG C, and heat preservation is carried out for 30-120min, so that raw material is fully melted into glass metal, the glass metal is poured into deionized water to be quenched into glass granules, and ball milling into 320-400 meshes is carried out, thus obtaining the unleaded glass powder. The invention provides an unleaded glass powder with low softening temperature, good chemical stability, appropriate expansion coefficient, acid-base resistance, good abrasive resistance, wide sintering temperature range, low manufacturing cost and no toxic heavy metal oxide, and the unleaded glass powder has wide application range.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
MnZn ferrite material and method of manufacturing the magnetic core
InactiveCN101183585AImprove DC Superposition CharacteristicsReduce power lossInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureManganese oxideNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a Mn-Zn ferrite magnetic material, a magnetic core and a related manufacturing method. The primary composition of Mn-Zn soft magnetic ferrite materials: 49.5 to 53.9 mol percentages of iron oxide Fe2O3, 34.6 to 39.8 mol percentages of manganese oxide MnO, and 8.5 to 13.8 percentages of zinc oxide ZnO. Furthermore, a first assistant component with a weight of 100 to 600ppm, as well as a second assistant component with a weight of 50 to 3000ppm are added into the primary composition; wherein the first assistant component refers to one or more materials as silicon dioxide SiO2 or tantalum oxide Ta2O5; the second assistant component refers to one or more materials as bismuth trioxide Bi2O3, niobium pentoxide Nb2O5 or \ tungsten trioxide WO3. A magnetic billet can be prepared according the formula, followed by high temperature sintering under 1280 to 1360 DEG C in a nitrogen-protected kiln. The manufactured magnetic core has the advantages of high anti-DC-superposing performance and lower power consumption.
Owner:GUANGDONG FENGHUA ADVANCED TECH HLDG +1
Strength retrogression preventer
ActiveUS20070039734A1Reduce or prevent the compressive strength of the set cement from decreasingSolid waste managementDrilling compositionSlurryUltimate tensile strength
Cementitious slurries capable of controlling and / or preventing strength retrogression during the cementing of a formation contain a bismuth salt or derivative thereof. Bismuth trioxide is preferred. The cementitious slurry may further contain a density modifying agent and / or strength enhancer. The cementitious slurries of the invention are suitable for use over a broad temperature range of from about 45° F. to about 500° F.
Owner:BJ SERVICES LLC
Magnesium-zinc soft magnetic ferrite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102344283AImprove quality factor Q valueLower sintering temperatureCopper oxideNickel zinc
The invention provides a magnesium-zinc soft magnetic ferrite. The magnesium-zinc soft magnetic ferrite comprises main ingredients and accessory ingredients, wherein the main ingredients comprise the following components in percentage by weight: 68.92 to 70.59 percent of ferric oxide, 16.03 to 18.52 percent of zinc oxide, 8.07 to 9.83 percent of magnesium oxide and 3.62 to 3.86 percent of copper oxide; and the accessory ingredients comprise the following components in percentage by weight: 0.1 to 0.3 percent of bismuth trioxide and 0.1 to 0.3 percent of vanadium pentoxide. The invention also relates to a method for preparing the magnesium-zinc soft magnetic ferrite. The performance of the material is close to that of a nickel-zinc soft magnetic ferrite, the loss of the magnesium-zinc soft magnetic ferrite is low when the magnesium-zinc soft magnetic ferrite is used at high frequency, and the cost is relatively lower.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Environment friendly microwave medium ceramic substrate
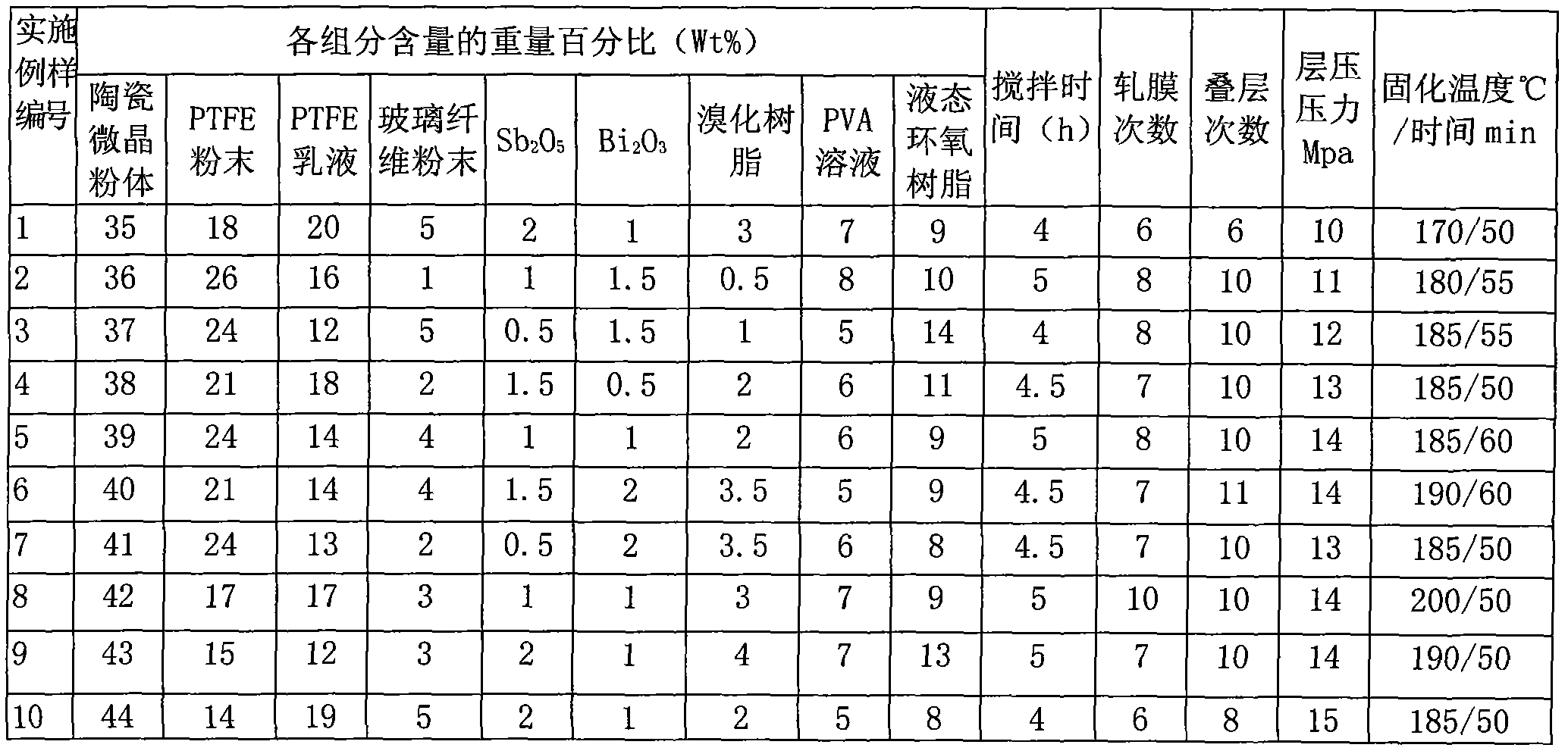
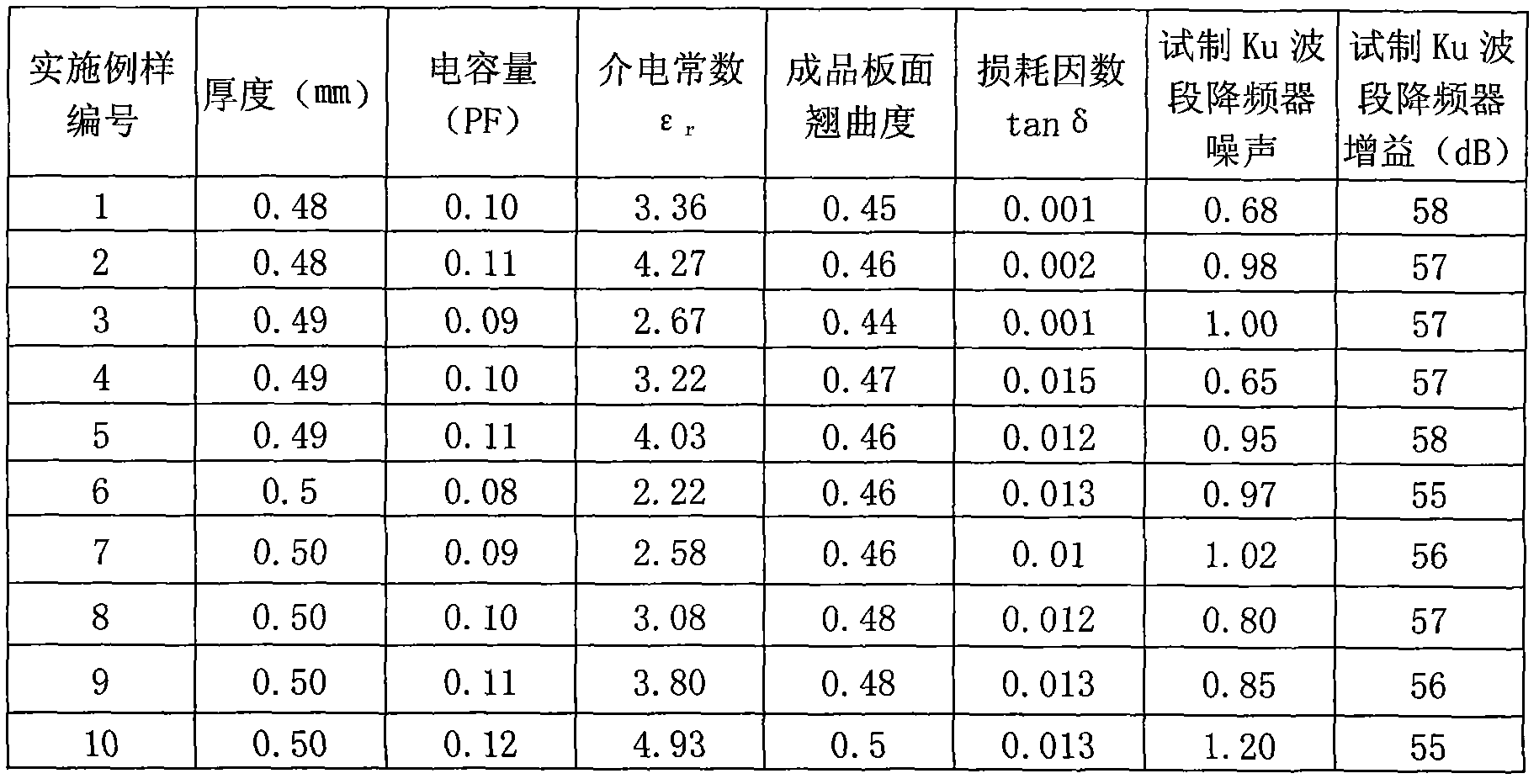
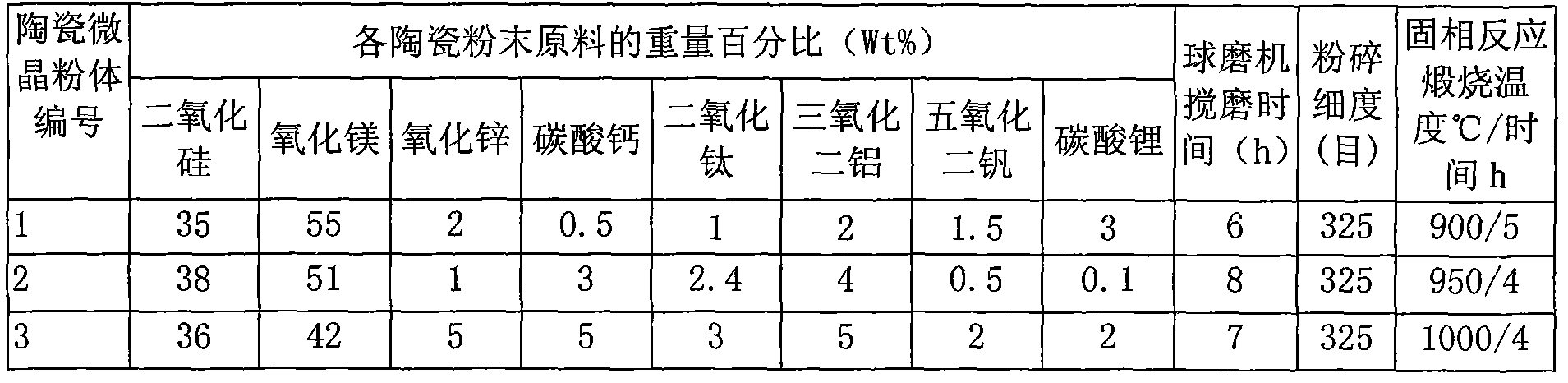
The invention relates to an environment friendly microwave medium ceramic substrate which is mainly used for the circuits of microwave and millimeter wave satellite communication products, military radar products, electronic navigation products, microwave safety monitoring products, and the like. The substrate is prepared by adopting the following steps of: directly mixing ceramic microcrystal powder with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) powder, PTFE emulsion, glass fiber powder, liquid-state epoxy resin and PVA (Polyvinylalcohol) solution raw material and micro flame-retardant additive raw materials: brominated resin, antimony pentoxide (Sb2O5) and bismuth trioxide (Bi2O3); carrying out blooming, primary drying, laminating, finish rolling, two-surface or two-way continuous sizing, redrying, two-surface or two-way continuous copper foil coating, tailoring and high-pressure lamination; then vacuumizing and curing for 50-60min at low temperature of 170-200 DEG C. The invention does not contain Nb heavy metal components and has good properties of microwave high frequency band low dielectric Epsilonr, low loss tan delta, high signal transmission efficiency and high stability and the advantages of simple process and low sintering temperature and can be cofired with a silver electrode.
Owner:CHENZHOU GONGTIAN ELECTRONICS CERAMICS TECH
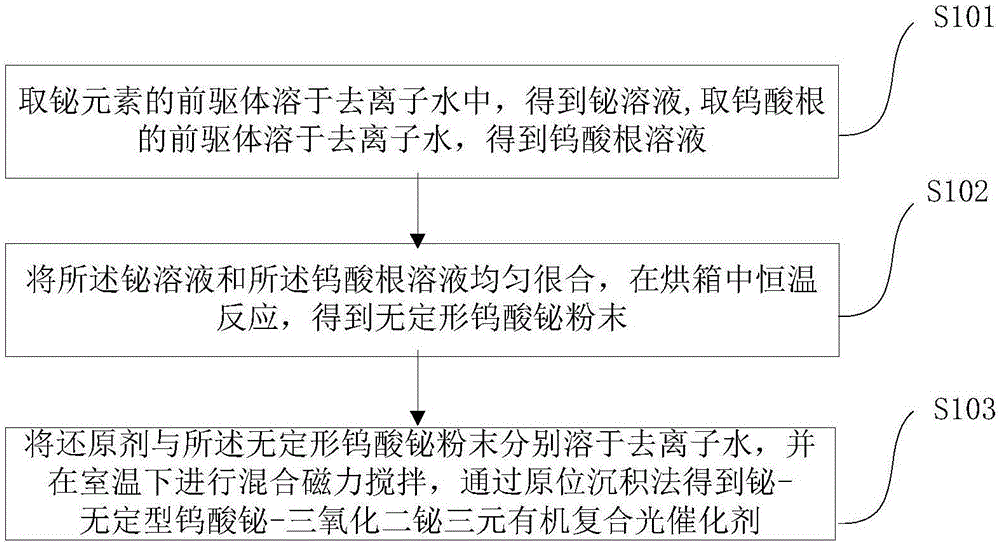
Bismuth-amorphous bismuth tungstate-bismuth trioxide ternary organic composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106807361AEasy to makeHigh priceGas treatmentDispersed particle separationHeterojunctionTungstate
The embodiment of the application provides a bismuth-amorphous bismuth tungstate-bismuth trioxide ternary organic composite photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a precursor of bismuth in deionized water to obtain a bismuth solution, and dissolving a precursor of tungstateradicle in deionized water to obtain a tungstateradicle solution; uniforming mixing the bismuth solution and the tungstateradicle solution, and performing a thermostatic reaction in a drying oven to obtain amorphous bismuth tungstate powder; and respectively dissolving a reducing agent and the amorphous bismuth tungstate powder in deionized water, performing mixing and magnetic stirring under the room temperature, and adopting an in-situ deposition method to obtain the bismuth-amorphous bismuth tungstate-bismuth trioxide ternary organic composite photocatalyst. In the organic composite photocatalyst obtained by adoption of the preparation method, the simple substance Bi is loaded on the surface of bismuth tungstate in situ and forms a heterojunction together with an oxide Bi2O3 of the simple substance Bi, so that separation of photo-induced electrons from electron-hole pairs of amorphous bismuth tungstate is quickened to the utmost extent, and furthermore, the photocatalytic activity of the ternary organic composite photocatalyst is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV
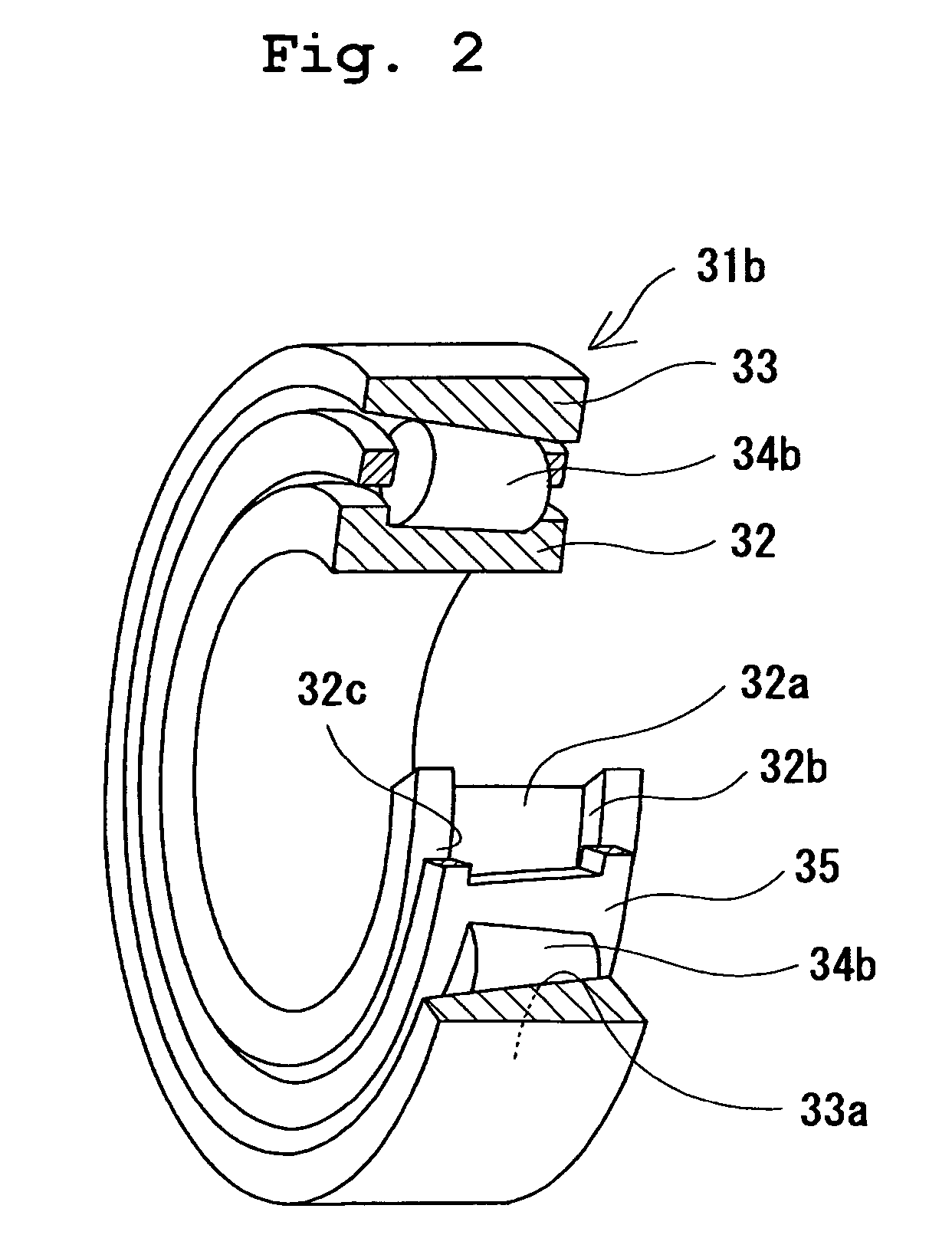
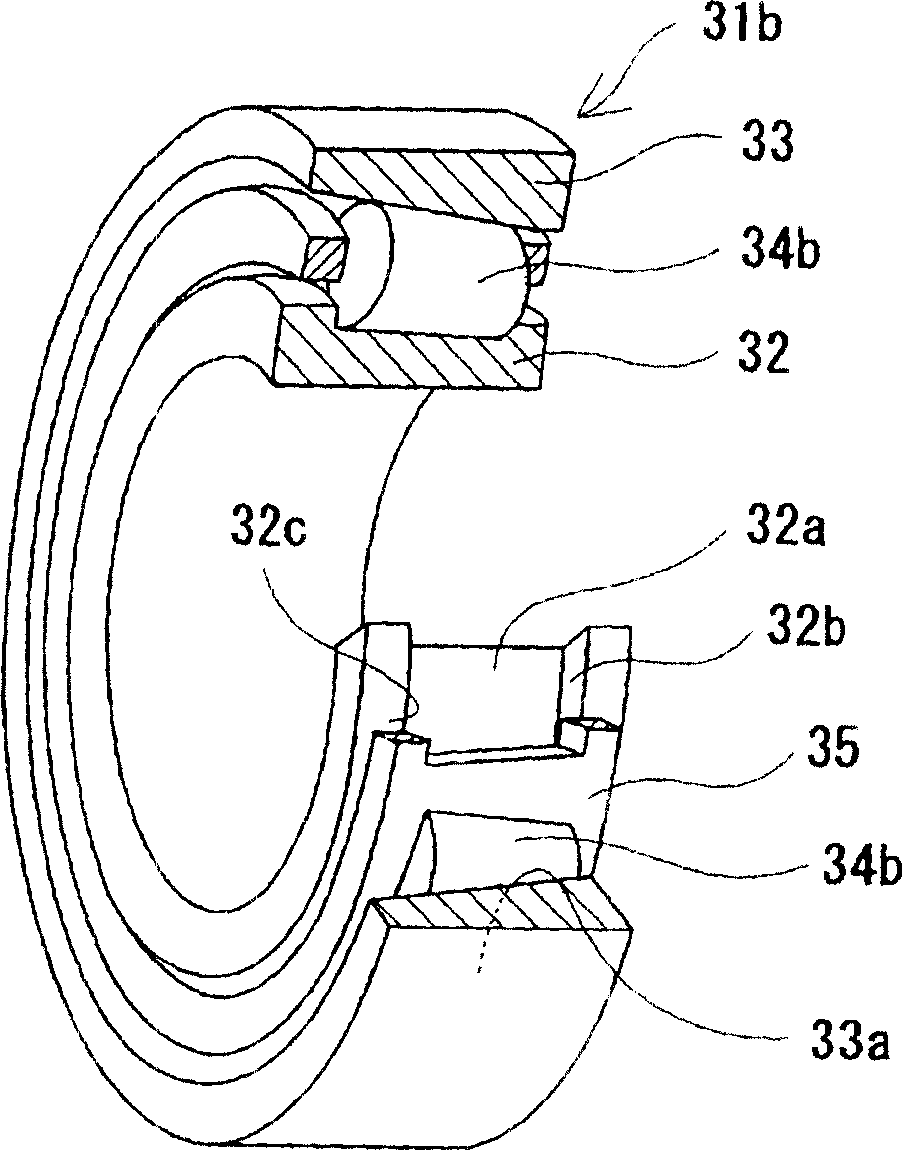
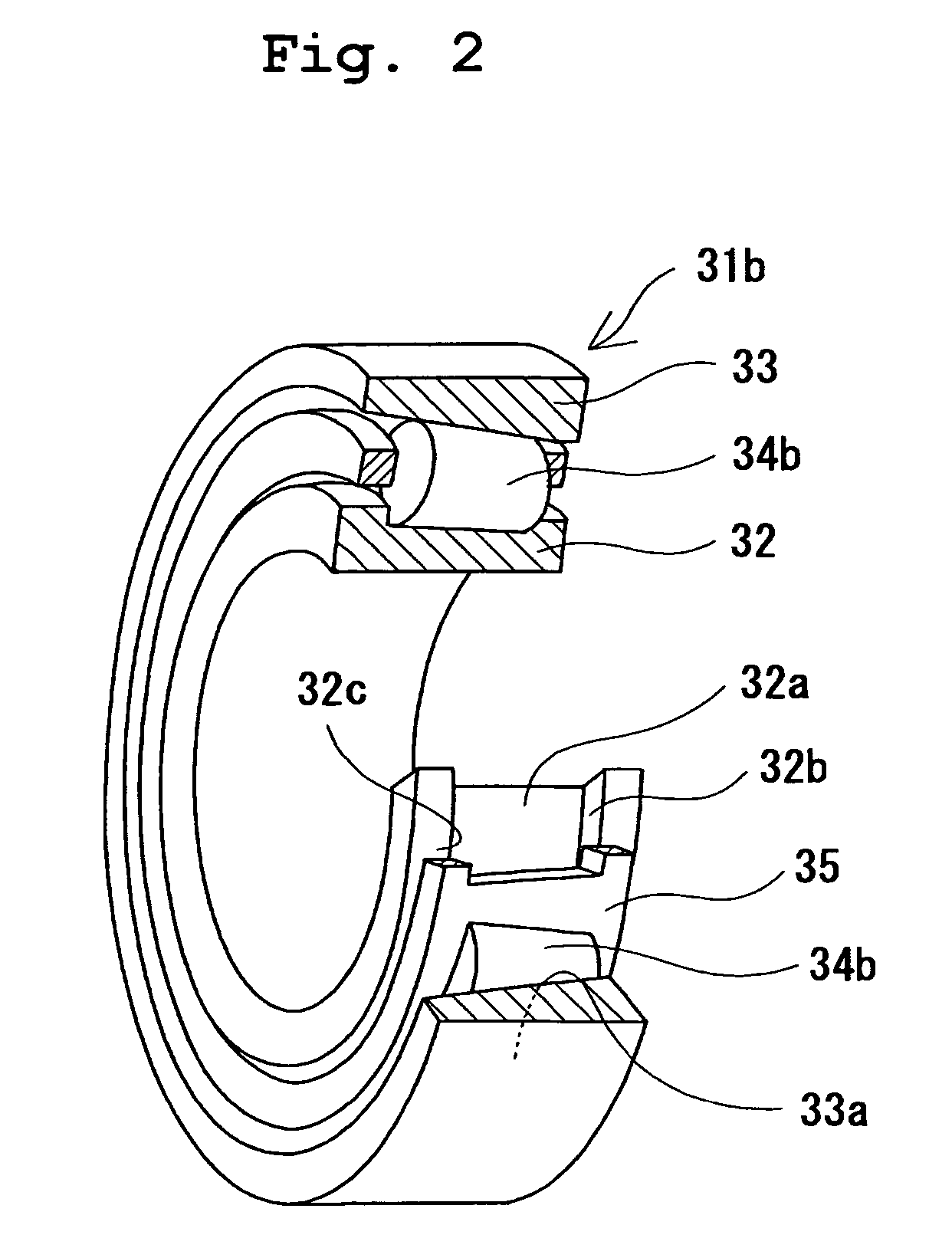
Grease, rolling bearing, constant velocity joint and rolling parts
InactiveCN1918269AInhibit wearLong-term sustained extreme pressure effectRoller bearingsYielding couplingLong term durabilityMaterials science
The present invention provides a grease capable of preventing wear on a lubricated surface, excellent in deflection prevention performance, heat resistance, and long-term durability, and a rolling bearing, a constant velocity coupling, and a rotating part filled with the grease. The grease is prepared by adding at least one substance selected from bismuth and inorganic bismuth in an amount of 0.01 to 15% by weight relative to the total amount of grease to a base grease prepared by blending at least a thickener with a base oil. Inorganic bismuth is at least one inorganic bismuth selected from bismuth sulfate, bismuth trioxide, bismuth carbonate and sodium bismuthate, the above-mentioned grease is used for rolling bearings and constant velocity couplings, and the rotating parts are formed on their surfaces selected from bismuth and inorganic bismuth A coating of at least one substance.
Owner:NTN CORP
Method for preparing bismuth trioxide nanowires by using solid-phase chemical reaction
InactiveCN103466701AEasy to prepareHigh yieldNanotechnologyBismuth compoundsNanowireChemical reaction
The invention aims at providing a method for preparing bismuth trioxide nanowires. In the method, by employing cheap raw materials and a simple operation method, the bismuth trioxide nanowires are prepared by a solid-phase chemical reaction. Bismuth nitrate and oxalic acid or an oxalate are taken as reactants and are grinded at room temperature for synthesis of a precursor, and the precursor is subjected to thermolysis for preparation of the bismuth trioxide nanowires. According to the method of the invention, based on the solid-phase chemical reaction, the bismuth trioxide nanometer material can be prepared by employing the cheap raw materials and performing simple grinding and proper heat treatment. The method of the invention has the characteristics of being simple, high in product yield, environment friendly, easily available in batch production, and the like, and thus the method has extremely wide application prospect.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Low-temperature sintering method of high potential gradient voltage-sensitive ceramic material
InactiveCN103073302AImprove performanceRaise the potential gradientManufactured materialVaristor ceramics
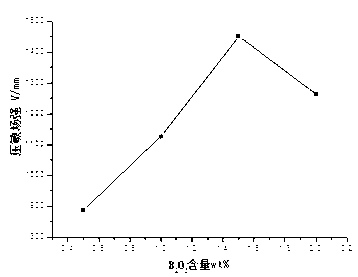
The invention discloses a ZnO-Bi2O3-based piezoresistor material with adjustable potential gradient of 600 V / mm to 1,450V / mm and a low-temperature sintering method thereof. The material consists of 92 to 98.5mol% of zinc oxide, 0.3 to 2mol% of bismuth trioxide Bi2O3 and the balance of additives such as Sb, Co,Mn, Cr, B elements and the like. According to a formula, the corresponding raw materials are weighed; and after heat is preserved for 2 to 5 hours at a temperature of 830 to 870 DEG C by utilizing a solid-phase sintering method, a corresponding voltage-sensitive ceramic material is obtained. The ZnO-Bi2O3-based piezoresistor material obtained by the invention has voltage-sensitive field intensity of 600V / mm to 1,450V / mm, nonlinear coefficient alpha of over 40 and leakage current IL of more than or equal to 0.1muA and has low sintering temperature and excellent comprehensive performance; and moreover, the preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple process, low energy consumption, green, environmental-friendliness and the like and has wide application prospect.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
Preparation method of bismuth silicate micro crystal
The invention relates to a preparation method of a bismuth silicate micro crystal, which comprises the following steps: mixing bismuth trioxide powder and quartz glass powder to obtain a mixture; adding the mixture into a high-purity alumina crucible which has a cover and is put into a muffle furnace in advance for melting, then pouring the molten glass metal into the middle part of a rotary water-cooled iron roller, and manufacturing the glass metal into a glass sheet in the cooling process; putting the glass sheet into the muffle furnace for heating and cooling to obtain the bismuth silicate glass; and putting the alumina crucible containing bismuth silicate glass into the muffle furnace for heating and insulating, and then, quickly taking out the alumina crucible and cooling to obtain the bismuth silicate micro crystal. In the invention, the amorphous quartz glass powder is used for preparing the bismuth silicate crystal; and the prepared bismuth silicate micro crystal has high purity, very few impurities, low cost of raw materials, rich sources, lower synthesis temperature and simple preparation processes, is beneficial to industrial production, and can be used as a high-quality raw material and a high-performance catalytic material for preparing the high-quality transparent bismuth silicate single crystal.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Solvothermal preparation method of bismuth trioxide microspheres and application thereof
ActiveCN103420414AGood chemical stabilityMeets friendly requirementsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationBismuth compoundsFluid phaseMicrosphere
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of inorganic nanomaterials and environmental materials, and relates to a solvothermal preparation method of bismuth trioxide microspheres and application thereof. The solvothermal preparation method of the bismuth trioxide microspheres adopts the technical steps as follows: dissolving soluble bismuth salt into ethylene glycol and dissolving soluble indium salt and urea into ethanol respectively; performing ultrasonic agitation and uniformly mixing, and obtaining a precursor through solvothermal reaction; centrifugally washing and drying the precursor, and roasting the precursor at high temperature to prepare the bismuth trioxide microspheres. The bismuth oxide (Bi2O3) microspheres with relatively uniform morphology are prepared at a low temperature through the solvothermal reaction by a liquid-phase method, the morphology thereof is a microspherical structure, and the diameter thereof is about 1-2 microns. When the bismuth trioxide microspheres prepared according to the solvothermal preparation method method can be applied to optical degradation of tetracycline-containing wastewater, and have the advantages of high chemical stability and the like. The solvothermal preparation method is simple in process and high in repeatability; used raw materials meet environment-friendly requirements; and by the solvothermal preparation method, mass production can be facilitated.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Flux compositions for sintering Ni-Zn ferrite material
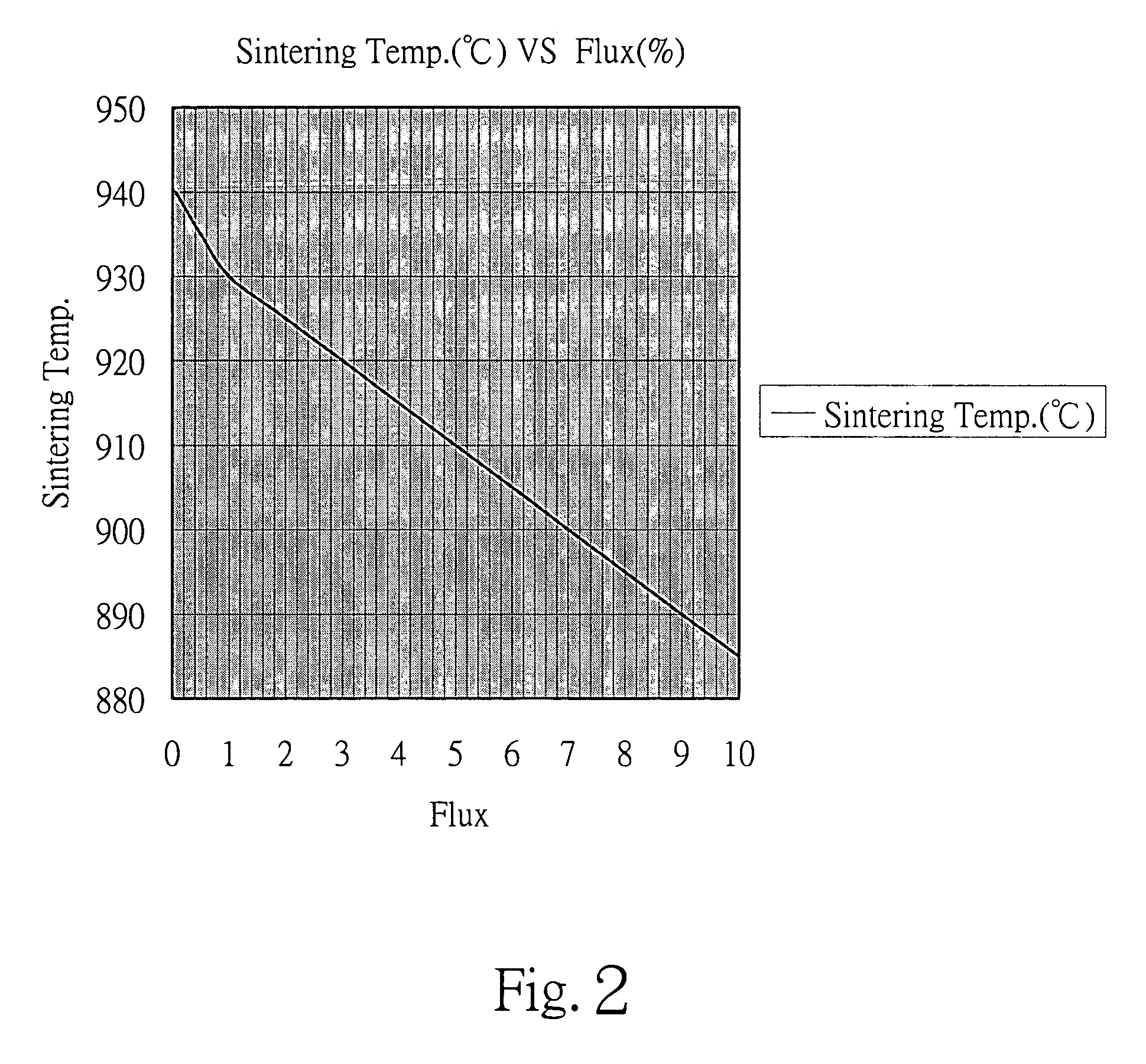
InactiveUS20050034633A1Lower sintering temperatureMaintain effective electric propertyOther chemical processesInorganic material magnetismPotassiumCopper oxide
Flux compositions for sintering Ni—Zn ferrite material are disclosed in the present invention, each flux composition basically and selectively has zinc oxide (ZnO), silicon dioxide (SiO2), boric oxide (B2O3), bismuth trioxide (Bi2O3), aluminum oxide (Al2O3), potassium trioxide (K2O3), barium oxide (BaO), sodium oxide (Na2O), calcium oxide (CaO), and magnesium oxide (MgO). Each flux composition is added into a mixture of Ni—Zn ferrite material composed of ferric oxide (Fe2O3), nickel oxide (NiO), zinc oxide (ZnO), cupric oxide (CuO) and cobalt oxide (CoO) and ranges from 0.05 to 10 weight percent based on the total weight of the Ni—Zn ferrite material. The flux compositions of the present invention decrease sintering temperature when the ferrite material is sintered and contain no lead (Pb) element so as to reduce toxic pollutants.
Owner:CHILISIN ELECTRONICS
High-gradient and high-capacity zinc oxide voltage dependent resistor disc and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN103021608AUniform particle sizeSmooth appearanceResistor manufactureOvervoltage protection resistorsEngineeringAntimony trioxide
The invention discloses a high-gradient and high-capacity zinc oxide voltage dependent resistor disc and a fabrication method thereof. The resistor disc comprises zinc oxide, bismuth trioxide, cobaltosic oxide, cobaltic oxide and antimonous oxide. The fabrication method of the resistor disc comprises the steps of ball milling, pelleting, glue discharging, prefiring and coating, firing, grinding, heat treatment, electrode spraying, glazing and the like. The potential gradient of the prepared zinc oxide voltage dependent resistor disc is raised greatly, the 2ms square wave through-flow capacity remains constant compared with the ordinary resistor disc having the same specification, and the fabrication method reduces procedures, saves energy, and avoids secondary pollution of accessory additives.
Owner:NANYANG ZHONGXIANG POWER ELECTRONICS +1
Full-solid electrochromic window, solid electrochromic glass and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN108254989ABoost rateImprove cycle lifeNon-linear opticsSolid state electrolyteRare-earth element
The invention relates to a solid electrolyte material. The chemical composition of the solid electrolyte material is LixSiyRezSmOn, wherein x is larger than or equal to 2 and smaller than or equal to3, y is larger than or equal to 0.5 and smaller than or equal to 2, z is larger than or equal to 0.3 and smaller than or equal to 0.6, (m+n) is larger than (x+4y+3z) / 2.1 and smaller than or equal to (x+4y+3Z) / 1.8, and Re is selected from rare earth elements Y, Gd, Gy or Sm. The solid electrolyte material is high in lithium ion conductivity, high in electron conductivity, wide in electrochemical window and high in temperature resistance. The invention further relates to a solid electrochromic device. An electrolyte is selected from the solid electrolyte material, an electrochromic layer is selected from at least one of tungsten oxide, bismuth trioxide, molybdenum trioxide or nickel oxide, and an ion storage layer is selected from at least one of lithium-embedded vanadium pentoxide, lithium-embedded titanium dioxide, lithium-embedded tungsten trioxide or lithium-embedded nickel oxide. The solid electrochromic device has the advantages of being short in color change response time and stable in performance.
Owner:NINGBO MI RUO ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Zinc-oxide piezoresistor raw material, preparation method thereof and piezoresistor
ActiveCN103396116AImprove uniformityIncreased surface state densityVaristor coresOvervoltage protection resistorsManganeseVoltage gradient
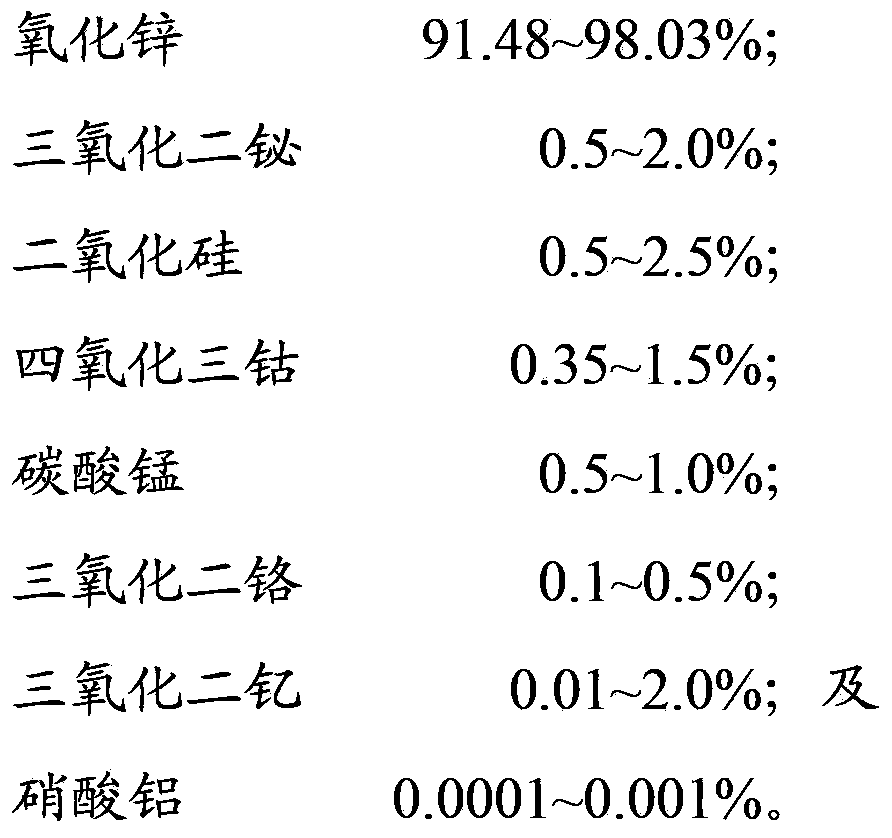
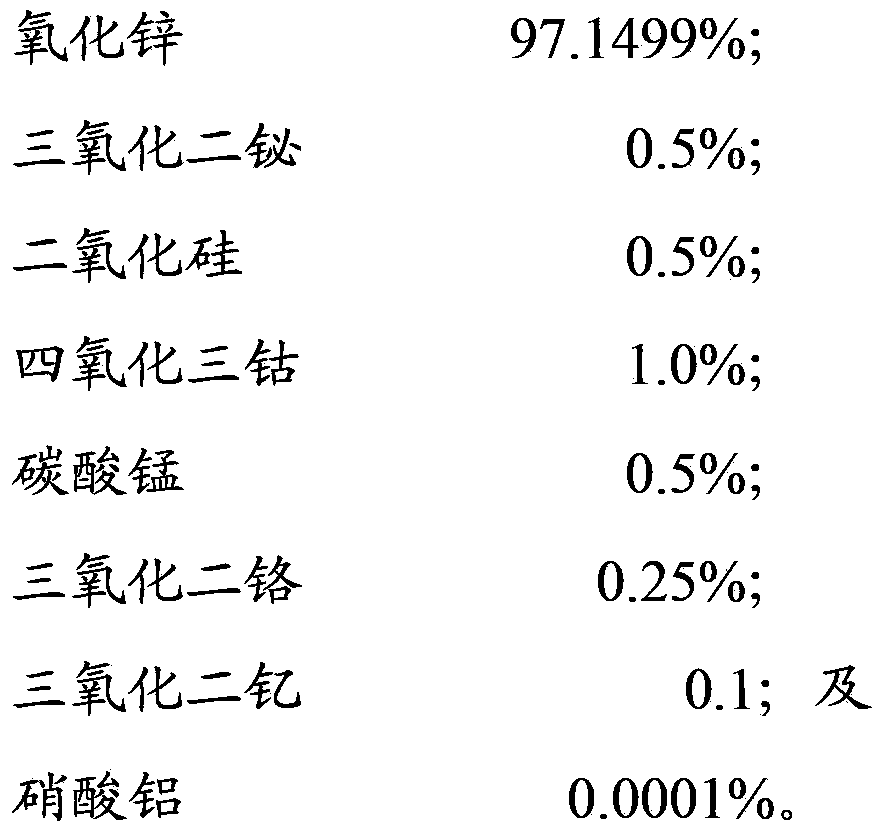
The invention relates to a zinc-oxide piezoresistor raw material, a preparation method thereof and a piezoresistor. The zinc-oxide piezoresistor raw material comprises the following components by mole percent: 91.48-98.03% of zinc oxide, 0.5-2.0% of bismuth trioxide, 0.5-2.5% of silicon dioxide, 0.35-1.5% of cobaltosic oxide, 0.5-1.0% of manganese carbonate, 0.1-0.5% of chromium oxide, 0.01-2.0% of yttria and 0.0001-0.001% of aluminium nitrate. The zinc-oxide piezoresistor raw material does not antimony, and due to the silicon dioxide, the characteristic of the piezoresistor is improved, the surface state density is increased, the voltage gradient, the barrier height and the nonlinear coefficient are improved, the leakage current is reduced and the current impact resistance is enhanced; due to the yttria, the conductivity, the current impact resistance, the nonlinear coefficient and the voltage gradient are improved, the limiting voltage rate and the leakage current are reduced, the grain growth is inhibited and the zinc-oxide piezoresistor has higher voltage gradient and excellent electrical property.
Owner:GUANGDONG FENGHUA ADVANCED TECH HLDG
Potassium-sodium niobate-based leadless piezoelectric material and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101302106AImprove sintering propertiesHigh degree of densificationSilver electrodeDrain current
The invention discloses a piezoelectric material for lead-free piezoelectric ceramic with potassium-sodium niobate and a preparing method, which strengthens the ferroelectric performance of potassium-sodium niobate ceramic and further improves the piezoelectric performance. The material of the invention comprises anhydrous potassium carbonate, natrium carbonicum calcinatum, niobium pentaoxide and dibismuth trioxide, the stoichiometric proportion of the lead-free piezoelectric ceramic is (K0.5 Na0.5) Nb3 + x weight percent Bi 2O3, wherein the x is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1, the piezoelectric material for lead-free piezoelectric ceramic with potassium-sodium niobate is obtained through mixture making, drying and burnishing, granulation, molding, sintering and after polarization by a silver electrode; therefore, the densification of the ceramic is improved, polarized drain current of the ceramic is reduced, and the polarization process is carried out more easily; moreover, the piezoelectric material adopts the material from a conventional process and industry, has the characteristics of good process stability and no pollution.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Ferromagnetic oxide powder for magnetic recording and preparation method thereof
Owner:BGRIMM TECH CO LTD
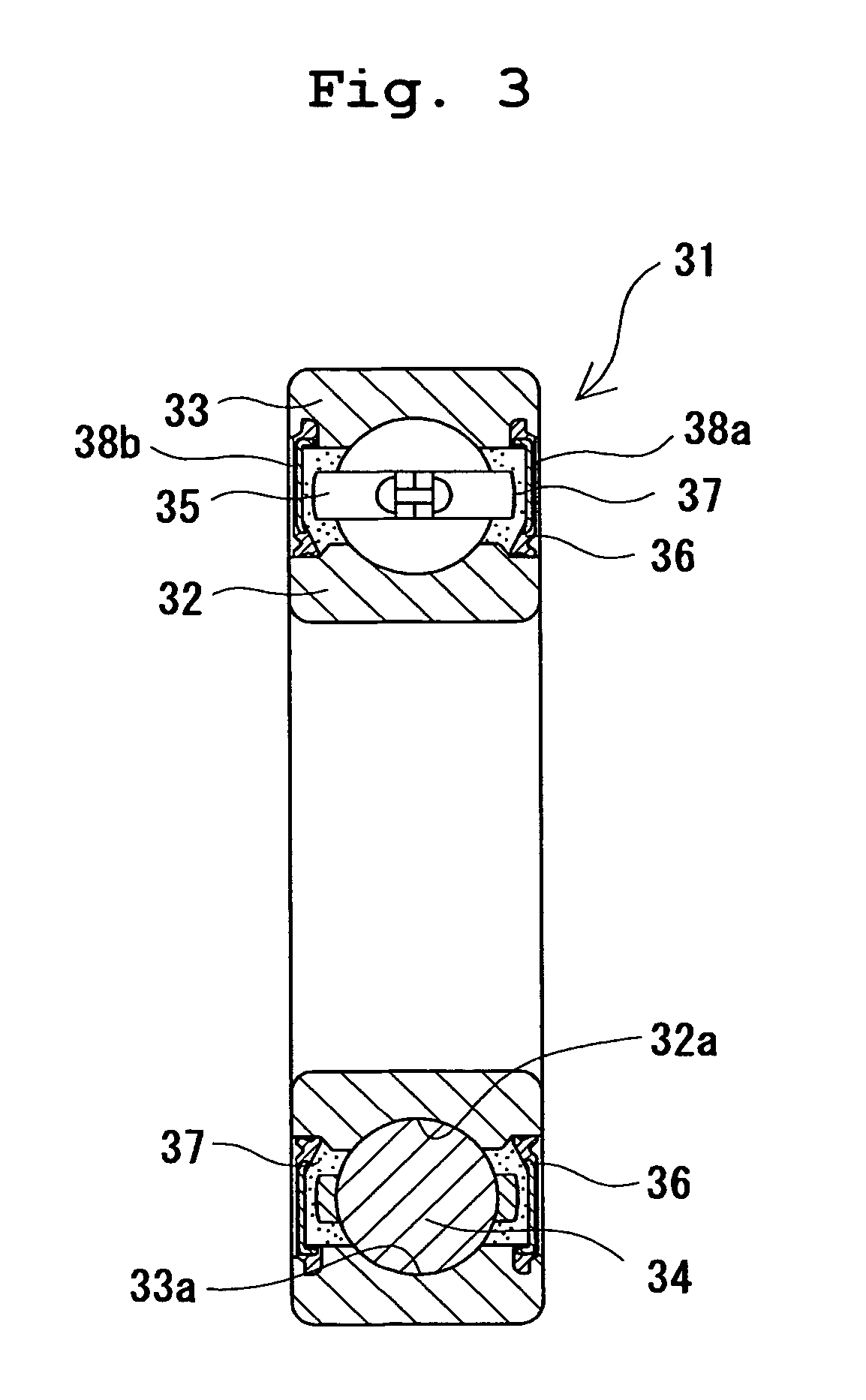
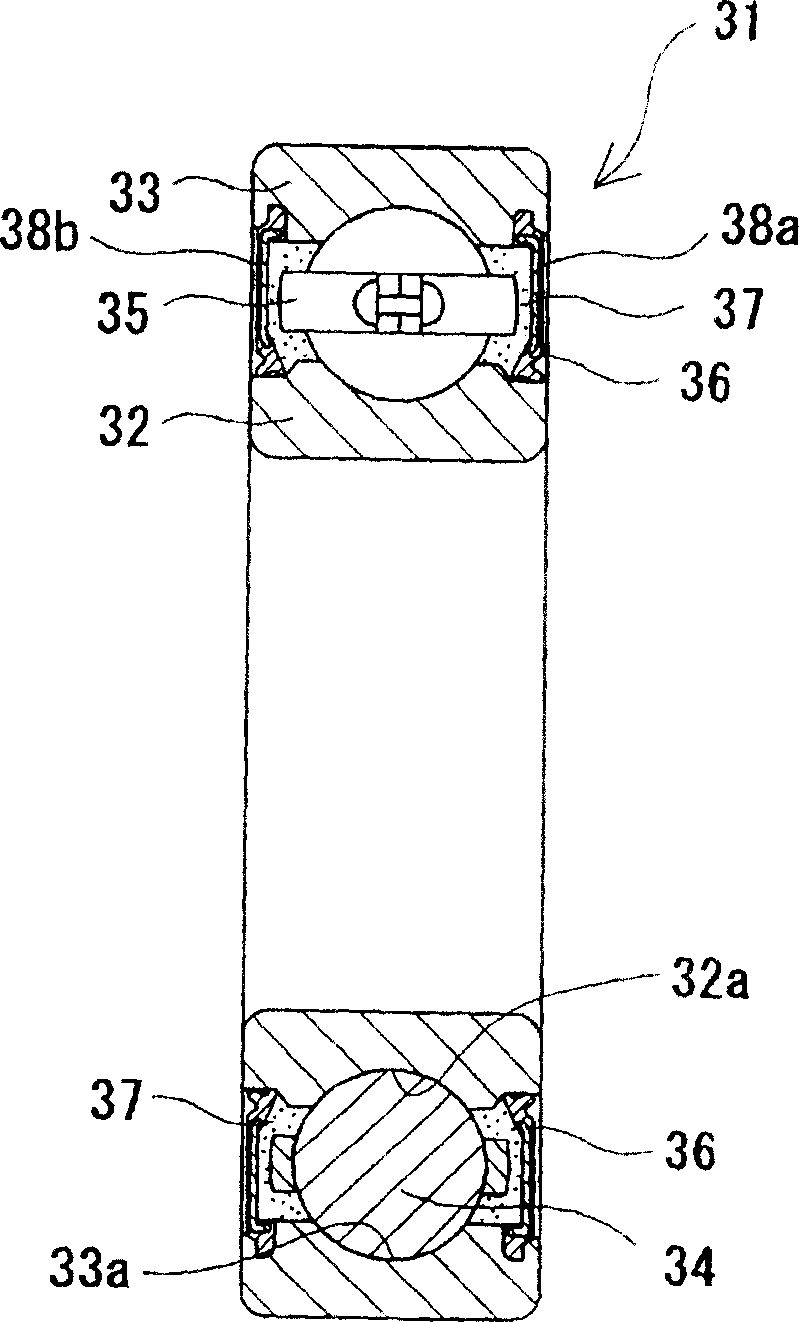
Grease, rolling bearing, constant velocity joint, and rolling parts
InactiveUS8003582B2Resistance to durabilityHeat resistantClutchesMachines/enginesSulfateBismuth compound
The present invention provides grease which prevents frictional wear on a lubricating surface and excellent in performance of preventing occurrence of flaking, heat-resistant performance, and long-term durability, a grease-enclosed rolling bearing, a constant velocity joint, and rolling parts. Grease is composed of base grease, essentially containing a thickener, to which at least 0.01 to 15 wt % of one substance selected from among bismuth and inorganic bismuth compounds is added. The inorganic bismuth compounds are at least one inorganic bismuth selected from among bismuth sulfate, bismuth trioxide, bismuth carbonate, and sodium bismuthate. The above-described grease is used for the rolling bearing and the constant velocity joint. A coating film of at least one substance selected from among the bismuth and the inorganic bismuth is formed on surfaces of the rolling parts.
Owner:NTN CORP
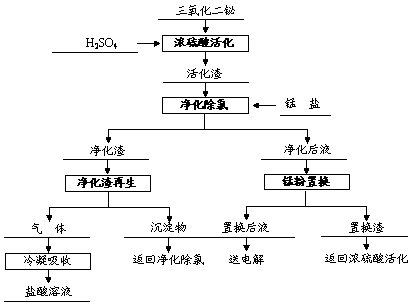
Method for purifying and removing chlorine by manganese sulfate electrolyte
ActiveCN108220998AAchieve regenerationAvoid emissionsPhotography auxillary processesElectrode potentialSlag
The invention discloses a method for purifying and removing chlorine by manganese sulfate electrolyte. The method comprises the steps that firstly, bismuth trioxide is activated in concentrated sulfuric acid to enable the bismuth trioxide to be converted into bismuth sulfate; secondly, the activating slag is added into a manganese sulfate solution, and the pH value of the solution is adjusted to an initial value by using a manganese salt, so that chloride ions in the solution are precipitated in the form of bismuth oxychloride; the residue is re-purified by using concentrated sulfuric acid toremove chlorine and realizing the regeneration of the precipitant, and finally the manganese powder is added to replace the residual bismuth ions in the purified liquid. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, bismuth oxide is converted into bismuth sulfate with relatively good activity; secondly, the characteristic that the dissolution rate of the bismuth oxychloride is small is further utilized, the chlorine in the manganese sulfate electrolyte is removed by using bismuth sulfate, and the property that hydrogen chloride is easy to volatilize is utilized again, so that the bismuth oxychloride is regenerated into bismuth sulfate; and finally, the property of the electrode potential of manganese is lower than the electrode potential of bismuth is utilized, so that residual bismuth in the purified liquid can be replaced and recycled. The method has the advantages of being short in process, good in product quality and low in cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Optical pigment and its preparation method
ActiveCN103911023AReduce dosageReduce thicknessInorganic pigment treatmentSesquioxideSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to an optical pigment comprising a substrate and a coating layer coating the substrate. The substrate is at least successively coated with three coating matters. The three coating matters are successively selected from titanium dioxide, stannic oxide, ferric oxide, ferroferric oxide, cobaltous oxide, cobalt sesquioxide, zirconium dioxide, chromic oxide or a mixture and a compound thereof; silicon dioxide; and aluminum oxide, bismuth trioxide or a mixture or compound thereof. The optical pigment provided by the invention overcomes the defects of small particle diameter reflecting surface and low color saturation due to small pigment particles in the prior art. At the same time, the invention also relates to a preparation method of the optical pigment, the preparation method overcomes the defects of ''layer lamination '' of the coating layer in the prior art, meanwhile the coating amount of the coating layer is reduced, and the number of particles per unit weight is increased, so that color of the prepared pigment is more full, rich and varied.
Owner:SHANTOU LONGHUA PEARL LUSTRE PIGMENTS CO LTD
Radiation attenuation elastomeric material, a multilayer glove for protection against ionizing radiations and their uses
ActiveUS20120217423A1Remarkable flexibilityRemarkable propertyOther chemical processesShieldingElastomerPlastic materials
The invention relates to a radiation attenuation elastomeric material of the type comprising an elastomer in which a powder of metal oxides is dispersed, and which is characterized in that the powder of metal oxides comprises from 70 to 90% by mass of bismuth trioxide, from 5 to 15% by mass of tungsten trioxide and from 5 to 15% of lanthanum trioxide.It also relates to the use of this elastomeric material for making individual protective articles against ionizing radiations.It further relates to a multilayer protective glove against ionizing radiations, at least one layer of which is formed by said elastomeric material, as well as to the use of this glove for protection against ionizing radiations emitted by powders of nuclear fuels, notably with plutonium.Fields of application: the nuclear industry for handling powders of nuclear fuels but also medical imaging, interventional radiology, nuclear medicine, processing of plastic materials, inspection and control of manufactured parts, etc.
Owner:PIERCAN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com