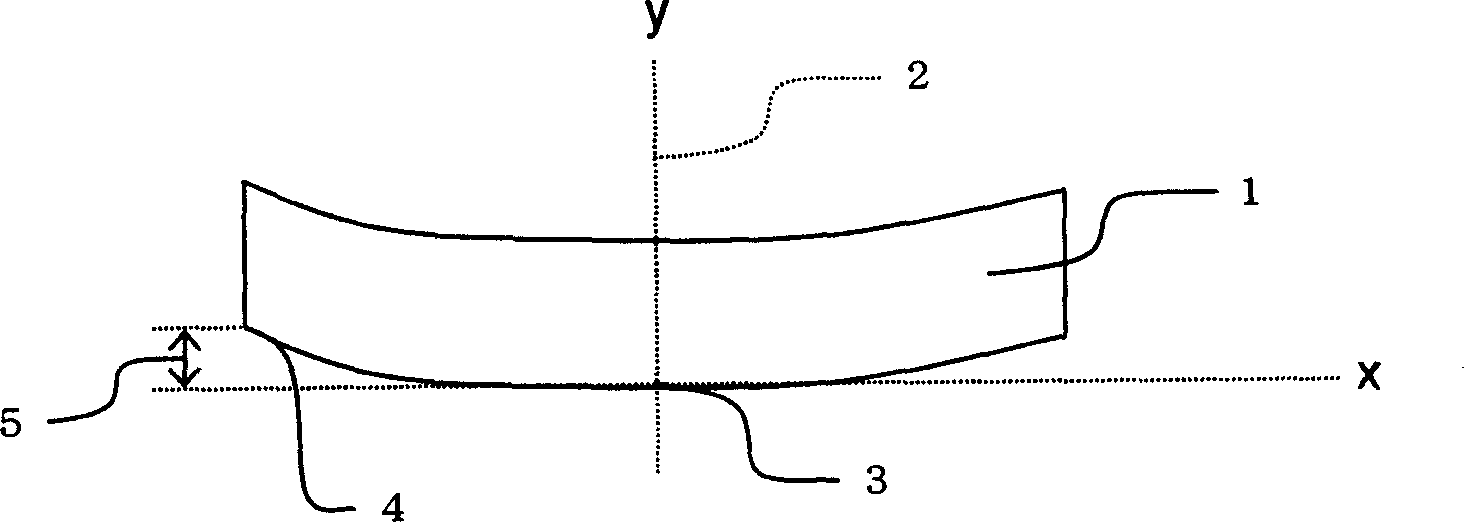
Process of mfg. Mo alloyed targeting materials
A target material and raw material technology, which is applied in the field of preparing Mo alloy target materials, can solve problems such as unfavorable shape changes, and achieve the effects of reducing shape changes, increasing packing density, and reducing segregation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Mo powder with an average particle size of 12 μm, W (tungsten) powder with an average particle size of 12 μm, Nb powder with an average particle size of 100 μm, Ti powder with an average particle size of 100 μm, and Zr powder with an average particle size of 100 μm were prepared.
[0053] The target making materials of samples Nos. 1 to 6 shown in Table 1, which are the present invention, were prepared by the following method.
[0054] (1) To prepare each sample, Mo powder and any one of transition metal powders were weighed in given amounts in atomic %.
[0055] (2) The weighed powders were mixed for 10 minutes using a V-shape mixer to obtain raw material powders.
[0056] (3) Press the raw material powder under a pressure of 265 MPa by a CIP machine to form a green body.
[0057] (4) Grinding the green body with a jaw crusher and a disc mill to prepare secondary particles.
[0058] (5) Mix the secondary particles in a V-shaped mixer for 10 minutes, and then put them...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Sintered bodies having the same chemical composition and the same dimensions as those of inventive sample No. 2 shown in Example 1 were prepared in the same manner as in the case of inventive sample No. 2, after the HIP process, at a temperature of It was hot-rolled three times together with a container for pressurization under the conditions of 1150°C and a shrinkage ratio of not more than 50%. The ideal size of target material is: width is 1500mm and length is 1800mm. Table 2 shows the rolling results of the sintered body.
[0084]
chemical components
(atomic %)
Size of sintered body
(mm)
Target size in rolling
(mm)
(℃)
2-1
95.0Mo-5.0Nb
81×812×1053
25.7×1500×1800
1150
[0085] Total rolling reduction
(%)
First rolling reduction ratio
(%)
Second rolling reduction ratio
(%)
Third roll...
Embodiment 3
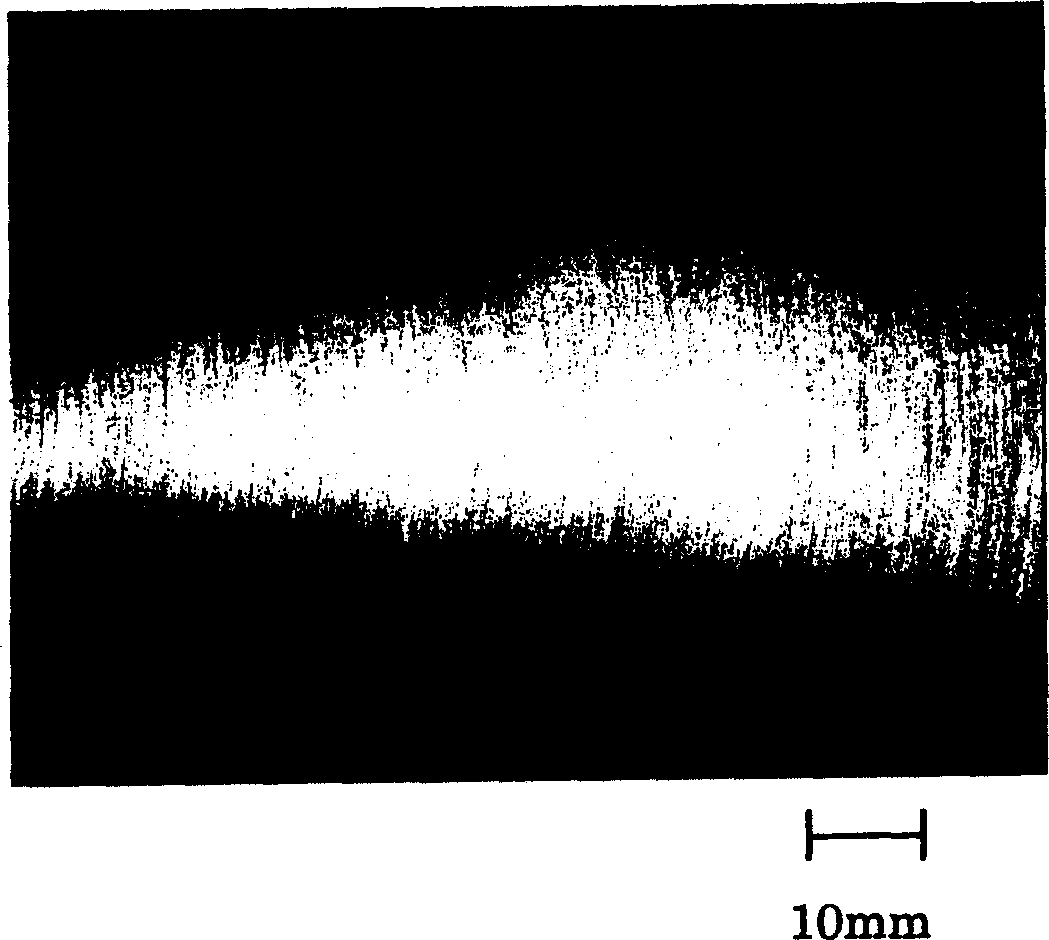
[0089] Recrystallization heat treatment was performed on the hot-rolled target materials in Example 2 at 900° C., 1150° C. and 1300° C. in vacuum, respectively. After heating the target material to the heat treatment temperature, the temperature is maintained for 1 hour, after which the workpiece is cooled. Sample Nos. 2-1-1, 2-1-2, and 2-1-3 were taken from the three types of workpieces, respectively. The microstructures of the samples were compared with each other using an optical microscope with a magnification of 100. The observed results are shown in Table 3. As for the samples subjected to recrystallization heat treatment at temperatures of 900 °C and 1300 °C, respectively, in Figure 4 and 5 Photographs of the microstructure of the samples shown by an optical microscope with a magnification of 100 are provided in , respectively.
[0090]
[0091] From Table 3, Figure 4 and 5 It can be seen that when the recrystallization heat treatment temperature is lo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com