Clock synchronizer and clock and data recovery apparatus and method
A synchronizer and clock technology, applied in synchronization devices, data conversion, electrical digital data processing and other directions, can solve problems such as loss of lock
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
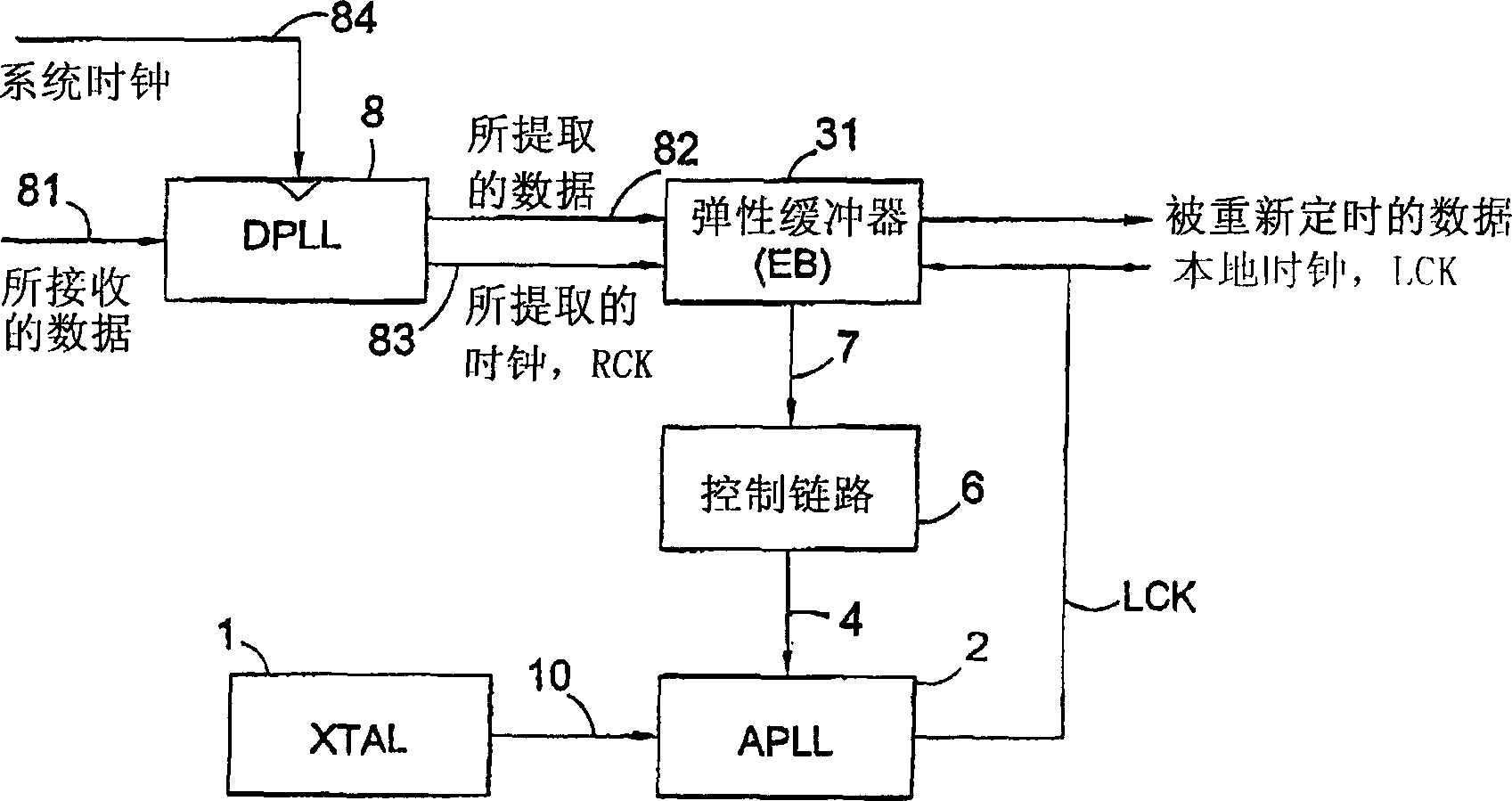
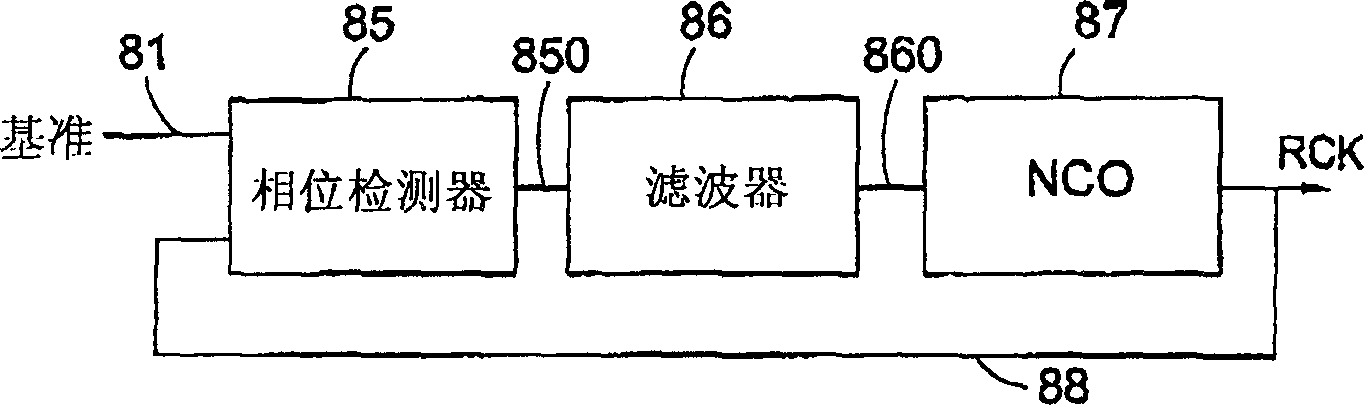
[0124] now refer to figure 2 , The clock and data recovery circuit (system) implementing the present invention includes a clock and data extraction circuit 8, and the clock and data extraction circuit 8 includes a digital phase-locked loop (DPLL). Received data stream 81 containing embedded clock information is supplied to DPLL which is used to lock onto incoming data and generate internal intermediate clock RCK 83 (which should be called received clock) and retimed internal data stream 82 (i.e. the data being extracted). Generation of an internal intermediate clock may also be described as extracting a clock signal from a received data stream, and thus an internal intermediate clock may also be referred to as an extracted clock.
[0125] The extracted data 82 and the extracted clock 83 are provided at the input of the elastic buffer (EB) 31 . EB is used to absorb any short or medium term timing variations between the local and remote clock domains. It also generates a poi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com