Method for removing lattice defect in pad area of semiconductor device
A lattice defect and pad area technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, etc., can solve not particularly reliable, pad area lattice defects, DRAM reliability effects And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
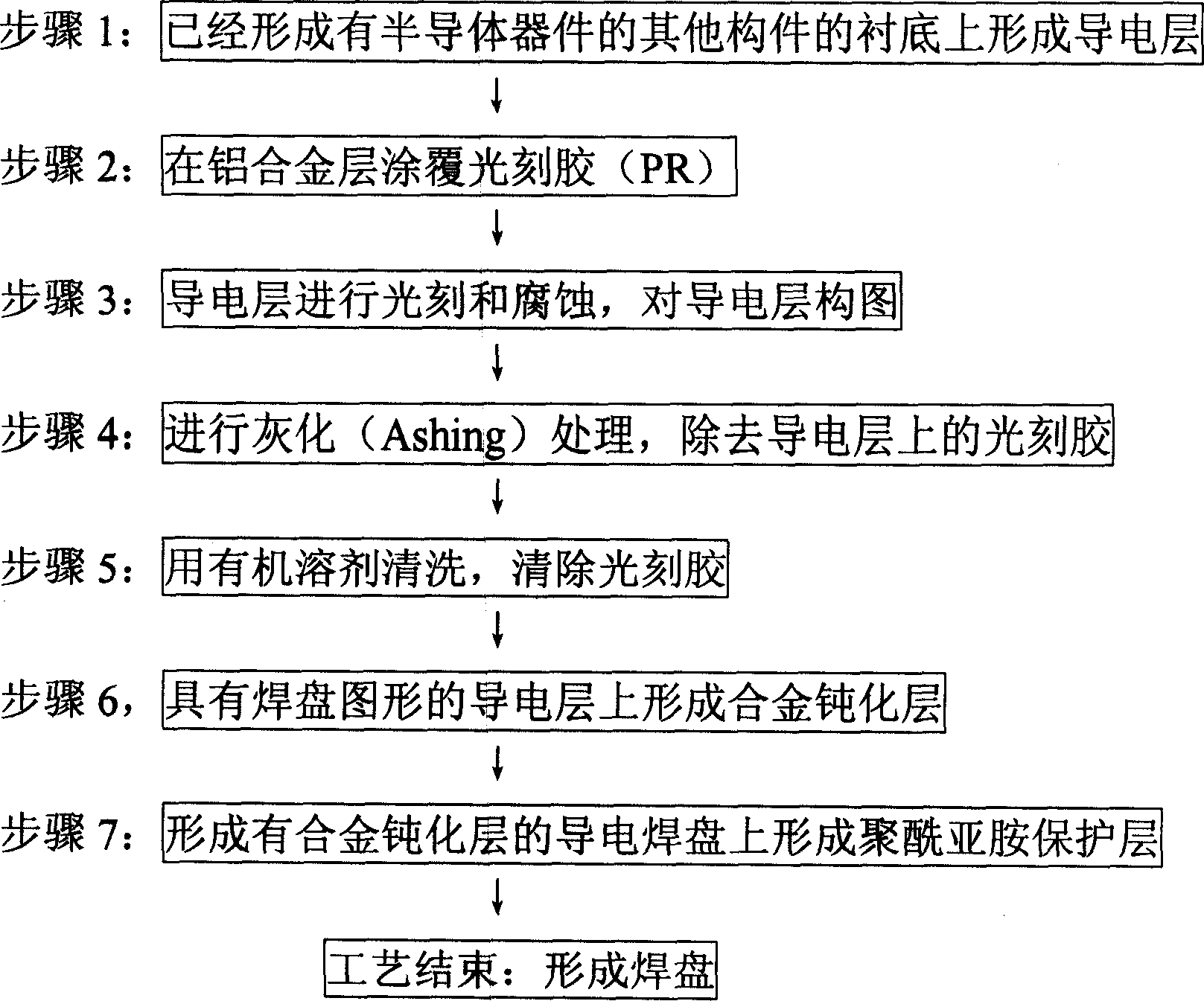
[0014] see below figure 2 A method for removing lattice defects in a pad (PAD) region of a semiconductor device using an argon (Ar) plasma sputtering repair process according to the present invention will be described in detail. figure 2 It is a flow chart of the bonding pad formation process of the semiconductor device according to the present invention.
[0015] exist figure 2 The pad formation process flow of the semiconductor device according to the present invention is shown in figure 1 After the step 7 (forming the polyimide protective layer) of the shown bonding pad formation process flow of the existing semiconductor device, an increase is made: step S1, whether there is a lattice defect in the detection pad region; and step S2, when the step When S1 detects that there is a lattice defect in the pad region, argon (Ar) plasma sputtering repair treatment is performed. In step S1, use an optical microscope (OM) to detect whether there is a lattice defect in the pad ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com