2,6-dimethylpyridine preparation method
A technology of lutidine and dimethyl, applied in 2 fields, can solve the problems of large investment in separation and purification, large influence of catalyst performance and high equipment requirements, and achieves low equipment requirements, low production cost and high safety. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 12
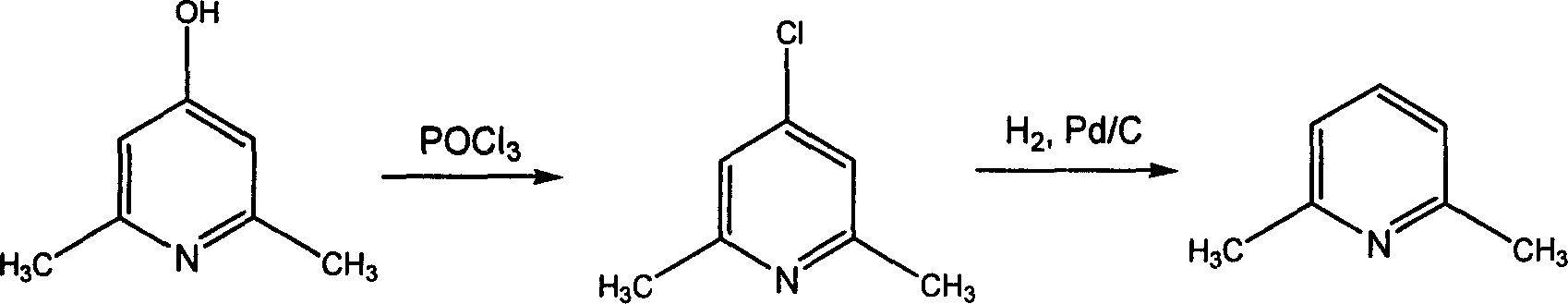
[0029] The preparation of embodiment 12,6-dimethyl-4-chloropyridine
[0030] In a 150ml three-necked flask, add 24.6g (0.2mol) of 2,6-dimethyl-4-hydroxypyridine and 4.2g (0.01mol) of phosphorus pentachloride, and add 46.0g of phosphorus oxychloride dropwise within 30 minutes at room temperature (0.3mol), after dropping, the temperature was raised to 110-115°C, and the reaction was continued for 9-11 hours, and finally the reactant turned brown. Phosphorus oxychloride is recovered by distillation. Naturally cooled to room temperature, the reactant was slowly poured into a 300ml ice-water mixture, washed with 20% Na 2 CO 3 Adjust the pH of the solution to 8, extract with 3×100ml chloroform, anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 Dry, distill to recover chloroform, distill the residue under reduced pressure, collect fractions at 92-93°C / 20mmHg, and obtain 26.7 g of light yellow liquid with a yield of 94.3% and a purity of 98.8%.
Embodiment 22
[0031] The preparation of embodiment 22,6-dimethyl-4-chloropyridine
[0032] Except that phosphorus pentachloride was not added, other operating conditions were the same as in Example 1 to obtain 15.4 g of light yellow liquid with a yield of 54.6% and a purity of 98.6%.
Embodiment 32
[0033] The preparation of embodiment 32,6-dimethyl-4-chloropyridine
[0034] Except that the charging amounts of phosphorus oxychloride and phosphorus pentachloride were changed to 30.7g (0.2mol) and 8.4g (0.02mol) respectively, that is, 2,6-dimethyl-4-hydroxypyridine: phosphorus oxychloride: five Except that the molar ratio of phosphorus chloride was 1:1:0.1, other operating conditions were all the same as in Example 1 to obtain 24.1 g of light yellow liquid with a yield of 85.2% and a purity of 98.8%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com