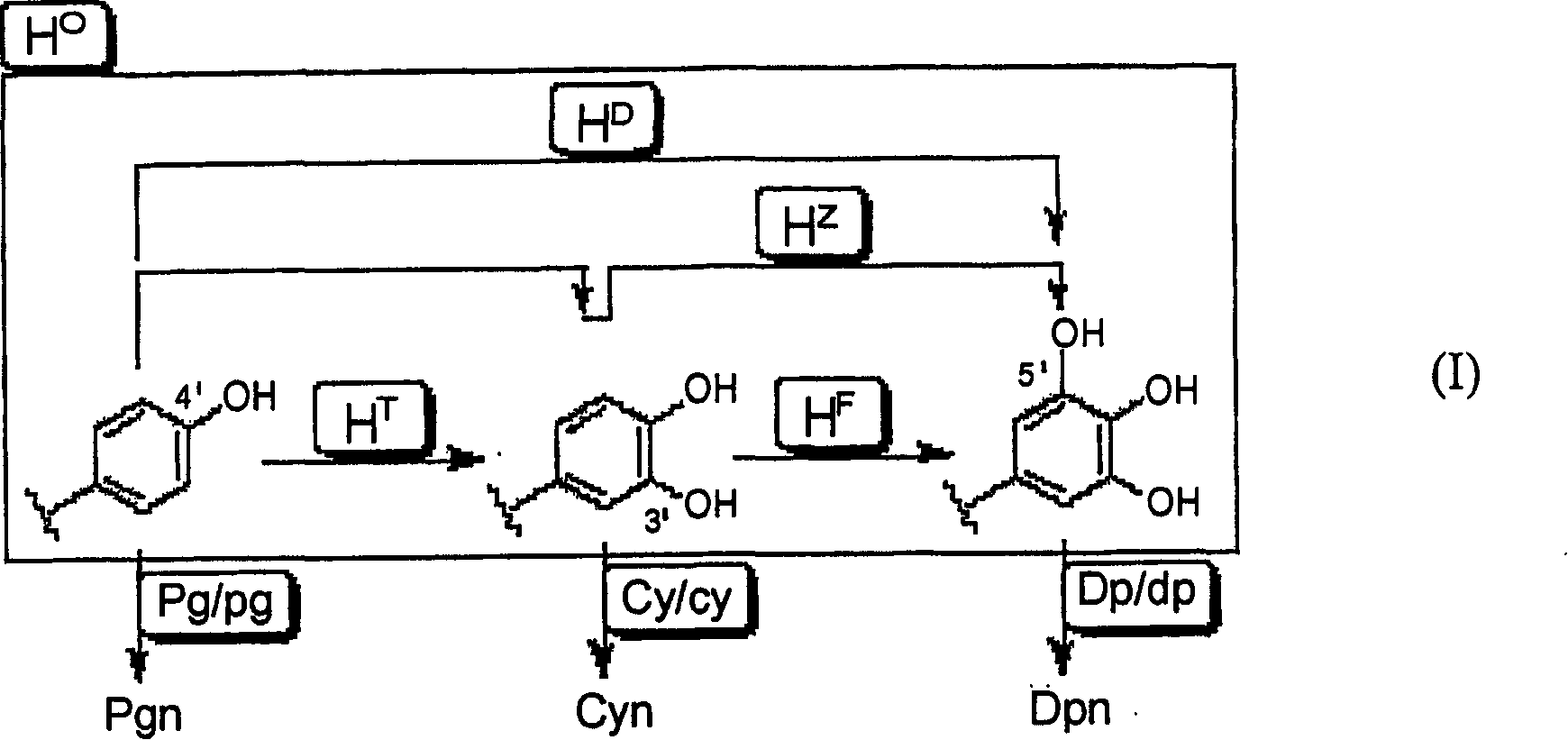
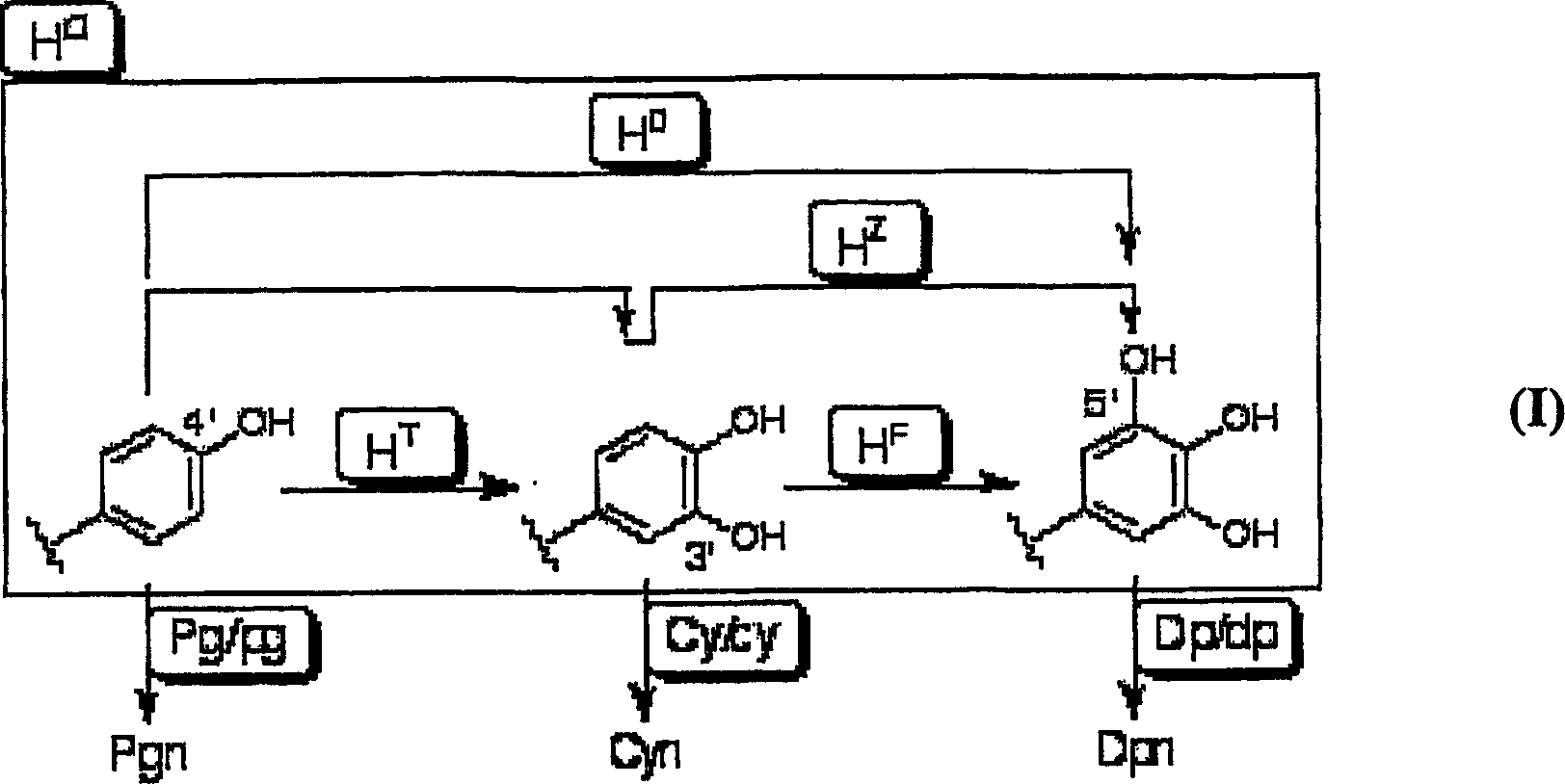
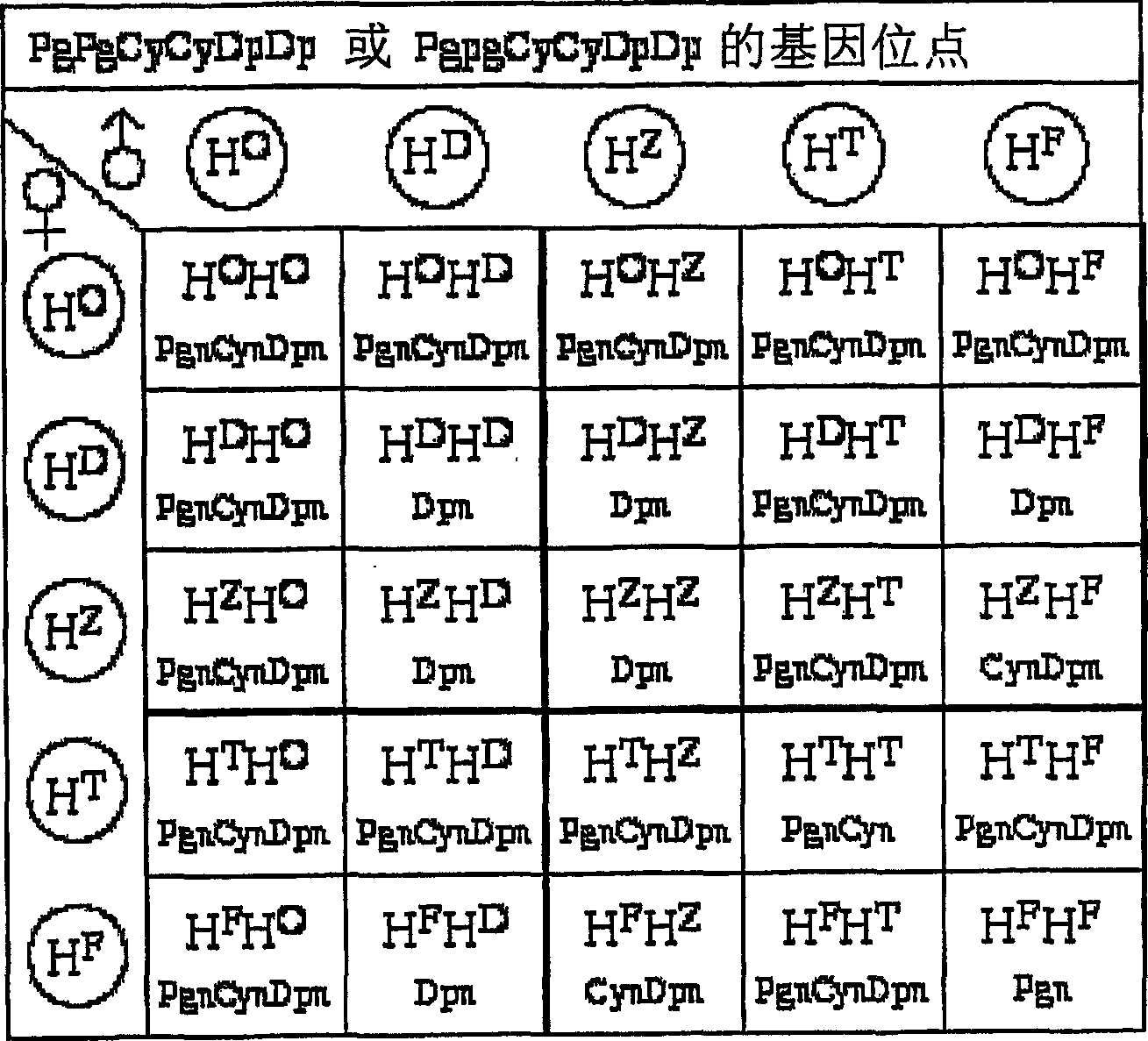
Method of crossing flower color genotypes
A technology of pigment gene and hybridization method, which is applied in the field of hybridization of flowers, new plants and their acquisition methods, and genotypes, and can solve problems such as doubts about the separation ratio of offspring, mutations, and genetic recombination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Collect petals, peels and leaves, and for petals and sepals, etc., cut out colored parts, parts of the same color, and white parts of the panchromatic type or lacy type (including double flowers), and weigh them accurately . Thereafter, an acidic solvent is added, such as 0.5N to 2N hydrochloric acid (0.5N to 2N HCl), and then the anthocyanins are extracted. The extraction is based on literature (Uddin et al.: J.Jpn.Soc.Hort.Sci., 71:40-47, 2002; Wang et al.: J.Plant Res., 114:213-221, 2001; Naotaka Matsuzoe and others 5 persons: Engakuzatsu, 68: 138-145, 1999). The extract is filtered with cotton, and then the filtrate is heated at 95° C. to 100° C. to perform hydrolysis to obtain a solution containing 1 to 6 types of anthocyanins. The hydrolysis is carried out according to literature (Uddin et al.: J.Jpn.Soc.Hort.Sci., 71:40-47, 2002). After the reaction was completed, the reaction mixture was filtered with a membrane filter, and then analyzed using an HPLC instrum...
Embodiment 3
[0064] With the eustoma's S shown in Table 3 1 As parents, they are self-pollinated and segregated to obtain S 2 Generation, detection of the S 2 Generation to determine the pigment genotypes of different lines. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0065] pigment phenotype
[0066] As Table 3 clearly shows, the G2D3B25F lines (white, red-white, cream or pink flowers) with only Pgn pigments were obtained from ddeeH F h F PgPgCyCyDpDp Pigment genotype. The G2D3B27Y line with only Cyn pigments (red-white or pink flowers) was obtained from ddeeH T h T pgpgCyCyDpDp Pigment genotype. The G2D3B26B line without pigment (white flowers) as a blank phenotype was obtained from ddeeH F h F pgpgCyCyDpDp Pigment genotype. J5A2H16B line (red-purple flowers) with CynDpn pigment phenotype was obtained from ddeeH O h O pgpgCyCyDpDp Pigment genotype. J5A2H110C1A line (purple flowers) with Dpn pigmented phenotype was obtained from ddeeH D h D pgpgCyCyDpDp Pigment genotype. ...
Embodiment 4
[0068] When red and white flowers with Pgn phenotype (G2D3B25F line, ddeeH F h F PgPgCyCyDpDp pigment genotype) and red-white flowers with Cyn phenotype (G2D3B27Y line, ddeeH T h T pgpgCyCyDpDp pigment genotype) when cross-pollination, obtain the PgnCynDpn phenotype (ddeeH T h F PgpgCyCyDpDp pigment genotype) reddish-purple flowers. Non-Patent Document 6 (Kanai Kobayashi, Journal of Breeding Science, 48: 169-176, 1998) (which proposes a conjecture of a pigment phenotype) discloses the acquisition of flowers with a PgnCyn phenotype, but cannot explain the red flowers with a PgnCynDpn phenotype. Isolation of purple flowers.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com